Improved Dairy Shed [不丹]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tshering Yangzom
- 编辑者: Haka Drukpa
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Rigsar Gi Nor Khim (རིགས་གསར་གྱི་ནོར་ཁྱིམ།)
technologies_6898 - 不丹
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Zangpo Shacha
不丹
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - 不丹1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Improved Livestock Farming System [不丹]
The approach involves a group of farmers implementing an improved dairy system. The system incorporates practices and technologies that enhance animal welfare, reduce environmental impact, and increase production.
- 编制者: Tshering Yangzom

Dairy Cooperatives and KOUFUKU linkage for milk marketing [不丹]
This approach links dairy cooperatives with a dairy plant, KOUFUKU International Limited (KIL), for milk marketing. It is an established dairy value chain that addresses milk and dairy product marketing issues and improves the livelihoods of many small dairy farmers in eastern Bhutan.
- 编制者: Nima Dolma Tamang
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
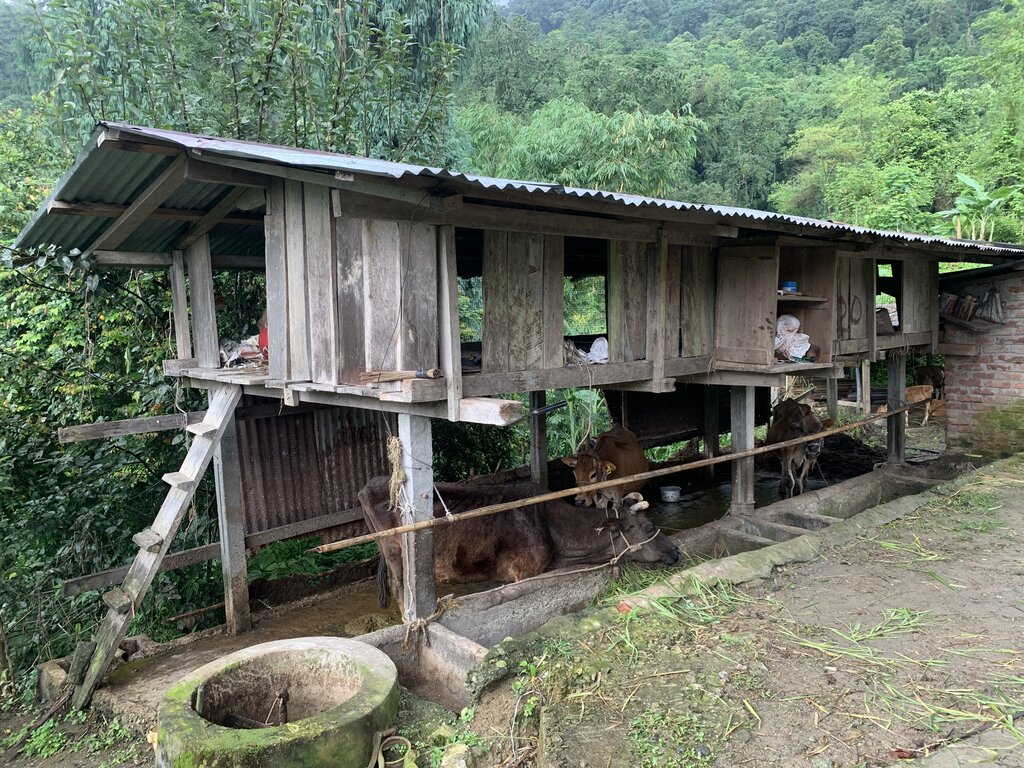
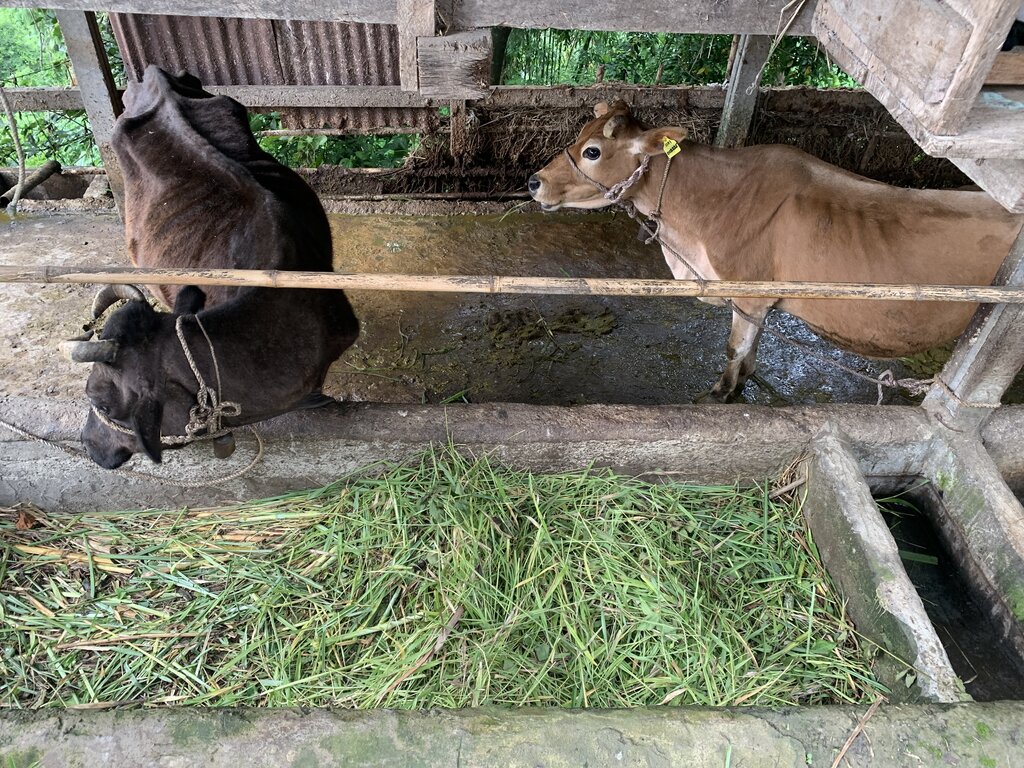
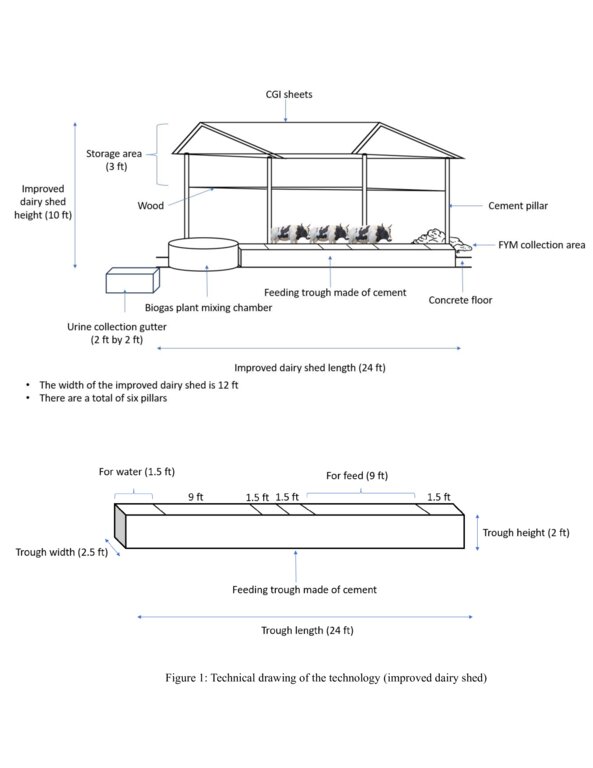
An improved dairy shed in Bhutan is characterized by concrete floors, cement pillars and troughs, enough sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, ample space for cattle movement, as well as urine and dung collection gutters and a farmyard manure collection area.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The main characteristics of the improved dairy shed are concrete floors, cement pillars and troughs, enough sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, ample space for cattle movement, urine and dung collection gutters, and a farmyard manure (FYM) collection area. The main purposes are to (a) enhance the overall well-being of animals, (b) optimize animal production, (c) minimize forest grazing and promote stall feeding, (d) increase the availability of FYM and urine for application to croplands, (e) develop pasture with fodder grasses, and (f) provide a comfortable working environment for land users.
The main inputs needed for establishment are cement for concrete floors, pillars, and troughs, and corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) sheets for roofing. The principal activities needed to maintain the technology are undertaking stall feeding instead of forest grazing, developing improved pasture with fodder grasses and trees, replacing low-yielding local cows with improved breeds dairy breeds such as Jerseys through buying or breeding (naturally or through Artificial Insemination [AI]), and better waste management.
The benefits of the technology include (a) the addition of nutrients to fields through the application of FYM and cattle urine, (b) an associated increase in organic matter, (c) better soil moisture retention, (d) availability of good quality fodder and a diverse range of forage options, (e) reduced labour due to less wild fodder collection and herding in the forest, (f) efficient waste utilization, (f) the potential manufacture and use of renewable biogas instead of liquid petroleum gas (LPG), (g) reduced land degradation due to reduction in forest grazing, (h) increased vegetation cover due to improved pasture development, (i) less soil compaction through decreased trampling by animals, (j) more comfortable working environment for land users, (k) improved livestock health and animal welfare, and (l) improved livelihoods of farmers through higher farm income. Besides these benefits, land users like the durability of the new sheds. However, one of the constraints of the technology is that the land users may lack funds to construct the sheds, or for improved cattle breeds, to justify the extra investment. These can hopefully be overcome by government support to land users through cost-sharing measures.
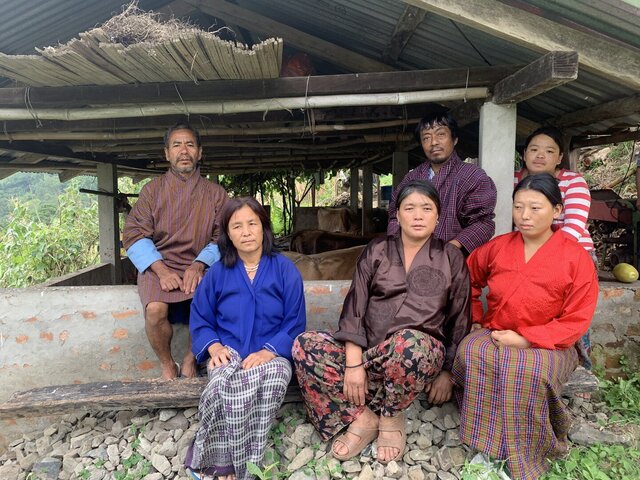
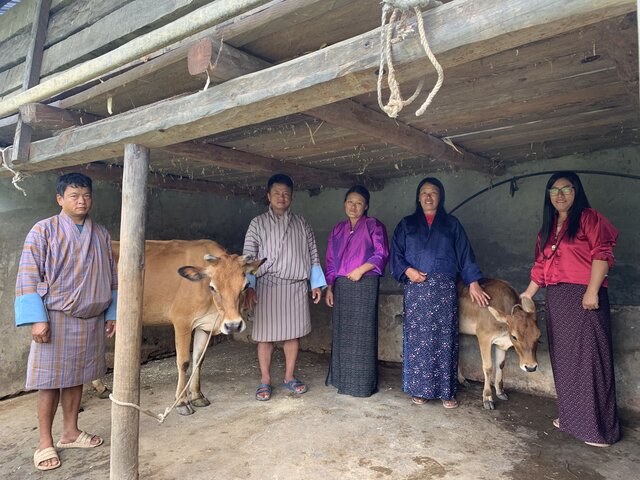
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Improved dairy shed (a)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ciXnVkJEOZw
Improved dairy shed (b)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-AySt7Bo9Os
日期:
10/07/2023
位置:
Martang village, Dewathang gewog, Samdrup Jongkhar Dzongkhag
摄影师的名字:
Tshering Yangzom
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
不丹
区域/州/省:
Martang village, Dewathang gewog, Samdrup Jongkhar Dzongkhag
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2014
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The land user adopted improved dairy shed partly at the suggestion of the livestock extension officer and partly due to his interest in improving his dairy shed.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- Cole crops, root crops, Solanaceous crops, Mustard Green
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 饲料作物 - 草
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 柑橘属
- Mango, pomegranate, jackfruit
具体说明:
Vegetables have one growing season. Maize is grown twice. Fodder grasses and fruit trees have many growing seasons.
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
There is intercropping among vegetables and intercropping between vegetables and fruit trees.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Vegetables are grown in rotation.

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 7 cattle (Jersey crosses)
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The crop residues serve as feeds for animals and livestock wastes such as cow dung and urine are used as organic fertlizers for crops. These organic fertlizers enhance soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertlizers.
产品和服务:
- 奶类
品种:
牛 - 奶制品
计数:
7
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S9:动植物庇护所
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Application of FYM to the field results in an increase in organic matter and an increase in nutrient availability in fields. There is better soil water retention by an increase in soil organic matter. Cattle urine also adds nutrients to the soil. Stall feeding under an improved dairy shed promotes the cultivation of fodder of good quality and variety. This helps maintain vegetative cover and prevent degradation of arable land. Similarly, stall feeding using crop residues from the field helps maintain vegetative cover and prevent the degradation of arable land. The land user feeds fodder grasses such as Super Napier and Napier that help stabilize soil and provide ground cover. Other feeds provided to cattle include banana stems, mustard cakes, straw, Guatemala grass, and processed feeds (Karma Feeds). The use of organic fertilizers such as cow dung and urine minimizes the need for chemical fertilisers that can cause loss of beneficial soil organisms, reduced organic matter, soil acidification, and nutrient imbalances in the soil.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Nu
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
82.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
500
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Deconstruction of old dairy shed that was made of wood and lacked cemented floor and pillars. | 2013 |
| 2. | Collection of raw materials to construct an improved dairy shed such as sand, stones, cement, and CGI sheets for roofing. | 2013 |
| 3. | Construction of the improved dairy shed (pillars, soling, roofing, storage area) | 2013-2014 |
注释:
The construction of the improved dairy shed took months as the land user was engaged in other farm activities and only worked a few hours some days.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | manpower | person-days | 15.0 | 700.0 | 10500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | CGI sheet (8", 0.05mm) | No | 31.0 | 900.0 | 27900.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Boulder | Truck load | 1.0 | 7000.0 | 7000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Gravel | Truck load | 0.5 | 17000.0 | 8500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand | Truck load | 0.5 | 22000.0 | 11000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Cement | Bag | 25.0 | 400.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Planks | Cft | 150.0 | 350.0 | 52500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Iron road | Kg | 150.0 | 75.0 | 11250.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 138650.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1690.85 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
140000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government
注释:
The government provided 15 bags of cement and 18 CGI sheets.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
注释:
There has been no requirement of maintenance to date. There would not be the need of maintenance unless the technology is destroyed by natural disasters such as earthquake, storm, flood and so on. The technology is durable with concrete floors, pillars and troughs and corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) sheets for roofing.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
There has been no requirement of maintenance to date.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Materials and transportation cost
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
1200-2500 mm
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under. Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Moisture content-21.66%
Organic matter-15.14 %
Organic carbon-8.80%
pH-6.24
Electrical conductivity-521.33 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.44
Phosphorus-2.42
Potassium-223.07 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Clay
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The site has a variety of crops including vegetables, fruit trees, trees, and fodder grasses.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
The total land area owned by the owner is 4.65 acres (1.88 ha) which is large-scale. The average land holding at the national level is 3 acres (1.2 ha)
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Crop production has increased due to the use of FYM and urine from improved cattle shed.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Crop quality has increased due to the use of FYM and urine from improved cattle sheds. These organic fertilizers add nutrients to the soil and enhance crop growth and development.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Fodder plantation has been encouraged due to stall feeding under the improved dairy shed technology. The land user has planted fodder grasses on 1.2 acres of land. The fodder grasses grown include Napier, Super Napier, Guatemala grasses.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
The land user has planted fodder grasses (a mix of Super Napier, Napier, and Guatemala) on 1.2 acres of land to be fed to cattle. A variety of fodder grasses are grown for stall feeding of cattle.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Animal production has increased due to improved fodder production and quality. The technology promotes integrated crop-livestock farming whereby the crop residues are fed to the cattle as feeds, another source of nutrients for the animals. Under the improved dairy shed, the animals have access to proper sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, and ample space for their movement resulting in the overall well-being of the animals.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Milk production has increased due to improved fodder production and quality grown for stall feeding. The milk provides raw material to produce a wide variety of dairy products.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Production area has increased with the land user growing fodder grasses in 1.2 acres of land. The land user feeds 7 dairy cattle with these fodder grasses.
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
The dung from shed is used in biogas plant to produce biogas. Biogas has reduced the use of LPG gas.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Farm income has increased due to integrated livestock farming that has been promoted by improved dairy shed. Crop production and quality have improved due to the use of FYM and cattle urine. The increased milk production from stall feeding of good quality fodder grasses has enabled the land user to become a member of a milk group where the land user earns some amount every month.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
The land user is now a member of a milk group. The increase in milk has encouraged the land user to join the group.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Food security and self-sufficiency have increased due to increased animal production and crop production.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Stall feeding has provided an opportunity for the land user to engage in recreational activities. Earlier when there was no stall feeding, the land user had to take cattle to a nearby forest and tend them for hours.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The land user realizes the benefits of FYM application, stall feeding, fodder production, and biogas plant usage.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
When stall feeding was not practised, land user had issues with his cattle entering into neighbours' fields and damaging their fields. This problem has been mitigated by the practice of stall feeding.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
The situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups has improved due to increased farm production.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Soil cover has increased due to fodder grass cultivation on 1.2 acres of land.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Nutrient cycling has increased due to integrated livestock farming.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Soil organic matter has increased due to the addition of FYM to fields.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation cover has increased due to fodder grass plantation on 1.2 acres of land.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Biogas plant has reduced the use of LPG gas and methane emissions.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
There hasn't been notable off-site impacts.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 增加 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
25 households out of 28 households have adopted the technology
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| An improved dairy shed made of cement, gravel, and stones is more durable than the old dairy shed made from wood. |
| Addition of nutrients in fields through application of FYM and cattle urine. |
| Increase in organic matter due to FYM application in the field. |
| Availability of good quality fodder and a diverse range of forage options. |
| Reduced labour due to reduced fodder collection and herding in the forest. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Efficient waste utilization. |
| Biogas has reduced the use of LPG gas. |
| Reduced land degradation due to reduction in forest grazing |
| Increased vegetation cover due to improved pasture development and reduction in forest grazing. |
| Stall feeding reduces soil compaction through trampling by animals. |
| Better soil moisture retention by increased soil organic matter. |
| Comfortable working environment for land users. |
| Improved livelihood of farmers through higher farm yields and better household income. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The land user has designed the slurry inlet chamber of the biodigester plant near feeding troughs so the inlet chamber has to be relocated. | Relocate the biodigester. |
| Lack of funds to buy improved breeds. | Government support to land users through cost-sharing measures. |
| Lack of funds for improved dairy shed construction. | Government support to land users through cost-sharing measures. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/07/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Thapa, L., Choden, D., & Tamang, N. B. (2019). Adoption of Improved Dairy Production Practices by Dairy and Non- Dairy Farmers’ Groups.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lokey-Thapa/publication/334507972_Adoption_of_Improved_Dairy_Production_Practices_by_Dairy_and_Non-_Dairy_Farmers'_Groups/links/5d2ec146299bf1547cbd248a/Adoption-of-Improved-Dairy-Production-Practices-by-Dairy-and-Non-Dairy-Farmers-Groups.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
National Soil Services Centre. (2011). Bhutan Catalogue of Soil and Water Conservation Approaches and Technologies. National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forests, Royal Government of Bhutan, Thimphu.
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/95/
7.4 一般注释
There is a need to increase number of respondents to get realistic data.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Improved Livestock Farming System [不丹]
The approach involves a group of farmers implementing an improved dairy system. The system incorporates practices and technologies that enhance animal welfare, reduce environmental impact, and increase production.
- 编制者: Tshering Yangzom

Dairy Cooperatives and KOUFUKU linkage for milk marketing [不丹]
This approach links dairy cooperatives with a dairy plant, KOUFUKU International Limited (KIL), for milk marketing. It is an established dairy value chain that addresses milk and dairy product marketing issues and improves the livelihoods of many small dairy farmers in eastern Bhutan.
- 编制者: Nima Dolma Tamang
模块
无模块