Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [ตูนิเซีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6669 - ตูนิเซีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Agricultural Economist:
Frija Aymen
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Forage Specialist:
Zaiem Anis
Office de l'élevage et des pâturages (OEP)
ตูนิเซีย
Agricultural and Resource Economist:
Boubaker Dhehibi
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Senior Livestock Scientist:
Rekik Mourad
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ตูนิเซีย
Director of ITGC research station in Setif, Algeria:
Louahdi Nasreddine
Institut Technique des Grandes Cultures (ITGC)
ตูนิเซีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - เลบานอน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

The 4-Wheels Approach for sustainable scaling [ตูนิเซีย]
The 4-Wheels Approach addresses the challenge of slow adoption of agricultural innovations among smallholder farmers by establishing Knowledge Hubs and partnerships with diverse stakeholders. The focus is on income-generating technologies and essential factors behind successful scaling up of innovations, ultimately driving agricultural modernization and sustainability.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
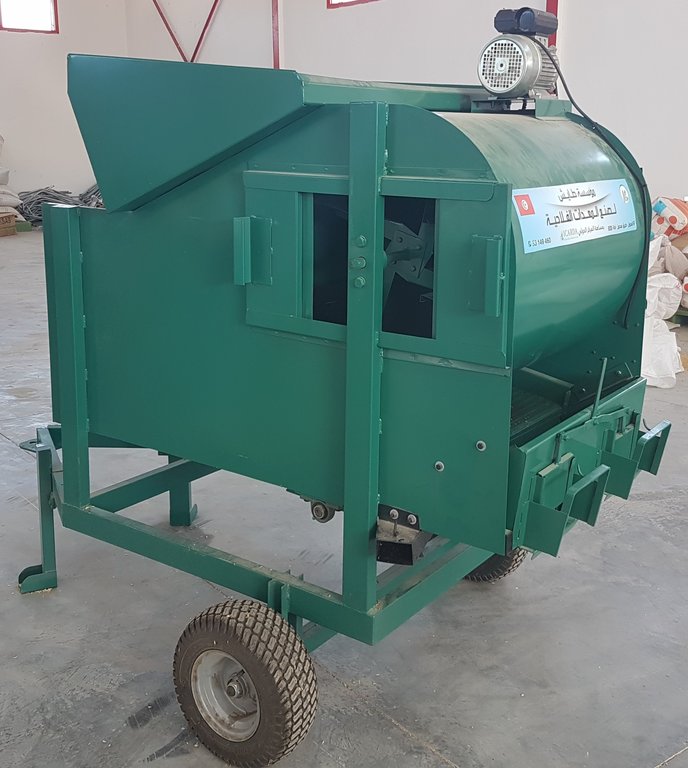
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
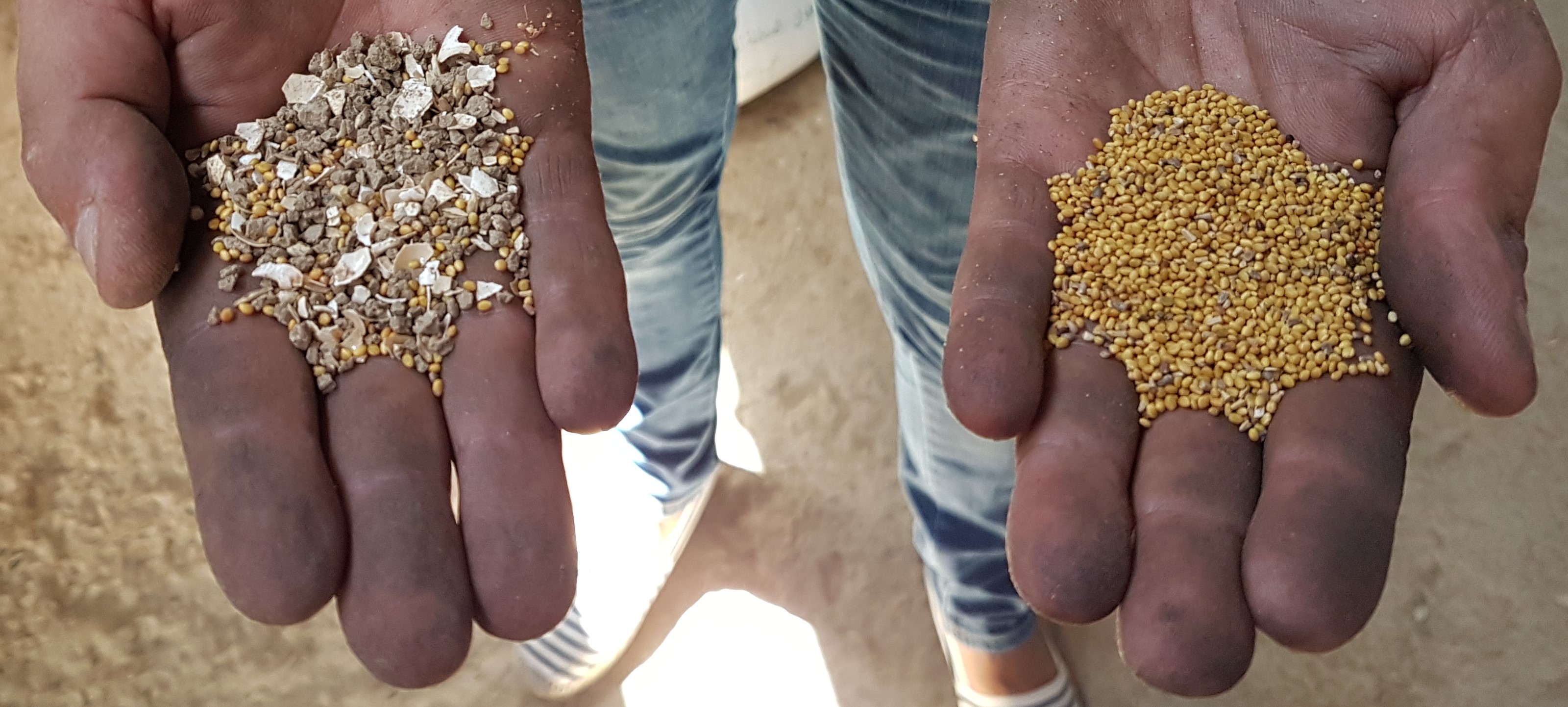
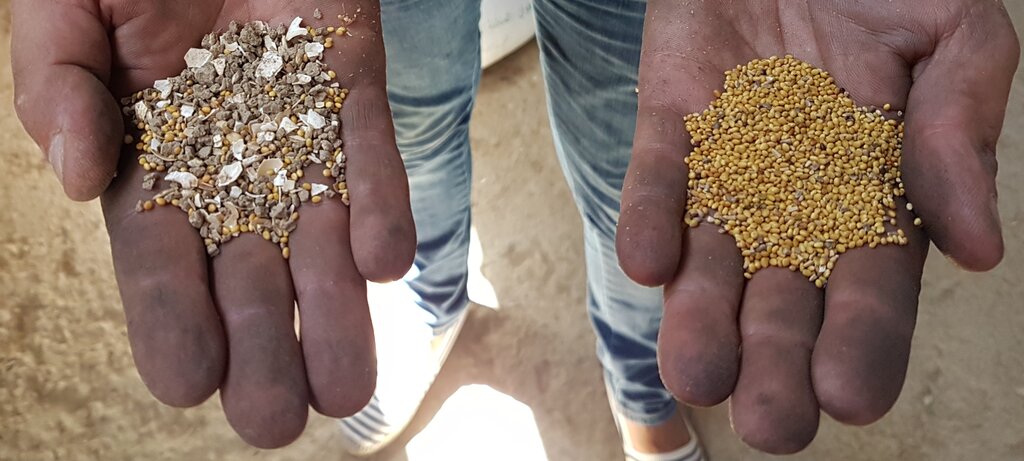
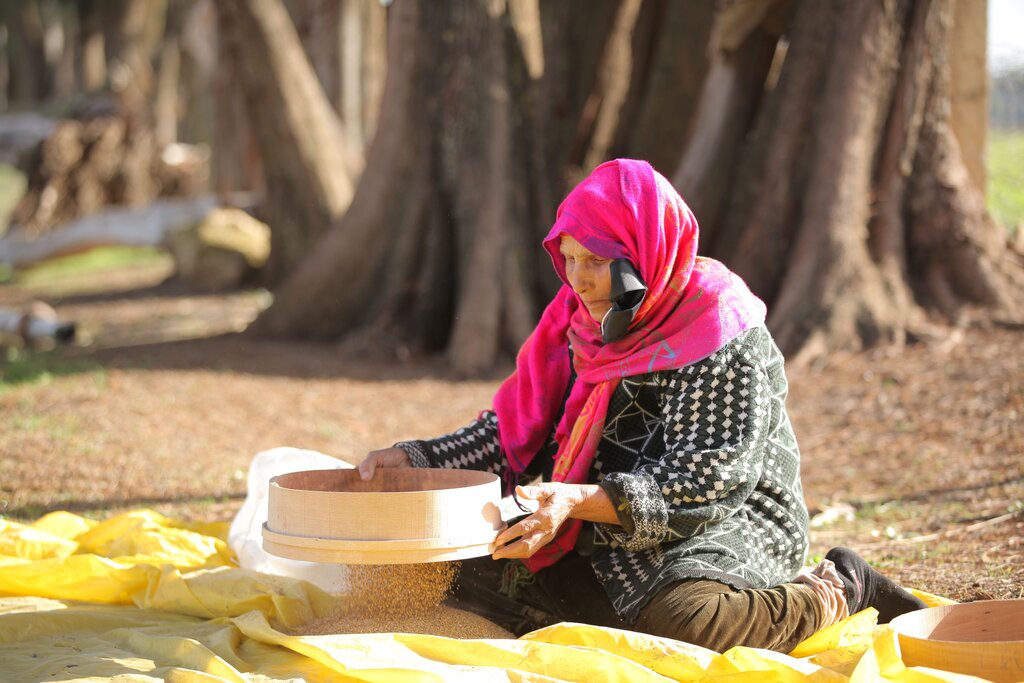
In Tunisia and Algeria, the agricultural system is characterized by low levels of mechanization, particularly among small and medium-sized farmers who cannot afford expensive imported machines. As a result, a substantial amount of manual labour is required to carry out various agricultural operations, such as seed cleaning, which is traditionally done by women and children. While seed production is often done by large suppliers, this does not always satisfy the demand. Therefore, many smallholder farmers in Tunisia prefer to use their own seeds, despite the time-consuming manual cleaning process and the risk of lower quality.
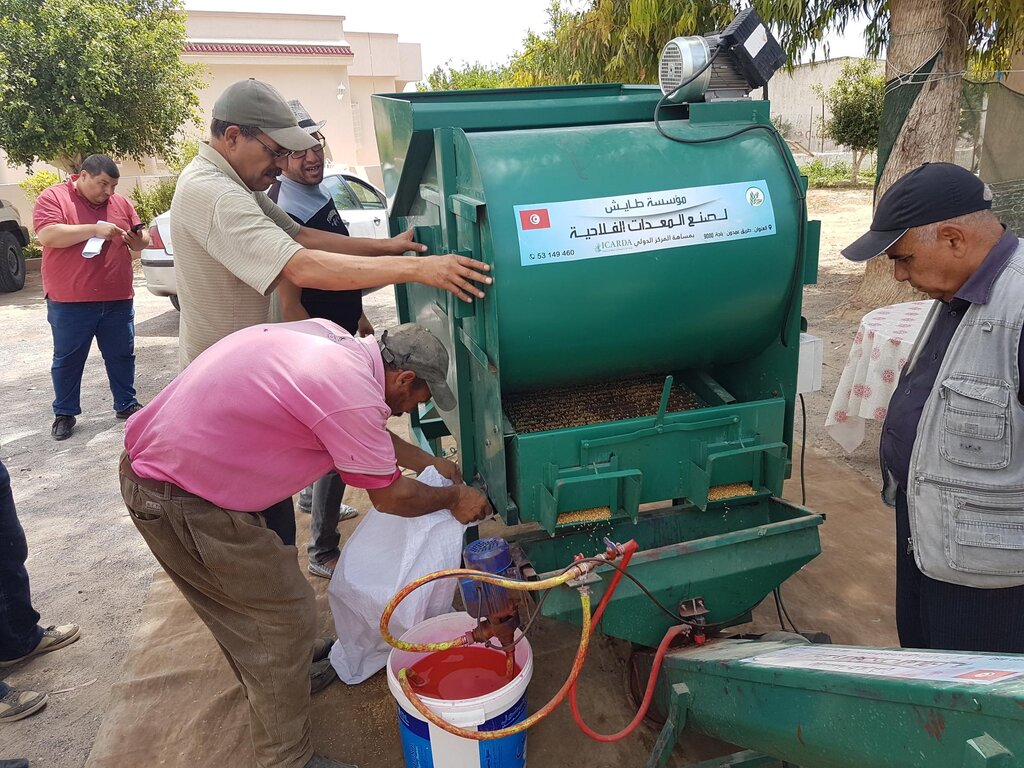
To address these issues, the International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) collaborated with national partners to develop a mobile seed cleaning machine for small-scale farmers. The prototype, designed and tested with input from a local manufacturer, is suitable for the primary field crops (such as wheat, barley, vetch, and faba beans) in Tunisia. The machine sort out damaged or small seeds and rock or pebbles, while treating the remaining seeds by removing contamination or weeds, to ensuring quality and longer shelf-life.
The mobile seed cleaning machine, with a capacity of approximately 800 kilograms per hour depending on the seed type, was distributed to four farmer cooperatives, serving a total of 1,000 small-scale farmers. In order to promote ownership, the farmers contributed to a portion of the costs and received training on how to operate the machine effectively.
When using the mobile seed cleaning machine, farmers have the option to choose between two methods: solely cleaning the seeds or cleaning and treating them. The cost for cleaning alone is around 2 Tunisian Dinar per 100 kilograms, while the cost for both cleaning and treating, which includes the application of a fungicide, is 8 Tunisian Dinar per 100 kilograms. Life time is estimated between 5 and 10 years and worn out parts can easily be replaced.
The introduction of the mobile seed cleaning machine has several advantages, including a decrease in workload for women and children, improved production and quality of crops, higher productivity of the land, reduced dependence on imported seeds and machinery, and the promotion of local value chains and social cohesion through cooperative ownership and utilization of the machines.
However, there are still some challenges to overcome. For example, the initial prototype required heavy bags of seeds to be lifted to a height of two meters, leading to additional labour requirements and reduced efficiency. This challenge was addressed by equipping the machine with a conveyor screw, which can double its capacity at an additional cost. Additionally, the cost of purchasing the machine can be a significant investment for farmers, but this can be overcome through collective buying and organizing themselves in cooperatives.
In conclusion, the mobile seed cleaning machine represents an innovative solution that improves the (local) value chain and livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by reducing workload and costs, particularly for women and children. This technology has the potential to be scaled up and benefit other regions and cooperatives.
ICARDA’s work on Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit is supported by the CGIAR Research Program on Livestock, the IFAD-Funded CLCA Project, the GIZ SWC@Scale project as part of the ProSol global program, and the CGIAR initiative on Agroecology in Collaboration with National Partners in Tunisia and Algeria (OEP-Tunisia, IRESA-Tunisia, INRAT Tunisia, ITGC-Algeria, GIZ Tunisie, DGACTA-Tunisie)
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ตูนิเซีย
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2019
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
see 2.2
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Crops like barley, vetch and faba beans, are cultivated to feed livestock. The manure from livestock is used to fertilize the lands.
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
Species:
sheep
Species:
goats
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- ประสิทธิภาพด้านพลังงาน
- มาตรการหลังเก็บเกี่ยว
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A5: การจัดการเมล็ดพันธุ์ การปรับปรุงพันธุ์

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S10: มาตรการในการประหยัดพลังงาน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The seed cleaning machine has the following dimensions:
-Length = 180cm
-Width = 80cm
-Height = 175cm.
Equipped with a high-quality sieve measuring 140cm in length and 65cm in width, the seed cleaning machine ensures that even the smallest impurities are removed from the seeds. With a hopper capacity of 200kg, the machine can accommodate large batches of seeds, allowing for uninterrupted cleaning.
The machine has a cleaning capacity of around 600 till 1000kg/h.
Its lifetime is estimated to be between 5 and 10 years. Worn-out parts are easily replaceable and locally available.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
100 kilogram cleaned and treated seed
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tunisian Dinar
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
3.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
25
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Seed cleaning machine with conveyor screw | 1.0 | 12500.0 | 12500.0 | ||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 12500.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4166.67 | |||||
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Operating | person-hour | 0.1 | 10.0 | 1.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Electricity | kWh | 3.0 | 0.066 | 0.2 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Uncleaned seed | kilogram | 100.0 | |||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fungicide (for treating) | litre | 0.2 | 30.0 | 6.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 7.2 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2.4 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers can choose to only clean or to also treat. Treating consists of applying fungicide as well. Farmers usually pay 2 TD/100kg for only cleaning and 8 TD/100kg for cleaning and treating.
Cleaning (and treating) 100 kilograms of seeds results in 70 kilogram of good useful seeds.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The costs of purchasing the machine is substantial. However, this should be shared among farmers within the cooperation.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
This innovation can be implemented in many different environments.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
This innovation also affects the children of the land users because the children are often the ones who do the seed cleaning
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Is improved due to better yields and no/less costs on purchased seeds
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cleaned seeds could be sold
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mechanically cleaning substituted the manual cleaning (often done by women and children)
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
Dependency on seed distributors
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Substantially reduced in workload. |
| Decreased costs, and decreased dependency on the seed market |
| Improved seed quality |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Improved gender equality because women and children mostly did the seed cleaning. |
| The unit is mobile hence many farmers can use it. |
| The seed cleaner unit and produced seeds improve the value chain on a local level |
| The seed cleaner unit is used within a farmer organization, hence it improves the cohesion within this organization. |
| Using cleaned seeds increased the productivity of the land. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Entering uncleaned seeds (bags usually weigh between 30 and 50 kilograms) into the machine, which is a lift around 2 meters, is too difficult for one person so additional labour is required. | The newer machines have a conveyor screw, to transport seeds from the ground to the entry. It is estimated that this will double the capacity. |
| Investment is required | Organizing in cooperations so costs can shared |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Rudiger, U., Zaiem, A., Idoudi, Z., Frija, A., Rekik, M. and Taher, A. 2021. Mobile seed cleaning and treatment unit improves forage seed quality and quantity and presents a successful business model for farmer cooperatives. Business Model Brief. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/10568/116748
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Aymen, F., Idoudi, Z., Rudiger, U. and Rekik, M. 2020. Collaboration between ICARDA projects and linkages to IFAD investment portfolio for enhancing seeds quality and forage production through entrepreneurship and farmers associations. Some examples from ICARDA activities in Tunisia. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://repo.mel.cgiar.org/handle/20.500.11766/11134
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Rudiger, U. 2020. Report on small mobile seed treatment units for cooperatives in Tunisia
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12323
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Udo Rudiger. (15/12/2020). Workshop with beneficiaries.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12556
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Frija, A., et al. 2022. Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security – ProSol: Towards the Effective Scaling of Soil and Water Conservation Technologies under Different Agroecosystems in North and Central West Tunisia – SWC@Scale/ProSol: Technical Progress Report/ January – August 2022. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67835
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Idoudi, Z. 2020. Encouraging Entrepreneurship with Mobile Grinders and Seed Cleaning Machines
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.icarda.org/media/blog/encouraging-entrepreneurship-mobile-grinders-and-seed-cleaning-machines
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Idoudi, Z., Najjar, D., Rekik, M., Frija, A. 2022. Integrating Gender in the Use of Conservation Agriculture for Crop and Livestock System (CLCA). Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67126
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Rekik, M., Frija, A., Idoudi, Z. 2022. Overview of CLCA Main Achievements in NA and LAC Countries. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68177
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Rudiger, U., Zaiem, A., Idoudi, Z., Frija, A., Rekik, M. and Taher, A. 2021. Mobile seed cleaning and treatment unit improves forage seed quality and quantity and presents a successful business model for farmer cooperatives. Business Model Brief. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/10568/116748
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

The 4-Wheels Approach for sustainable scaling [ตูนิเซีย]
The 4-Wheels Approach addresses the challenge of slow adoption of agricultural innovations among smallholder farmers by establishing Knowledge Hubs and partnerships with diverse stakeholders. The focus is on income-generating technologies and essential factors behind successful scaling up of innovations, ultimately driving agricultural modernization and sustainability.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล