Dug-Out Well [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
Chahala
technologies_1088 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Kar Monoranjan
Project implementing agency, 9437287808
SLM专业人员:
Mohanty Rajib
Watersheds office, DRDA, Balangir, 09437241751
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Watershed Office DRDA - 印度1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
It can be defined as combination of structural & agronomic measures where along with other technology like Water harvesting structures & field bunding on the upper reaches & a dug out well is constructed in the periphery of the drainage line which is a govt land. The 15 acres of land near to its sphere of influence which reamained fallow earlier could yield good production system throughout the year.It is in the semi-arid climatic zone with moderate slope in medium soil depth conditions. The whole idea is to avail water & link with self-subsistance & market oriented production systems from private lands.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
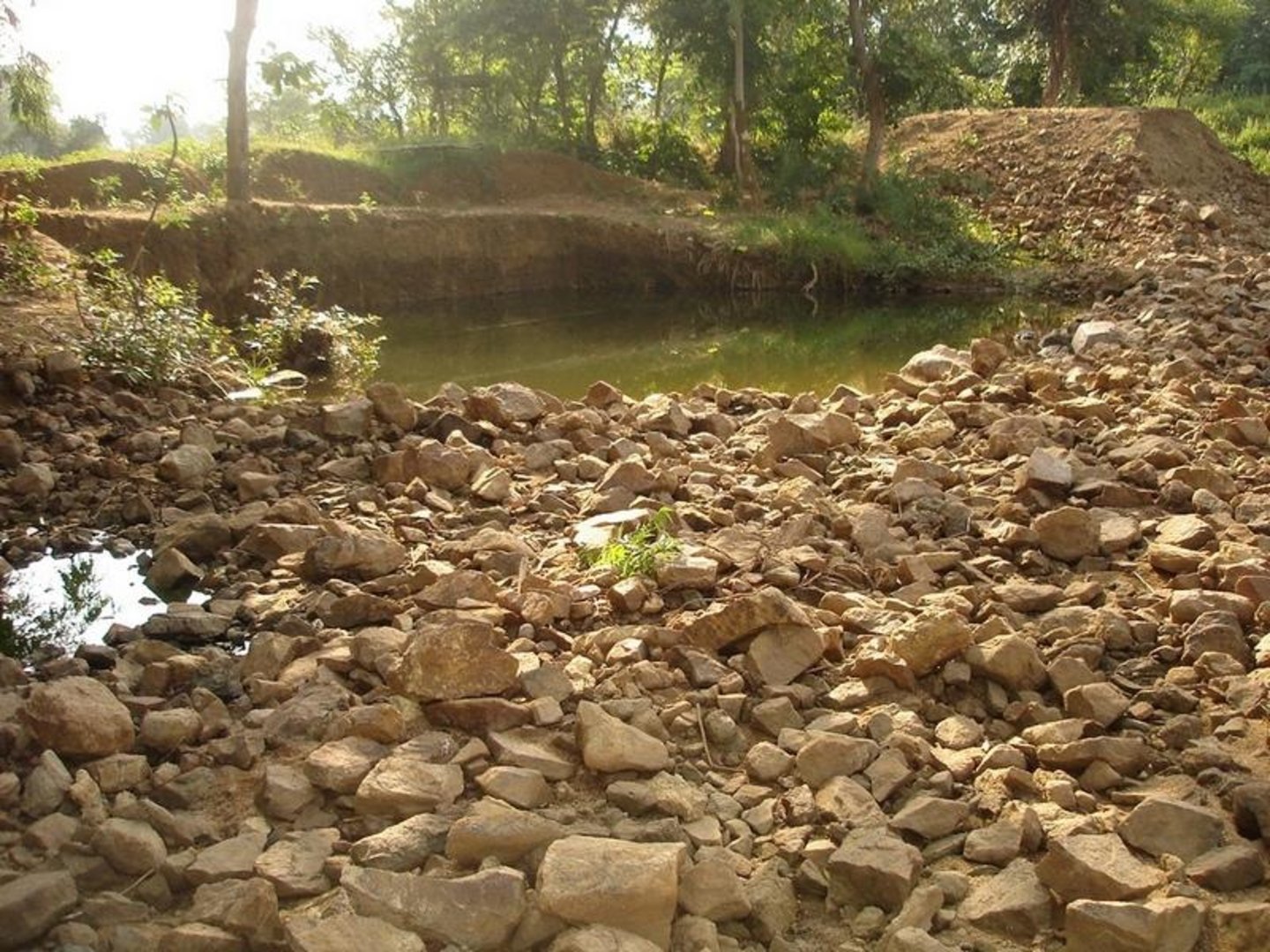
The area is located at the foot-slopes on the major drainage line of the watershed. The technology area is located near the main drainage line, therefore, the sub-surface water availability is more & can be utilised for cultivation of crop even in dry spell of the year. Earlier the farmers near to this place tried to dig a small well & could irrigate for only 2-3 months of the year to get some subsistence crops. Therefore, water availability throughout the year is a first priority of the farmers. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected & the owners of the land are poor people (defined by villagers). Usually the land users used to migrate in search of labour due to loss in the agriculture. It is because the water availability is not there at the time of requirement. The people of this patch are ready to contribute at least 10% of the cost as the structure is to be constructed in government land. In the mean time the project sent the PIA to Water technology centre for eastern region, Bhubneswar to study the linking of water harvesting structure & dug-out well & its relevance in this context of our situation. The technology was done in the village Chareimara which is one out of 3 villages of one watershed, located at the lower reach of the watershed. In the meantime many water harvesting structures & field bunds were constructed due to which the water could be stored in the recharge zone. This area is again a mix of stony patches in the crop land. One water harvesting structure was constructed just at the upper reaches. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with clay loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go for a deeper dug well which can feed water through out to at least 15 acre of land. The requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & rabi crop including summer vegetables. A four-day in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers (SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. At the same time there was a blind belief that large water harvesting structures are more useful to farmers. So the land users demanded for a large WHS on the drainage bed which requires huge investment & high maintenance cost. But when some farmers of that watershed could get good result by digging well these land users also started thinking about a "community dug-well". After many rounds of discussion with the land users by the SWC specialist followed by a detail transact along with land users, the results of first round transact was mentioned in the micro-plan. But the aim behind subsequent transact was to looking at problems & demarcating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of the well was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The lay-out is also little bit different from traditional well i.e. square shaped in stead of round shape. The work was implemented by the land users & 7 outside labourers with the supervision of the User's group leader & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The priority by the land users was agronomic measures like changing the crop in the land. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The structural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintenance cost.
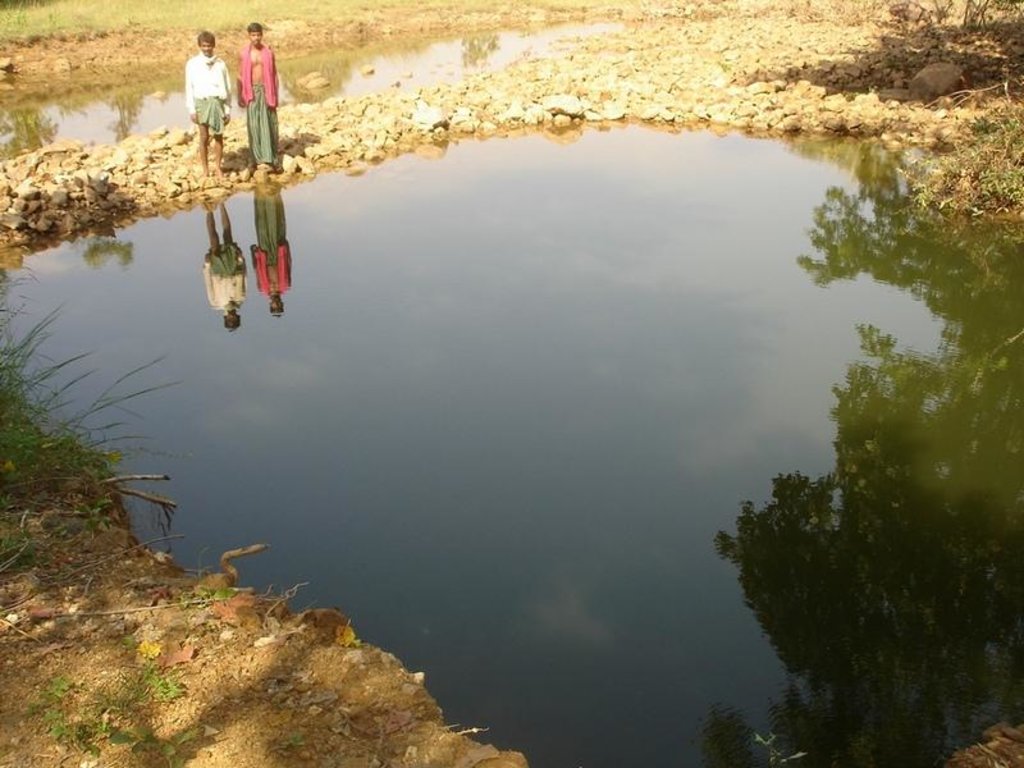
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
有关地点的进一步说明:
Orissa, Balangir, Suktel/Mahanadi
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.6
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.6 km2.
The concerned watershed is a subsidiary system of the Suktel river drainage sytem. The area of operation is micro watershed , i.e. 500 hac as a unit of the tributary of the Suktel river
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
A group of SWC proffessionals were sent to WTCER, Bhubaneswar to study the replication of ' Linking of water harvesting structure with dug-out wells. . When SWC specialist share their experience to land users, some of the farmers agreed to have a experimentation of the technology. Therefore, modification has been done by the SWC specialists as per the suitability & requirement of the land users.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 香瓜、南瓜、南瓜或葫芦
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
- rice
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 甘蔗
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 80Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Feb
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Gourd, Brinjal, onion, sugarcane,water melon
Remarks: After the Kharif crop
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This patch of the land used to remian fallow in comparison to other lands of the village, with high concentration of marginal farmer. Due to less water availability at the time of need of crop the farmers were quite hesitant to take up diversified crop. They used to migrated instead of taking up any agriculure due to loss year afte year. The main requirement of water throught out the year.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Run-off was severe at the time of rainy season but difficult to capture water for other period of the year.2. Long duration crops is not possible, ex- paddy,pulses, sugarcane, vegetables etc. 3. Although land is there but it remained fallow in the past due to water availability. They were the migrants because of onstraint in agriculture.
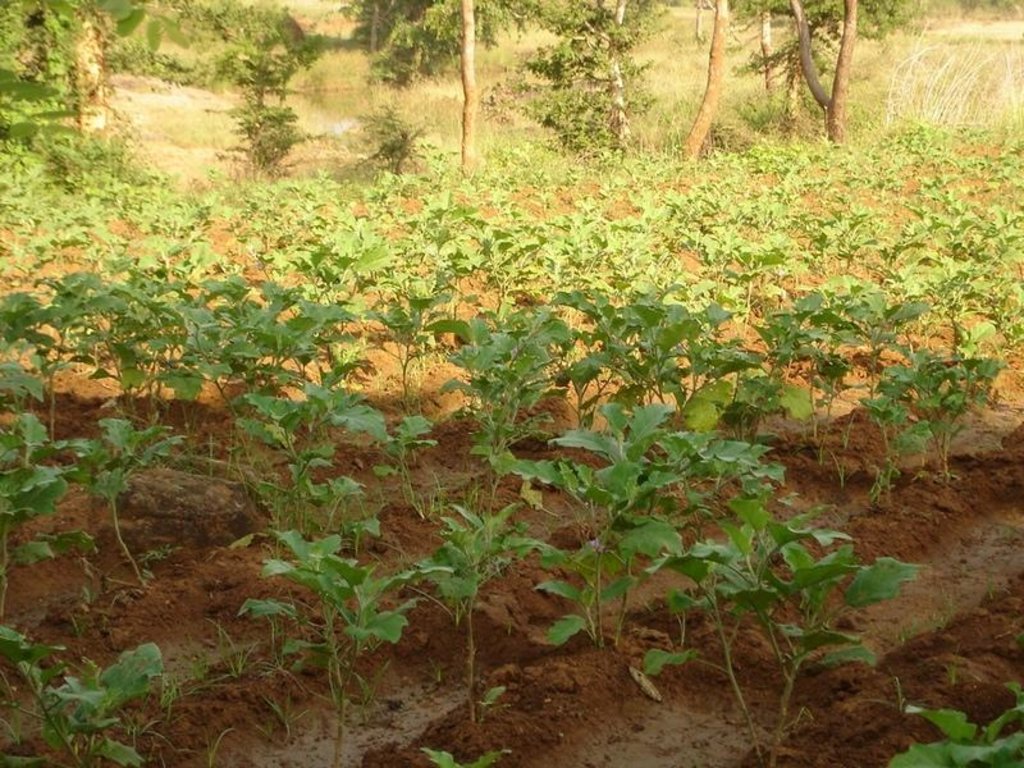
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Paddy/Kharif rainfed vegetables, Winter vegetables & spices, summer vegetables. Gourd, Brinjal, onion, sugarcane,water melon
3.4 供水
其它(比如洪水后):
- all of them
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种
- A7:其它

结构措施
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, early planting, mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, deep tillage / double digging
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Dug Well in Chareimara
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water spreading
Better crop cover
Material/ species: paddy, vegetables,
Quantity/ density: Average
Remarks: Paddy for subsistence & vegetables in the land with rainfed & market demand.
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Gourd, Brinjal, onion, sugarcane,water melon
Quantity/ density: ealy harve
Remarks: After the Kharif crop
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: 4 -5 cartloads of cow-dung
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Minimum basal doses
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: the cultivation of crop started after the availability of water.
Remarks: Rainfed paddy with vegetables
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: As the land was fallow earlier, breaking of compact soil is necessary.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: The land where vegetables was grown, deep tillage was required
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 26ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 35ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 33ft
Construction material (stone): Stone excavetd from the well was put as protection embankment
Construction material (concrete): A concrete guard wall will be put on the periphery of well which will be started in the current year
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:150
Change of land use type: After paddy & kharif vegetables,rabi & summer vegetables .Th e bunds of the patch need to be covered with plants
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Inter crops, mixed crops have to be practiced to get optimum benefit.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Grazing was restricted in these areas & land was optimally used, like bund cultivation.
Major change in timing of activities: Early varieties of vegetables will fetch at least double benefit.
Control / change of species composition: The improved varities seed need to be introduced
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupee
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey | April-May |
| 2. | Demarkation on map | April-May |
| 3. | Estimate & lay-Out | April-May |
| 4. | Implementation of work | May-July |
| 5. | Survey & demarkation of water line | April |
| 6. | Digging of well | May-July |
| 7. | Water-way | August |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Medium | hectare | 1.0 | 1250.0 | 1250.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1250.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 25.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | April-May / |
| 2. | Intercultural operation with manure & compost application | June / |
| 3. | Sowing of paddy & rainfed vegetables | July & sep for two crops / |
| 4. | weeding & intercultural operation, if required. | July / |
| 5. | Harvesting of paddy orvegetables or sugarcane. | Nov / |
| 6. | Winter early variety vegetables like onion, brinjal, leafy vegetables, gourds etc. | Dec / |
| 7. | Harvesting of winter spices & vegetables | Feb-March / |
| 8. | Sowing of summer vegetables like water melon etc | March / |
| 9. | Intercultural operation | April / |
| 10. | Harvesting of vegetables | May / |
| 11. | Management of surplus water | Rainy Season/annual |
| 12. | Collapsing of bund | annual |
| 13. | Well must be desilted | Dry season/each cropping season |
| 14. | Control of surplus water-flow | August-Sep / annual |
| 15. | Stabilisation of bund at weak points | Nov-Dec / annual |
| 16. | Desiltation of well | April-may / annual |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Stones are to be excavated from such a height of 26 ft.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
1% of the land users are poor (2-3 acres of land).
Off-farm income specification: Others have also activities like NTFP collection, keeping small ruminants like goats, chicks etc.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 0.5-1 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water availilbilty |
| A vibrant community institution could be strngthed. |
| A well is much better than a large water harvesting structure, it became a eye opener in the surrounding villages. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Water availability in the dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated & threes season land use practice |
| The water availability will be there through out the year.Therefore, 15 acres of land can be irrigated & three seasonal crop can be taken up. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块