Government funded demonstrations [South Africa]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Klaus Kellner
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2341 - South Africa
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
Barac Anushka
Potchefstroom University for Christian Higher Education
South Africa
SLM specialist:
Van den Berg Loraine
Potchefstroom University for Christian Higher Education
South Africa
SLM specialist:
J van Rensburg Anja
Potchefstroom University for Christian Higher Education
South Africa
SLM specialist:
SLM specialist:
Van der Walt Izak
Provincial Soil Conservation Department in Northern Province
South Africa
SLM specialist:
Monque Augustine
Provincial Soil Conservation Department in Northern Province
South Africa
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO (Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO) - South AfricaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Department of Agriculture of Zambia (Department of Agriculture) - ZambiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Dept. of Agriculture, Northern Province (Dept. of Agriculture, Northern Province) - South Africa1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
Revegetation and re-seeding [South Africa]
Revegetation of old, degraded land. Restoring area to increase grazing capacity and production.
- Compiler: Klaus Kellner
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
Government funded restoration demonstration site to restore degraded land - by community participation. Community becoming the key sake holders - Capacity building.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Aims / objectives: Awareness raising and community participation. Capacity building, to teach the aim and type of technologies to the communities with the help of extension workers, scientists and academic staff, including postgraduate students. The main aim is to improve the condition of the land for high grazing capacity and production potential.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
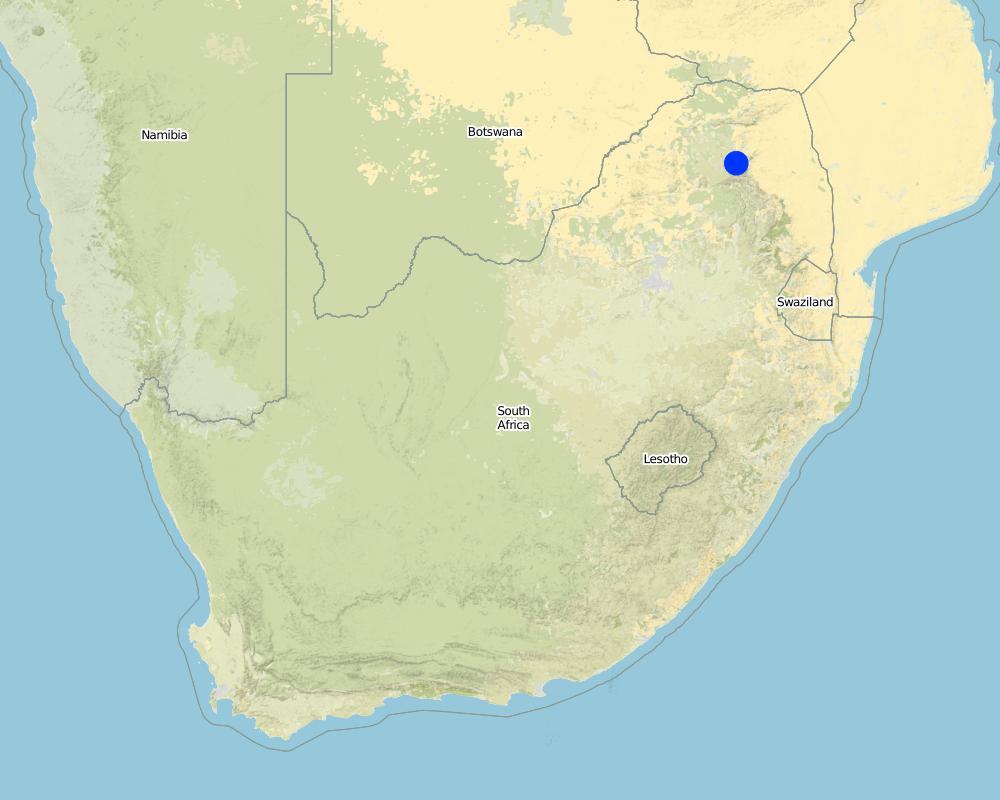
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
South Africa
Region/ State/ Province:
North West Province
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Year of termination (if Approach is no longer applied):
2002
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Capacity building of SWC technicians and community members.)
Awareness and participation. Training of technologies for restoration. On site or 'On-Farm' technology application.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Restoring degraded land (old lands) by cultivation and oversowing technologies.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
No money for restoration. Negative cost/benefit ration in short term.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Apply more cost effective technologies
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Help: land users again appreciated the role and importance of the natural resources. Hinder: lack of land tenure and ownership.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
No awareness and skills
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Capacity building and job creation. Commitment by stake holders and rural communities assured.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Specific ethnic groups: Sotho's
Work done and technology carried out by community. Mostly women as they need to earn money for food and household. Community councils; tribal authority - Chiefs make decisions.
- NGO
University helped with implementation of technology
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
Funded mainly by NDA
- international organization
Funds
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
National specialists improved and designed technologies and land users gave inputs with regard to type of area, plants and usage of grazing land.
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | passive | Mainly:public meetings; partly: workshops/seminars |
| planning | passive | Mainly: workshops/seminars; partly: public meetings |
| implementation | external support | Mainly: responsibility for major steps; partly: casual labour |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | |
| Research | interactive | on-farm |
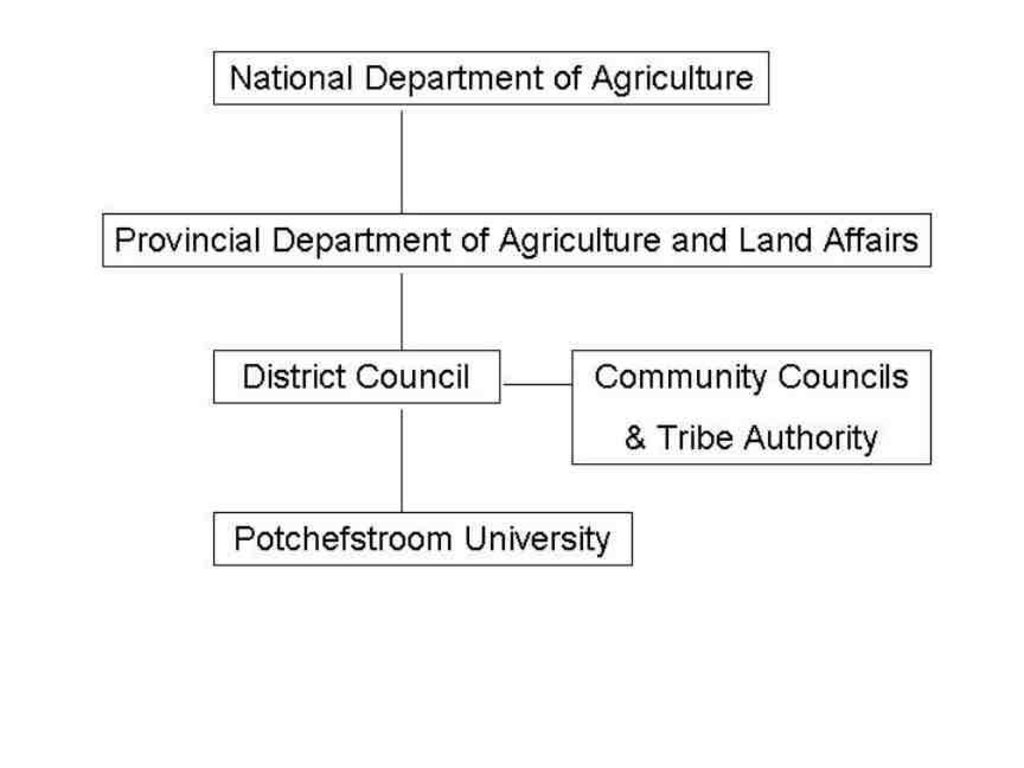
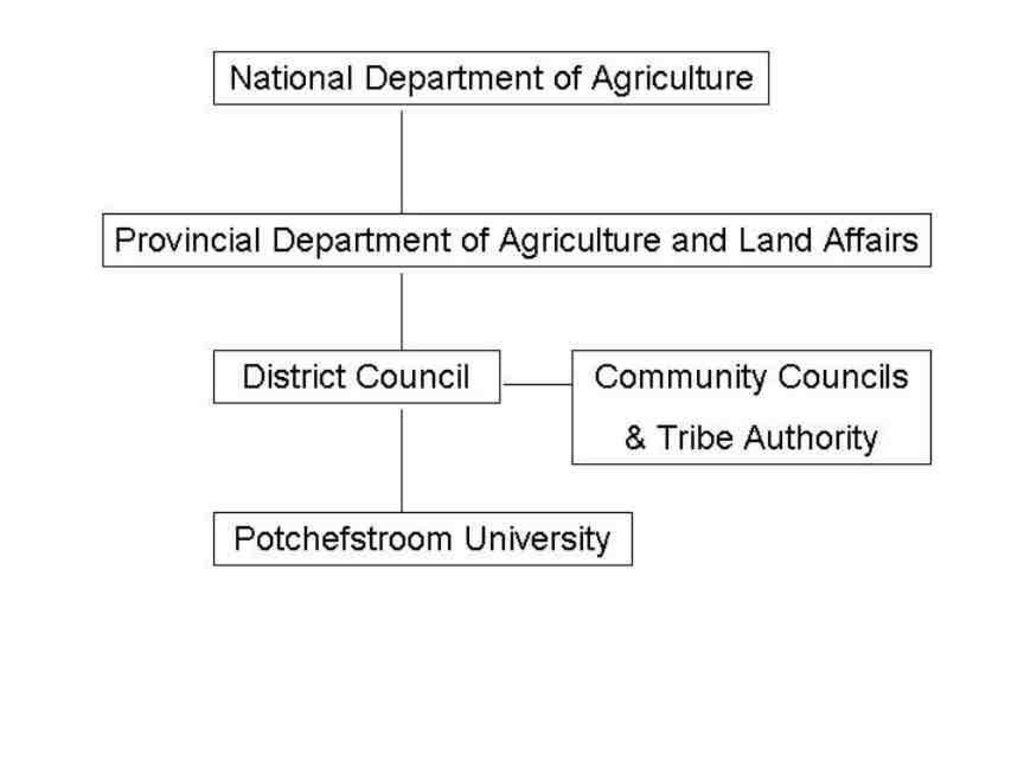
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
Explain:
consultative.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. consultative.
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Form of training:
- farmer-to-farmer
- demonstration areas
- public meetings
Subjects covered:
Ecological principles; Restoration technologies; NRM principles.
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
Describe/ comments:
Name of method used for advisory service: Demonstration/Participation; Key elements: 'Learning by Doing'; 1) Mainly: government's existing extension system, Partly: non-governmental agency.
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Monitoring, data analysis and presenting of results will be conducted by Research staff and project implementation. Expert advice needed on a continuous basis.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, a little
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- capacity building/ training
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: This was one site establishment for demonstration purposes of technologies.
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- ecology
- technology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
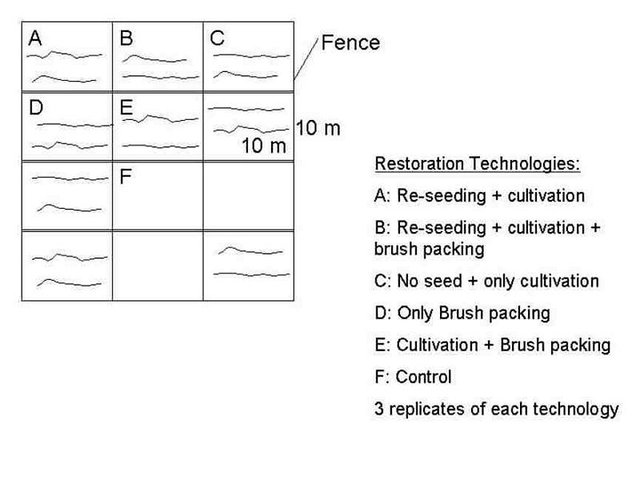
Vegetation and soil monitoring/analysis. Application of restoration technologies in demonstration plots.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- < 2,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - Agriculture): 80.0%; national non-government (University): 20.0%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| machinery | partly financed | |
- agricultural
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| seeds | fully financed | |
| fertilizers | fully financed | |
- construction
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| Fence | fully financed | |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- paid in cash
Comments:
Job-creation incentives
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Oversowing and better soil seed bank; good cultivation methods; certain adapted grass species used.
Land users do not own the land - any SWC application can be of more value and land users will be more committed if they take ownership.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Approach will be extended to other rural areas.
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
If yes, describe how:
Extension workers have learned the SWC technology from specialists (University researcher) and he/she together with the land user will hopefully extend the technology to larger and other areas on that own. Specialist must however make results available o
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Learned a lot - especially with regard to the restoration process |
| Earned money - job-creation |
| Knowledge about sustainable rangeland management strategies improved |
| School children and teachers involved. School projects on SWC technologies and restoration ecology in particular |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Co-operation between all stakeholders (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By making data and analysis scientifically sound - results better) |
| Land users, technicians/extension, researcher, policy makers |
| SWC technology will be monitored by scientists - value added to project |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Often too long before action is taken | Faster action. Extension better and more committed |
| Linguistic abilities. Land user has another language (Sotho), not spoken by specialist | Take local language classes and learn local language |
| SWC technology application must not only be build on job-creation incentives, but must be sustainable in the long term and applied by land user without payment. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Often too long before action is taken | Faster action. Extension better and more committed |
| Linguistic abilities. Land user has another language (Sotho), not spoken by specialist | Take local language classes and learn local language |
| SWC technology application must not only be build on job-creation incentives, but must be sustainable in the long term and applied by land user without payment. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Revegetation and re-seeding [South Africa]
Revegetation of old, degraded land. Restoring area to increase grazing capacity and production.
- Compiler: Klaus Kellner
Modules
No modules