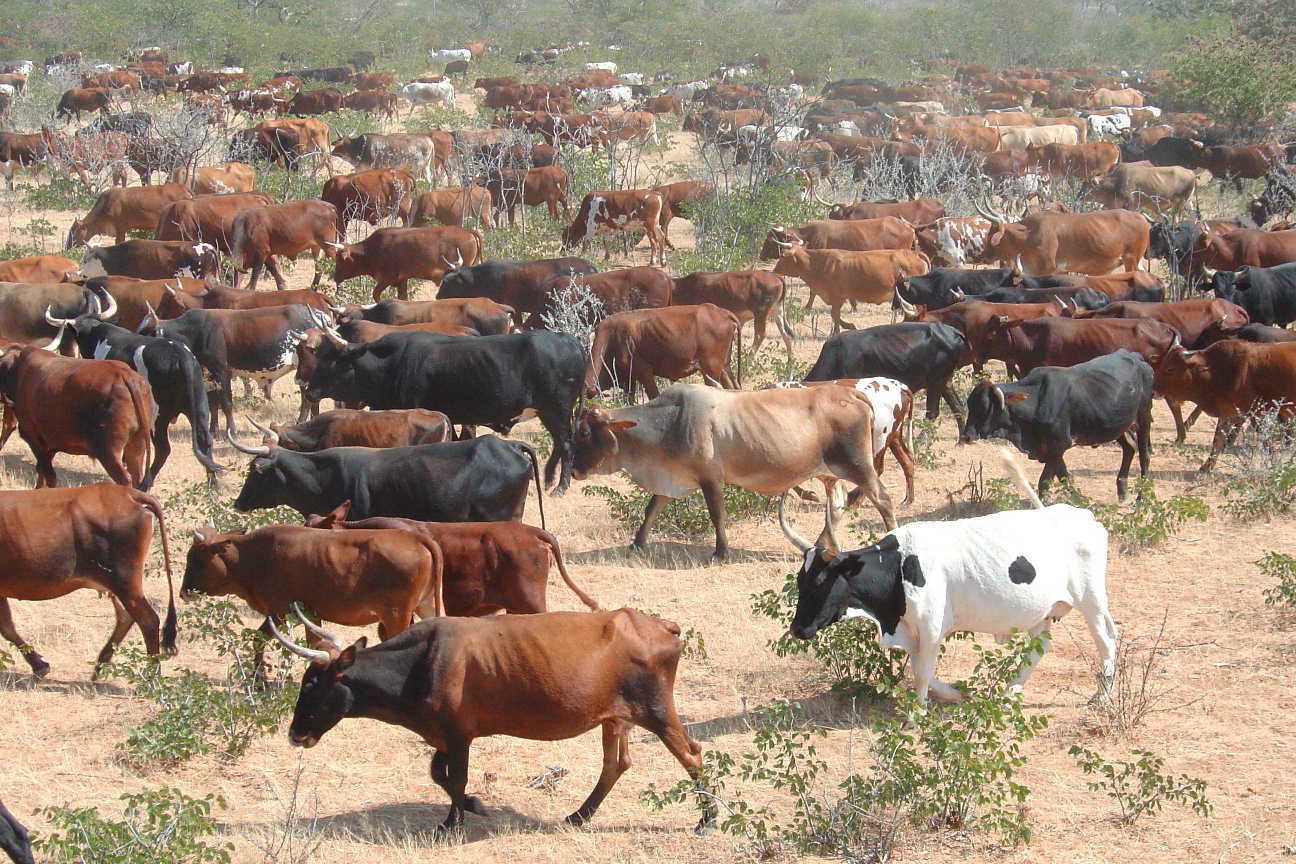
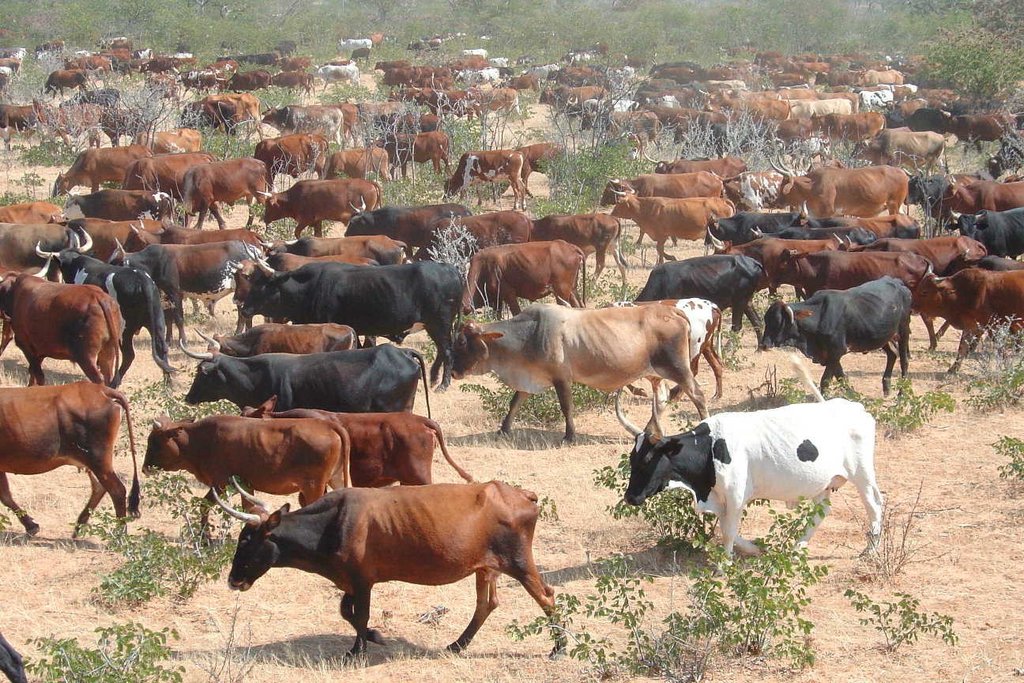
Combined herding for planned grazing [ناميبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Ibo Zimmermann
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, Donia Mühlematter, Brigitte Zimmermann, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Omarisiro wovinamuinjo motjimbumba
technologies_3326 - ناميبيا
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 11 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 11 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 31 مايو، 2019 (inactive)
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 23 فبراير، 2018 (inactive)
- Combined herding for planned grazing: 4 فبراير، 2018 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Southern African Science Service Centre for climate change and Adaptive Land management (SASSCAL)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Namibia University of Science and Technology ( NUST) - ناميبيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Conservation Agriculture Namibia (Conservation Agriculture Namibia) - ناميبيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Community grazing management [ناميبيا]
Agreement among community members to jointly manage their communal grazing area by combining their livestock into a single herd. The herd is managed and moved according to an agreed growing season plan that provides sufficient recovery for perennial grasses, and a non-growing season plan to graze in a way that …
- جامع المعلومات: Ibo Zimmermann
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Daily combining of livestock from all households into a single herd to be driven to different designated portions of the communal grazing area. Grass can then recover by replenishing its reserves before being re-grazed some months later.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
This technology is currently being applied in communal areas as well as commercial farms of Namibia. It is particularly effective in areas with no fences, and areas with high incidence of stock theft and predator losses. The technology aims to replace continuous, open grazing with a planned system. This gives grass a chance to recover in the growing season, and prepares the soil and grass for the forthcoming rainy season. In addition, fixed stocking rates based on carrying capacities are replaced by flexible stocking rates which track availability of forage. Two grazing plans are developed for one year; one when perennial grasses are growing and the other when they are dormant. Grazing plans may change, depending on the season and unanticipated events such as fire. A grazing plan is put in place for the growing season, that ensures plants are not re-grazed before they have recovered their root reserves. It is targeted at good animal performance . In the non-growing season, animal numbers are adjusted to ensure that there is sufficient grass to last until the next rains .
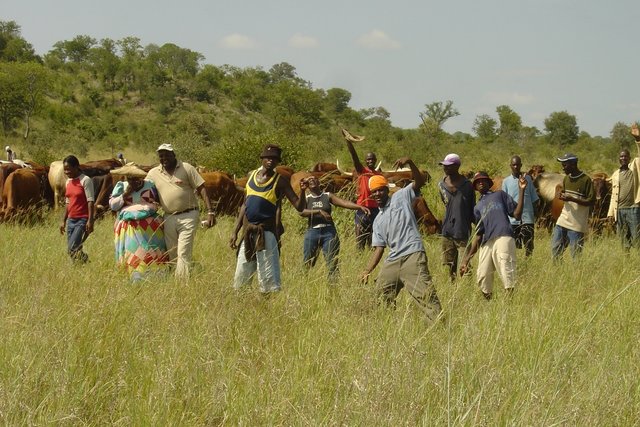
The grazing plans must take into account all factors that affect livestock performance as well as capacity of the livestock owner . These factors include occurrence of the first rains, presence of natural water pans, current and projected animal performance, availability of good quality forage for cows prior to bulling, avoiding poisonous plants, and timing of vaccinations, etc. Once the plan has been developed, the animals are moved by herders using low stress handling techniques to various parts of the farm or communal grazing area, according to the plan. Strategic moving of livestock by herding enables fire breaks to be created by deliberate over trampling. Each night the livestock are brought back to a kraal ( Afrikaans for corral) where they are kept overnight. Watering of livestock can take place in the kraal at night, in the morning, or alternatively in the field depending on water availability. This process is repeated day after day by the herders.
At the end of each growing season, the amount of forage available to the current herd is estimated. Animal numbers are adjusted to make sure that there is still sufficient forage to support them before the rains – and to leave enough ground cover to feed the soil organisms and protect the soil from erosion. Deciding when the forage produced will run out needs to be done using a method that livestock owners relate to. Livestock owners may decide to meet and reach consensus on this based on their knowledge and past experience of the effectiveness of rainfall. If it is decided that there is sufficient food to see the animals through until the next rains, then livestock owners will be satisfied; if there is excess forage they may be able to re-stock. If, however, a forage shortage is expected then de-stocking is required: the severity of the forage shortage determines how many livestock can be carried on the land during the off-season. Again, livestock owners can reach consensus on this. Deciding whose animals to sell and how many is always a thorny issue, so livestock owners will always move excess livestock to other areas if possible, or alternatively sell unproductive animals.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Combined herding to manage communal grazing
www.youtube.com/watch?v=xNyFkDUH6MQ
التاريخ:
2007
الموقع:
Erora
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Andrew Botelle
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Stress-free herding
www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Ey5v40KtkI
التاريخ:
2007
الموقع:
Erora
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Andrew Botelle
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Managing water flow to repair gully erosion
www.youtube.com/watch?v=6C4V_Cib8ts
التاريخ:
23/04/2015
الموقع:
Erora
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Andrew Botelle
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
ناميبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kunene Region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
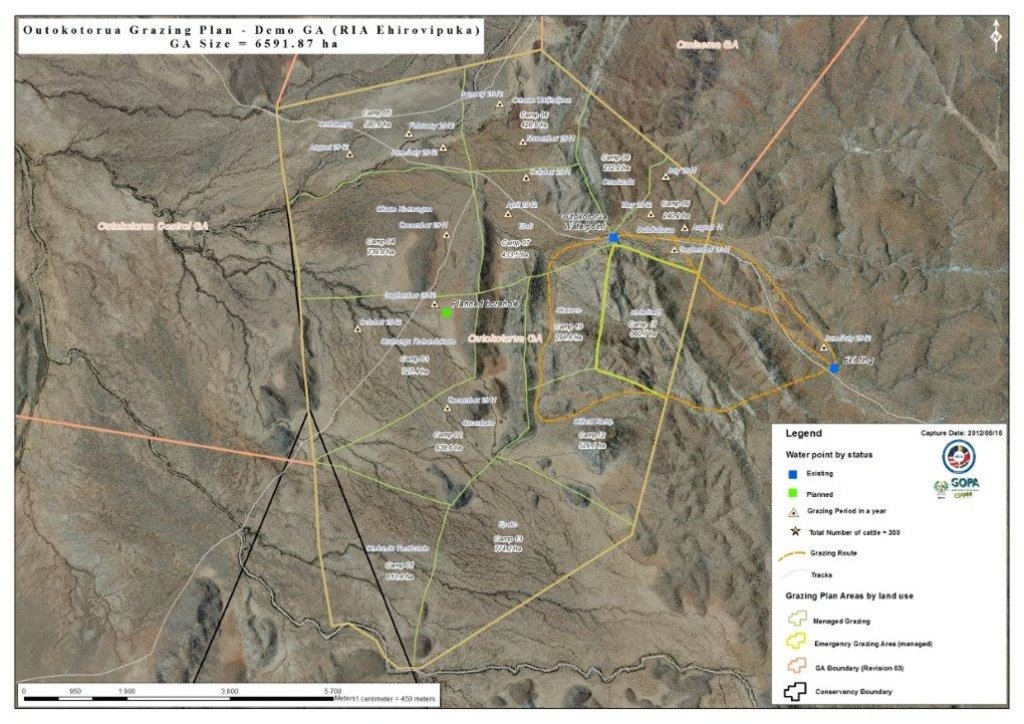
Communal grazing areas of Erora, Outokotorua and Nsindi
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Animals are herded over the entire area – except areas that are too steep for livestock to walk up.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2004
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Community projects facilitated by NGO "Conservation Agriculture Namibia".
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
- Reduce human-wildlife conflict
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
التعليقات:
Main animal species and products: Livestock, increased forage production, improved animal performance.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: Livestock density is high as a result of herding, but stocking rate varies.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M4: تغيير كبير في توقيت الأنشطة
التعليقات:
The technology does not involve a change in land use. The grazing plan means that livestock will only be on a particular piece of land twice in any given year (once in the growing season and once in the non growing season). The animal density is however high, leading to increased impact for a very short period.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات:
The control of over-trampling which otherwise leads to rill and gulley erosion.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Land is severely degraded but can be restored by change in management.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
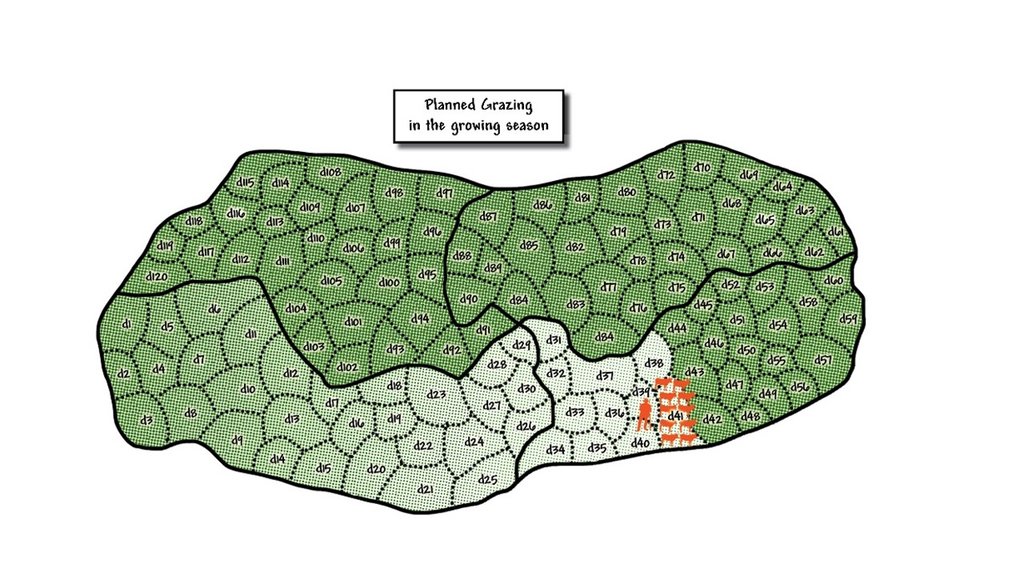
Schematic of planned growing season grazing. In this diagram grazing started in the bottom left hand camp (plot), marked d1, and the livestock were grazed in this area for one day. The next day the herd of livestock were taken to the area marked d2 and grazed there. This continued until day 41 where the livestock are currently. If deviations from the plan occur then the grazing map is marked according to what actually happened. This is the map that helps inform next year's grazing plan - to avoid using certain camps at the same time of year. The degree of greenness in the diagram indicates the recovery of grass. It is lightest in the area just grazed, marked d40. By the time the herd reaches day 120, which has the darkest green indicating readiness to be re-grazed, then the grass in the area marked d1 was calculated to have recovered sufficiently to be re-grazed. This plan has a built-in recovery period of 120 days. It is possible that growth rates are slower than expected and it may be necessary to reduce numbers of cattle in the herd to slow down movement to ensure an adequate recovery period.
المؤلف:
Colin Nott
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
5000 ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
USD 4
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
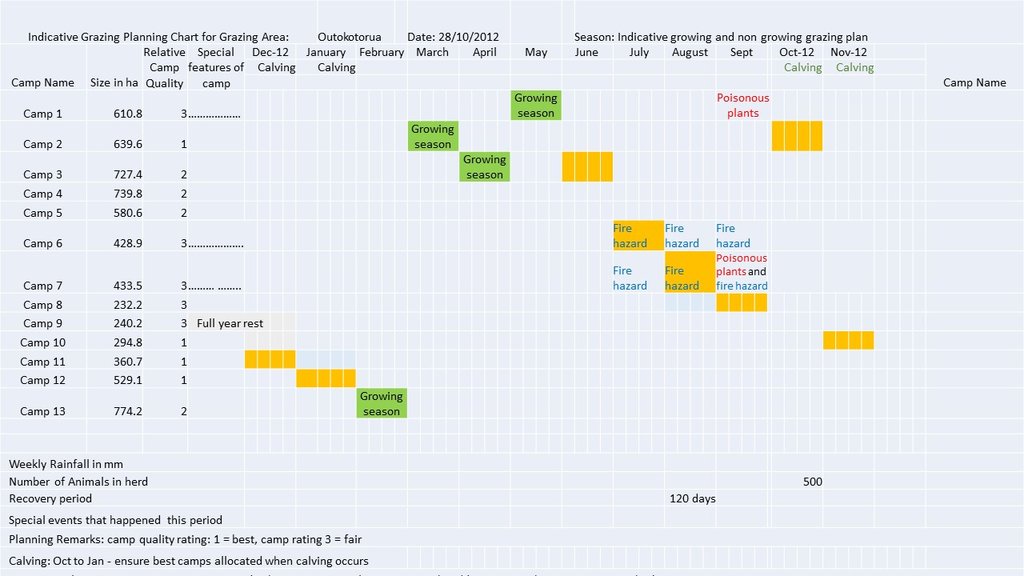
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Three meetings for mobilisation of communities | Month 1 |
| 2. | Exchange visit to local livestock owners using this practise | Month 4 |
| 3. | Assess water infrastructure, site and drill and install additional water point | Month 6 |
| 4. | Grazing planning meeting with stakeholders | After adequate grass growth to enable planned grazing |
| 5. | Appoint, equip and train herders | After 4 |
| 6. | Planning meeting and determination of starting date | After 5 |
| 7. | Build overnight kraals at new water points | When needed |
| 8. | Build temporary kraals for improved grass growth | When needed |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Six herders (four on duty per day) for 400 cattle | Month | 6,0 | 77,0 | 462,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | One manager | Month | 1,0 | 115,0 | 115,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Overalls, boots and hat that may need replacement after one year | Set | 7,0 | 100,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Housing for herders built from mud and dung | Shelter | 3,0 | 100,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Laminated grazing chart and map per year | Document | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1597,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1597,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Grazing maps and charts prodcuded by CAN (support NGO), but will be taken over soon by farmers.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Daily herding, watering of livestock and health checks and treatment | Daily |
| 2. | Maintenance of kraals and water points | Quartery |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Six herders (four on duty per day) for 400 cattle | Month | 6,0 | 77,0 | 462,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | One manager | Month | 1,0 | 115,0 | 115,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Overalls, boots and hat, replaced annually | Set | 7,0 | 100,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Maintenance of clay and dung housing for herders | Shelters | 3,0 | 100,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Diesel for pumping water per month | Litres | 100,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Laminated grazing chart and map per year | Documents | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 1697,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1697,0 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Appreciation by land users that investment in herders will pay back, especially from the second year onwards.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Summer rainfall December-March.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Opuwo
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
In dry years all livestock may move to another cattle post. But they return to the sedentary site as their main grazing area. A significant number of land users take up employment in the nearest town.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
Communal land is not owned or leased, but the community has rights to use it for agricultural purposes.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Land is communal and organised but no rights to enforce management are yet in place through formal structures.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
خطر فشل الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved, not simplified
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
فروقات اقتصادية
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
خطر الحريق
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
Community's cattle no longer graze on land of neighbouring communities.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة رعدية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
| حريق الأرض | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The ability to bring back perennial grasses into the system allows higher stocking rates, less drought risk and better quality animals, therefore higher income over time and consequently a better cost-benefit analysis.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
20,000 ha
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
This is a key issue undergoing lobbying of government and the communal farmers union to establish through a consultative process legislation that enables grazing plans to be enforced from within and from outside. This is lacking at the moment.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
Adaptive management
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
Addition of erosion control and overnight kraaling to assist with gully control. Refining re-planning in response to monitored results that deviate from aims.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| It is cost-effective; genuine improvement is seen in grass production, while livestock losses to predators are significantly reduced. |
| For absentee owners they can leave a manager and herders in place to get on with the work and this can be easily evaluated after time since animals wondering around leave evidence. |
| Livestock are better cared for than they used to be, and a sense of community has been restored. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| This is a viable and upscaleable technology for both communal and commercial farmland in Namibia and beyond. |
| It addresses the root cause of livestock related degradation and on a larger scale could have a significant impact on mitigating climate change if all the degraded rangelands of the dry climates of the world were restored by using the principles embodied in this approach – one which has been adopted in the National Rangeland Management Policy and Strategy. Moreover it can improve the quality of lives of millions of people who live in areas where livestock is the only viable land use. |
| This is a true “triple bottom line” technology that improves the resource base whilst increasing profits and enables improved quality of life for residents. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Herders are difficult to find, train and keep. | National level vocational training of herders is required. |
| Water infrastructure tends to result in overtrampling of the same routes. | The Directorate of Rural Water Supply should change its water specifications to include the provision of water for livestock – which can be cheap and effective. |
| Grass poaching takes place by neighbours and the majority will of people in an area is sometimes overrun by a small minority. | Farmers Unions must address these issues and get enforceable mechanisms in place for improved rangeland management. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There is insufficient national buy-in from line ministries in terms of implementation to address many of the issues that have been raised. | Line ministries should support implementation to address these problems. Joint implementation, joint review and adaptation by government, unions, livestock owners and support providers will assist in solving many issues for resource-base improvement. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/06/2017
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Holistic mangement, Savory, A. & Butterfield, J., 1991
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Island Press
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Volkmann, W. (2011). Community based rangeland and livestock management. Windhoek: GOPA-CBRLM.
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://rmportal.net/groups/cbrlm/cbrlm-for-review/namibia-community-based-rangeland-livestock-management-cbrlm-2nd-edition/view
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Community grazing management [ناميبيا]
Agreement among community members to jointly manage their communal grazing area by combining their livestock into a single herd. The herd is managed and moved according to an agreed growing season plan that provides sufficient recovery for perennial grasses, and a non-growing season plan to graze in a way that …
- جامع المعلومات: Ibo Zimmermann
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية