Contour Farming using hedgerows [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Eduardo Alberto, Alexandra Gavilano
Contour Farming
technologies_1287 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Luistro Aida
DA_STIARC, RFO IV-A
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Gregorio Elizabeth
DA_STIARC, RFO IV-A
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
DA-BSWM
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Gutierrez Albert F.
alfergu@yahoo.com
LGU of La Libertad, Negros Oriental
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
LGU of La Libertad - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Southern Tagalog Integrated Agricultural Research Center (STIARC) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Regional Field Office N0. 4A (RFO IV-A ) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/05/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Conservation Farming Village [菲律宾]
A modality in mobilizing resources for sustainable upland development which utilizes a basket of strategies, technologies, and interventions to catalyze the widespread transformation of traditional upland farming systems into resilient and sustainable upland production systems.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
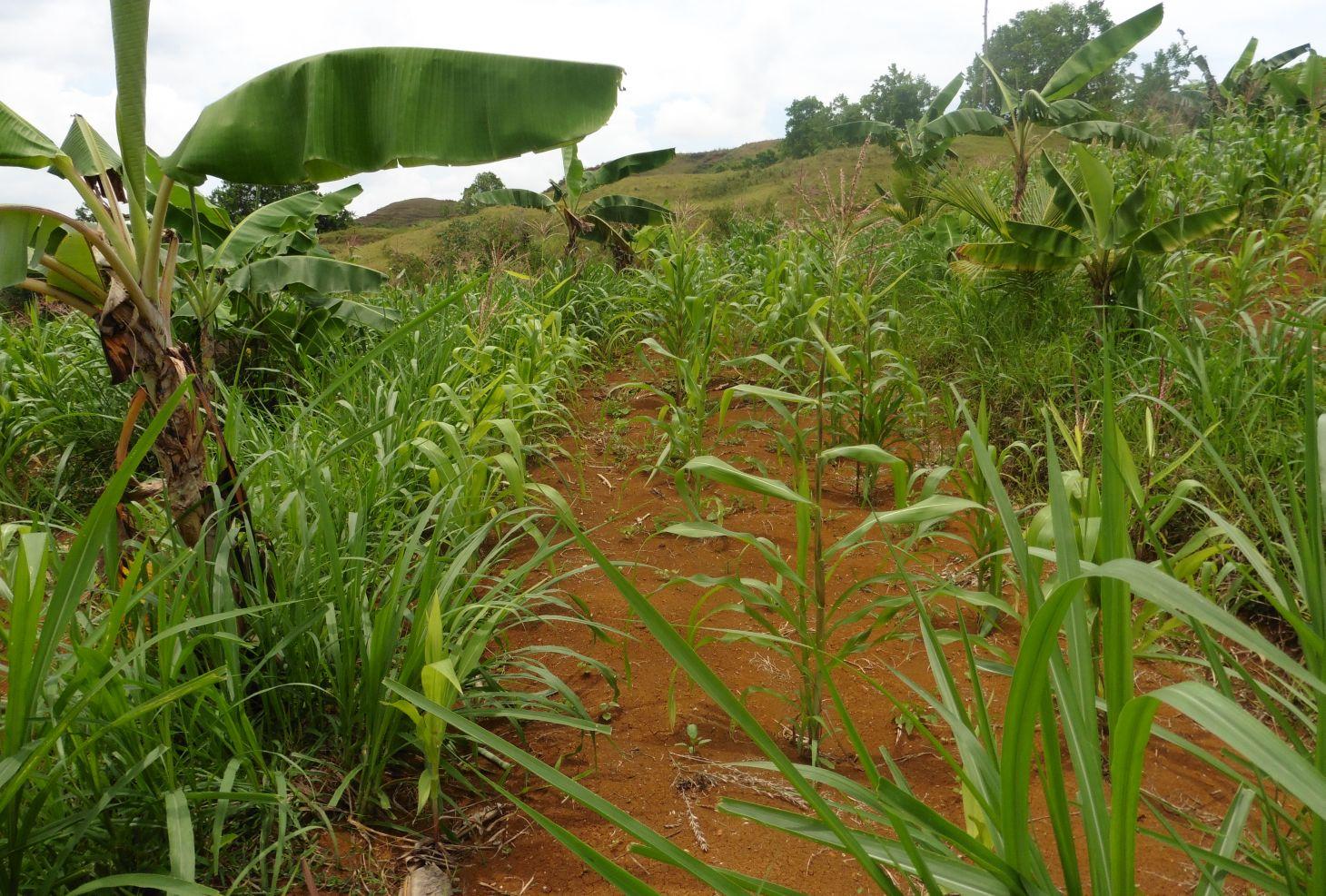
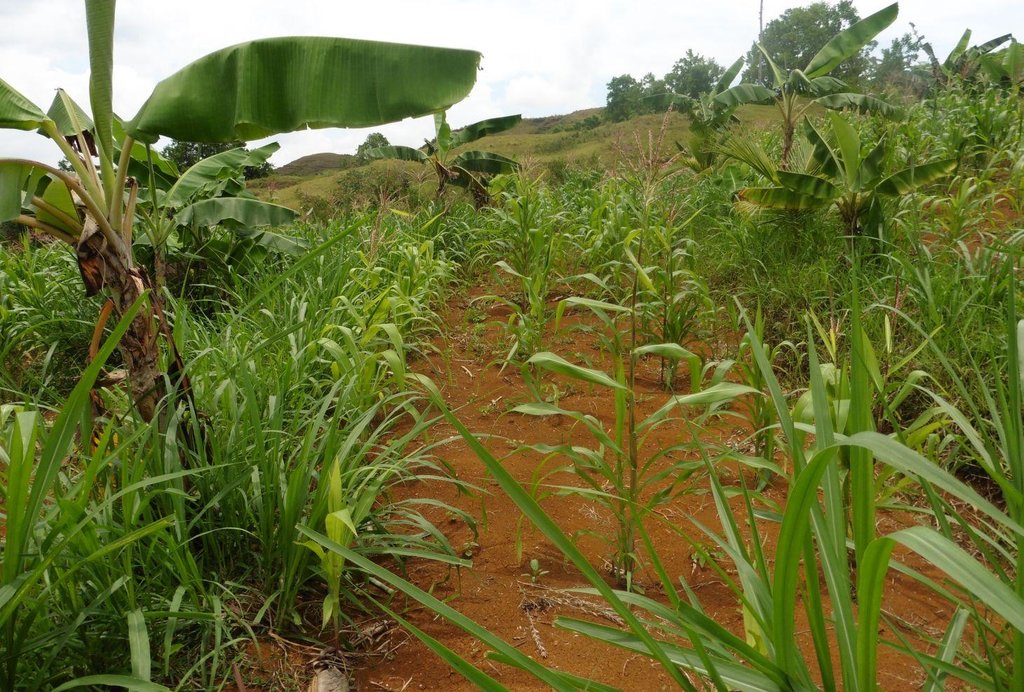
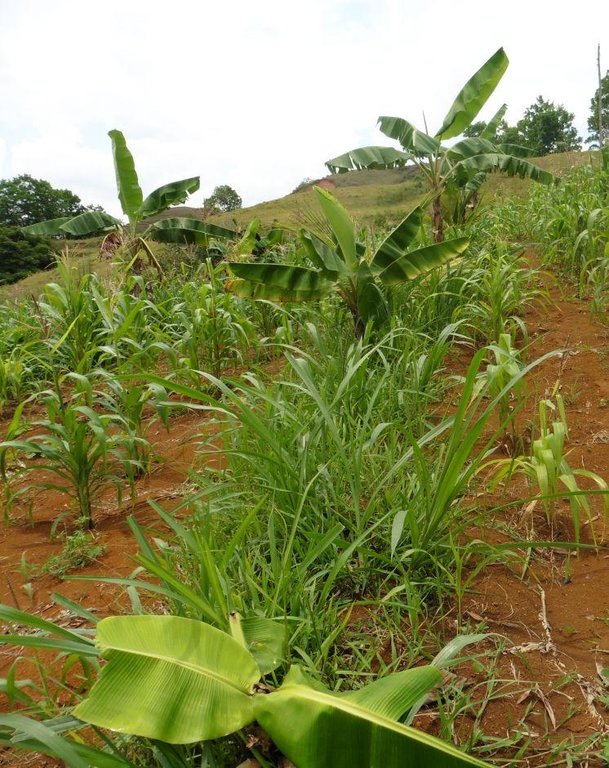
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
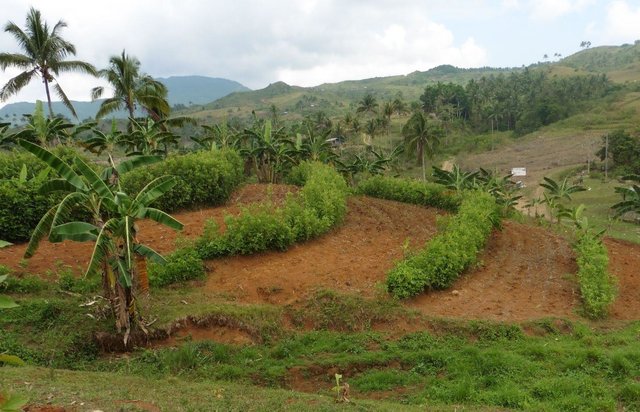
Contour farming is being practiced by the farmers in sloping areas to prevent or control soil erosion. Hedgerows are established along contour lines using napier grass and permanent crops like banana and coconut. In between contour lines, corn is inter-cropped with peanut. It is a traditional practice of farmers and one of the conservation techniques for the Conservation Farming Village Approach (CFV).
Purpose of the Technology: This is practiced by farmers to control surface run-off, erosion and to conserve natural soil fertility. Napier grass is also planted as source of feeds for the livestocks. The technology controls dispersed runoff, reduce slope angle and length.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Contour lines were established using an A-frame to determine the location of the hedgerows to be planted. Napier grasses are planted along the contour at 8x8m and 4X4m distance. Grafted cacao trees are also inserted in between banana at 4X4 distance. The alleys between hedges measuring 4m wide and 30m long are planted with corn and peanut. Napier grass is regularly trimmed to maintain a height of not more than a meter, using the cuttings as livestock fodder.
Natural / human environment: The area is under a humid climate condition with an average annual rainfall of 1000-1500 mm. Its elevation is 500-1000 m above mean sea level.The average cropland size of land users is less than or equal to 0. 5 hectare with a slope ranging from 18-25%. Income of land users are derived from the crops sold. The Local Government Unit (LGU) provides truck to transport the harvested crops of the farmers from the village to the town market twice a week.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
La Libertad
有关地点的进一步说明:
Negros Oriental
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
The technology is a traditional practice in the Philippines and was integrated as part of the conservation techniques under the Conservation Farming Village approach.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: peanut
major food crop: corn, banana, cacao, coconut
Other: Napier grasses
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and soil fertility decline.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of animal grazing areas and limited plain or level areas for crop production.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0025 m2.
Farmers practice contour farming only in small areas or parcels of land
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, breaking crust / sealed surface
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of knowledge on fertilizer usage), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intensive tillage due to crop production), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (illegal logging, slash and burn), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (charcoal making for livelihood)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
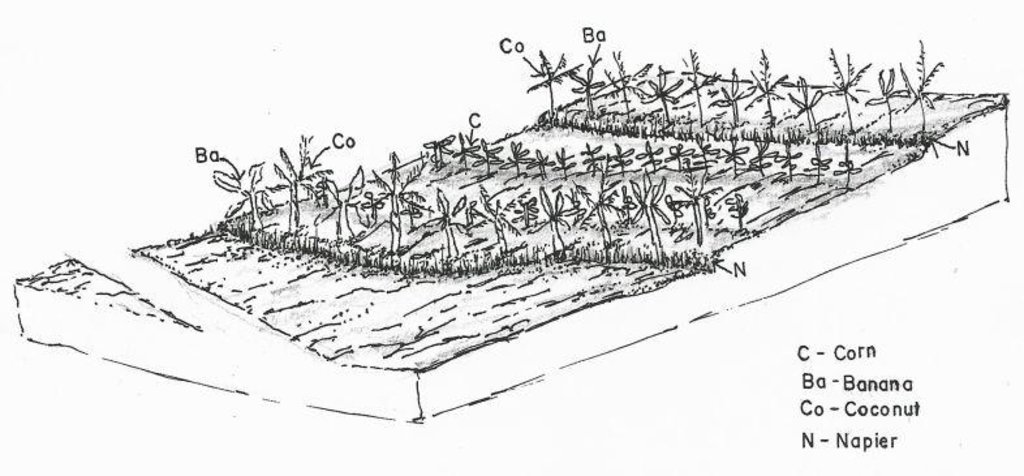
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Crops planted in the contour.
Location: Brgy. Talaon. La Libertad, Negros Oriental
Date: May28, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, Minimize soil erosion due to runoff, Serve as soil nutrient traps
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: corn and peanut
Quantity/ density: 10kg/.25ha
Remarks: in between contour hedges
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: napier, banana, coconut and cacao
Quantity/ density: 20kg/.25ha
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 20kg/.25ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: vermi-compost
Quantity/ density: 500kg
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: rotavator
Remarks: plowing two times
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): drill
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vegetative measure: contour (banana)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 64
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: contour (cacao)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 64
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: contour (cococnut)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 32
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: banana, cacao, coconut
Grass species: napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 3-5%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 hectare
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
49.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.22
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedgerows | 植物性的 | before onset of rainy season |
| 2. | Planting of hedgerows (Napier grass) | 植物性的 | Rainy season. one week after laying out |
| 3. | Planting of perennial crops along contour | 植物性的 | Rainy season. 1 week after laying out |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果可能,按下表分列技术建立费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出建立该技术的总成本估算。:
122.77
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Laying out and establishment of contour | Person/day | 3.0 | 2.22 | 6.66 | 40.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting of crops and hedgerows | Person/day | 10.0 | 2.22 | 22.2 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | napier seeds | kg | 300.0 | 0.0133 | 3.99 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | banana seeds | plants | 64.0 | 0.11093 | 7.1 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | cacao seeds | plants | 64.0 | 0.55565 | 35.56 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | coconut seeds | plants | 32.0 | 0.88875 | 28.44 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | herbicide | liter | 1.0 | 17.78 | 17.78 | 40.0 |
| 施工材料 | bamboosticks | picks | 50.0 | 0.012 | 0.6 | 40.0 |
| 施工材料 | A-frame | unit | 1.0 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 40.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 122.77 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing/ preparation (plowing, rotavating, harrowing) of alleys between contours | 农业学的 | Before onset of rainy season |
| 2. | Furrowing | 农业学的 | |
| 3. | Planting of corn (first cropping) | 农业学的 | Raining season |
| 4. | Weeding, insect control | 农业学的 | |
| 5. | Harvesting of first crop | 农业学的 | |
| 6. | Land Preparation for the second cropping (plowing, harrowing/rotavating, furrowing) | 农业学的 | |
| 7. | Planting of corn + Planting of peanut (second cropping- corn + peanut) | 农业学的 | |
| 8. | Weeding / Insect control | 农业学的 | |
| 9. | Harvesting of corn and peanut | 农业学的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果可能,按下表分解技术维护费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出维护该技术的总成本估算。:
146.63
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land Preparation with machine / furrowing | Person/day | 3.0 | 7.11 | 21.33 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Animal Labour | Person/day | 2.0 | 2.67 | 5.34 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Other Labour: Weeding, harvesting | Person/day | 14.0 | 2.22 | 31.08 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Corn seeds | kg | 10.0 | 0.444 | 4.44 | |
| 植物材料 | Peanut seeds | kg | 20.0 | 2.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds undefined | kg | 10.0 | 0.444 | 4.44 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 500.0 | 0.08 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 146.63 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: rotavator
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The slope of the area contributes to the additional labor cost in the establishment of contours.The steeper the slope, the higher labor cost will be incurred.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zones: 720 m
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
70% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Hired laborers for the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) Project on National Greening Program
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
10 bags
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
1350 bundles
饲料质量
产品多样性
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
Improved livelihood and human well-being
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
风速
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
More income added from Napier grass
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
18 land user families have adopted the Technology
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Single farmer focused on napier production and used as hedgerows
28% of land user families (4) who have adopted the Technology did it spontaneously.
4 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Practiced contouring but some are partial adoption (rock wall)
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Additional barangays will be adopting the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Availability of labor force in the community. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage more farmers to adopt the technology and utilize available labor force. |
|
The technology generated jobs and increase the income of the landusers practicing the technology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To conduct continuous capacity building to land users and their children to ensure sustainability. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Soil erosion was reduced because of the presence of the hedge rows that traps eroded soil. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Include other structural measures such as silt traps and brush dams to trap silts. |
|
The kind of hedgerows planted depends on the need of the landusers. Farmers with livestock used napier and forage grasses as hedges while others planted perennial and cash crop to supplement their food requirement. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conduct crop suitability evaluation and market study. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Poor road network from the center of the town to the barangay. | Construction of farm-to-market road to improve the accessibility of the barangay. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of irrigation system in the cropping area | Provision of irrigation system such as solar pump and small farm reservoir. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Conservation Farming Village [菲律宾]
A modality in mobilizing resources for sustainable upland development which utilizes a basket of strategies, technologies, and interventions to catalyze the widespread transformation of traditional upland farming systems into resilient and sustainable upland production systems.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块