Reafforestation of Tugai floodplain ecosystem [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Rustam Nugmanov
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1509 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Nickalls Tom
ACTED
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agency for Technical Cooperation and Development Tajikistan (ACTED Tajikistan) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Reforestation of the Tugai floodplain ecosystem with reed stands, poplars, djigda, and tamarisk thickets to strengthen the river bank area along the Pyanj river.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
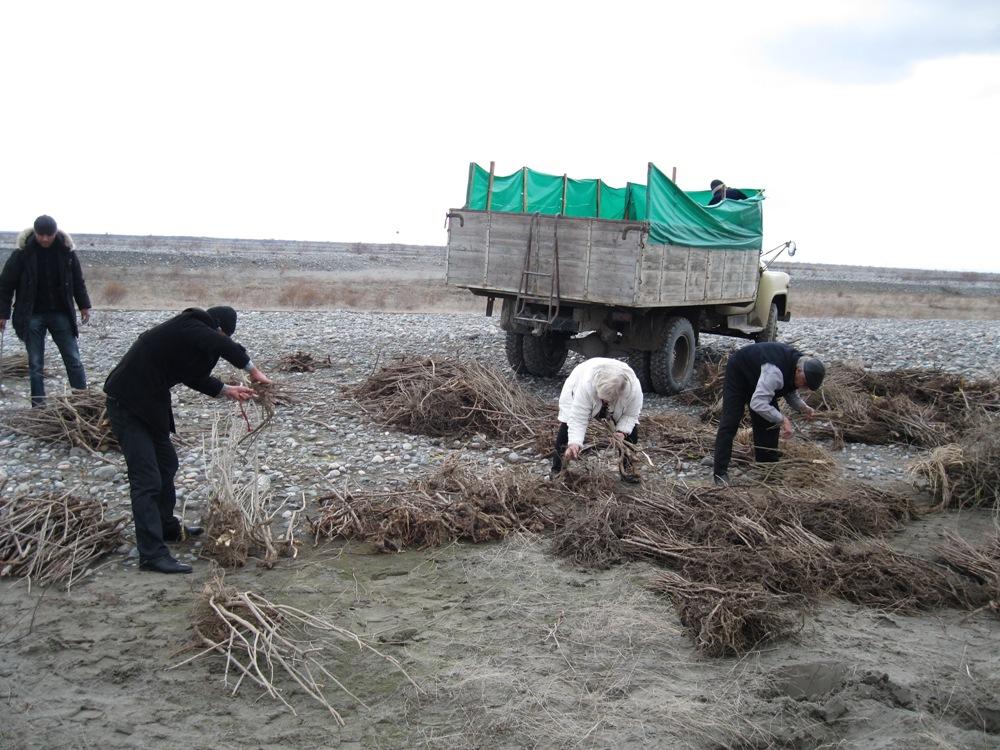
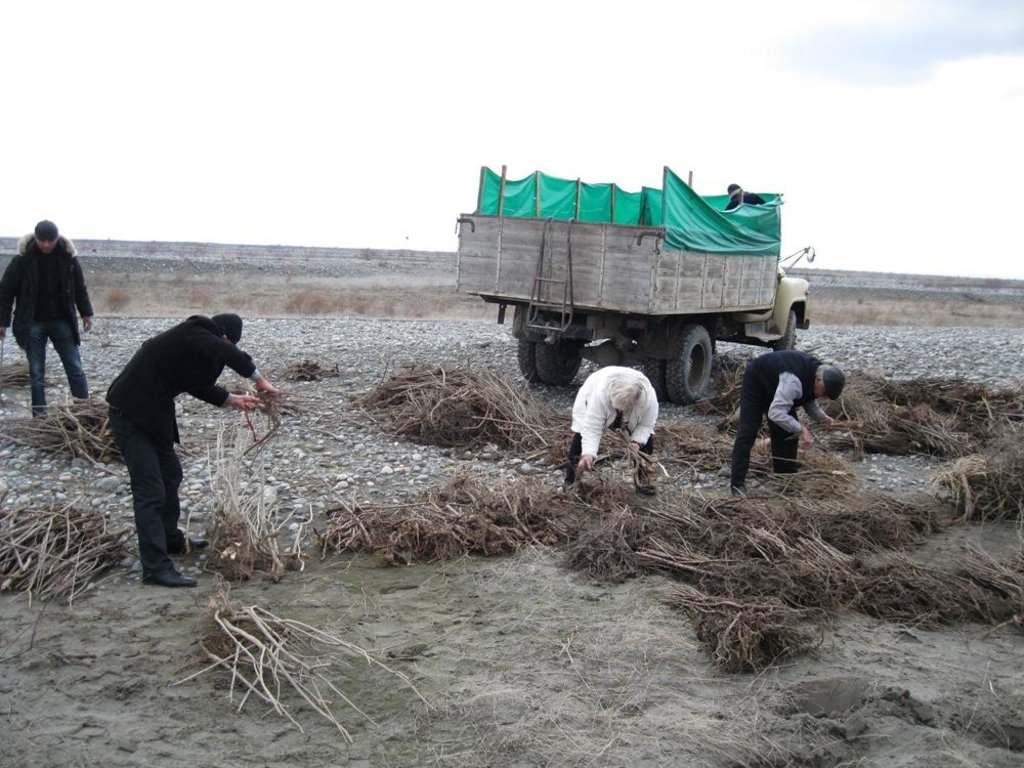
Reforestation works are being carried out in an area of 18.2 km2 in four demarcated zones each measuring 4.55 km2. ACTED and CAREC have entered into labour agreements with household representatives of villages near the riparian area to carry out the plantation of seedlings and bushes. 520 household representatives will plant a variety of 150,000 seedlings and bushes in the floodplain area (prone to flooding).
Reforestation works will help to reinforce the river bank area and protect it against potentially large scale floods. It will also diminish the effect of river bank erosion caused by flood waters. The activity will also protect the natural ecosystem in the target area and provide greater security for both the animal and human habitat. As a secondary purpose the reforestation works will also encourage local communities to be more aware of, and to hopefully motivate them to address some of the serious environmental and socio-economical problems affecting them.
The area was preselected by an expert as an area that was a degraded Tugai floodplain forest ecosystem. The area was assessed to ensure it still maintained a Tugai ecosystem. The extensive area was broken into smaller manageable parts of 3.5 h.a., these areas were then allocated to Jamoats who then further reassigned the responsibility to households. The next step is the development of a planting plan and schedule that includes fruit trees, timber and thickets.
The seedlings are obtained from the National Park area in collaboration with the state forestry department. The households are taught basic planting techniques, and supervised during the planting from November to March. A maintenance plan was established to ensure the upkeep of the ecosystem including watering, composting, and pruning.
The issue was that the Pyanj river was encroaching towards villages and cultivated lands that are essential to the livelihood of the local inhabitants. There is a lack of natural resources and increasing pressure on the available land for subsistence farming.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon
有关地点的进一步说明:
MSA Hamadoni
注释:
Specify the spread of the Technology:
evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 4 km2.
The Vakil (village representant) was not sure about the area, between 300 to 500 ha.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 18.2 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
In 2008 the Asian Development Bank did their initial appraisal of the Tugai ecosystem.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
- Poor natural Tugai forest ecosystem
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The seasonal flooding has resulted in severe river bank and soil erosion that has caused a reduction in the area of cultivated land, which provides an increasing threat to the village settlements. An increasing population is also adding to pressures on the limited land available, so threatening the livelihoods of local farmer households.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Local people highlight a lack of income and energy sources that lead them to cut down trees and vegetation for use as fuel and animal feed.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: It is a degraded forest with little economic value.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

森林/林地
- 植树造林
- reed stands, poplars, djigda, tamarisk thickets
注释:
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 220, Longest growing period from month to month: March - October
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 森林种植管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, change of seasonal rainfall, population pressure, poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Border guards exploited/cleared the area during their patrols)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
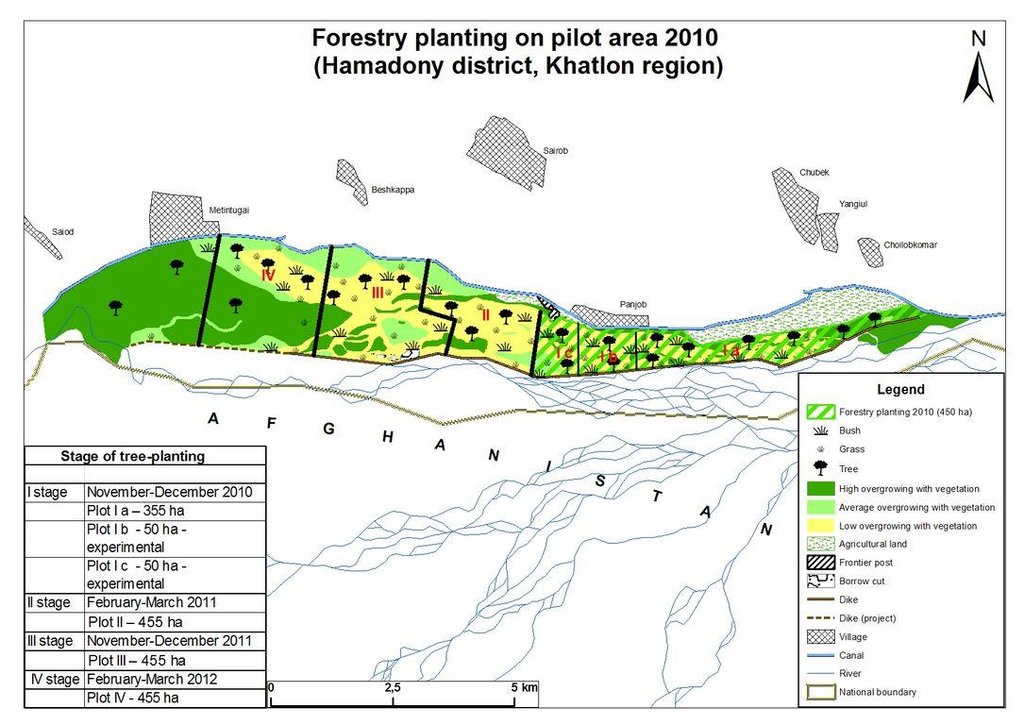
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Shows the different parts of the reforestation zones in the target area for the rehabilitation of the Tugai floodplain ecosystem.
Location: MSA Hamadoni. Khatlon
Date: 21 May 2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Once they are trained, the actual activities are just basic planting and care of the vegetation.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), improved wild animal habitats
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 80
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 12
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Trees/ shrubs species: reed stands, poplars, djigda, tamarisk thickets
作者:
CAREC, ACTED/CAREC
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tajik Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of tree seedlings | autumn |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting of tree seedlings | person day | 5.0 | 5.44 | 27.2 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | machine hours | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | pieces | 5.0 | 4.44 | 22.2 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | Pieces | 80.0 | 1.10625 | 88.5 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | kg | 80.0 | 0.22125 | 17.7 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 255.6 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 56.8 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of vegetation cover | annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance of vegetation cover | person days | 18.0 | 5.5555 | 100.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Pieces | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 110.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 24.44 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: shovel, knife
The costs are based on an area of 1 h.a. using 2010 prices, split from the entire scheme.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The intial costs of the activities are met by the donor project budget, the labourers are paid directly for their efforts under a `food for work' scheme. The seedlings, transport and tools are provided for planting, and the inhabitants are reimbursed in the longer term by the establishment of tree nurseries and fruit tree orchards.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Also medium
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
80% of the land users are poor.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: There is significant income from remittances sent back from Russia.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average of 3.5 ha per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Different parts of the Tugai system are allocated to individual households through the local Jamoat, as there are no formal land user certificates.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Helps to protect the land on which the inhabitants make their living and provides them with environmental education on land use systems.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
其它生态影响
River bank protection
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Increased protection to cultivated lands and settlements.
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
The choice of species are those that are able to grow in very wet/flood conditions.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
The inhabitants will not see any returns in the short term, and will have to maintain the forest for several years before they will reap the benefits in the longer term.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
520 families and 100% of the area covered
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
520 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The entire area selected for the project was reforested.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Land users are happy that their land is protected and that they are being provided with added incentives through food for work and the construction of orchards and nurseries. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The Tugai ecosystem acts as natural mitigation system for large scale flooding in the target area. It does not rely on heavy structural maintenance such as artificial dikes or gabions. |
| Involves representatives of target communities in the mitigation works. It gives them a sense of ownership towards the activities. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Mitigation is not an instant and obvious return, so the benefits are less obvious. | Land users need to be educated about the environmental and risk mitigation benefits of the project. Practical demonstrations are advisable. Furthermore, as there is no instant benefit it is also advisable to offer land users incentives (e.g. food for work and construction of household orchards and nurseries). |
| Maintenance of the reforested area requires labour post-reforestation phase (e.g. watering). | The use of incentives is advisable to increase motivation to participate. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/05/2011
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块