Aserpiado [สเปน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wolfgang Duifhuizen
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Gema Guzmán
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Aserpiado or Alumbrado
technologies_907 - สเปน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Jiménez Manuel
Finca Cañada Navarro
สเปน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Jiménez Santiago
Finca Cañada Navarro
สเปน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) (Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)) - เนเธอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas - Instituto de Agricultura Sostenible (CSIC - IAS) - สเปน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
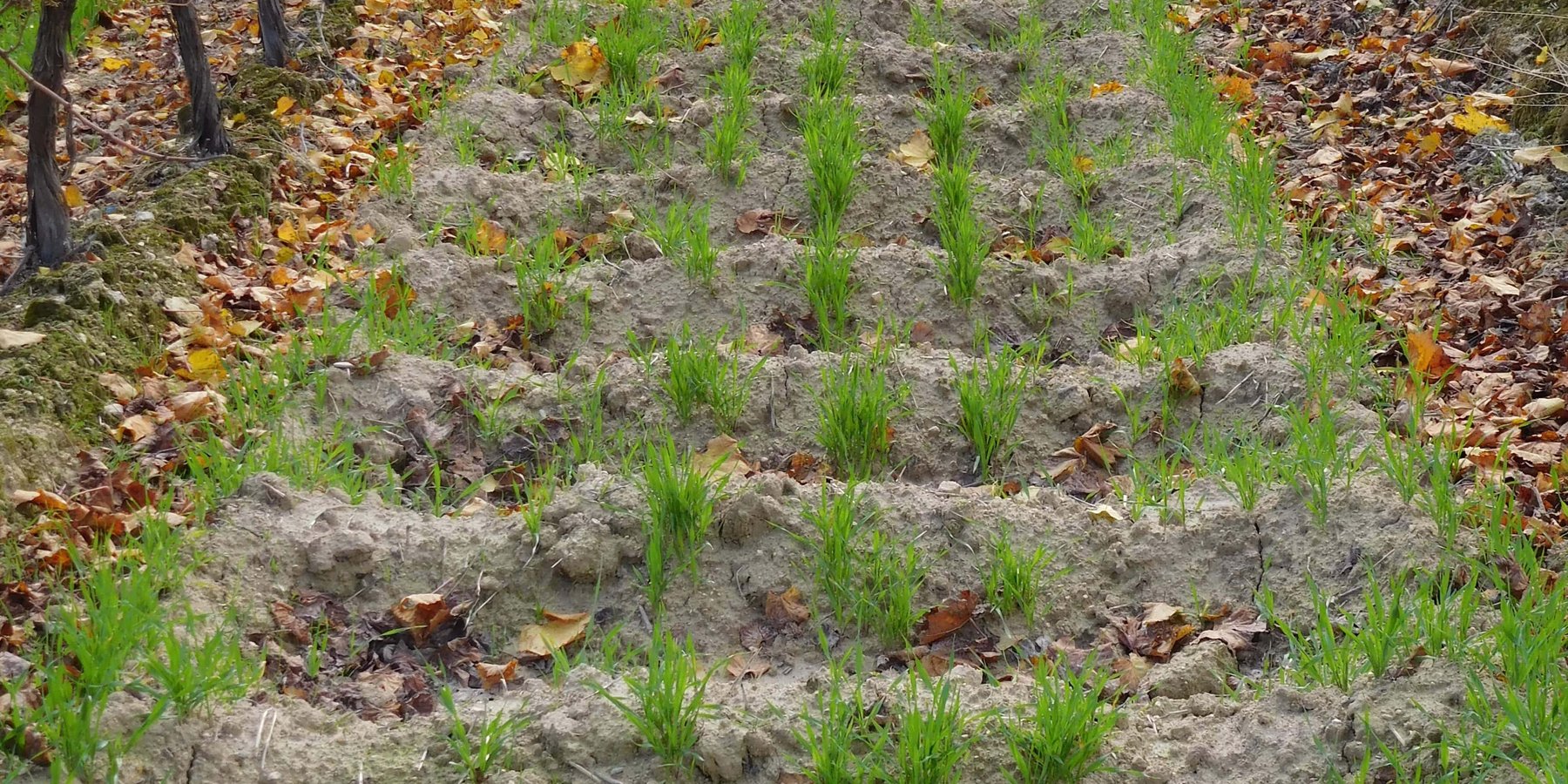
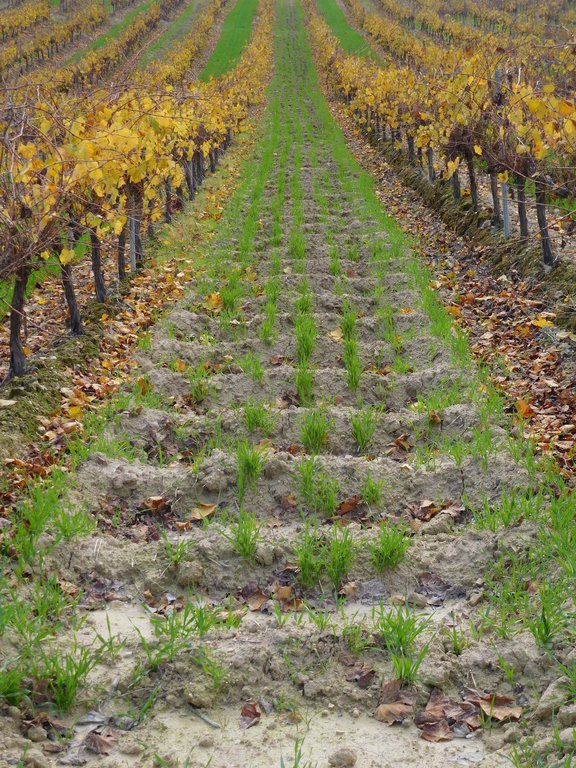
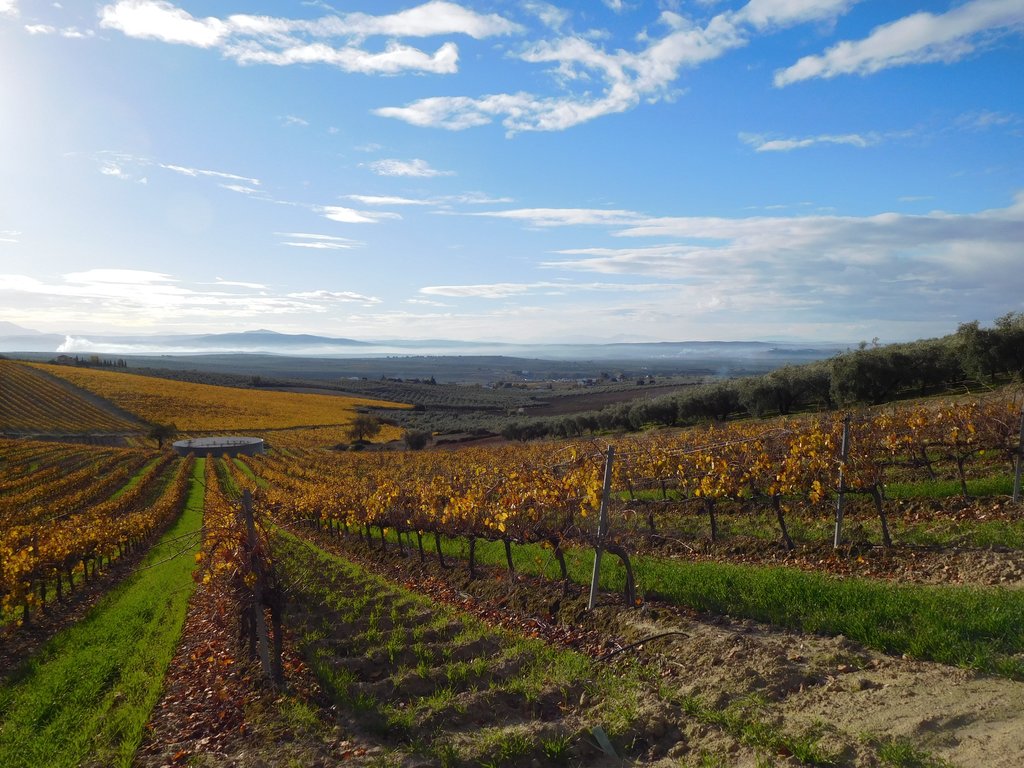
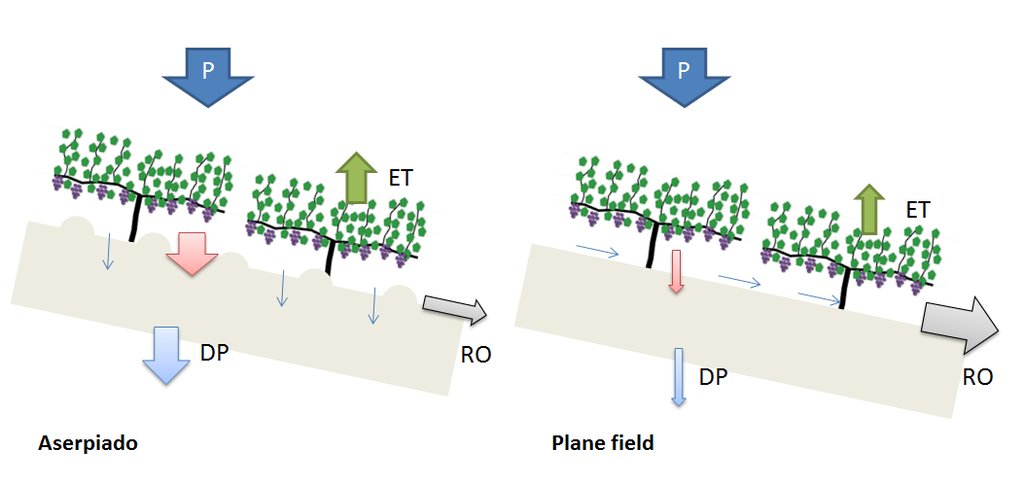
Aserpias are micro-depressions within a field along all or alternate inter vines rows, made by a tillage tool. The main objective of implementing Aserpiado is to let water infiltrate on-site, thereby increasing soil moisture and plant available water, decreasing runoff and associated losses of soil.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
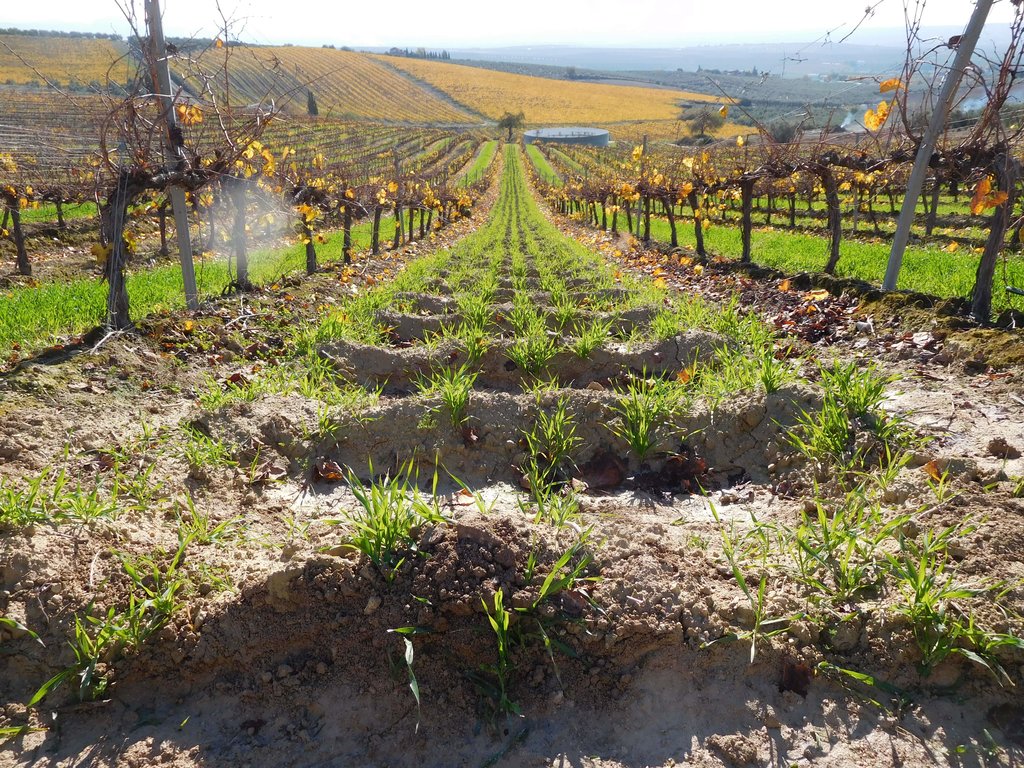
Aserpiado (also known as Alumbrado) is applied in vineyards in Southern Spain in lower and mid altitudes where the climate is characterized by relative high rainfall during winter, but almost none in summer. This requires adoptions in the water management like irrigation or on-site storage of water.
With the aserpiado technique, seasonal soil bunds are made every autumn in order to limit irrigation requirements and to protect the soil against erosion. These contour bunds in the allies remain in place the entire winter to make best use of precipitation that occurs mostly during this period.
The functioning of Aserpias was analysed in a vineyard within the Appellation of Origin Montilla-Moriles in Córdoba, the only previously existing documentation on this measure comes from vineyards in the Jerez wine region. Farmers use Aserpiado because it is the only way to get enough water without irrigation, as when irrigation is applied it cannot get the protected ‘Jerez-Sherry’ label.
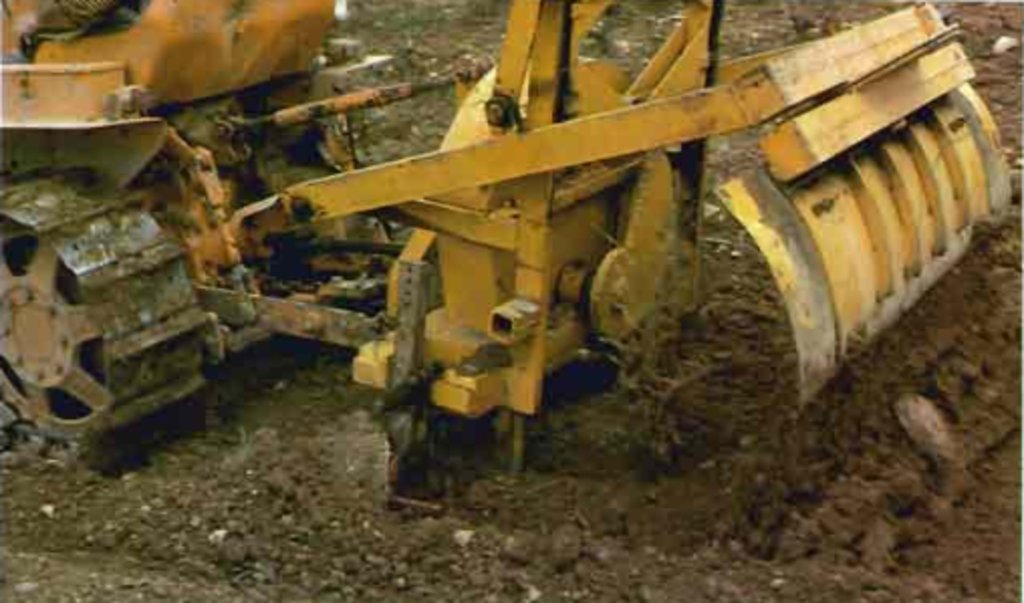
The microbasins are made in the inter-row area by dragging a caterpillar tractor pulled (see picture Aserpiadora) hydraulic beam over the field which lifts leaving a heap of soil behind. The speed and interval of the beam are set in such a way that a bund is made every 1.5 meter. Some users sow barely directly in advance of making the aserpiado which results in a high plant cover of the bunds during winter. The main function of Aserpiado is to catch rainwater which otherwise would be lost runoff. With Aserpiado the runoff is close to zero this means more water should become available for the crops.
The required inputs for creating and maintaining aserpias depends upon whether the bunds are permanent or seasonal. If permanent the ridges should be checked regulary and maintained by hand. When the aserpiado is only present during the winter season regular tillage in summer is necessary to keep the soil workable so the 'aserpiadora' (specialized tillage tool) can create the aserpias in autumn which are removed in spring to ease field traffic. With a modern-day Aserpiadora a farmer can create 3 to 5 ha of aserpias a day (Narvaez, 1980). The impacts of establishing aserpias are less soil erosion, less runoff and more water storage in the soil. Land users like Aserpiado as it is a very effective way to increase soil moisture and reduce soil erosion, when used in combination with cover crops the soil quality also improves over time.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
url source of Aserpiadora picture: http://www.mapama.gob.es/ministerio/pags/biblioteca/hojas/hd_1980_19.pdf
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สเปน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Andalucia, Cordoba Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Finca Cañada Navarro, Montilla
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The only previously existing documentation on Aserpias features vineyards of D.O. Jerez, but is also used elsewhere like in the D.O. of Montilla-Moriles data was compiled. Popularity of this measure is unknown as very little documentation exists.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Written texts exist of Aserpias being used in vineyards near Jerez de la Frontera in the 1860's which were made either by hand with a hoe or with a mule dragging a beam (Gonzalez Moreno, 2011). It is not an easily found in the Montilla-Moriles region; it is mainly developed in the Appellation of Origin of Jerez. However, the combination of Aserpiado and cover crops is the result of the innovation of some farmers who have been implementing it since 2011.
Aserpias have been used since the XIX century mainly in the Jerez being a common practice not only in vineyards but also in olive orchards, especially in steep slopes farms. No data found about the actual extension of this practice. The combined used with cover crops is fundamentally implemented by this farmer who started doing this practice in 120 ha.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- grapes
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Aserpias are only used if vine rows are perpendicular to slope. Documentation exists also of Aserpias being used in olive orchards (Narvaez, 1980).
Biodiversity was not analyzed.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Measure is applied to decrease necessity of supplemental irrigation.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cover crops are not used in all sites with Aserpiado
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Local circumstances and agricultural practices make agricultural soils very prone to water erosion.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The main goal is to increase water availability, but also decreases soil losses in inter-row areas.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
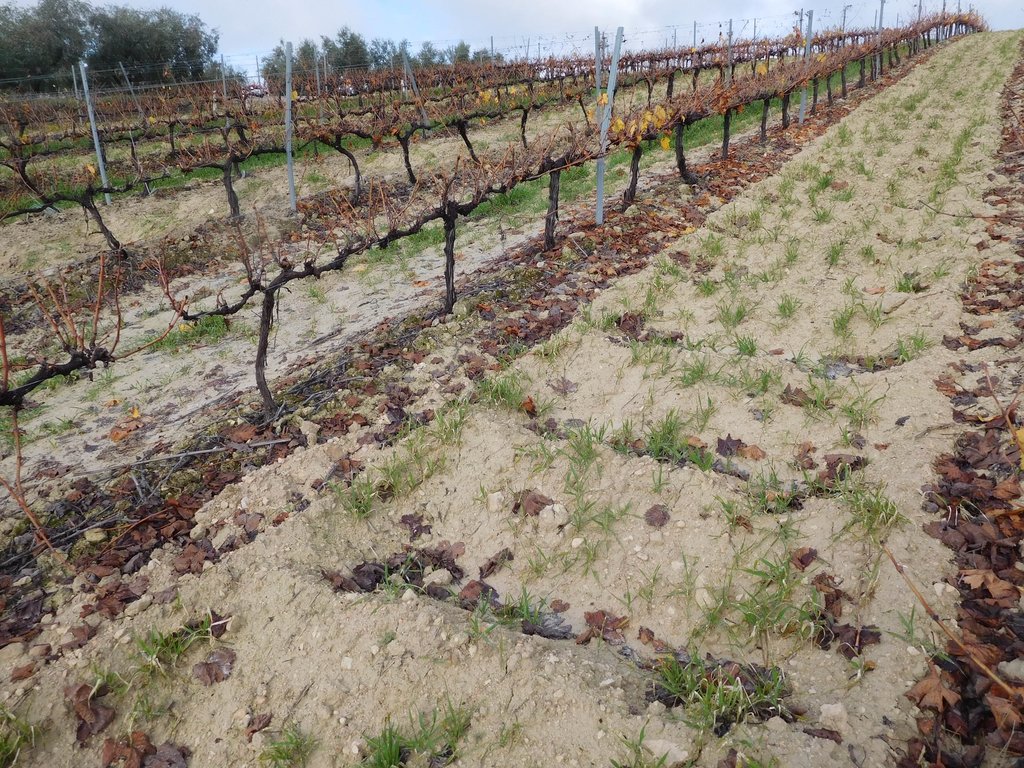
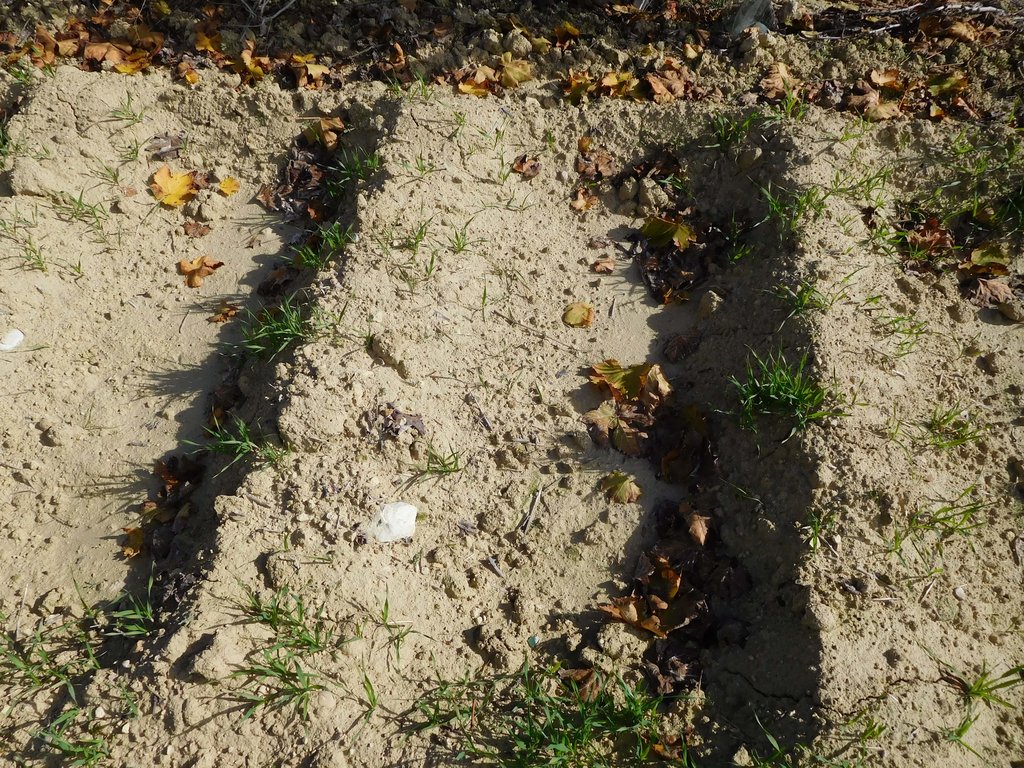
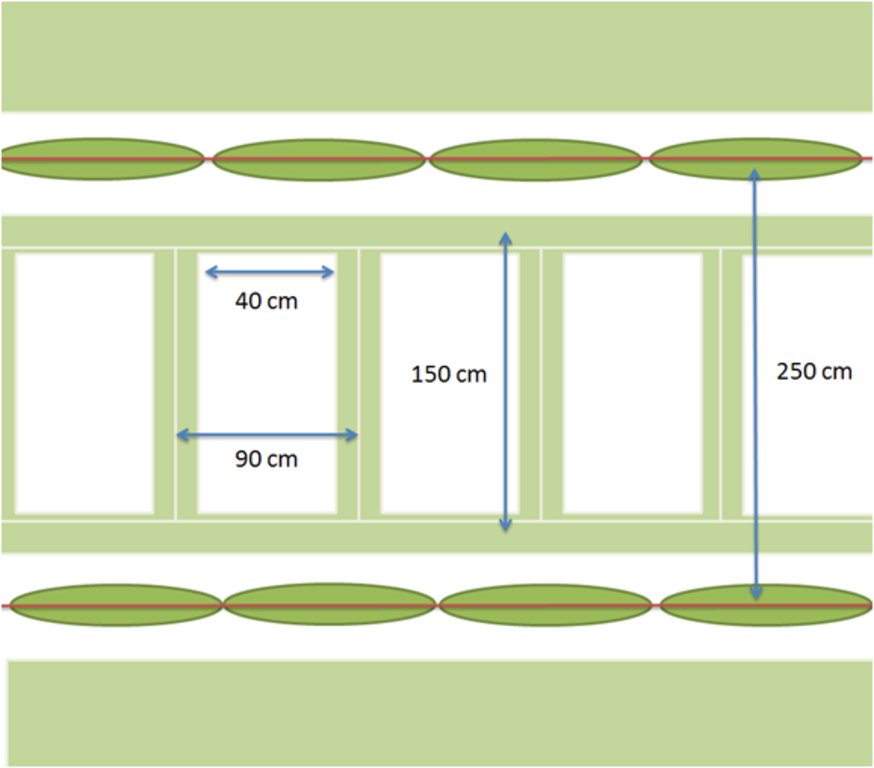
The bunds stretch over most of the inter-row alley, but in order not to expose superficial roots the bunds are 1.5 m wide so at each side there is about half a meter distance from the stems. Often the bunds are covered with barley and pruning residues. The bunds itself are 15 to 20 cm high and usually spaced 90 cm apart leaving 40 cm space at the base. At Cañada Navarro the Aserpia-bunds and sides are covered with barley as a cover crop during winter, in other sites where Aserpiado is applied the bunds remain bare.
ผู้เขียน:
Wolfgang Duifhuizen
วันที่:
23/01/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
22 hectares
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euros
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.94
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage with cultivator (15-20 cm deep) | After harvest crop |
| 2. | Sowing barley in allies | Autumn |
| 3. | Making aserpias in every other alley | Soon after sowing barley |
| 4. | Killing cover crop | Early in march |
| 5. | Tillage with cultivator (removing aserpias) | After killing the cover crop |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Tractor driver | h/ha | 5.5 | 40.0 | 220.0 | 96.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Scarifier | h/ha | 1.5 | 40.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Seeder | h/ha | 2.25 | 40.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Aserpiadora | h/ha | 1.5 | 40.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Cultivator | h/ha | 1.5 | 40.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Barley seed | kg/ha | 80.0 | 0.2 | 16.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicide** | l/ha | 3.0 | 6.67 | 20.01 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 526.01 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 559.59 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
*herbicide is not used when mechanical control is applied
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The cost of Aserpiado and sown tasks compared to conventional farming.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
600.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
High annual variability and erratic rainfall patterns, historical precipitation records show an annual variation between 300 and 1200 mm.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Santaella IFAPA station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
The Montilla region characterized by hot and dry summers, chilly winters and very few days of rainfall.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Most soils in the region are Cambisols by FAO classification with quite homogeneous well-drained soil consisting mostly of silty clay loam which has a good water holding capacity.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Biodiversity was not analyzed
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- สหกรณ์
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- บริษัท
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water balance modelling on aserpiado fields indicate a high percolation rate
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
120 ha (in Montilla-Moriles region)
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
1. Storage of water from winter rainfalls. 2. Control of soil erosion. 3. Benefits associated to the cover crops. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Control of erosion Increasing infiltration |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| No significant disadvantages or higher cost have been noticed compared to a cover crop farm. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| If the aserpiado fails, concentration of runoff in rills will easily occur. | To make aserpiado large enough to not be overtopped by regular rainstorms, also bunds need to be checked for stability. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Interview with Manuel Jiménez and Santiago Jiménez; agricultural engineers/ vinegrowers working for the Lagar Cañada Navarro wine farm.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/12/2016
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
El Alumbrado para acumalacion del agua en cultivos leñosos de secano, Revilla Narvaez (in Spanish)
URL:
http://www.mapama.gob.es/ministerio/pags/biblioteca/hojas/hd_1980_19.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
APROVECHAMIENTO DE LAS LLUVIAS EN VIÑEDOS SITUADOS EN LADERAS Y PENDIENTES MEDIANTE “ASERPIADO”, José Mª González Moreno, 2011
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Los viticultores del Marco de Jerez apuestan por la Producción Integrada
URL:
http://www.mapama.gob.es/ministerio/pags/biblioteca/revistas/pdf_vrural/Vrural_1999_87_54_55.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล