Combating of invader plants and bush packing [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1373 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Meyer Schalk
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Gauteng Department of Agriculture and Rural Develo (Gauteng Department of Agriculture and Rural Develo) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Awareness raising [南非]
To make the people aware of veld degradation, rehabilitation & the participation of the people
- 编制者: Belly Mpoko Malatji

Technical and scientific support & Job creation in … [南非]
To make the community aware of precious resources like water and the preservation of it, the control of alien encroachment, creation of job opportunities and the training of the undeveloped communities.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The combating of Invaders to preserve water resources & the rehabilitation of the bare ground by means of brush packing to prevent soil erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
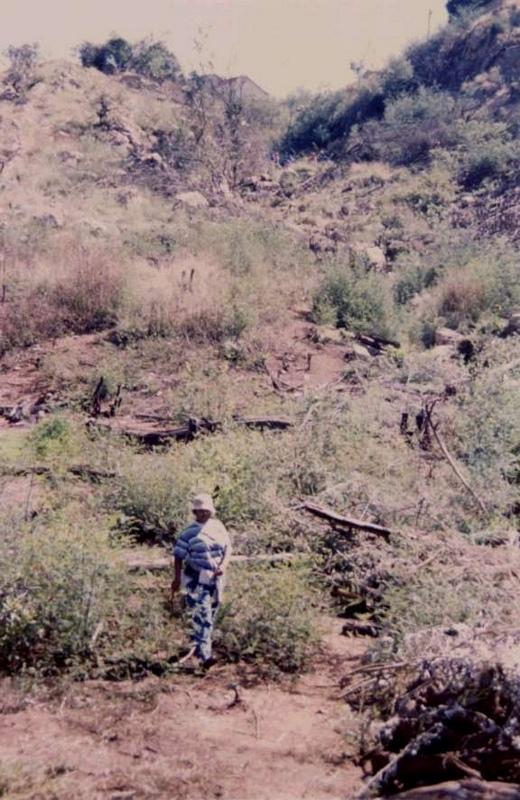
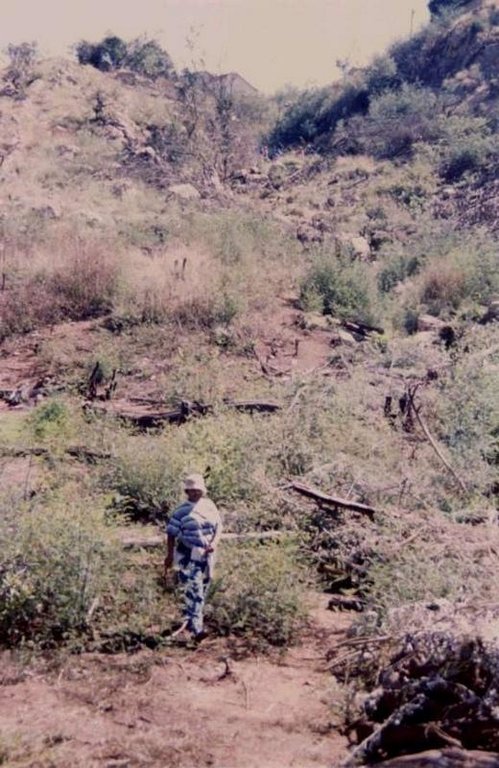
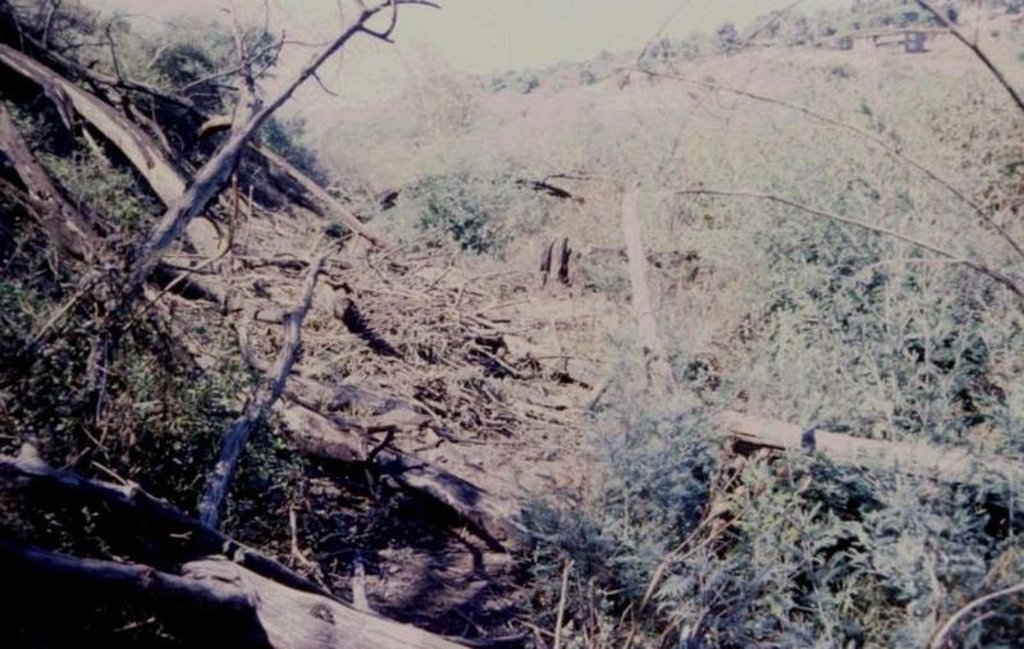
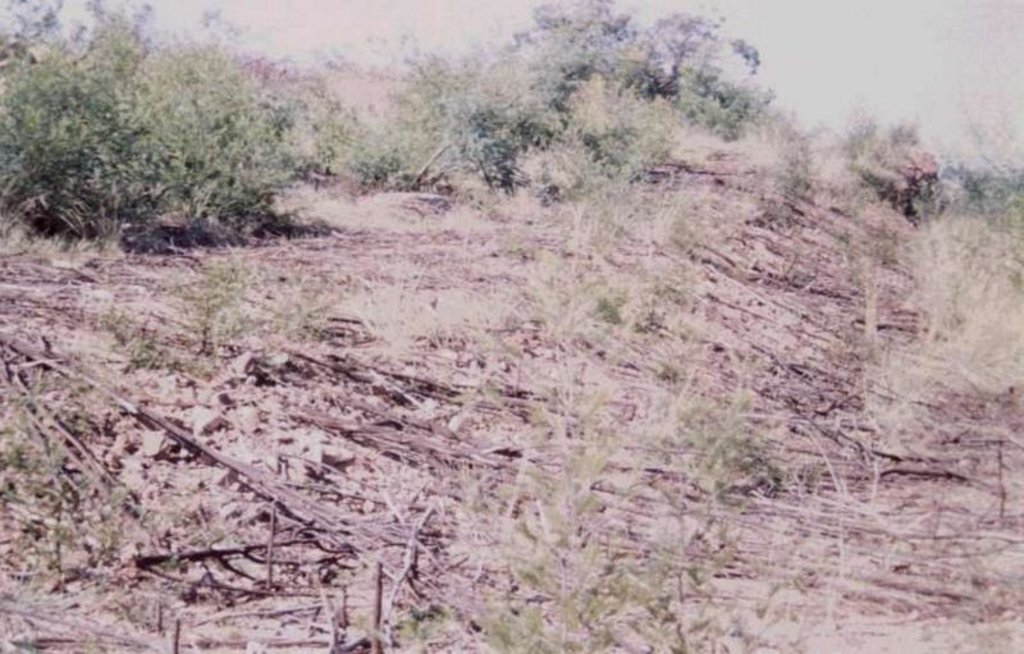
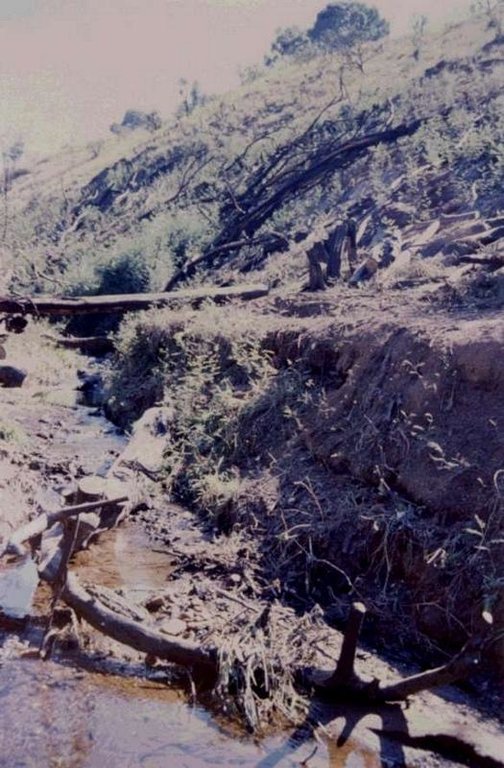
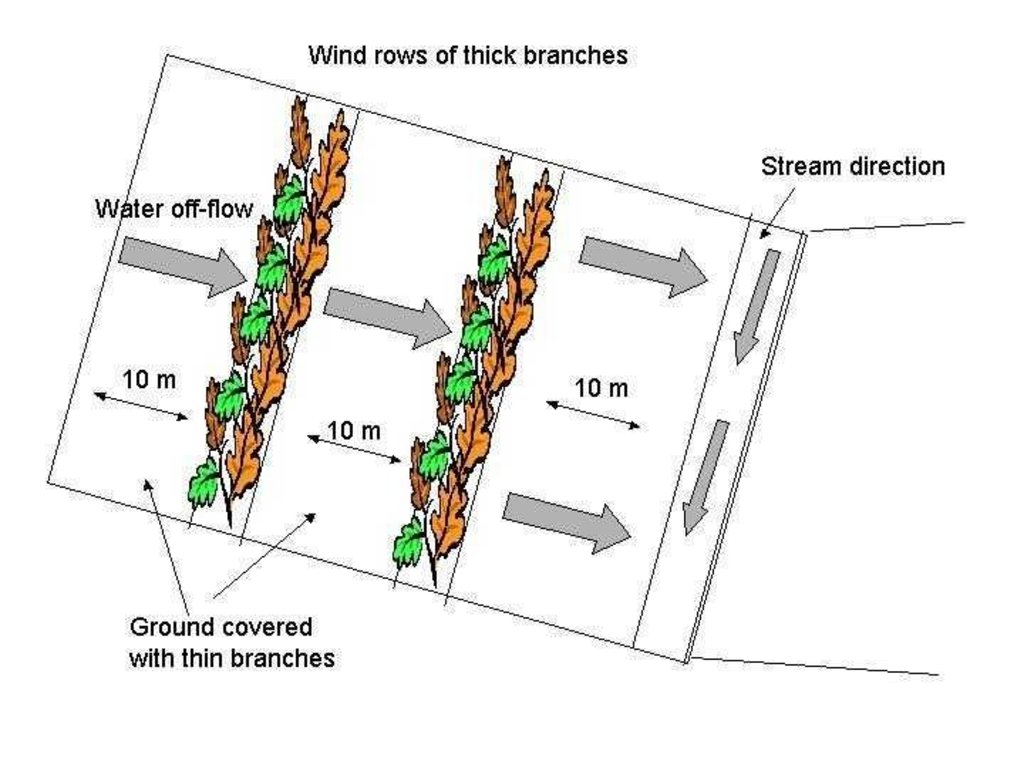
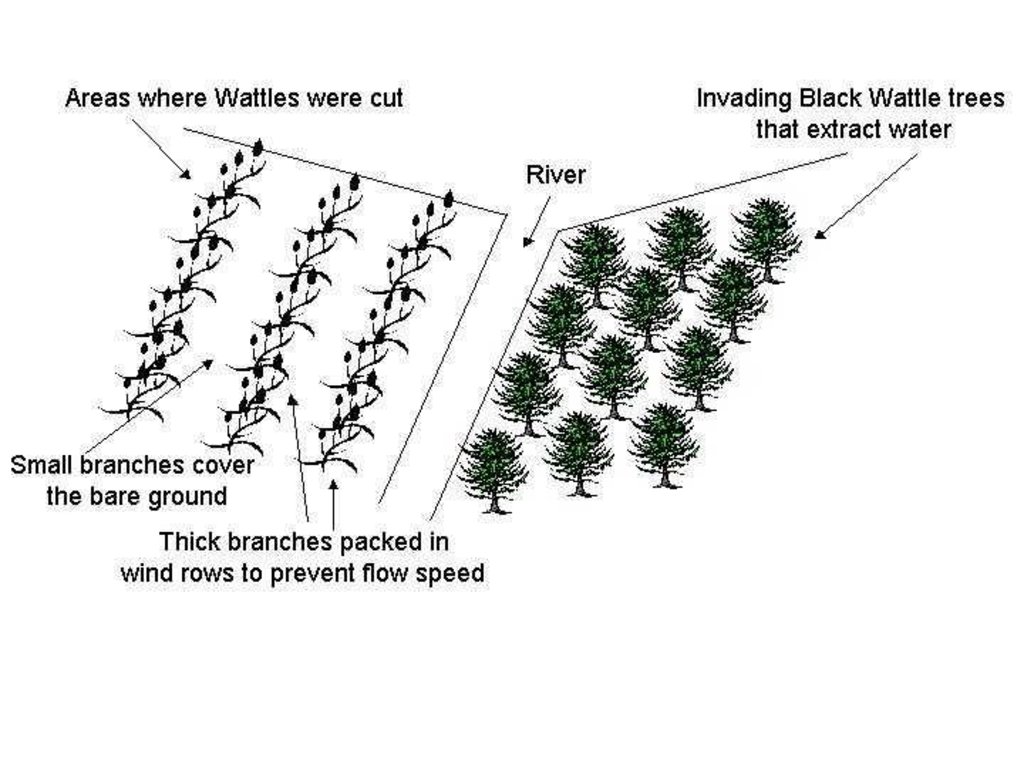
The technology is applied in areas under the 'Working for Water' projects that are run by the National Department of Water Affairs in South Africa, in the fight to combat invaders exhausting our valuable water resources. Catchment areas are fields that are infected by invader species on riverbanks, and catchment areas that extract enormous amounts of water out of the system. The trees (Black wattle - Acacia meansii) are cut or ring barked. After the trees are felled, large areas of bare ground are exposed. In order to prevent soil erosion until the natural succession processes are completed and the area is in equilibrium with the rest of the environment, soil needs to be stabilised and sometimes also rehabilitated.
These exposed areas must first be treated with a follow-up to prevent the coppice, re-growth and seedlings from growing again. Sometimes in agricultural grazing areas, the bare areas are re-seeded with natural climax grasses, and in urban areas left to be stabilised by successional species, or pioneers and aveads etc. The small branches of the felled trees are packed on bare areas, after the re-seeding to stop the topsoil from eroding. This reduces the off-flow and flow speed of the rainwater, lowering the raindrop impact, increasing the moist regime and preventing wind erosion. The thick stumps are either used for firewood or for the charcoal industry, as well as packed in windrows horizontal with stream flow.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Gauteng
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gauteng
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
2.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 km2.
2 Sites at Krugersdorp, one along a public rood where no development is done yet & the second at Kenmeare Kloof that divided two residential areas. Elandsfontein is bits & pieces that scatters over several farms.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was experimented by the University of Potchefstroom and also applied at other typical Working for Water projects in the country and technical advise by experts of Water Affairs.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
- cattle
注释:
Main animal species and products: Not many cattle, people still poor - average
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Tremendous bush encroachment by wattle species or other similar invaders like blue gum trees, the area has no further land use after the bush encroachment.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The problem is similar, no land use in encroached areas, the trees are to close and no grasses grow underneath for cattle to feed on, and the bush provided shelter for criminal activities.
Constraints of settlement / urban: Preventing of fires in the dry trees
Constraints of recreation: Preventing of fires in dry trees/area
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 210; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Clearing of alien plants
Working for Water
Gauteng
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: No grazing for first 3 years after reseeding
Control / change of species composition: Follow-up - eradication and control of regrowth
作者:
Schalk Meyer
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting of trees | Summer |
| 2. | Packing of branches | Before winter (wind) & spring (rain) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cutting of trees and packing branches | persons/day/ha | 500.0 | 30.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 125000.0 | 125000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 140500.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 23416.67 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Where reseeding took place the grazing must be maintained | 3 years after planting / 3 years |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The total implementation of the technique: Costs of chemicals & tools, labour for the whole project, the cutting of the regrowth and the treatment of it (follow-up) and the packing of the branches.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour: The work team of 25 people is very expensive/costly. Chemicals for the invader eradication treatment is very expensive.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
600.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Also rolling
Landforms: Hill slopes at Krugersdorp
Altitudinal zone: 1542 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average : Very shallow at hillside at Krugersdorp more predominantly and shallow at more farm soils at the plains of Elandsfontein.
Soil fertility is medium in plains and low in hillsides
Topsoil organic matter: Not very fertile, no grasses to enhanced biomass
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium for the soil of plains of Elandfontein (not so compacted - better drainage) and poor for Krugersdorp (hillside highly compacted)
Soil water storage capacity is medium for Elandsfontein (less compacted) and low for Krugersdorp (more compacted)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Elandsfontein, upcoming farmer).
60% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land (Communities that is not fully commercialized).
Off-farm income specification: Family members are working in the city, to provide for the family (the children and brothers etc.)
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (self-supply) for Elandsfontein: workers that are living on the farm
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Where reseeding was done the bare soil will be replaced with grasses
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Where reseeding was done the bare soil will be replaced with grasses
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Better grazing for cattle and selling of fire wood
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Selling of wood for fire wood & charcoal to charcoal industry
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Training and job creation
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Better technologies and experience
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
90
SLM之后的数量:
30
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
soil fertility
biodiversity
conserve water resource while reducing invader bush
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
No Wattle's to extract water, reduced runoff
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Soil is stabilized
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Elandsfontein: prevent soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve farm soils - control overgrazing |
|
Elandsfontein: Improve grazing capacity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Rotational grazing and rest for first 3 years after rehabilitation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Prevent soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? Packing of branches correctly and maintained - preventing of veld fires (wood from burning) |
|
Reseeding of perennial grasses that enhanced grazing capacity and biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Correct seed mix & seeding method; preventing from grazing and veld fires |
|
Conserve water resource How can they be sustained / enhanced? Eradication and control of invaders |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive | No recommendations |
| Time consuming | No recommendations |
| Expensive | No recommendations |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Business plan and work reports from government officers / officials & NGO's like universities
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
NGO's and Universities
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Awareness raising [南非]
To make the people aware of veld degradation, rehabilitation & the participation of the people
- 编制者: Belly Mpoko Malatji

Technical and scientific support & Job creation in … [南非]
To make the community aware of precious resources like water and the preservation of it, the control of alien encroachment, creation of job opportunities and the training of the undeveloped communities.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块