Use of organic matter (manure and compost) [布基纳法索]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dieter Nill
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Apport de matière organique (French)
technologies_1220 - 布基纳法索
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
德国
SLM专业人员:
Sani Mamadou Abdou
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive
尼日尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - 德国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Misereor - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Soils treated with compost or manure produce better yields, because they retain water better and are more fertile.
2.2 技术的详细说明
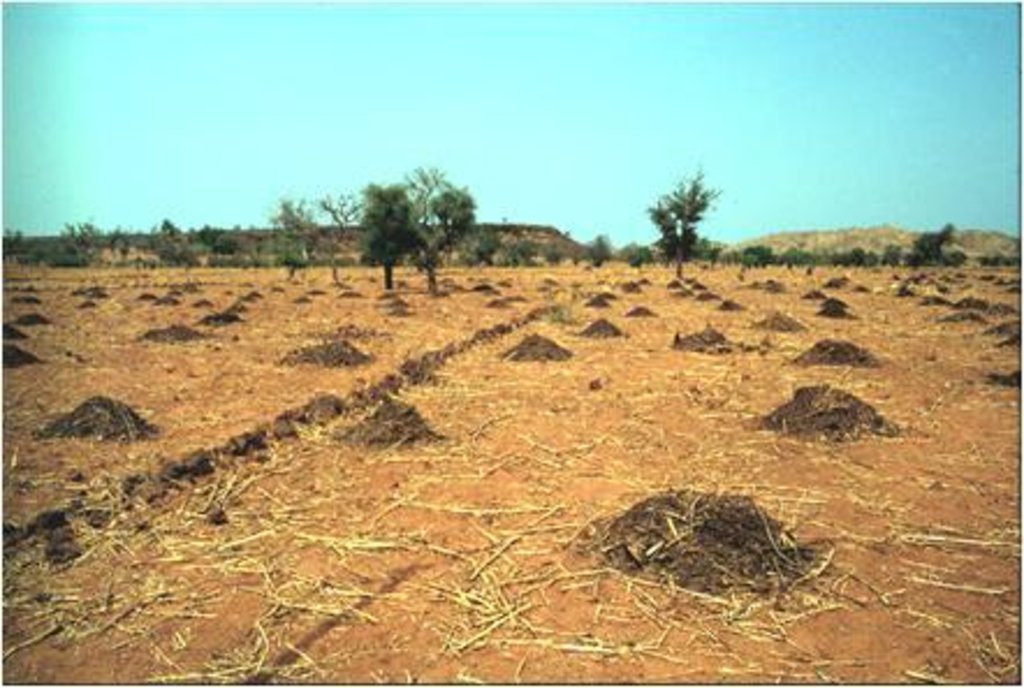
说明:
The regular application of manure and/or compost in sufficient quantities makes farming more intensive and reduces the need to bring more land under cultivation. Manure is used on cropland and compost is recommended particularly for market gardening.
Purpose of the Technology: The use of organic matter on cropland has three major effects: it reactivates biological activity, increases soil fertility by providing nutrients and improves soil structure by increasing the amount of organic matter in it. The improved soil structure also increases the infiltration of water into the soil. These effects favour crop growth and increase yields. The denser vegetation and improved soil structure make the land more resistant to water and wind erosion.
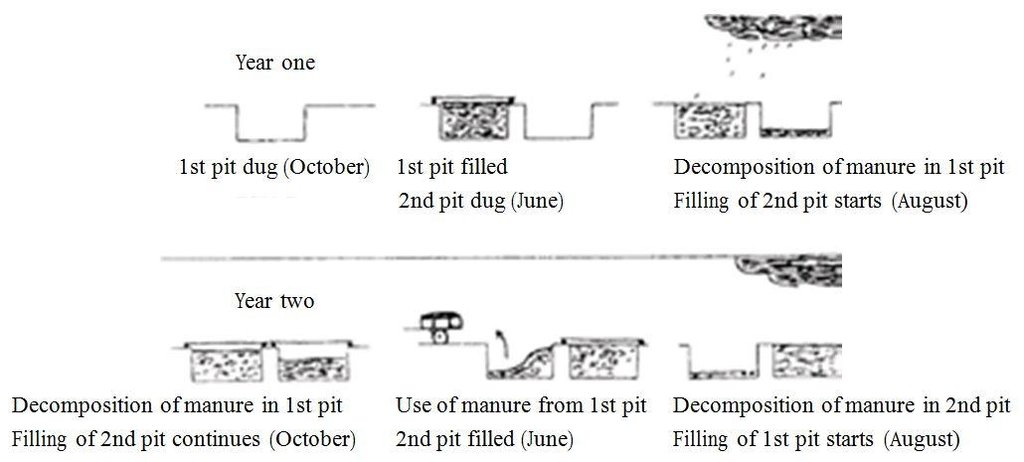
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are two methods for obtaining organic matter for use as a fertiliser: the production of compost and the collection of manure. Manure is collected from improved livestock pens or sheds where livestock is kept on litter or bedding. Compost can be made in the dry season or in the rainy season. Biodegradable matter is mixed with animal waste for rapid decomposition or just with millet, sorghum or other plant stalks for slow decomposition. Both types of compost can be enriched with ash and/or natural phosphate. The biodegradable matter is placed in a pit. In the dry season, it is regularly sprinkled with water until decomposition is complete. It is then spread evenly over the land before sowing or planting.
Unlike compost, manure collected from improved pens or livestock sheds is not completely decomposed, and the decomposition process continues over several years.
The recommended amount varies depending on the type of soil the availability of manure and compost: 6 t/ha every third year (heavy clayey soils), 3t/ha every two years (sandy-clayey soils) or 2t/ha every year (light soils).
Natural / human environment: The use of compost and manure is recommended in conjunction with all other SWC/SPR measures to achieve the maximum benefit from investments in land improvement.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
布基纳法索
区域/州/省:
Burkina Faso, Niger
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord), and PATECORE (project for land development and resource conservation in Plateau Central Burkina Faso)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- improve fertility
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low biological activity, low soil fertility, bad soil structure, low amount of organic matter, surface runoff, aridification, erosion by water and wind
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), floods, droughts, population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Biodegradable matter is mixed with animal waste for rapid decomposition or just with millet, sorghum or other plant stalks for slow decomposition. The biodegradable matter is placed in a pit. In the dry season, it is regularly sprinkled with water until decomposition is complete. It is then spread evenly over the land before sowing or planting.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Biodegradable matter, animal waste, plant stalks, ash and/or natural phosphate, manure collected
作者:
PASP
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Biodegradable matter is mixed with animal waste for rapid decomposition or just with millet, sorghum or other plant stalks for slow decomposition | |
| 2. | The biodegradable matter is placed in a pit. | |
| 3. | In the dry season, it is regularly sprinkled with water until decomposition is complete | |
| 4. | It is then spread evenly over the land before sowing or planting. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: shovel, wheelbarrow, etc.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Production of compost:
• constructing pits or basins
• water
• equipment (shovel, wheelbarrow, etc.).
Use of compost:
• transportation to plot by cart (100 kg of manure per donkey cartload)
• transportation to plot in head baskets (20 kg of manure per basket)
• spreading the compost on the plot (labour).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor - medium
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: > 10 m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
traditional land use rights on fields, communal land on pasture and forest land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The use of compost and manure improves yields and output, thereby improving food security. The sale of surplus production also increases household income
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
The use of partially decomposed manure also exposes crops to certain pests and to the risk of being scorched
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: transporting manure and compost poses a major hurdle for poor farmers who do not have a cart. This is a particularly serious problem when plots are at a distance from the village (outfields)
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| reactivates biological activity, increases soil fertility by providing nutrients and improves soil structure by increasing the amount of organic matter in it |
| The improved soil structure also increases the infiltration of water into the soil |
| The use of compost and manure improves yields and output, thereby improving food security. The sale of surplus production also increases household income. |
| The denser vegetation and improved soil structure make the land more resistant to water and wind erosion. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Manure and compost are often not available in sufficient quantities | In spite of these drawbacks, manure is the form of fertilisation most commonly used by farmers, as it requires less work than compost. |
| Water is required to moisten compost during the dry season in order to ensure that it is kept at the right temperature for the decomposition of the biomass | |
| transporting manure and compost poses a major hurdle for poor farmers who do not have a cart. This is a particularly serious problem when plots are at a distance from the village (outfields). | |
| farmers are deterred from composting in the dry season because a nearby supply of water is needed and it involves a considerable amount of work | |
| The use of manure on farmland entails some risks and disadvantages. As the manure is only partially decomposed – decomposition starts after the first rains begin – crops do not have enough nitrogen for a time. The use of partially decomposed manure also exposes crops to certain pests and to the risk of being scorched. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/07/2012
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块