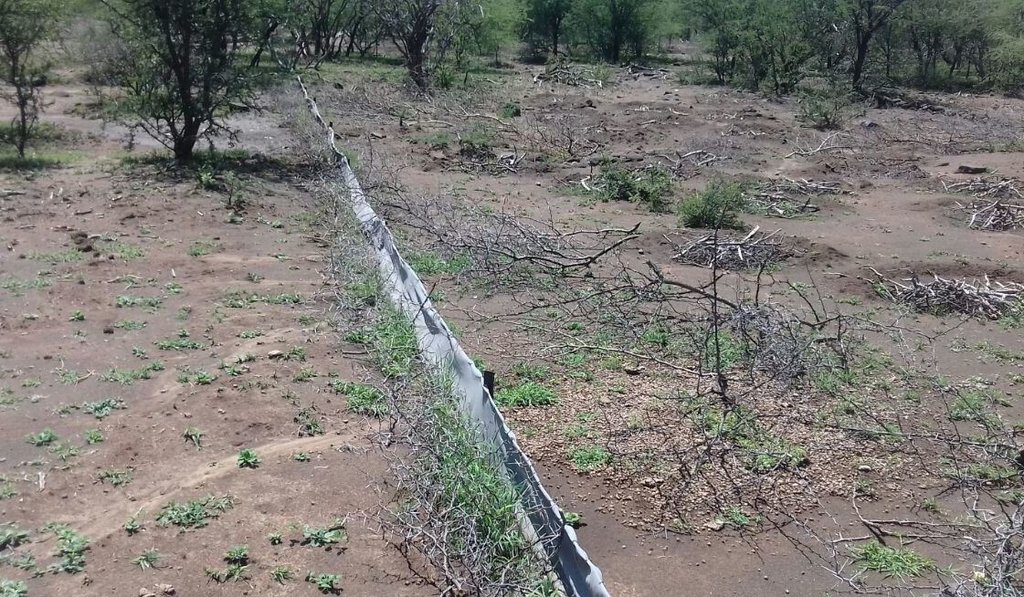
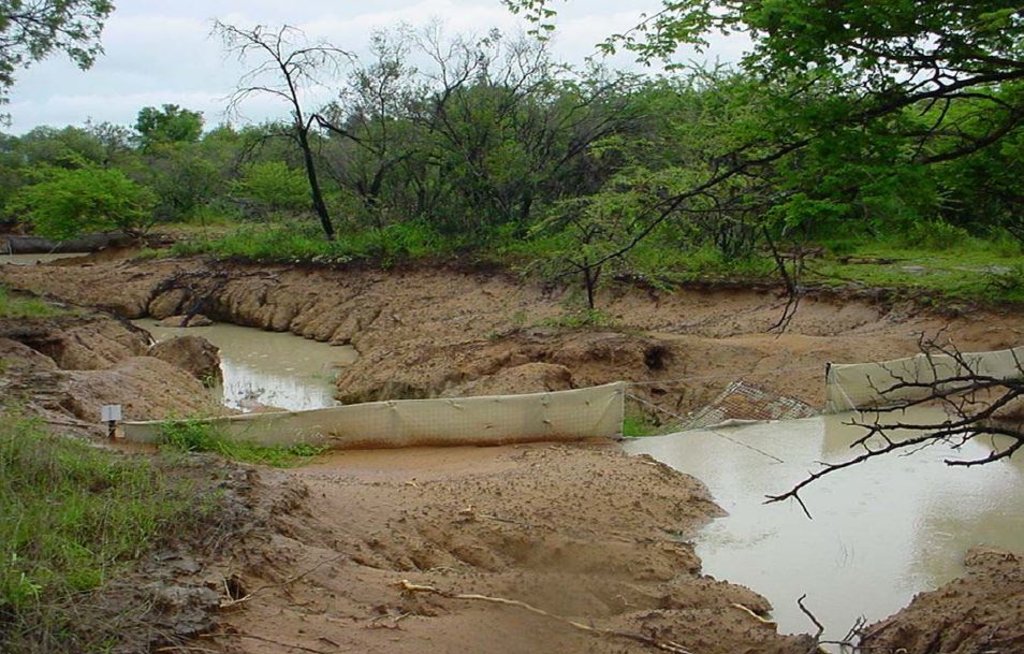
Silt fences to trap sediment in areas affected by gully erosion [جنوب أفريقيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dirk Pretorius
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Silt fences
technologies_6174 - جنوب أفريقيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Van Heerden Heinrich
Eco Rhythm Management
جنوب أفريقيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Working for Water (Natural Resource Management Programmes – DEA, South Africa)?1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Working for Water [جنوب أفريقيا]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- جامع المعلومات: Klaus Kellner
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
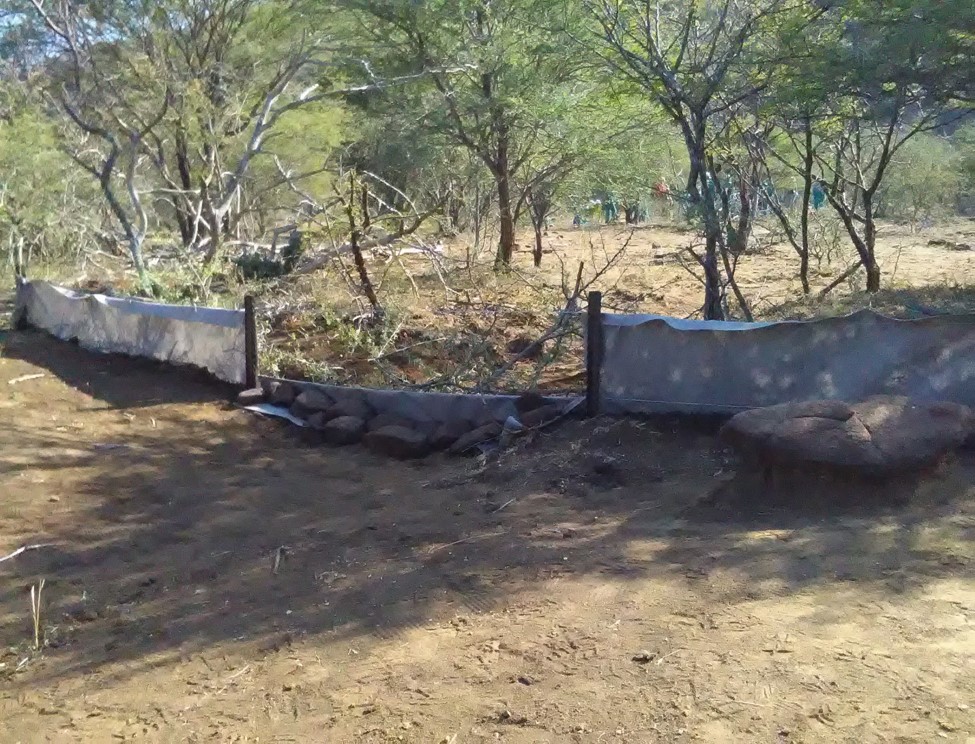
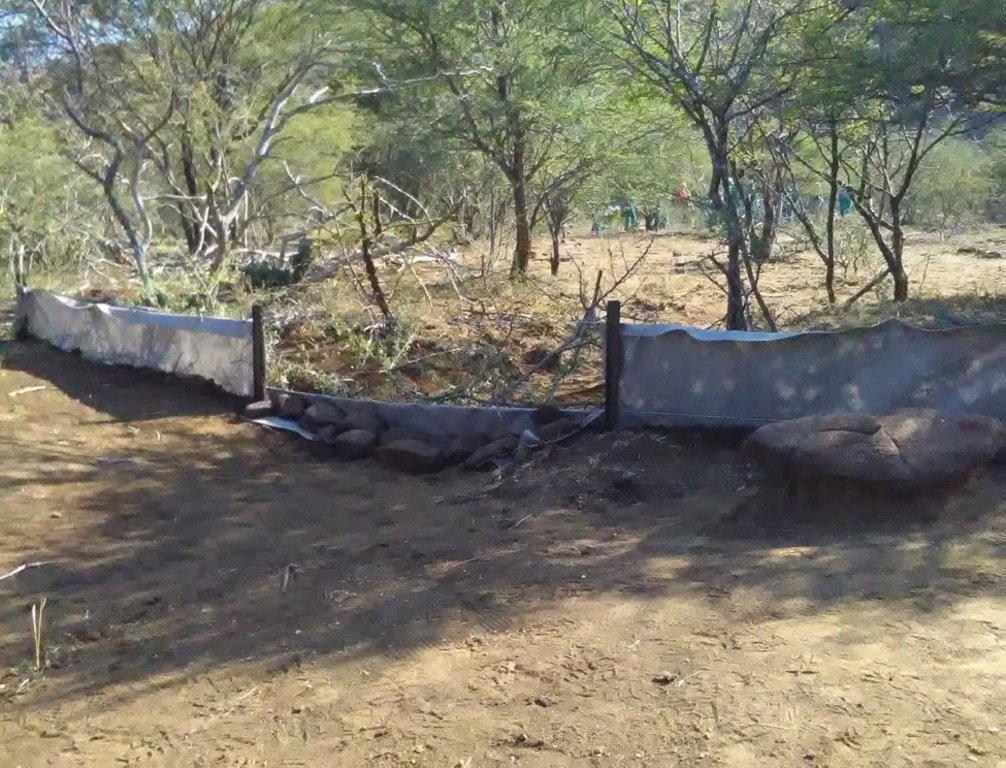
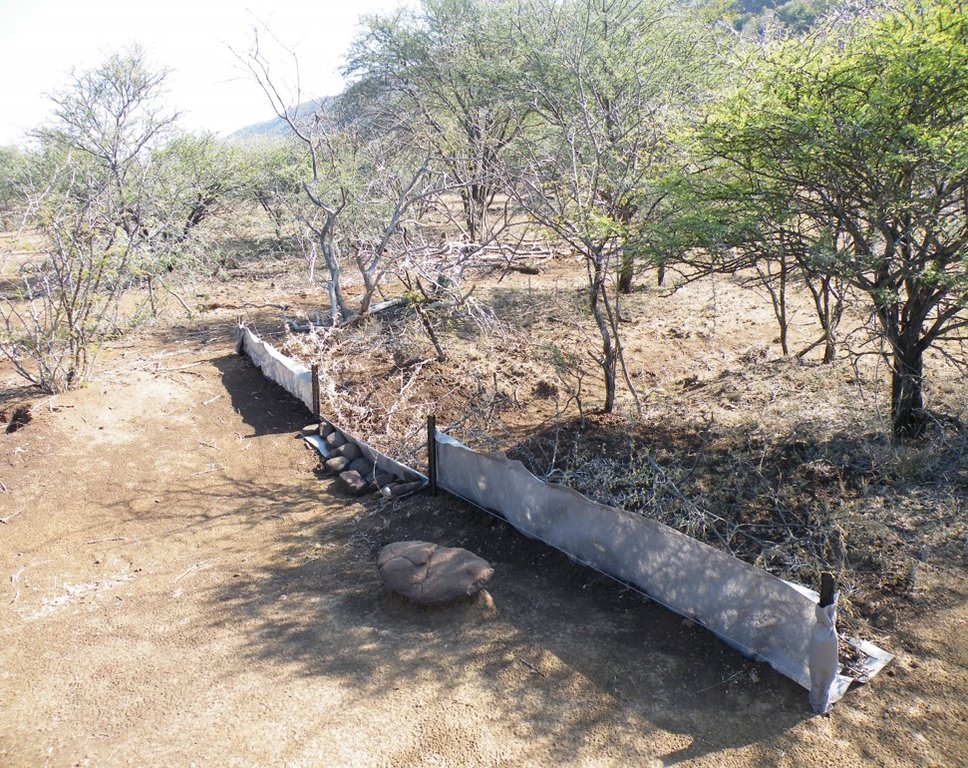
Silt fences together with brush packing were introduced to reduce sediment transport and restoration of gully erosion in the Potlake nature reserve, Limpopo Province, South Africa.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Silt fences, together with brush packing were introduced in the Potlake Game Reserve (2817 ha) in the Limpopo Province of South Africa to rehabilitate areas affected by serious rill and gully erosion. Due to overgrazing on highly erodible soils, gully headcuts are actively migrating upstream. Implementation of the technology leads to enhanced vegetation cover and reduced sediment transport in the gullies. Silt fences are temporary structures and are therefore placed closer together than permanent structures. The placing is such that the silt from the downstream structure builds up against the upstream structure to delay the perishing of the restoration materials. Vegetation must be established in the gully (donga) as soon as possible so that, when the materials decay after about ten years, the area will be restored. Altitudes vary from 1 174 m to 780 m above sea level. The reserve is located in a summer rainfall region and receives an average annual rainfall of 438 mm per year. Clayey duplex soils are prone to both natural and man-induced erosion. The vegetation comprises Central Bushveld vegetation units of the Savanna Biome. Savanna is characterized by a herbaceous layer (usually dominated by grasses) with a woody component. In Southern Africa, Bushveld is an apt description of the vegetation structure, as the vegetation most often does not comprise distinct shrub and tree layers. Instead, the shrubs and trees occur in a matrix with a grass-dominated herb layer. A number of large gullies exist along drainage lines on highly erodible soils. Some of the gullies are up to 1.5 m deep and 5 m wide. A total of around 200 m of silt fences were erected at selected sites in the reserve to retain sediment and to establish vegetation. The following steps were followed in the establishment of the silt fences:
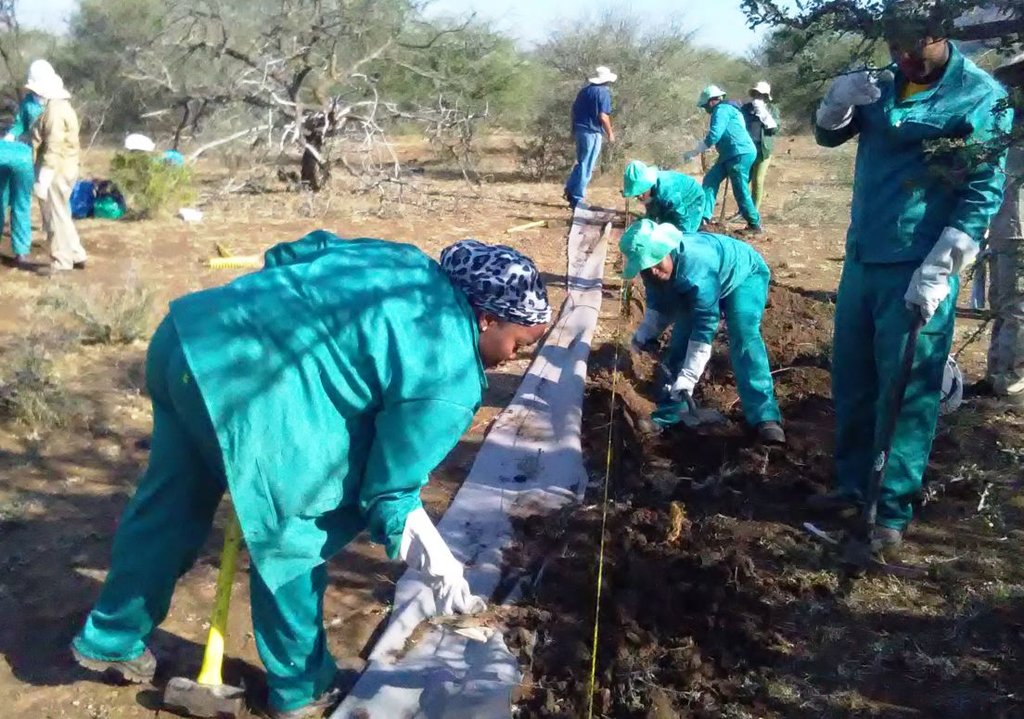
1. Identification of priority sites to erect the silt fences - using Google Earth imagery and field surveys.
2. Acquisition of restoration material and training of local community members on the implementation of the technology (training by Mr. Buckle at that stage from the Department).
3. Levelling of the area where fences would be erected.
4. Construction of fences.
5. Brush packing (upstream of fence) stone packing (downstream in the gully).
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جنوب أفريقيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Limpopo Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Potlake nature reserve
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Located in the Potlake nature reserve
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

غير ذلك
حدد:
Protected area
ملاحظات:
Potlake nature reserve
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
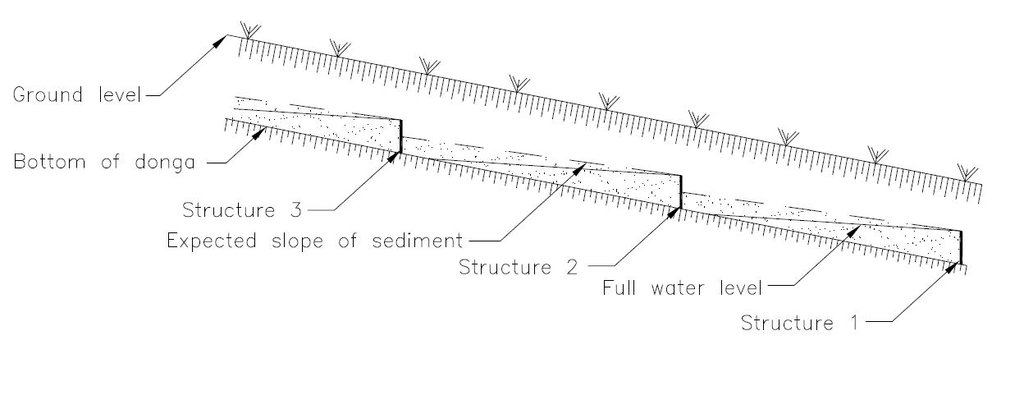
Silt fences are cheap and easy to erect, but the overflow depth must be limited. Silt fences are therefore erected in the wider section of a gully.
المؤلف:
Jan van Heerden
التاريخ:
01/01/2012
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Silt fences are temporary structures and are therefore placed closer together than permanent structures. The placing is such that the silt from the downstream structure builds up against the upstream structure to delay the perishing of the restoration materials. Vegetation must be established in the gully (donga) as soon as possible so that, when the materials decay after about ten years, the area will be restored.
المؤلف:
Jan van Heerden
التاريخ:
01/01/2012
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
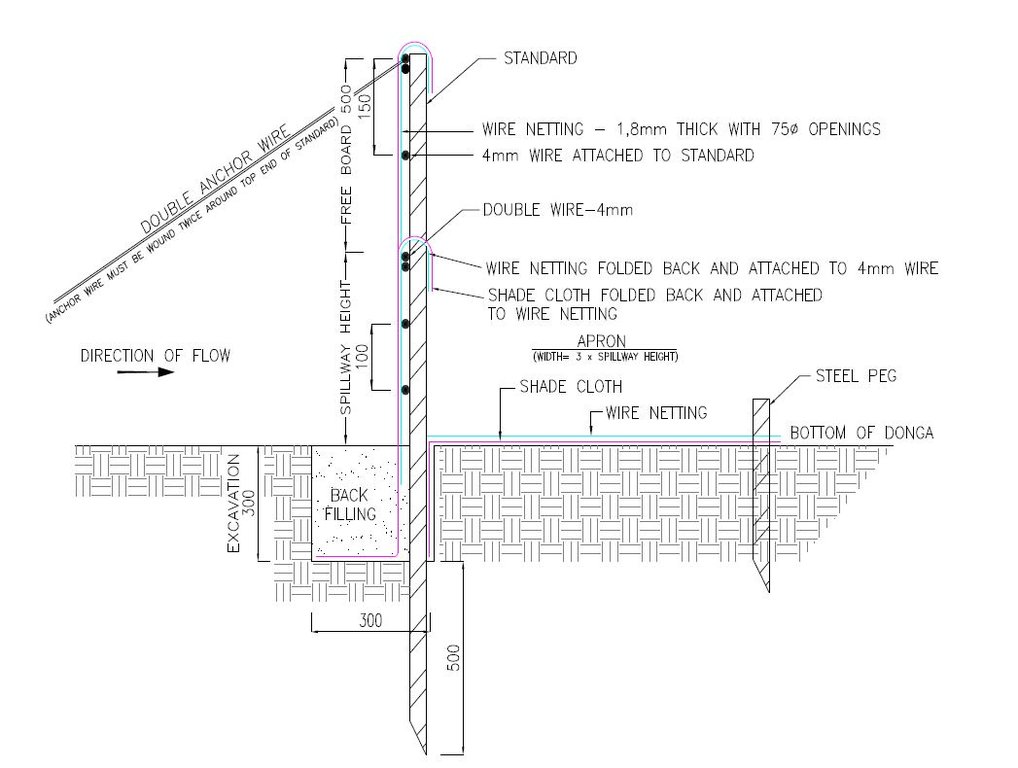
1. Dig a pit trench 300 mm × 300 mm from peg to peg over the entire width of the gully.
2. Drive iron standards (iron pole) in on the sides of the spillway length followed by more standards around 1.5 meters apart - ensure equal spacing between standards (standards must be driven in at least 500 mm deep - ensure that eyes (holes in standards) point upstream and that poles are in line with the others. Place apron on the ground from the excavation downstream. The width of the material must be three times the height of the overflow height and it must be at least 500 mm longer on both sides than the spillway length.
3. Span a 4 mm wire between the spillway poles on the total height of the structure. Tighten only manually and fasten on both sides of the two standards.
4. Drive in two anchor poles in line with the structure on both sides of the donga wall.
5. Saw off or cut heads of standards on the height of the structure’s height. Place anchor wires between two outer poles and anchor poles and tighten.
6. Thread 4 mm wire through on spillway height from side to side and bind to the two poles anchored to the anchor poles.
7. Also place wire between the spillway width poles and the end pole on the structure height and tighten.
8. Span wires from the spillway height wire on 100 mm to 150 mm distances apart, downwards until the last wire is at least 100 mm below the surface.
9. Place netting material (course plastic grid placed behind the filter material) on upstream side of the poles into the excavated pit trench and cut according to shape of the structure.
10. Place filter material flat in the pit trench and in front of the netting material on the upstream side of the poles and cut according to the shape of the structure. Tie the material to the structure with binding wire and fill the pit trench with soil.
11. Place netting material on the apron and tie it to the structure with binding wire and drive in T pegs at strategic places on downstream side.
12. The construction of the drop inlet is built in the same way as a weir structure as close as possible to the head of the donga. The gap between the structure and the donga head is filled with soil and must be filled again after the first rains. The spillway is made ±100 mm higher than the normal ground surface. The structure can be built to a maximum of 1 000 mm from the gully floor to the ground level.
13. Brush packing in front of the silt fence and stone packing downstream of the apron in the gully.
14. In order for silt fences to function more efficiently, it is recommended that that portion of the veld is fenced and withdrawn from grazing. Sowing of grasses or planting of common reed or vetiver grass can speed up the repair process considerably.
المؤلف:
Jan van Heerden
التاريخ:
01/01/2012
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
silt fence
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
6 to 8 meters
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Rand
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
16,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
R200
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the site to be restored | Winter (outside raining season) |
| 2. | Installation of silt fences followed by brush and stone packing | Winter |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Unskilled labour (including transport) | Per day | 6,0 | 280,0 | 1680,0 | |
| معدات | Power tools - electric power generator, angle grinder, hammer drill, | Per day | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | |
| معدات | Measuring tape, wire tensioning tool, pole driver, heavy and light hammers, pick, spade, pliers and scissors | Per day | 10,0 | 20,0 | 200,0 | |
| مواد البناء | 4mm wire | Per meter | 100,0 | 15,0 | 1500,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Standards | Per piece | 6,0 | 90,0 | 540,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Netting | Per meter | 15,0 | 90,0 | 1350,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Anchor poles | Per piece | 6,0 | 10,0 | 60,0 | |
| مواد البناء | T pegs | Per piece | 20,0 | 20,0 | 400,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Binding wire | Per kg | 5,0 | 40,0 | 200,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Filter material (UV treated shade cloth - 80%) | Per meter | 86,0 | 20,0 | 1720,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 9150,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 571,88 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment - South Africa
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of fences after floods | After flooding event |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Repair of fences | Per day | 2,0 | 280,0 | 560,0 | |
| معدات | Pliers, hammers, wire tensioning tool, pick, spade, pliers and scissors | Per day | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Binding wire and filter material | Per meter | 4,0 | 150,0 | 600,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 1260,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 78,75 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
1. Timing - during the raining season these areas could be inaccessible due to clayey soils and water in gullies.
2, Availability of labour.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
438,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
A variety of soil forms occur in the reserve and can generally be grouped according to the vegetation unit it supports. Sekhukhune Mountain Bushveld soils are predominantly shallow, rocky and clayey, with lime soils of the Glenrosa and Mispah soil forms often occurring in low-lying areas. Steep slopes commonly have rocky areas with no soil. The Dwars River valley is characterised by prismacutanic horizons with melanic structured diagnostic horizons.
Sekhukhune Plains Bushveld mainly occurs on red apedal clayey soils rich in metals. Soils on the plains are characterised by deep loamy Valsrivier soils. Shallow Glenrosa soils are found on the low-lying, rocky hills. Small mountains commonly have erodible black, melanic structured horizons.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Although the reserve has a very high biodiversity it also includes a potential 16 plant species of conservation concern, of which one is critically endangered and two are endangered.
The reserve has a fair representation of game for its size, but it should be noted that the area is very prone to erosion if its ecological capacity is exceeded. During an aerial census conducted in the reserve a total of 582 head of game was recorded. There are currently 78 verified avian species occurring at the reserve, of which 10 occur on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. A total of 33 reptile species has been recorded and a possible 32 amphibian species. No data is currently available for the fish species occurring at the reserve.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
أخرى (حدد):
Tourists
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Nature reserve - tourism
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- State land
- State land
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Job creation
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراكم التربة
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The on-site impact assessment mainly includes a visual assessment of the amount of sediment trapped behind the silt fences and the establishment of vegetation.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة رعدية محلية | باعتدال |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان مفاجئ | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 11-50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Very important to stabilise landscapes. |
| Helps to improve the habitat for wildlife, biodiversity in the protected area. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Helps to improve the habitat for wildlife, biodiversity in the protected area. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Sensitive to floods | Timing of construction crucial - ready before the floods occur |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Same as above |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Revisited the restoration sites by Mr. Van Heerden
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Various discussions with Mr. Van Heerden and Mr. Buckle
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Silt fence report by Mr. Jan van Heerden (Agricultural Research Council) and the Strategic plan for the Potlake Nature Reserve (Limpopo Department of Economic Development, Environment and Tourism - LEDET)
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
09/09/2021
التعليقات:
Meetings commenced with Mr. Buckle
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Combating erosion with silt fences, Jan van Heerden, 2006, ISBN 1-919849-76-9
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://www.arc.agric.za/arc-iae/Documents/Publication%20List%20and%20Orderform.pdf
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Five-year strategic plan for the Potlake Nature Reserve, Limpopo Province, South Africa
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
LEDET - no cost
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Working for Water [جنوب أفريقيا]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- جامع المعلومات: Klaus Kellner
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية