Stone faced soil bund of Tigray [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Emni Getsu hamed zala
technologies_980 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Tesfaye Tadele
S/Samre office of Agriculture and Natural Resources
เอธิโอเปีย
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
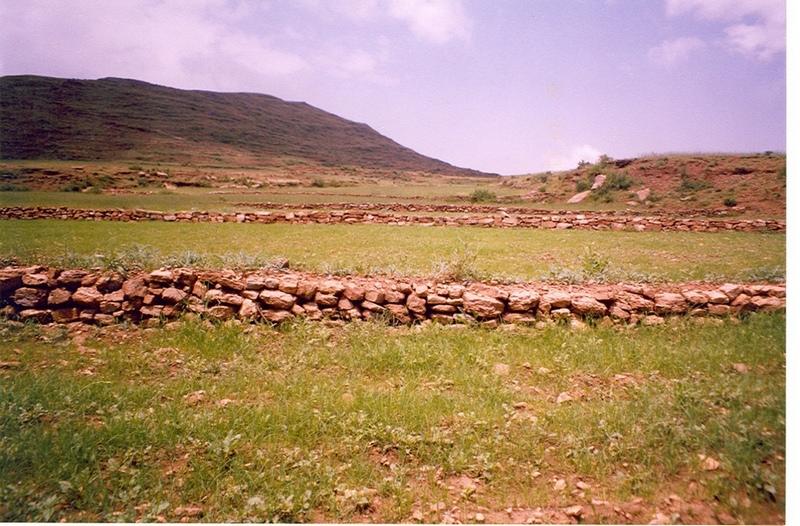
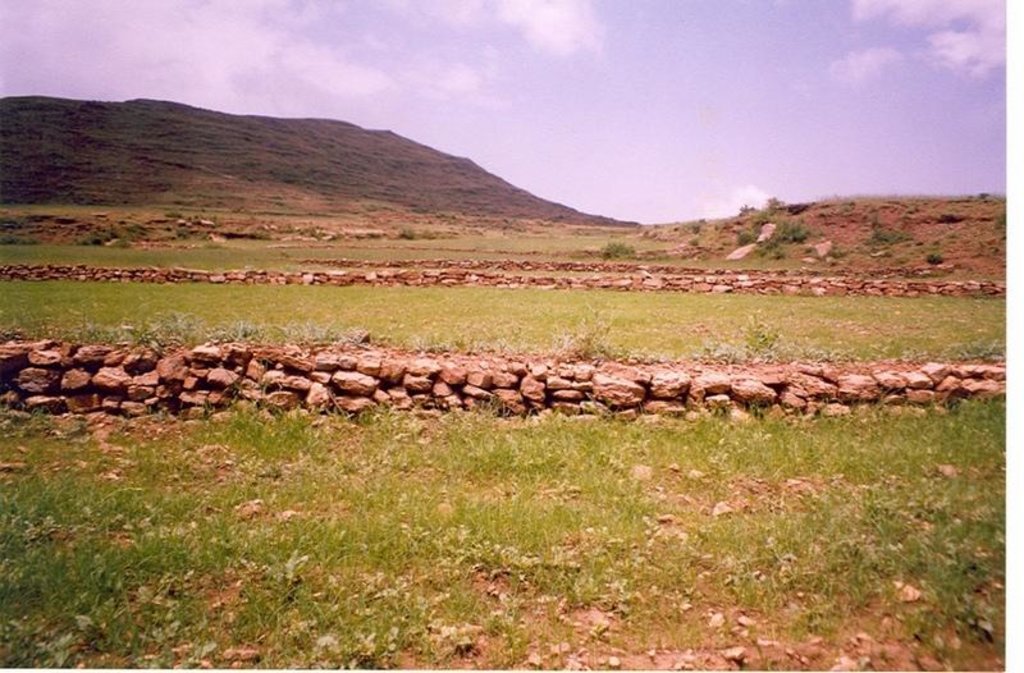
Stone walls placed downslope in an inclined manner having embankment of soil on upstream along the contour line having tieridge.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Description: Along the contour 30 cm width and 420 cm depth of foundation is excavated and stones are cplaced upto a height of 0.5-0.75 with 1 m width and 30 cm top width. On the uper side embankment soil is added and a basin with 5-10 m tie is excavated. Purpose: To reduce soil erosion, shorten slope length and retain soil moisture. Establishment/Maintenance: Integrate with biological SWC activities, Farmers maintain Environment: Enhance vegetation growth, improve micro-climate, decrease land degradation
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tigray
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Woreda
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 327.53 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - sorghum
- legumes and pulses - beans
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
- teff, horse bean
- Leucanea, sasbanea
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Teff and sun flower

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- Free grazing
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, deforestation, overgrazing, decline of fertility, low moisture holding capacity
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity, low rainfall, soil erosion, deforestation
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Water supply: post-flooding
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Teff and sun flower
Remarks: direct sowing
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1000/ha
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucanea, sasbanea
Grass species: local grasses
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 60-80m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-0.75mm
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60-80m
Construction material (earth): none clay and sandy soils
Construction material (stone): medium sized stone
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Birr
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.6
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.88
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedling production | Dec-June |
| 2. | Pitting | May |
| 3. | Planting | July |
| 4. | Survey & layout | January |
| 5. | Fundation excavation | February-April |
| 6. | Stone collection | February-April |
| 7. | Construction and digging the basin and put the soil at the upper side of the bund | February-April |
| 8. | Forming farmers groups | |
| 9. | Discussion among group members | |
| 10. | Plan of activities | |
| 11. | Implementation of measures | |
| 12. | Guarding |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 33.75 | 33.75 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Person days | ha | 1.0 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 229.45 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 26.68 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour plowing | April-may / 3 times |
| 2. | Enrichment planting | August /annual |
| 3. | Weeding and cultivating | September /annual |
| 4. | Stone collection | January/annual |
| 5. | Construction | January/annual |
| 6. | Planting/replanting | |
| 7. | Implementing water harvesting measures |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 10.9 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1.27 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Length of structure and number of seedlings
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
steep slope, transport for construction materials (stone), dry soils (land), shallow soils.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1000-2500 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also mountain- and hill slopes
Slopes on average: Also hilly and moderate
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: Also medium (ranked 2) and fine/heavy (ranked 3)
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good-poor
Soil water storage capacity is low-high
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Employed as daily labourer for weeding, plowing and harvesting.
Market orientation is subsistence (the area is drought prone and production is very low)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
0.5-1ha for both grazing and cropland per household. Average land holding size is 0.5 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
200 kg
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Space taken by structure is small
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
If proper placing of stone not followed
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
Enriching ground water
Risk of damage on properties if the structure breaks
Waterlogging
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
in clay soils during wet seasons it is high
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing siltation of dam and cultivated area
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
98328 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Especially the maintenance of the structure is done by individuals holding the land
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cut and carry, area closure, Integrating physical SWC measures with biological SWC measures. |
|
Availability of water near byareas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water harvesting structures and practices |
|
Animal feed increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting fodder trees and grasses |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
It conserves soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? The work has to be continued in organized way. |
|
It conserves moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Include contour cultivation and other methods enhancing the soil moisture build up. |
|
Increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integration of biological measures use of manure and other fertility improving measures. |
|
Enhancing spring development How can they be sustained / enhanced? Practice more water retaining measures upslopes |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It reduces cultivated land | Make the land productive by integrating with biological SWC measures, planting grass on the bund |
| It creates problem in farm activities | Design the structure in such a way that it can not create problem for farming. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It takes land | By integrating with biological measures make the land productive. |
| In some places hinder farm operation | Increase width of cultivable strips |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล