Contour Stone Bunds [ภูฏาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nima Dolma Tamang
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Kuenzang Nima
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
རྡོའི་གད་ཚིགས།
technologies_6891 - ภูฏาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Yangzom Pema
NA
ภูฏาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - ภูฏาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology reduces soil erosion and conserves soil moisture
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Community Mobilization for SLM Interventions [ภูฏาน]
Community mobilization in implementing sustainable land management technologies is indispensable in engaging the community to identify their priorities, resources, needs and solutions. It ultimately promotes bottom-up participation and fosters accountability.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nima Dolma Tamang
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
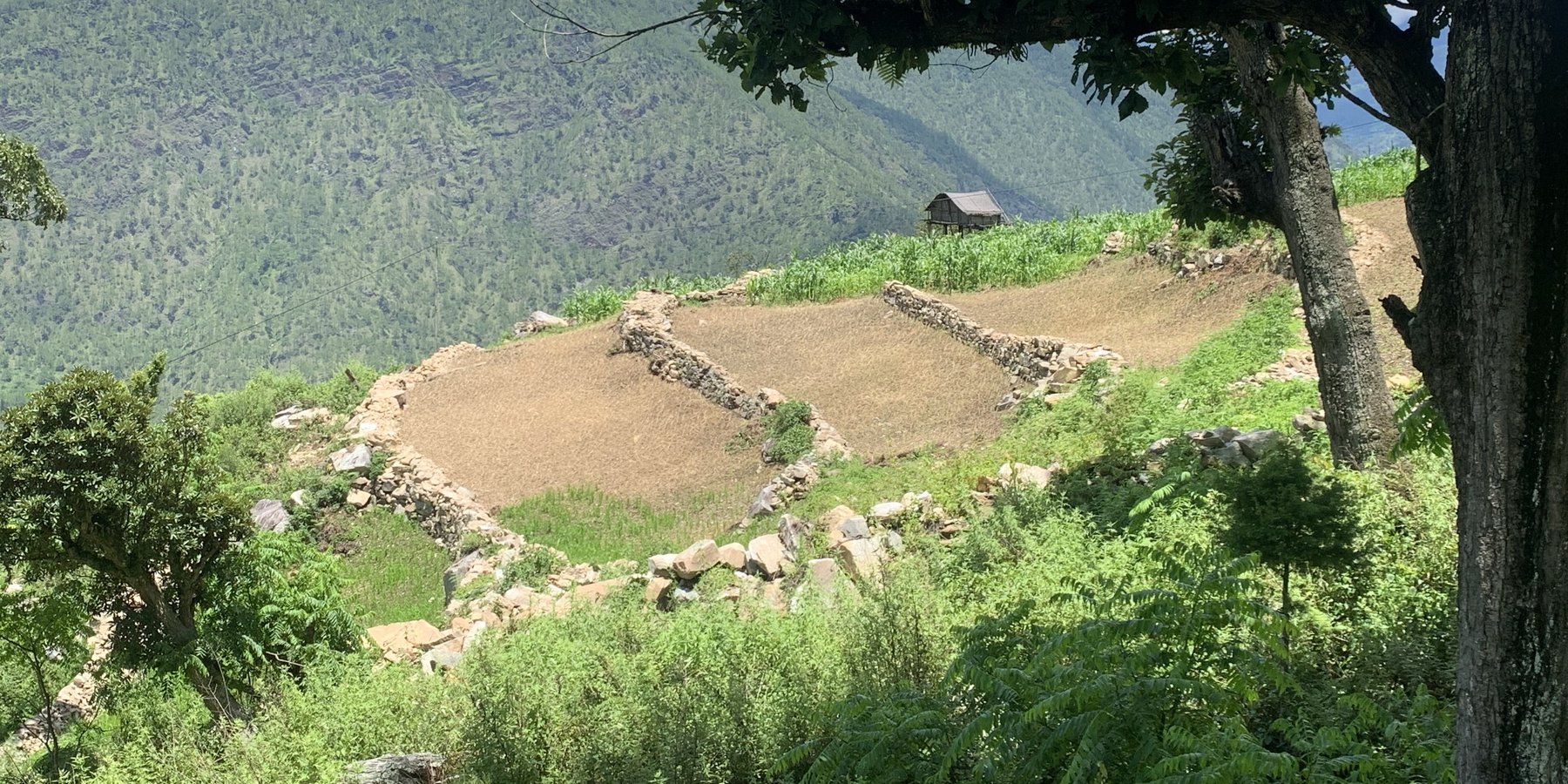
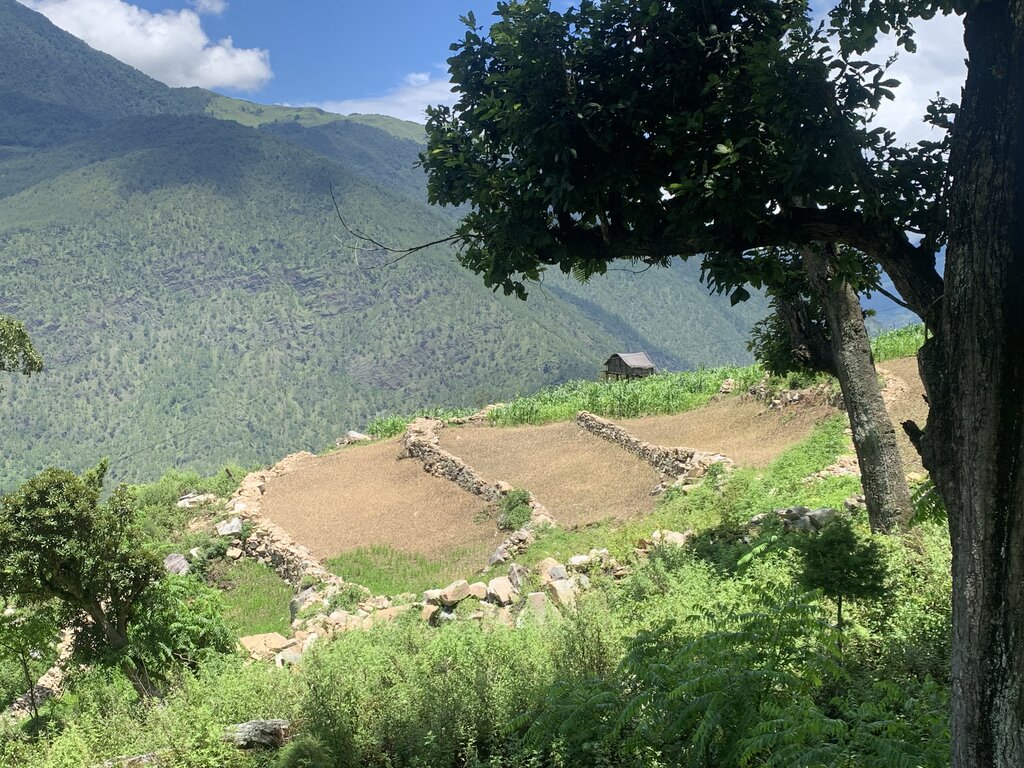
Contour stone bunding on sloping agricultural lands reduces soil erosion and conserves soil moisture in order to retain soil productivity. It is promoted /recommended on slopes where there is adequate surface stone.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
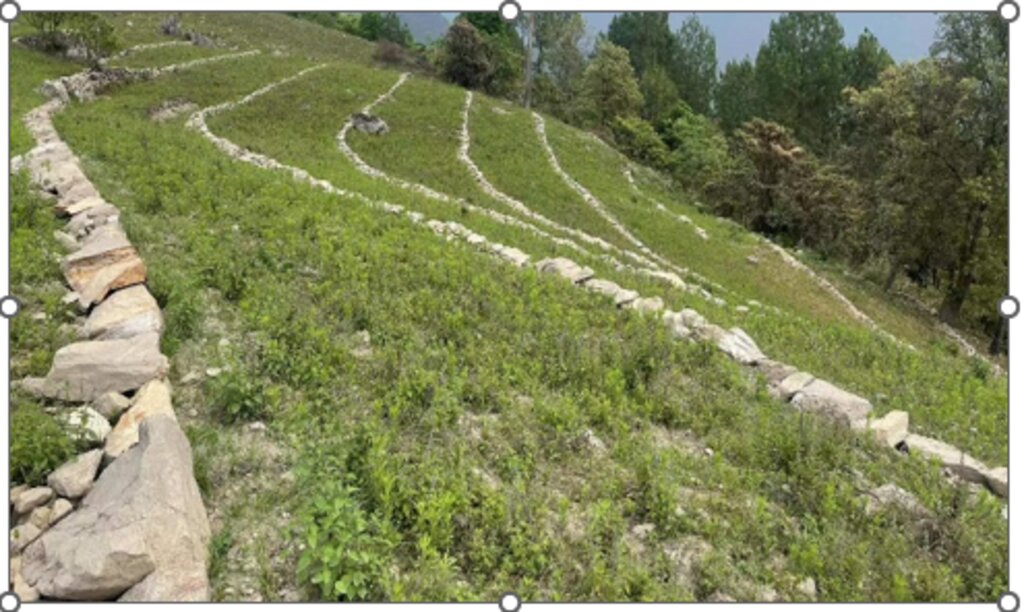
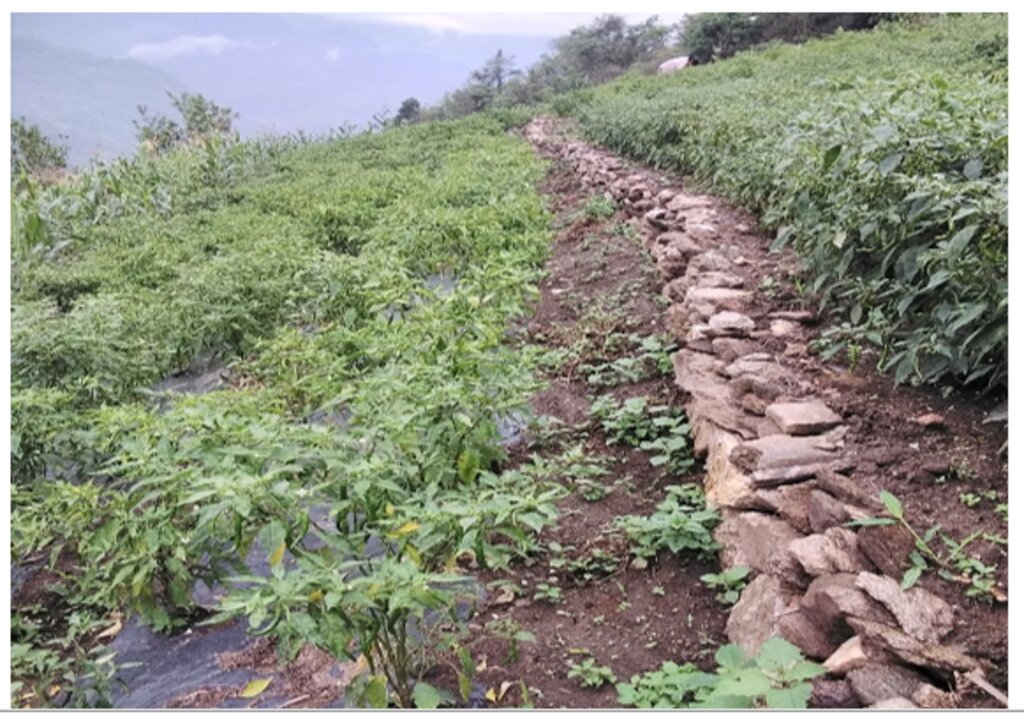
Contour stone bunds are small walls of stone that are laid out along the contour line to help reduce soil erosion, conserve soil moisture, increase soil fertility, to ease workability, increase cropping area, and ultimately ensure sustainable use of lands for enhanced food and nutrition security. This practice is recommended in fields that have plenty of surface stones (> 20%). Construction of contour stone bunds not only helps to get rid of the excess surface stones and gravel but also reduces the slope gradient through formation of partial terraces over a few years.
The stone bund is not new to Bhutan, being a mountainous country, forefathers used the technique to remove stones from the field and stabilise the land for agricultural purposes. Therefore, there were some traditional stone lines constructed in the study area.
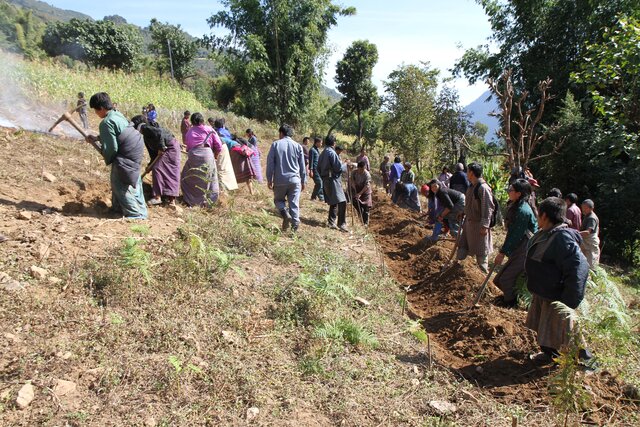
Constructing stone bund is labour intensive, therefore land users resort to a labour sharing approach where all the land users from the community come together and work on a rotational basis until every household in the community has established stone bunds.
The major activities and inputs required to establish the contour stone bund includes sensitization of beneficiaries, followed by SLM action planning, and hands-on-training. Field implementation follows this sequence: (a) determination of intervals between stone bunds, (b) demarcation of contour lines using an ‘A’ frame, (c) digging a trench of 0.1 - 0.2 m deep and 0.5 m wide to establish a foundation along the contour lines, and (d) constructing stone lines along the trenches with the larger stones at the base to set a sound foundation. A typical stone wall is 0.3 m high (1 ft) and 0.3 - 0.5 m wide, but this depends on the slope and availability of stones in the field. Contour stone bunds are commonly spaced 6 metres apart on slopes of 60%. In some cases, the fodder grass slips are also planted at the base of the stone bund for better stabilization of the bunds and fodder availability.
The major drawbacks of this SLM technology according to respondents are (a) labour demanding, (b) no immediate return, and (c) the space between piled stones harbours rodents leading to crop damage.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ภูฏาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Lhuentse Dzongkhag
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Zangkhar Village, Yabi-Zangkhar Chiwog, Jaray Gewog
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
The region where this SLM technology was implemented falls under Phrumsengla National Temperate Park. Phrumsengla National Park is a temperate park with large tracts of old-growth fir forests, its altitudes ranging from 700 metres (2,300 ft) to 4,400 metres (14,400 ft). Phrumsengla has scenic views, including forests ranging with elevations from alpine to sub-tropical. Because the soil of Phrumsengla's biomes is particularly fragile, the land is unsuitable for logging or other development
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2015
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The National Soil Service Center (NSSC), Semtokha, Thimphu initiated this activity as part of three-year (2015 to 2017) SLM project funded by Bhutan Trust Fund for Environmental Conservation (BTFEC).
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- Chili, cauliflower, cabbage, onion, brinjal and garlic.
- Peach, pear, fig, chayote
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Maize in summer is followed by cole crops in winter.
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Brinjal, beans, onion and chayote.
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Maize cultivation followed by vegetables (cabbage)

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
- การจราจร ทางถนน รถไฟ
- พลังงาน ท่อส่งก๊าซธรรมชาติ สายส่งไฟฟ้า
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology also incudes vegetative measures where some land users plant fodder grass slips at the base of the stone bunds for better stabilization and fodder availability.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
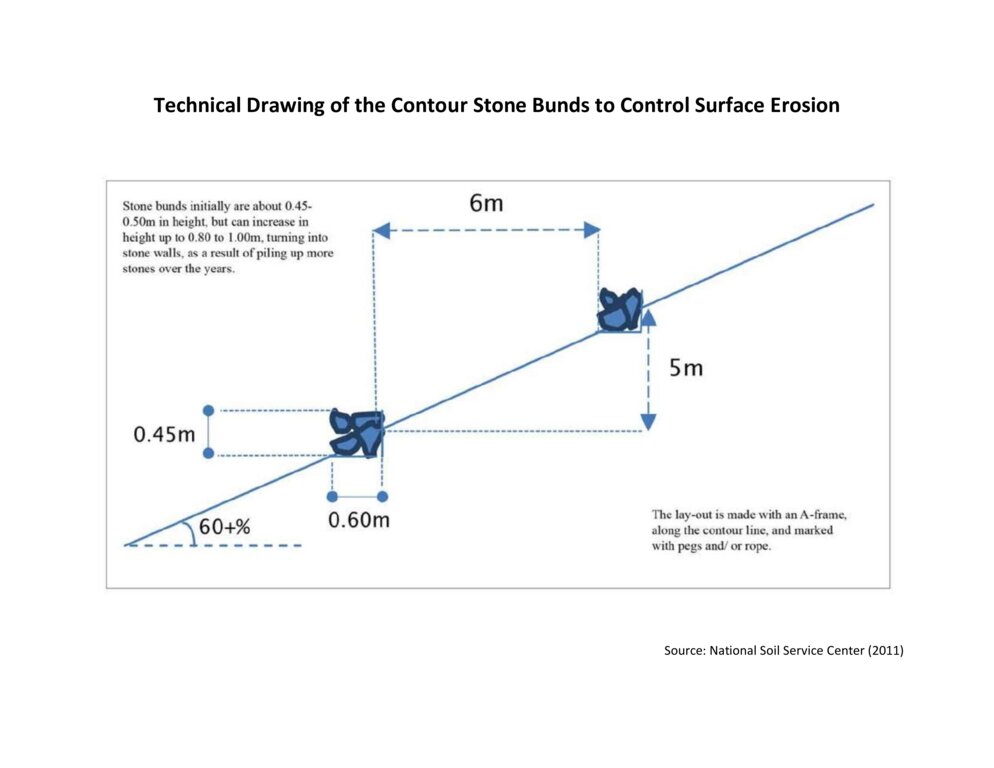
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The specifications provided in the technical drawing (NSSC, 2011) may vary based on the field situation and slope of the land. Variations may be in the width of the terrace (3 m to 6 m), the height of the stone bund (0.45 m to 1m), and minimal variations are observed in the width of the stone bund (0.6 m).
ผู้เขียน:
National Soil Service Centre
วันที่:
2011
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
3 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Nu
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
80.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
400
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Traditional stone bund construction | 50 years earlier |
| 2. | Sensitization, SLM action planning, and Hands-on-training | 2015 |
| 3. | Field implementation of the activity | 2015 |
| 4. | Provision of incentives (Nu. 3000 per acre) | 2015 |
| 5. | Project phase-off | 2017 |
| 6. | Scaling up of this technology through GEF-LDCF | 2022 |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Traditionally stone bunds were constructed by forefathers during land preparation on the slopes. The stones were piled at the contour lines to make the soil workable and improve the gradient of the land.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | Person/day | 49.0 | 400.0 | 19600.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Project incentive | Per hectare | 1.0 | 6420.0 | 6420.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 26020.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 325.25 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs and inputs needed for stone bund establishment are calculated for 1 hectare of land.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The most important factor affecting the cost is labor.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1250.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The rainfall received in the region may vary from 1000 to 1500 mm.
The rainfall data of the Gewog is not available. The area shares a border with the Medtsho Gewog and has similar agroecological zones. The data provided is for Medtsho Gewog.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Website, Lhuentse Dzongkhag Administration
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
The Gewog falls under dry sub-tropical to warm temperate region (1500 to 2400 meters above sea level) from the six agroecological zones of Bhutan. It is characterized by extreme cold in winter and moderate in summer, humid and foggy.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Moisture content 3.10%, organic matter 7.15%, Organic carbon 4.15%, pH 6.79, electrical conductivity 209.20 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.21%, phosphorus 1.00 ppm, Potassium 121.40 mg/100ml, texture loamy sand.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The area is rich in species diversity as it has pockets of microclimate ensuring habitat diversity.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
There are 11 Household members of which only the land user and her mother (86 years old) stay at home. Nine household members have migrated to the city for better opportunities.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user has 4 acres of land of which the technology is applied in 3 acres. The average land holding in Bhutan is 3.4 acres per household in 2021. Therefore, more than 3.4 acres are characterized as large-scale in the Bhutanese context.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
- Family
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The cultivation of potatoes increased due to an increase in the cultivable area as the stones are removed.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crops appear greener and healthier due prevention of soil erosion as the topsoil is retained. Maize leaves were dark green and potatoes were bigger.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the removal of stones from the soil, it is suitable for diverse crop growth (deep-rooted and shallow). Therefore, the land user can cultivate diverse crops throughout the year. Crop diversity and increased growing season will ensure land user with stable household income even if one crop fails.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology reduces workload (mechanization) and increases cultivable area leading to the cultivation of diverse crops for market purposes.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased due to the removal of stones from the land.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Expenses on agriculture input are reduced. For example, with the use of a power tiller which costs Nu. 1500 per day, it takes 2 days to complete ploughing. If it is done by oxen then it takes 8 days and Nu. 400 is paid as a labour charge per day. The total amount required using the power tiller is Nu. 3000 and using oxen is Nu. 3200 with an additional cost of food for the labourers.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Previously the land user was not able to meet the demand for maize as a feed for the cattle. With the introduction of stone bunding and increased production, the land user can meet her domestic demand for maize and additionally sell processed maize alcohol as a source of farm income.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is an increased diversity of income sources as the land user can grow different crops throughout the year and also sell some processed products.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced work load due to farm mechanization. The removal of stone from field had eased workability, lesser wear and tear of farm tools.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
With the increase in cultivable areas, technology has ensured food self-sufficiency and generated income to meet other household demands for food.
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced workload is directly related to an increase in the available time for recreational opportunities.
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Support provided by the NSSC and land users' active participation in the implementation of the technology enabled the national agency to have a better understanding of the land users. Labour sharing enabled the community to work together to achieve a common goal which improved collaboration among the community members.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Awareness was created during the introduction of the technology by SLM specialists. Further, the field observation on the neighbours' fields who have already established stone bunds has led to 90% of the population knowing about the stone bunding in the locality.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Human-wildlife conflict was reduced as wild boars were not able to climb the stone bund. Although other wild animal such as procupine continued to cause harm to the crop.
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology improved soil quality leading to improved production and increased household income.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The stone bund holds irrigation water preventing surface runoff. Further, the gradual labelling of the land increases soil moisture retention capacity.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased due to crop diversification and year-round cultivation.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil erosion and surface runoff is reduced leading to decreased soil loss.
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Eroded soil is accumulated at bunds.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil organic matter is decreased at the upper part of the terrace and increased at the lower part of the terrace due to runoff from the slopes.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased with the practice of year-round cultivation.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology increased suitability of the soil for diverse crops increasing plant diversity.
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The better crop stand resists pest and diseases attacks on crops. To some extend, the stone bunds keep the wild boars away.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced surface runoff leads to decreased landslides or debris flow.
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
The impact percentage given in this section is a mixture of farmer and professional estimates.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
No off-site impact of the technology is expected or measurable on this small scattered scale.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology does not cope well with increased annual rainfall as it loosens the foundation soil on which the stone wall is built leading to the collapsing of the stone wall.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The benefits compared with the establishment costs for the short term are positive due to the subsidy provided.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
Total of 33 households adopted stone bunds technology.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
All the households received incentive in the form of cash and machinery.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Sloping land is challenged by soil erosion and it has a poor ability to retain water. This challenge was alleviated by stone bunding as it significantly reduced soil degradation. |
| The land user shared that there is an increased cultivable area after the implementation of the technology. Bigger stones were excavated and piled as stone bunds increasing the total area for cultivation. |
| The technology eased farming, as agronomic practices such as tilling became efficient due to the use of power tillers. Soil depth was increased leading to ease in weeding, bed making and other management practices. |
| Stone walls prevented wild boar from entering the field reducing crop loss. Therefore, the farmers need not guard the field from wild boar. |
| Increased cultivable area and easy working conditions of the soil lead to increased production, and improved livelihood of the farm household. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology contributed to reducing rural-urban migration and generated employment. Stone bunding indirectly helped the farming community to engage in agricultural activities and stay back in the village rather than going out to the city in search of employment. |
| Prevent natural disasters. The Gewog is located in the steep slopes and there is a risk of landslides leading to loss of agricultural land, property, and life. Stone bunding prevents surface runoff which could aggravate and lead to land slides. |
| Once the stone and boulders are removed and piled along contour line, it improves workability on the farm. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Construction of stone bunds is a laboursome and has no direct benefit to the land users. | Practice labour sharing working modality. |
| If stone bunds were not constructed properly, it could be easily damaged by cattle, washed or collapsed by heavy rainfall. | Proper piling of stones during the stone bund construction. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Some sort of incentives is required to scale out the adoption of technology as its requires huge labour and time with no immediate benefits. | Incentive of Nu 3000 tied with construction of 1 ac of stone bunds |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Three field visits was conducted
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Randomly picked land user from the community for documentation. One land user was interviewed.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
22/07/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
NSSC. (2011). Bhutan catalogue of soil and water conservation approaches and technologies. National Soil Service Center (NSSC), Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forests, Royal Government of Bhutan, Thimphu
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Book and soft copy from https://www.wocat.net/documents/140/Bhutan_catalogue_of_SLM_Technologies_and_Approaches.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Sustainable Land Management for improved land productivity & community livelihood in Thangrong
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-XS-qFv2dYQ
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Community Mobilization for SLM Interventions [ภูฏาน]
Community mobilization in implementing sustainable land management technologies is indispensable in engaging the community to identify their priorities, resources, needs and solutions. It ultimately promotes bottom-up participation and fosters accountability.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nima Dolma Tamang
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล