Communal grazing management [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Using benchmarks as demonstration of NRM strategies. Camp system vs. Open system.
technologies_1382 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO (Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO) - 南非有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture (Department of Agriculture) - 赞比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Communal stakeholders [南非]
Government funded project aimed at rangeland management to enhance natural recourse management. The community being the key stake holders.
- 编制者: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Rangeland management of communal grazing land, to improve grazing capacity by applying rotation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
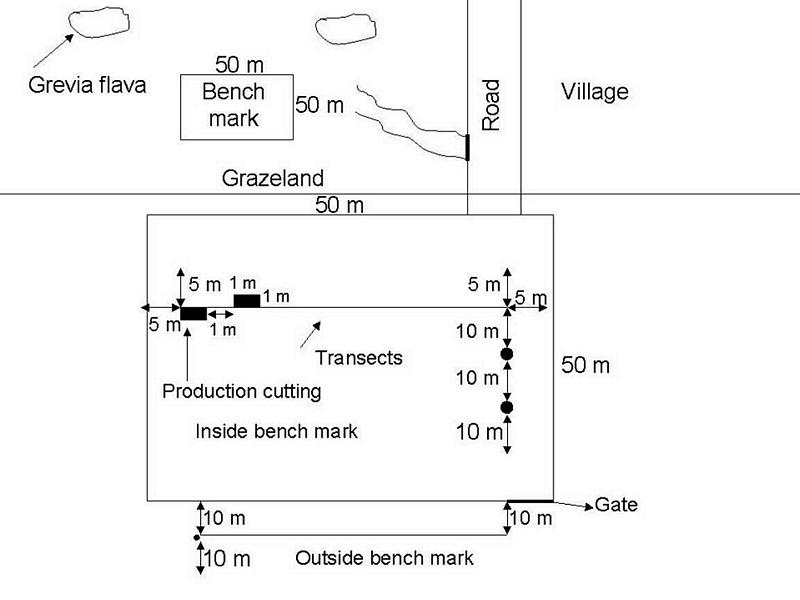
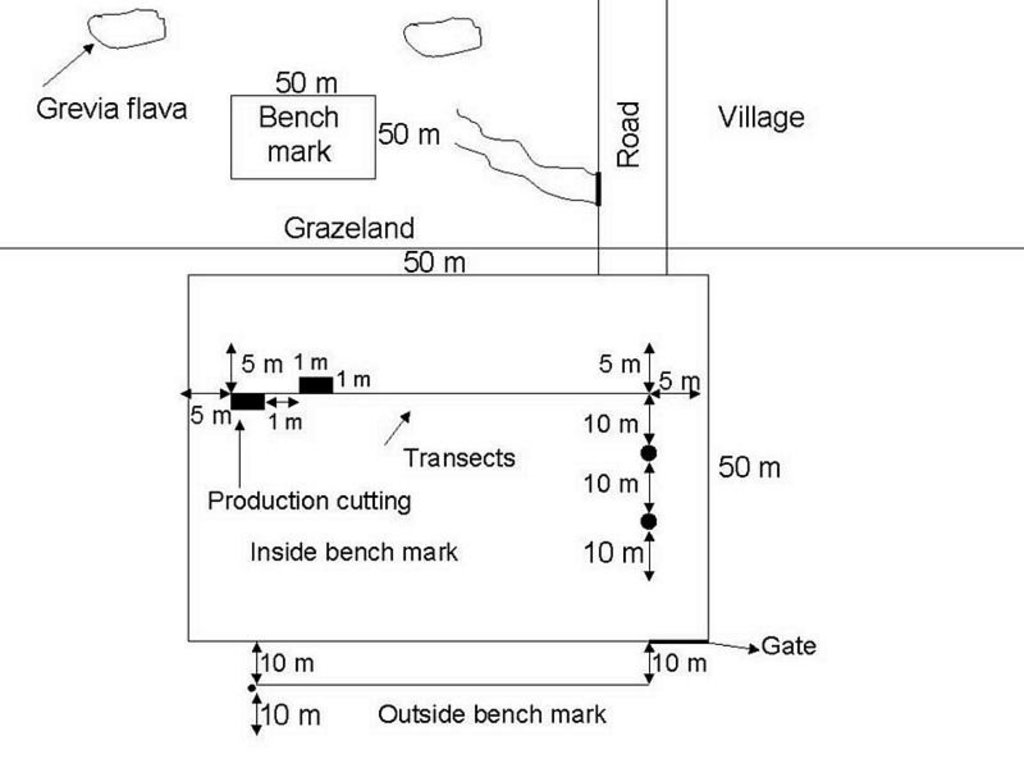
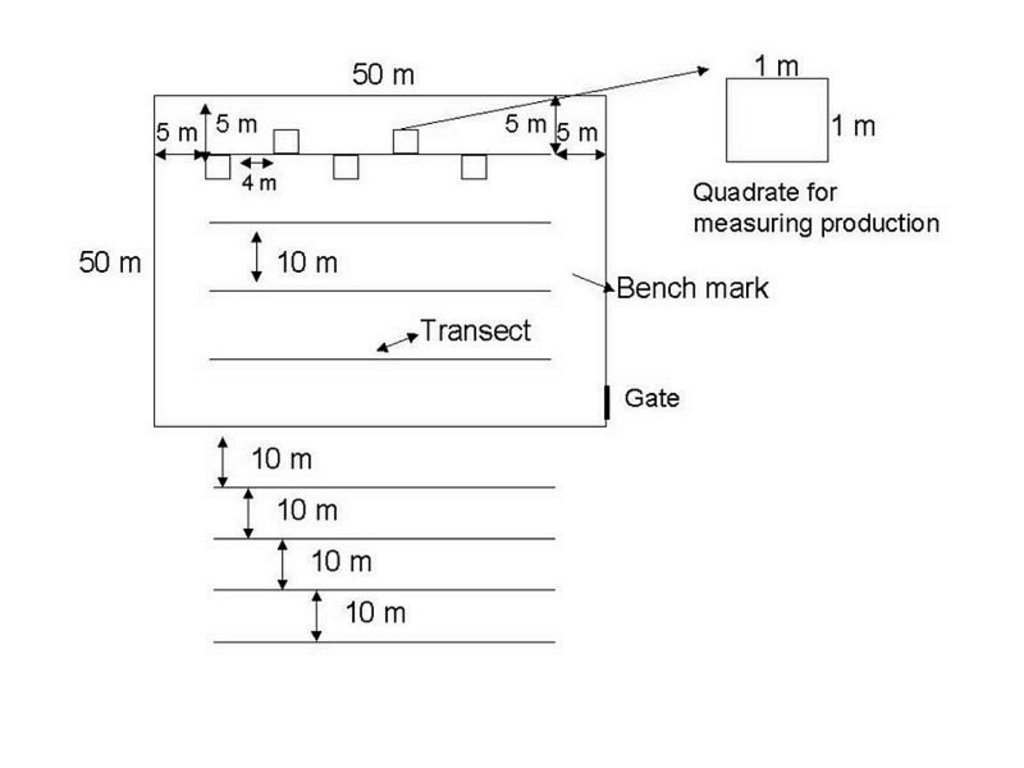
Benchmarks were identified and monitored to see how the production and vegetation would change if proper management was applied to a specific area. The benchmarks will only be grazed in the winter and rested in summer. The benchmarks were constructed with goat-proof fencing. Benchmarks will illustrate how grazing land can improve with the right management system.
Monitoring of vegetation is done twice a year.
2.3 技术照片
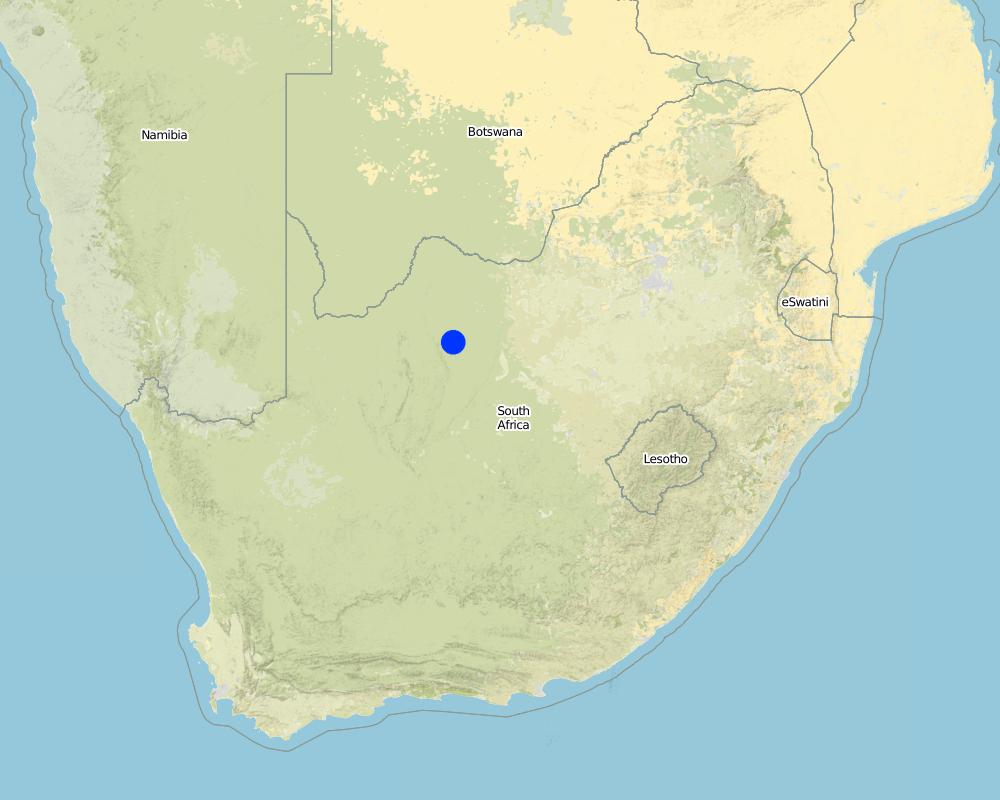
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kudumane
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
1.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 km2.
Settlement situated 30 km from Kuruman. Lots of sheep and goats. Also cattle, donkeys and horses. Communal grazing.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The need to improve grazing lands.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- Monitoring SLM Technology
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- 山羊
- cattle
注释:
Main animal species and products: Communal grazing (free roaming goats)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Over grazing, loss of palatable species and thus nutrients for cattle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduced animal performance.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Communal grazing (free roaming goats)
Grazingland comments: Large community owned livestock herds.
Type of grazing system comments: Large community owned livestock herds.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 210; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Apr
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
注释:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technology
Location: Maketlele. North West Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Change of land use type: Area divided into camps.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Camps, benchmarks, fences constructed.
Other type of management: Rotational grazing.
作者:
Anja Jansen van Vuuren
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
-0.8
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.60
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Area divided into camps. | 6 months |
| 2. | Identification and construction of benchmarks. | 1 month |
| 3. | Initial survey. | 1 week |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Constructing benchmarks | persons/day/ha | 133.0 | 3.2 | 425.6 | |
| 施工材料 | Fencing material | ha | 1.0 | 914.64 | 914.64 | |
| 其它 | Transport (10-7km/l) | ha | 1.0 | 67.07 | 67.07 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1407.31 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | -1759.14 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Further surveys. | 2 weeks / twice a year |
| 2. | Data analysis. | 3 months / after each survey |
| 3. | Establishing a gradient. | 2 weeks / once |
| 4. | Maintenance of fencing. | continued / when necessary |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance and monitoring | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 3.2 | 32.0 | |
| 其它 | Paper bags | ha | 1.0 | 8.05 | 8.05 | |
| 其它 | Data sheet | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| 其它 | Transport (10-7km/l) | ha | 1.0 | 129.27 | 129.27 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 170.32 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | -212.9 | |||||
注释:
Fencing of benchmark, conducting surveys and soil analysis.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of transport depends on the fuel price. The sites are situated far from accommodation. Maintenance of fences and soil analysis.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1337 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Sandy
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
20% of the land users are rich.
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: State pension, mine workers, family working in the city.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Inside benchmark
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Inside benchmark
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Nobody wanted to help with surveys
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
soil fertility
biodiversity
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Will increase with awareness adoption of technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Improved rangelands. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better cattle. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The committed ADC-manager How can they be sustained / enhanced? Meetings |
| The maintenance of benchmarks as examples. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Cattle must be reduced | Improve rangeland - larger carrying capacity |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Community participation | Give more information |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Communal stakeholders [南非]
Government funded project aimed at rangeland management to enhance natural recourse management. The community being the key stake holders.
- 编制者: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
模块
无模块