Panicum coloratum for irrigated fodder [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: GERBA LETA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Panicum
technologies_6563 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
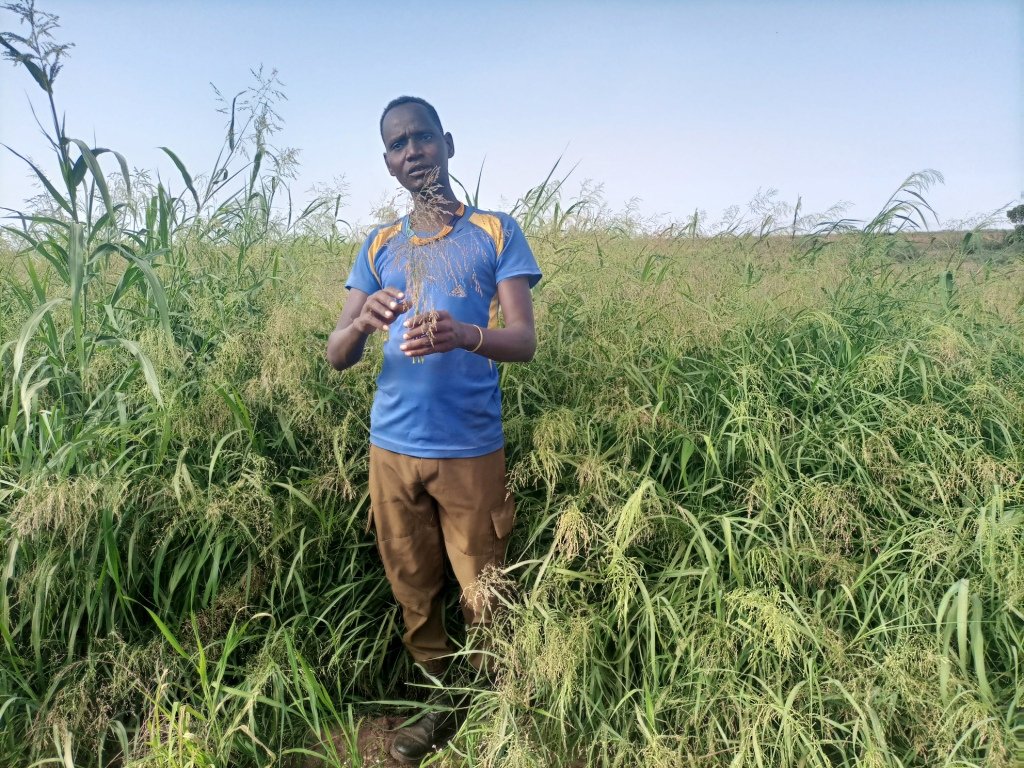
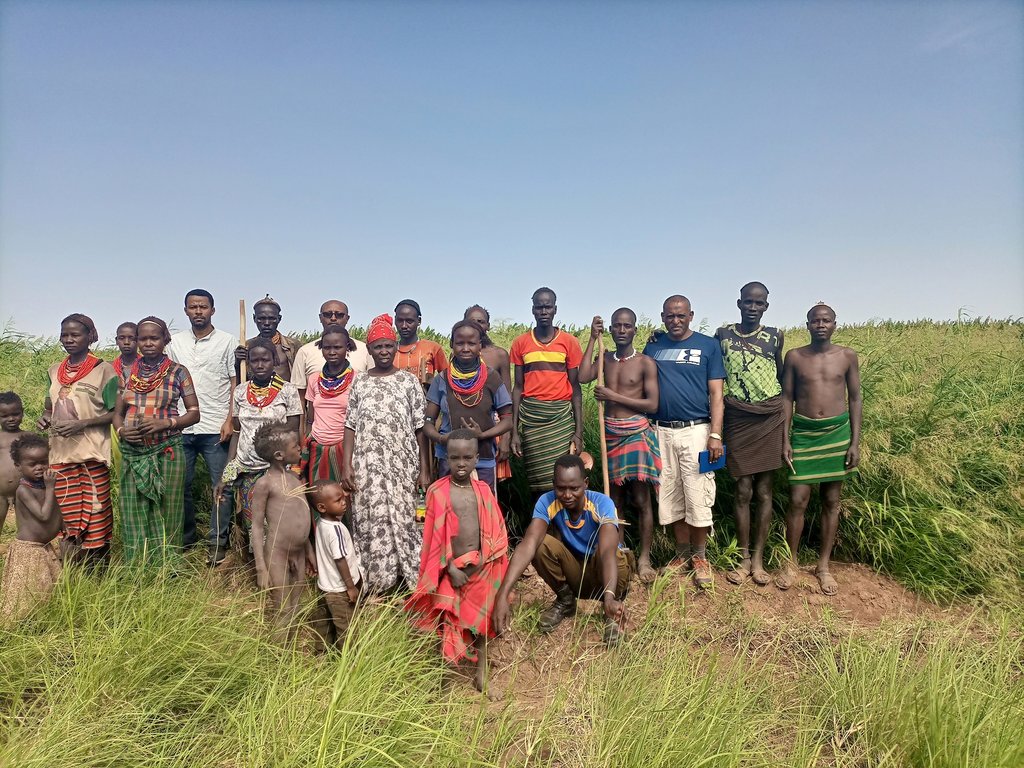
Lutulya Abebe
Agro-pastoralist (fodder producers group leader)
เอธิโอเปีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Resilient in Pastoralist Areas (RIPA)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Development Enterprises - Ethiopia (iDE-Ethiopia) - สหรัฐอเมริกา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is a regenerative practice friendly to the environment.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
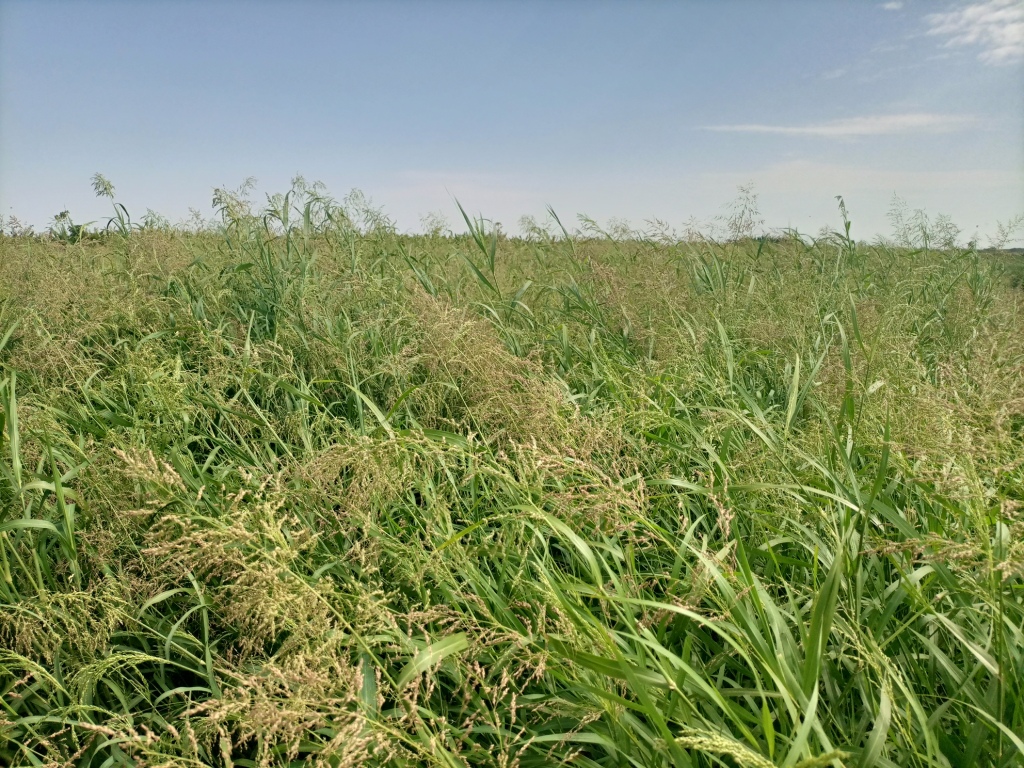
Panicum coloratum is a palatable tropical grass with high biomass production potential. It is grown in the irrigated fodder development areas of Dassenech district. Panicum is a fast-growing perennial which can be repeatedly harvested once it reaches maturity. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortage in dry periods – which are becoming worse with climate change.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Irrigated fodder production is carried out by pastoralist groups in arid areas of South Omo. Among a number of fodder grasses, Panicum coloratum is a fast-growing species. Panicum is grown as livestock fodder, particularly for the dry season when feed availability is in short supply. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortages which are becoming worse with climate change. Also, growing fodder grass allows resource-poor pastoralist communities to generate income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Irrigating at least twice a week, good weed management, and fertilization ensure sustained production.
In Dassenech district of Southwest Ethiopia, Panicum’s annual fresh biomass and dry matter production potential is over 63 and 18 tons/ha, respectively. It can reach its first harvest after about 60 days and subsequently can be harvested every 45 days. Panicum germinates and establishes readily on any soil type under both irrigated and rainfed conditions. It is also drought tolerant and resilient to climate variability, and does particularly well on alluvial soils with high fertility. Panicum is mainly used for grazing, but it is also suitable for cut-and-carry feeding systems. Each member of the pastoralist group grows panicum on 0.04 ha of land. In the flood lowlands of the Omo River basin, panicum is known for tolerating periodic flooding, salinity, & disease.
Previously, the land users were unfamiliar with this particular grass and its associated management practices. Also, irrigating on a regular schedule and keeping the grass free from roaming animals adds a work burden to the pastoralist community. However, the Resilience in Pastoral Areas (RIPA) project has introduced and familiarized the community with fodder production and management practices. The project also assists in linking the output to sustainable market. In this regard, the contribution of the RIPA project of the International Development Enterprises (iDE) is immense. The pastoralists appreciate their livestock’s access to year-round feed, as well as the generation of income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Fodder production also creates year-round employment opportunity. However, the community's reliance on government and civic organization support for land preparation and access to irrigation water (conveyance services) might be considered a threat to ensuring sustainability of fodder development by the pastoralist groups.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Videos of the technology is not documented.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Southern Nations, Nationalities and People Region (SNNPR).
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Omorate, Dassenech.
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Panicum production site is closer to the mouth of the Omo river. The technology is piloted in two sites and scaling up sites have been increasing around the irrigable areas.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2021
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Resilient Initiatives in Pastoralist Areas project of the International Development Enterprises has implemented fodder development along with other perennial crops such as banana as part of promoting resilient agriculture in the dry areas of South Omo Zone of SNNPRS.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- natural grasses
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
The area receive bimodal rainfall but not reliable to grow crops.
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
Animal type:
- camels
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- goats
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- economic security, investment prestige
- milk
- skins/ hides
Species:
goats
Count:
12
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
8
Species:
camels
Count:
1
Species:
sheep
Count:
9
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The site is pastoralist area who used to rely on flood retreat agriculture in the past. However, due to the construction of Gibe III hydroelectric power dam, the spill over during plenty of rain remain still as artificial lake over thousands of hectare for long period of time. As a result, the conventional agriculture practices abandoned. Thus, a shift to irrigation agriculture is in the process at least to produce fodder crops and other perennial crops such as banana for consumption and market.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- herbs, chili, capsicum
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area used to receive short rain twice a year. However, rainfall distribution is unreliable. So, the introduced perennial fodder and banana production persist throughout the year using irrigation.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Fodder and tropical fruit crop production is entirely practiced using full irrigation from Omo river.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Perennial fodder production contributes to SLM through permanent soil cover.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As a perennial crop, the grass covers the ground permanently and reduces moisture loss to excessive evaporation in the dry areas.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
This is the photo of the pastoralist group. There is no specific sketching that portrays the technology but the following points provide tips for adopters of the technology:
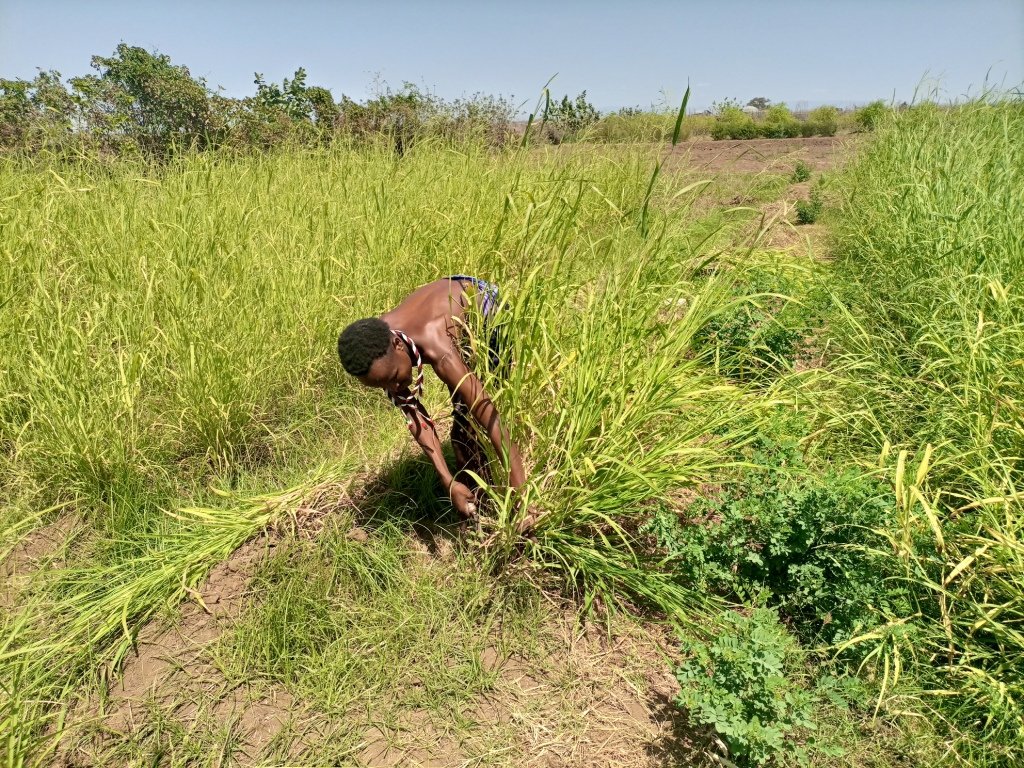
- The land is tilled and harrowed by a tractor for two to three rounds.
- On the third-round ridge and furrow are formed using tractor or hand tools.
- The seeds or splits are planted in rows along the ridge.
- Spacing between ridges varies with the purpose: for haymaking 25 -30 cm and for seed production 50-60 cm to simplify the application of intensive management practice for the latter one.
- The farm/crop should be irrigated twice a week for better production.
- Need Fertilization to ensure good production/harvest.
ผู้เขียน:
Gerba Leta
วันที่:
19/08/2022
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 timad
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
4 timad
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Ethiopian Birr (ETB)
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
53.438
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
It is variable based on the types of work (from 50 birr to 100) for half day before the sun gets too hot. That is equivalent to one day in dry lowland areas.
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing and land preparation | Any season for irrigated fodder production, |
| 2. | Planting/sowing | During the start of season for irrigation fodder production. |
| 3. | Fertilizing | At planting and at boot height. |
| 4. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 5. | Weeding | Twice starting 3- 4 weeks post planting. |
| 6. | Harvesting the grass (fodder) | During harvest maturity. |
| 7. | Hay making (bailing) | Post harvest. |
| 8. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | Harvesting season and post harvest. |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As fodder development is based on irrigation, it can be started any time/season of the year.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Clearing and land preparation | PDs | 12.0 | 200.0 | 2400.0 | 50.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting/sowing | PDs | 5.0 | 100.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 14.0 | 200.0 | 2800.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weeding (twice a season) | PDs | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | Pcs | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoes | Pcs | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seed | kg | 4.0 | 300.0 | 1200.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | NSP | kg | 50.0 | 50.0 | 2500.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 15200.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 284.44 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Other than cost of labor, some inputs and material costs are covered by the RIPA project of the iDE.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Irrigation-based fodder development is in the pilot phase. There is growing interest among the government organization (Woreda Office of Agriculture) to adopt and scale up the promising development. Please note, the cost is estimated only for a season or one round of production. Once reaches its first harvest, Panicum can be harvested every other 45 days onward. Of course, it needs the application of necessary management practices, every season.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning irrigation ditch | During off-season or before the start of next growing season. |
| 2. | Fertilizer (NSP) | Twice: at the beginning of the season & when the fodder reaches boots height. |
| 3. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 4. | Weeding (2x) | Based on the density or prevalence of weeds. |
| 5. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | When the seed reaches harvest maturity. |
| 6. | Harvesting and hay making | At harvest and post harvest. |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As there is no structure such as fodder banks, maintenance cost is not documented.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cleaning irrigation ditch | PDs | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 12.0 | 200.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weeding (at least twice during the growing season) | PDs | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | NSP Fertilizers | kg | 50.0 | 50.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 10900.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 203.97 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
NA
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost estimation is only for one irrigation season that may range from 45 days to 60 days or some more including the harvesting and drying of the outputs. Once established, the cost of production is gradually declining.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Economic crisis and increasing Inflation rate affect the establishment as well as maintenance costs. Particularly, fuel, fertilizer, and labor costs are consistently changing.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Erratic and unpredictable.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Rainfall distribution is unreliable to produce crops under rainfed conditions.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The site is in the lowland around the mouth of Omo River basin.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil pH is over 7 and the soil is slightly saline alluvial.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Diversion/river water is used for irrigation. There is ample water provide that there is pump to convey the water to the nearby farm. In the rainy season, the river is turbid and full of eroded soil from the upstream catchments. However, the depth of the water table is variable based on the distance of the farm from the edge of the river. Around the main river basin, the water table is shallow but too deep as one go away from the river basin.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Around the farmland, diversity of crops and vegetation is limited. Away from the farmland, there are a few lowland shrub species and faunas common to the dryland.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The water pump is used to convey water and the tractor for land preparation. Therefore, a mix of mechanization and manual systems are employed in the area. Irrigation land was allocated to the group but they partitioned and distributed to each member of the group.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As their animal is freely roaming, only small size of land is permantantly owned around the river side and homestead.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- กลุ่ม
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
The pastoralist, still freely move and settle where they think appropriate and shift after certain years.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Apart from the irrigable land which are located around the river basin, land is openly accessible to the pastoralist community.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Access to facility and the services is mainly to those pastoralist community who are residing closer to the Omorate, the woreda capital.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Access to irrigation water increase the fodder production throughout the year.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the alluvial soil around the river bank is suitable for Panicum, it increases the quality of fodder.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase in livestock production is related to the availability of feed/fodder.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Access to irrigation water highly reduced risk of production failure.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-1
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The land that used to be ideal is now converted to farming.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Panicum as perennial fodder increases ground cover throughout the year and contributes to land management from wind erosion in the dry land areas.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-3
หลังจาก SLM:
1
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
-1
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As Panicum is harvested at least six times a year post reaching the first maturity, farm income is significantly increases.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income can be generated from the sale of fresh fodder, hay and seeds.
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-2
หลังจาก SLM:
0
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Irrigated fodder production needs intensive management practices. Panicum is perennial fodder that remain on the field all year round. So, irrigating, weeding and looking after the farm... increases the workload.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-1
หลังจาก SLM:
2
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-1
หลังจาก SLM:
1
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
1
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-2
หลังจาก SLM:
2
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-2
หลังจาก SLM:
2
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-2
หลังจาก SLM:
1
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As it permanently covers the ground, it has high likelihoods of reducing surface runoff.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improve water drainage.
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Decreases surface evaporation but not transpiration.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The farm remains covered by perennial grass. Irrigating the farm also favor the regrowth of other wild species.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Above ground biomass is highly increased as described in the description section.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced with increased management practices. Invasive alien species such as Prosopis juliflora is less common in this part of the River basin.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Animal diversity correlates with fodder availability.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It reduces the impacts of drought on livestock by providing access to adequate feeds throughout the year.
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As Panicum increase ground cover and store the carbon above and below the soil surface, it reduces the emission of the carbon.
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It breaks the velocity of wind in the lowland, one of the main issues.
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Slightly ameliorate the micro-climate of the area.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
0
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It is expected that downstream flooding is reduced as the perennial fodder crop cover the ground throughout the year.
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-3
หลังจาก SLM:
0
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-1
หลังจาก SLM:
0
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Permanent ground cover expected to increase the filtering capacity.
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It has expected positive effects of reducing wind transportation.
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As perennial crops cover the ground and absorb the carbon, it has an inevitable positive effects on reducing carbon emission.
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The fodder development is a pilot practice. Its up scaling will have a positive off-site effects to the surrounding areas.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดีมาก |
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ดี |
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Panicum has drought, flood and disease tolerating feature.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology was piloted two years ago. The cost of establishing it is partly supported by the RIPA project. Land preparation and conveying irrigation water covered by the local government.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
So far, the pastoralist piloted the technology through government and NGO support.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Supply year round feed for the land users' livestock. |
| Allow pastoralists/agro-pastoralists to generate income from the collection and sale of fresh fodder, hay and seed. |
| The technology supplies feed that can be reserved for the emergency time through hay making. |
| Introduction of fodder production technology enables the pastoralist group access usufructs to irrigable land that promotes the changing in farming practices from entirely pastoralist to agro-pastoralist on a gradual basis. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology considered as one of the regenerative agricultural practices that have positive contribution to carbon sequestration. |
| It reduces risks of feed shortage during the extended dry season. |
| A prompt sources of income for the pastoralist community via the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. |
| Feeding livestock on grass reduces methane production as compared to feeding them on processed feeds. |
| The onsite shattering of the seed increases the density of grass every other season. Thus, it improves the ground cover and production of huge biomass per unit of land. |
| Panicum harvested 15 cm high that simplify regrowth/tillering and propagation of the grass from the ratoon. The practice stimulates prompt ground cover and year-round sequestration of carbon. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Access to irrigation facility and service is via government and project support. | Try to secure multiple sources of finance, and encourage market oriented production to enhance the pastoralist groups develop reliance on their own. |
| Smaller size of land is accessible to irrigation. | Increase intensification of fodder development and diversify sources of income via production and marketing of fresh fodder, hay, and the seed. |
| Shortage of baling machine to fasten the hay for simplicity of storage and transportation | Improve pastoralist access to the facility and services so that their resilience to feed shortage and associated issues are promptly increases. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Shortage of storage structure or fodder bank to store/ reserve the harvest for market and/or later uses. | To promote the establishment of storage or fodder bank by the land users group themselves, and try to find sources of finance to support them in this regard. |
| Lack of sustainable market links for Panicum seed. | Establish reliable market value chain with private suppliers/distributors to the other part of the country. |
| Lack of legume fodder species to improve the dietary value of the grass family. | Introduces important legume species with high biomass production potential or other leguminous tree species with multiple uses such as windbreak or as buffer plants around the periphery of the fodder farm. |
| Panicum needs longer time to reach harvest if intended for seed production that may dishearten the pastoralist to wait longer time. | Allocate separate plots for seed production, or else, make the right choice for the types of outputs that suits the pastoralist's urgent needs. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Over 20 members of the pastoralists group are met.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
One knowledgeable land user who is representative of the pastoralists group.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Three
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Published articles and locally developed guideline for growing Panicum.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
20/08/2022
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Field visit was made from 17 August to 19, 2022.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
ILRI. 2013. Colored Guinea grass (Panicum coloratum) for livestock feed on small-scale farm. ILRI Forage Factsheet.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Free online
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Hitiso, W. & Guyo, M. 2017. Biomass Production of different grass species available at irrigated lowland of Dassench woreda in Southwestern Ethiopia. Bangladesh Journal of Animal Science, 46 (3): 188-191.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Free online
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Adicha, A., Sultan, M., 2022. Production and Commercialization Status of Improved Panicum Grass Cultivation in the Lowland Livestock Production System of South Omo South-Western Ethiopia. Research on World Agricultural Economy, 3 (4): 694. DOI:10.36956/rwae.v3i4.694
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Free online
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Tropical Forage. 2020. Panicum coloratum
URL:
https://www.tropicalforages.info/text/entities/panicum_coloratum.htm
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is very comprehensive and inclusive to socio-economic and environmental benefits, and the effects of a specific SLM technology.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล