Integrated rain-fed farming of cereals for adaptation to climate change [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Umed Vahobov
Интегрированное ведение земледелия на богарных землях для адаптации к изменению климата
approaches_4317 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Negmatov Negmatjon
negmatdzhon.negmatov@giz.de
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
GIZ Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
28/11/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies

Applying zero tillage technology for climate change sensitive … [Tajikistan]
Direct sowing and application of fertilizer without ploughing reduces land degradation risks associated with conventional arable farming and saves costs for farmers while improving the resilience against climate change impact, in particular drought.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
Rain-fed agriculture faces challenges from climate change impact, inappropriate crop varieties and inadequate inputs. The approach of integrated rain-fed farming reduces the adverse effect of climate change impacts and improves the income of farmers.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Rain-fed cultivation of wheat and other crops is hampered by poor agricultural practice and these challenges are increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation, more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt. These factors all cause a reduced availability of moisture in soil during the growth season. Increasingly irregular rainfall patterns make it difficult for farmers to predict during the season of drilling if soil moisture will be sufficient for rain-fed farming.
Other problems in rain-fed farming are caused by inadequate agricultural practice. Crop varieties producing high yield of good quality under the local conditions of rain-fed fields are not available for local farmers. Classical tillage causes loss of humus content of topsoil, wind and water erosion and high evaporation. Insufficient knowledge about the use of agrochemicals, difficult access to these and financial shortages experienced by farmers during the time of planting and growing of crops cause the inadequate application of fertilizer and pesticides and cause crop losses and quality issues. Only wealthy farmers are able to purchase timely sufficient amounts of agricultural inputs. Most farmers apply insufficient amounts and inadequate combinations of fertilizers, thus contributing to the decline in soil fertility. Unreliable harvest amounts reduce the marketability of the agricultural products and cause low income levels of farmers, again affecting their ability to work their lands effectively and sustainable.
The approach aims at reducing these risks and obstacles in an integrated way under consideration of ongoing trends and predicted impacts of climate change. The approach therefore combines several elements through an agricultural extension service:
•Agricultural extension service providing tailored assistance to the farmers;
•Provision of agricultural inputs through the extension services to ease the application of technical advice and reduce transaction costs for the farmers;
•Packages of agricultural inputs include seeds/planting material, fertilizers and pesticides as well as growth regulator with the instruction for their correct use;
•The agricultural extension service provides access to crop varieties, which are adapted to the local site conditions and produce reliable high yields of best quality;
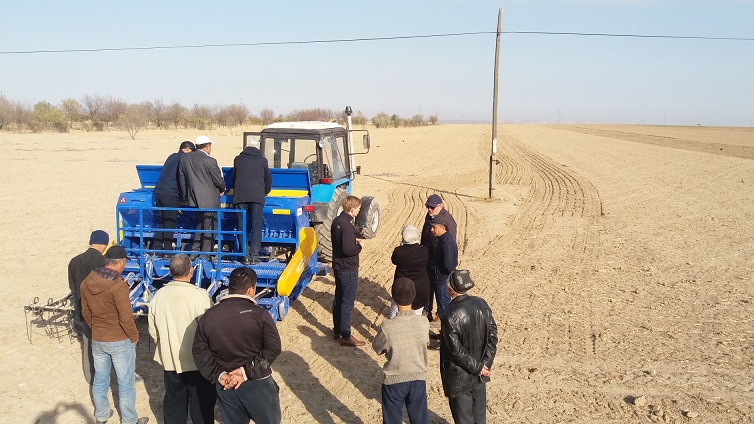
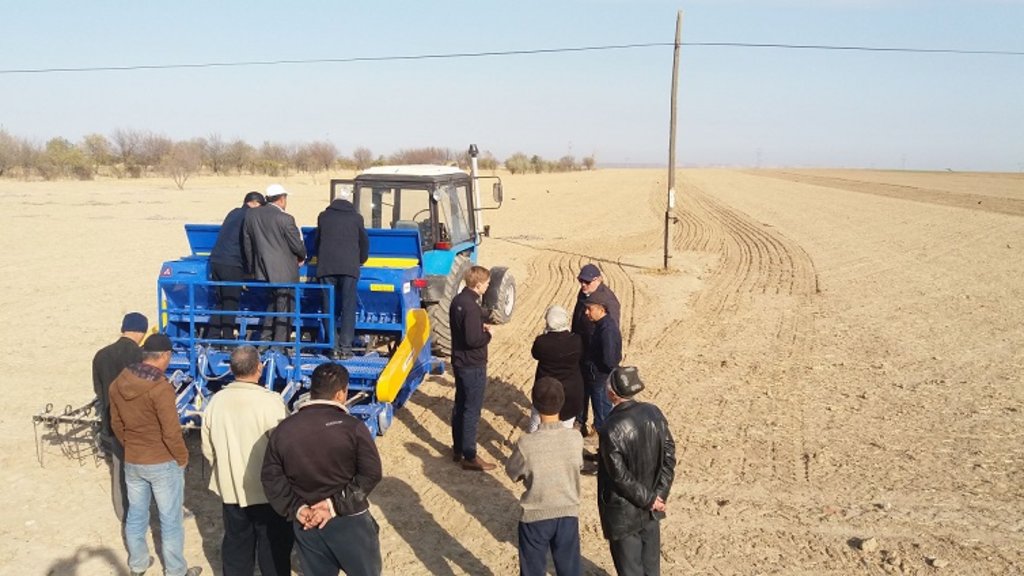
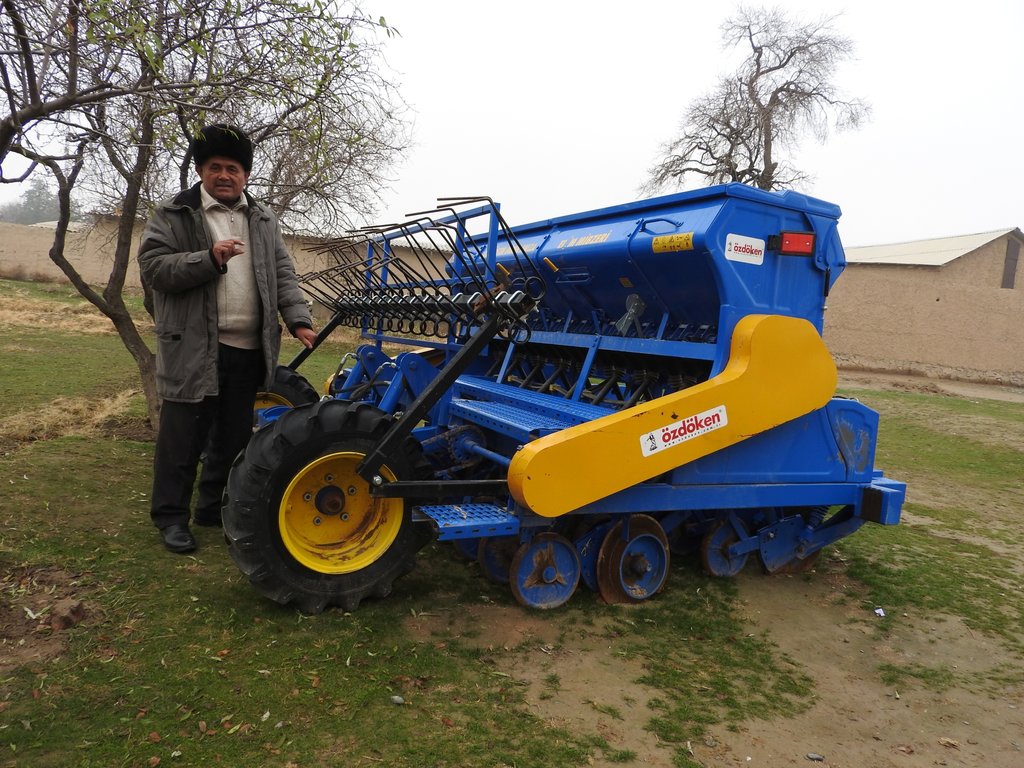
•Provision of machinery for drilling in combination with application of tailored amounts of fertilizer;
•Agricultural inputs are provided to farmers on a part loan basis by the extension service: farmers pay 50% of the costs of the package when purchasing, the remaining 50% are paid after harvest, with a zero interest rate (the extension service buys the inputs at bulk price and sells them to the farmers at retail price, which is 115% of the bulk price);
•Technological assistance includes cultivation technology like zero tillage and the use of modern drilling machines.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Sughd region
Further specification of location:
Devashtich and Istaravshan districts
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date when the Approach was initiated:
less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
Improved agricultural productivity in terms of yields and quality under conditions of climate change.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
Farmers have difficulties to afford agricultural inputs at the beginning of the growth season. This issue is addressed in the approach through part loans.
institutional setting
- enabling
Agricultural extension service collaborates with GIZ and was ready to jointly develop and adopt the approach.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Farmers
Applying the approach on their lands.
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
Agricultural experts
Providing technical advice.
- NGO
NGO "Agra va iqlim"
Agricultural extension service - advisory role, provision of inputs, purchase of drilling machine and its provision to farmers.
- local government
Agricultural department of Devashtich district
Interested in improvement of agricultural production and resulting well-being of the local population and economic prosperity of their districts. Political backing and support, provision of information, facilitation of contacts.
- international organization
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Implementation of the project on behalf of the German government.
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Discussion of testing of elements of the approach on their lands |
| planning | interactive | Selection of land plots and discussion of testing of elements of the approach on their lands |
| implementation | interactive | Applying elements of the appraoch on their lands |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | Recording of yield and crop quality, reporting experiences in applying the elements of the approach. |
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
- research findings
- personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Form of training:
- demonstration areas
- public meetings
- courses
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, moderately
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Agricultural extension service developed as provider of package of agricultural inputs and machinery. Expanded its fields of work and reach of farmers.
Specify type of support:
- financial
- capacity building/ training
- equipment
Give further details:
Drilling machine purchased for testing and demonstration. Income from provision of drilling machine will be used to purchase additiona machinery.
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
Documentation of yields, recording of inputs, recording of return for machinery.
If yes, is this documentation intended to be used for monitoring and evaluation?
No
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
No
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 10,000-100,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Government of Germany, implemented via Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). The approach has been implemented in the frame of a much larger program and the specific budget for the SLM component of the Approach cannot be determined.
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
Loan of 50% of the costs of agricultural input packages, to be recovered after harvest at zero interest rate.
Drilling machine purchased with project support and thus available for farmers at lower cost than would be possible if purchased commercially.
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| machinery | partly financed | Drilling machine purchased with project support and thus available for farmers at lower cost than would be possible if purchased commercially. |
- agricultural
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| seeds | partly financed | Loan of 50% of the retail price of agricultural input packages, to be recovered after harvest at zero interest rate. |
| fertilizers | partly financed | Loan of 50% of the retail price of agricultural input packages, to be recovered after harvest at zero interest rate. |
| Pesticides | partly financed | Loan of 50% of the retail price of agricultural input packages, to be recovered after harvest at zero interest rate. |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- voluntary
Comments:
Work on their own fields for their own income generation.
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
Yes
Specify conditions (interest rate, payback, etc.):
Loan of 50% of the retail price of agricultural input packages, to be recovered after harvest at zero interest rate. (The extension service buys the inputs at bulk price and sells them to the farmers at retail price, which is 115% of the bulk price.)
Specify credit providers:
Agricultural extension service / provider of agricultural inputs.
Specify credit receivers:
Farmers
5.5 Other incentives or instruments
Were other incentives or instruments used to promote implementation of SLM Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify:
The combination of advisory service, provision of a complete package of inputs and financial support (loan).
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach empower local land users, improve stakeholder participation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Participating farmers increased their confidence and status.
Did the Approach enable evidence-based decision-making?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The direct link between the quality of agricultural input and practices and resulting yield and crop quality became visible.
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The farmers were enabled to apply technical advice from the extension service as necessary machinery was provided and agricultural inputs became easier available and affordable.
Did the Approach mobilize/ improve access to financial resources for SLM implementation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Farmers were enabled through a part loan to purchase input packages. Machinery was made available through an extension service (NGO), which otherwise would not have the means of purchasing this machinery and provide it to farmers at affordable costs.
Did the Approach improve knowledge and capacities of land users to implement SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Provision of targeted extension, demonstration plots showing the approach and its results.
Did the Approach improve knowledge and capacities of other stakeholders?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Involved extension service and agricultural departments gained knowledge.
Did the Approach build/ strengthen institutions, collaboration between stakeholders?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Existing collaboration between farmers, extension services and agricultural departments consolidated.
Did the Approach lead to improved food security/ improved nutrition?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Increase in yields and reduced risk of crop failure.
Did the Approach improve access to markets?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
More reliable quantities of crop allow improved market access.
Did the Approach improve the capacity of the land users to adapt to climate changes/ extremes and mitigate climate related disasters?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Improved soil mositure, retained soil fertility, reduced erosion and adapted crop varieties reduce risk of crop failure caused by drought and allows for optimum yield under conditions of increasing aridity.
Did the Approach lead to employment, income opportunities?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Higher yields increase incomes of farmers. Reduced risk of crop failure makes farmers more economically resilient. Demand for inputs and machinery improves economic situation and employment opportunities of extension service.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
- increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
- reduced risk of disasters
Reduced risk of drought caused crop failure.
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- uncertain
If no or uncertain, specify and comment:
Many farmers will not be able to purchase the package of advise and inputs without loan support. Such loans are currently not available from commercial financial institutions at affordable conditions. Machinery for direct drilling and fertilizer application is only affordable for large farmers and service provider (extension service).
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Improved crop production. |
| Reduced risk of crop failure in case of drought. |
| Reduced costs for cultivation and fertilizer application. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Improved crop production effectiveness and cost efficiency. |
| Reduced risk of crop failure in case of drought. |
| Preservation of soil fertility. |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| High costs of inputs can by most farmers only be met with loan, at better conditions than typical commercial loans. | Loans at affordable conditions. |
| Dependence on extension service for use of machinery and potential availability issues. | Reinvestment of payments for machinery use in additional machinery as demand grows. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| High costs of inputs can by most farmers only be met with loan, at better conditions than typical commercial loans. | Loans at affordable conditions. |
| Dependence on extension service for use of machinery, potential availability issues and risk of monopoly situation. | Reinvestment of payments for machinery use in additional machinery as demand grows. Development of more service providers. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Applying zero tillage technology for climate change sensitive … [Tajikistan]
Direct sowing and application of fertilizer without ploughing reduces land degradation risks associated with conventional arable farming and saves costs for farmers while improving the resilience against climate change impact, in particular drought.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
Modules
No modules