Silt fences to trap sediment in areas affected by gully erosion [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dirk Pretorius
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Silt fences
technologies_6174 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Van Heerden Heinrich
Eco Rhythm Management
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Working for Water (Natural Resource Management Programmes – DEA, South Africa)?1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Working for Water [南非]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
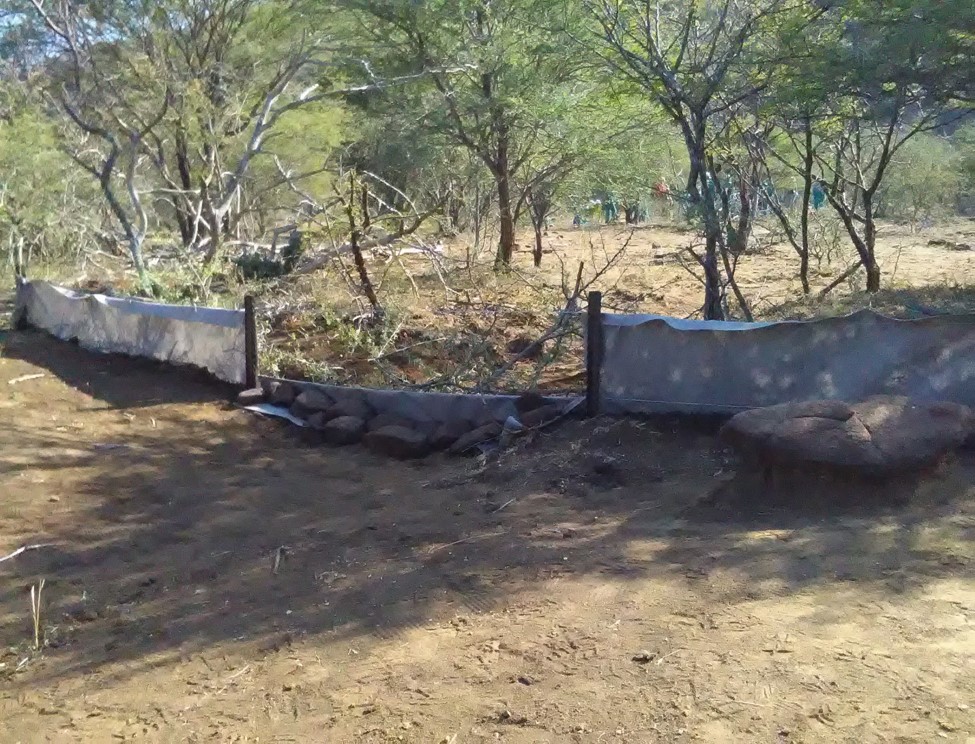
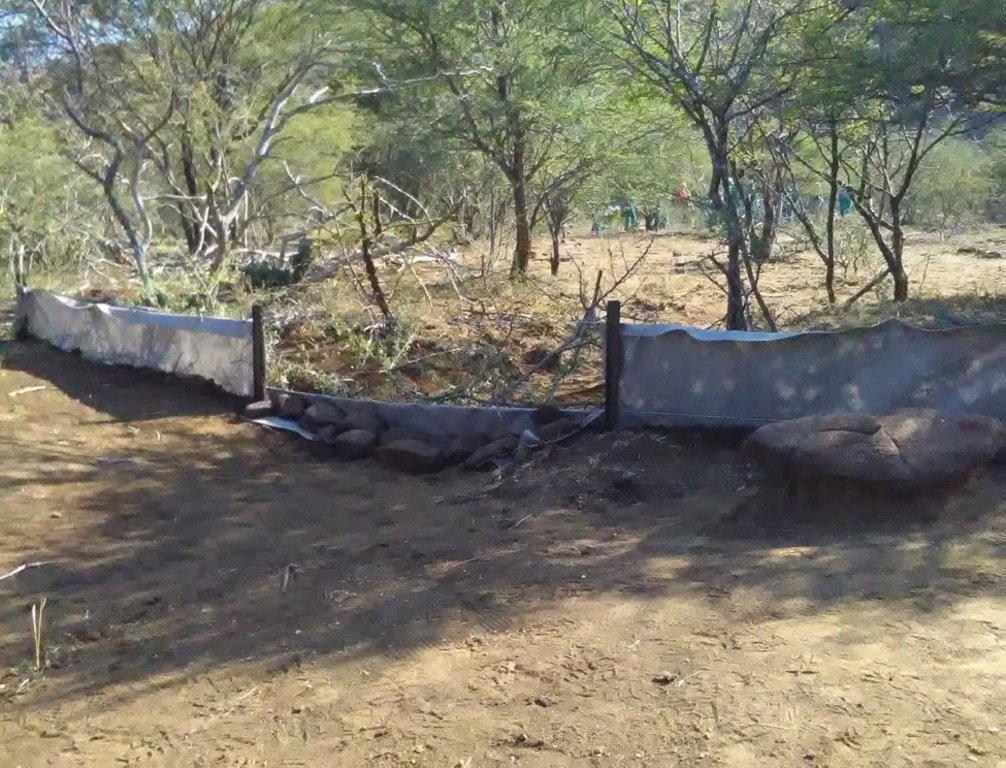
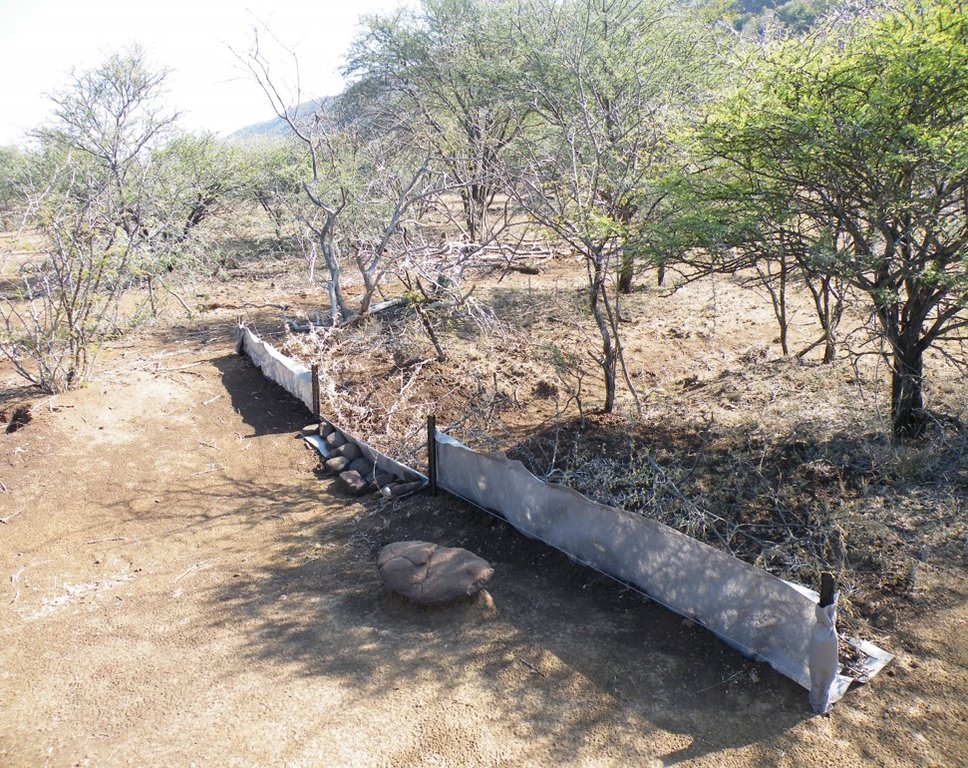
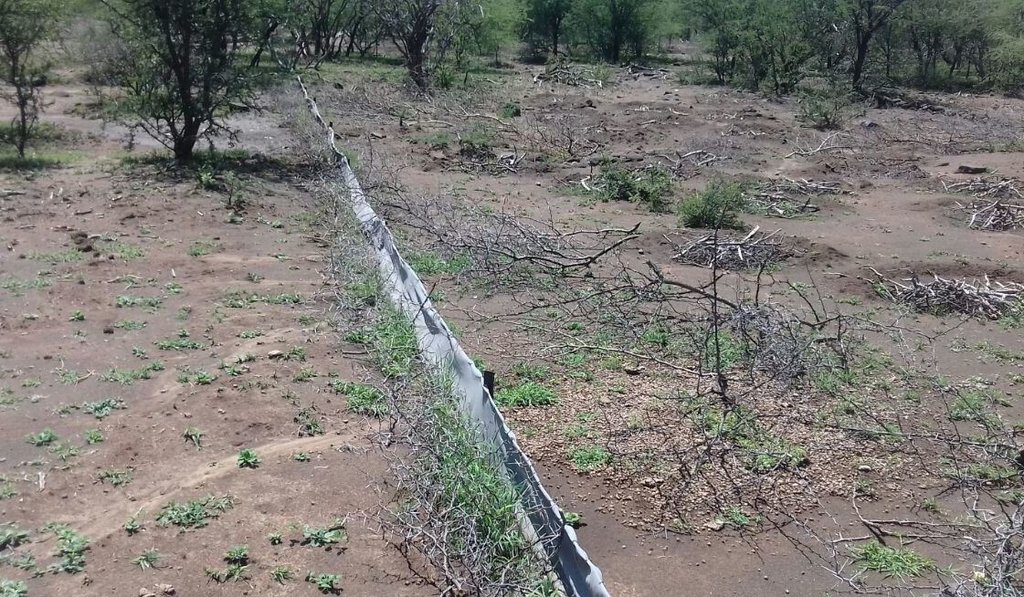
Silt fences together with brush packing were introduced to reduce sediment transport and restoration of gully erosion in the Potlake nature reserve, Limpopo Province, South Africa.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
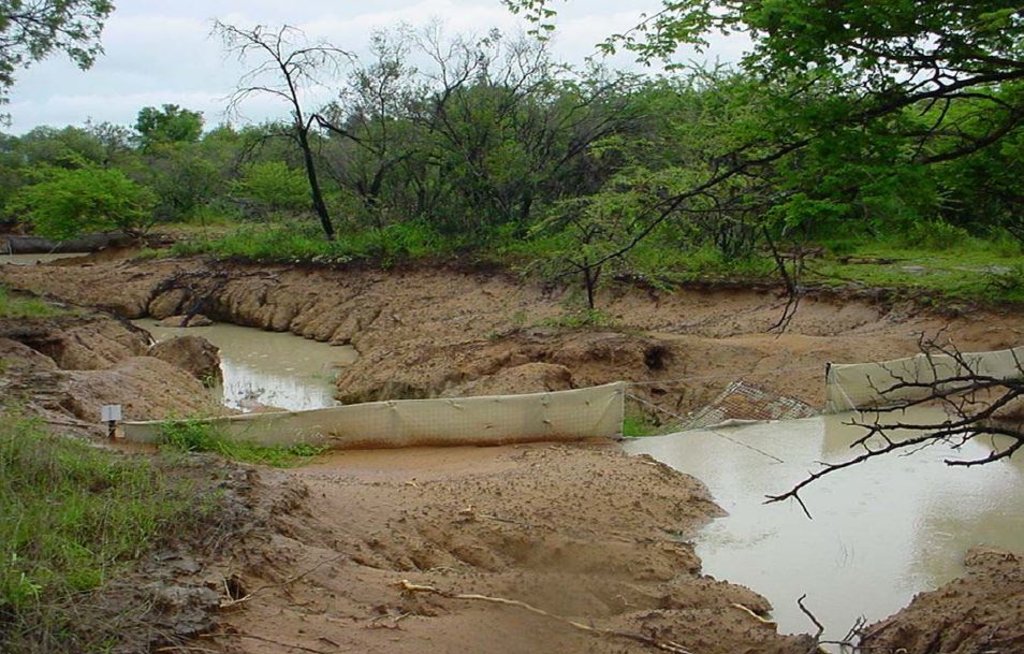
Silt fences, together with brush packing were introduced in the Potlake Game Reserve (2817 ha) in the Limpopo Province of South Africa to rehabilitate areas affected by serious rill and gully erosion. Due to overgrazing on highly erodible soils, gully headcuts are actively migrating upstream. Implementation of the technology leads to enhanced vegetation cover and reduced sediment transport in the gullies. Silt fences are temporary structures and are therefore placed closer together than permanent structures. The placing is such that the silt from the downstream structure builds up against the upstream structure to delay the perishing of the restoration materials. Vegetation must be established in the gully (donga) as soon as possible so that, when the materials decay after about ten years, the area will be restored. Altitudes vary from 1 174 m to 780 m above sea level. The reserve is located in a summer rainfall region and receives an average annual rainfall of 438 mm per year. Clayey duplex soils are prone to both natural and man-induced erosion. The vegetation comprises Central Bushveld vegetation units of the Savanna Biome. Savanna is characterized by a herbaceous layer (usually dominated by grasses) with a woody component. In Southern Africa, Bushveld is an apt description of the vegetation structure, as the vegetation most often does not comprise distinct shrub and tree layers. Instead, the shrubs and trees occur in a matrix with a grass-dominated herb layer. A number of large gullies exist along drainage lines on highly erodible soils. Some of the gullies are up to 1.5 m deep and 5 m wide. A total of around 200 m of silt fences were erected at selected sites in the reserve to retain sediment and to establish vegetation. The following steps were followed in the establishment of the silt fences:
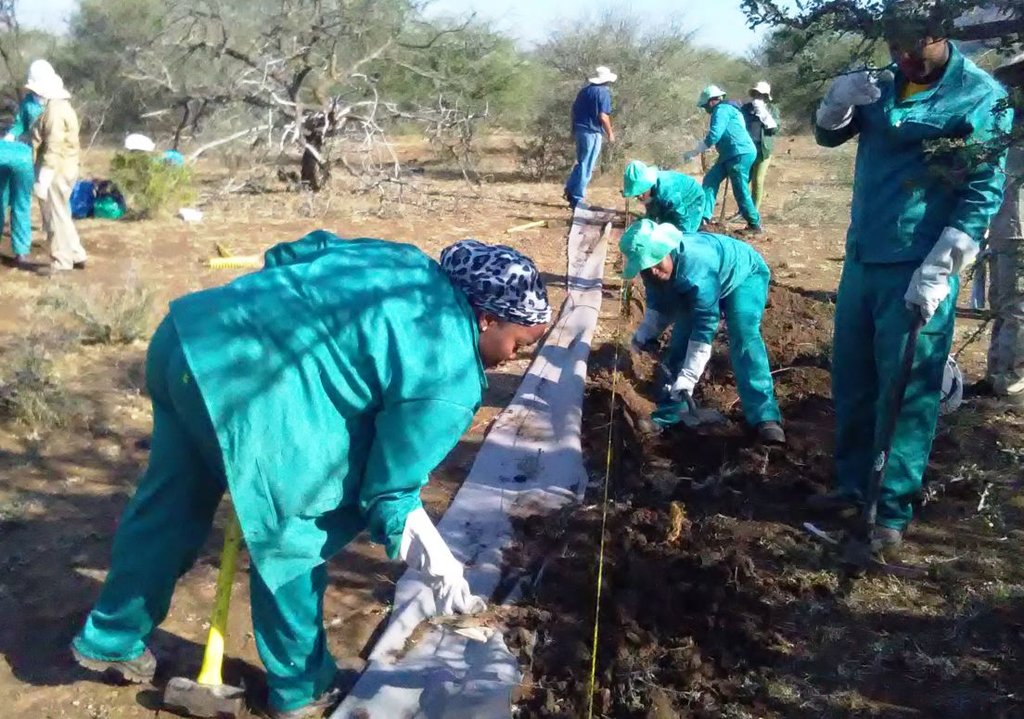
1. Identification of priority sites to erect the silt fences - using Google Earth imagery and field surveys.
2. Acquisition of restoration material and training of local community members on the implementation of the technology (training by Mr. Buckle at that stage from the Department).
3. Levelling of the area where fences would be erected.
4. Construction of fences.
5. Brush packing (upstream of fence) stone packing (downstream in the gully).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Limpopo Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Potlake nature reserve
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Located in the Potlake nature reserve
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

其它
具体说明:
Protected area
注释:
Potlake nature reserve
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
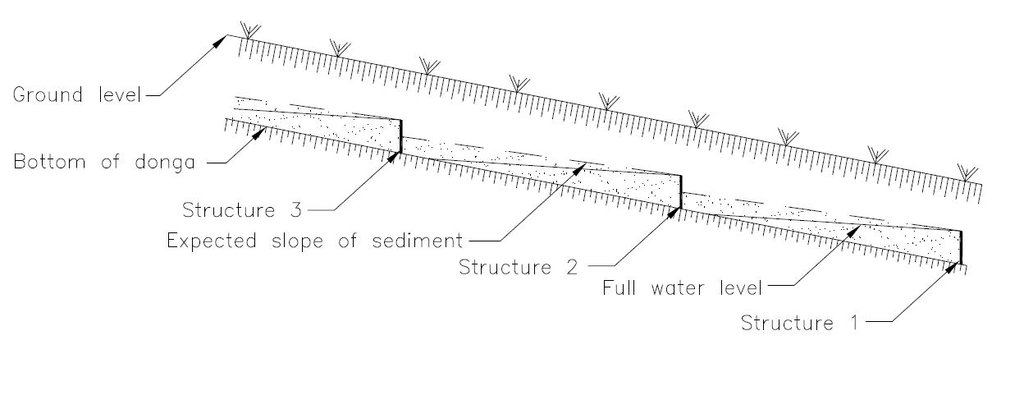
Silt fences are cheap and easy to erect, but the overflow depth must be limited. Silt fences are therefore erected in the wider section of a gully.
作者:
Jan van Heerden
日期:
01/01/2012
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Silt fences are temporary structures and are therefore placed closer together than permanent structures. The placing is such that the silt from the downstream structure builds up against the upstream structure to delay the perishing of the restoration materials. Vegetation must be established in the gully (donga) as soon as possible so that, when the materials decay after about ten years, the area will be restored.
作者:
Jan van Heerden
日期:
01/01/2012
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
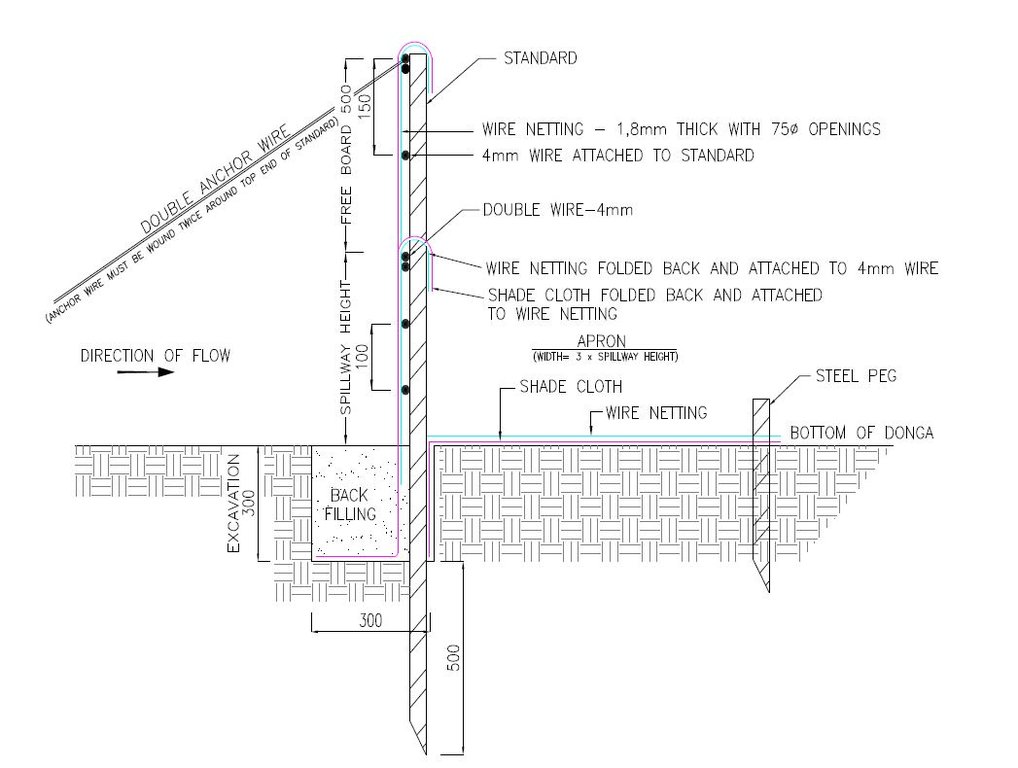
1. Dig a pit trench 300 mm × 300 mm from peg to peg over the entire width of the gully.
2. Drive iron standards (iron pole) in on the sides of the spillway length followed by more standards around 1.5 meters apart - ensure equal spacing between standards (standards must be driven in at least 500 mm deep - ensure that eyes (holes in standards) point upstream and that poles are in line with the others. Place apron on the ground from the excavation downstream. The width of the material must be three times the height of the overflow height and it must be at least 500 mm longer on both sides than the spillway length.
3. Span a 4 mm wire between the spillway poles on the total height of the structure. Tighten only manually and fasten on both sides of the two standards.
4. Drive in two anchor poles in line with the structure on both sides of the donga wall.
5. Saw off or cut heads of standards on the height of the structure’s height. Place anchor wires between two outer poles and anchor poles and tighten.
6. Thread 4 mm wire through on spillway height from side to side and bind to the two poles anchored to the anchor poles.
7. Also place wire between the spillway width poles and the end pole on the structure height and tighten.
8. Span wires from the spillway height wire on 100 mm to 150 mm distances apart, downwards until the last wire is at least 100 mm below the surface.
9. Place netting material (course plastic grid placed behind the filter material) on upstream side of the poles into the excavated pit trench and cut according to shape of the structure.
10. Place filter material flat in the pit trench and in front of the netting material on the upstream side of the poles and cut according to the shape of the structure. Tie the material to the structure with binding wire and fill the pit trench with soil.
11. Place netting material on the apron and tie it to the structure with binding wire and drive in T pegs at strategic places on downstream side.
12. The construction of the drop inlet is built in the same way as a weir structure as close as possible to the head of the donga. The gap between the structure and the donga head is filled with soil and must be filled again after the first rains. The spillway is made ±100 mm higher than the normal ground surface. The structure can be built to a maximum of 1 000 mm from the gully floor to the ground level.
13. Brush packing in front of the silt fence and stone packing downstream of the apron in the gully.
14. In order for silt fences to function more efficiently, it is recommended that that portion of the veld is fenced and withdrawn from grazing. Sowing of grasses or planting of common reed or vetiver grass can speed up the repair process considerably.
作者:
Jan van Heerden
日期:
01/01/2012
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
silt fence
指定单位面积(如相关):
6 to 8 meters
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
16.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
R200
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the site to be restored | Winter (outside raining season) |
| 2. | Installation of silt fences followed by brush and stone packing | Winter |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled labour (including transport) | Per day | 6.0 | 280.0 | 1680.0 | |
| 设备 | Power tools - electric power generator, angle grinder, hammer drill, | Per day | 3.0 | 500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| 设备 | Measuring tape, wire tensioning tool, pole driver, heavy and light hammers, pick, spade, pliers and scissors | Per day | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | |
| 施工材料 | 4mm wire | Per meter | 100.0 | 15.0 | 1500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Standards | Per piece | 6.0 | 90.0 | 540.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Netting | Per meter | 15.0 | 90.0 | 1350.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Anchor poles | Per piece | 6.0 | 10.0 | 60.0 | |
| 施工材料 | T pegs | Per piece | 20.0 | 20.0 | 400.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Binding wire | Per kg | 5.0 | 40.0 | 200.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Filter material (UV treated shade cloth - 80%) | Per meter | 86.0 | 20.0 | 1720.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 9150.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 571.88 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment - South Africa
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of fences after floods | After flooding event |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Repair of fences | Per day | 2.0 | 280.0 | 560.0 | |
| 设备 | Pliers, hammers, wire tensioning tool, pick, spade, pliers and scissors | Per day | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Binding wire and filter material | Per meter | 4.0 | 150.0 | 600.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1260.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 78.75 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1. Timing - during the raining season these areas could be inaccessible due to clayey soils and water in gullies.
2, Availability of labour.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
438.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
A variety of soil forms occur in the reserve and can generally be grouped according to the vegetation unit it supports. Sekhukhune Mountain Bushveld soils are predominantly shallow, rocky and clayey, with lime soils of the Glenrosa and Mispah soil forms often occurring in low-lying areas. Steep slopes commonly have rocky areas with no soil. The Dwars River valley is characterised by prismacutanic horizons with melanic structured diagnostic horizons.
Sekhukhune Plains Bushveld mainly occurs on red apedal clayey soils rich in metals. Soils on the plains are characterised by deep loamy Valsrivier soils. Shallow Glenrosa soils are found on the low-lying, rocky hills. Small mountains commonly have erodible black, melanic structured horizons.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Although the reserve has a very high biodiversity it also includes a potential 16 plant species of conservation concern, of which one is critically endangered and two are endangered.
The reserve has a fair representation of game for its size, but it should be noted that the area is very prone to erosion if its ecological capacity is exceeded. During an aerial census conducted in the reserve a total of 582 head of game was recorded. There are currently 78 verified avian species occurring at the reserve, of which 10 occur on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. A total of 33 reptile species has been recorded and a possible 32 amphibian species. No data is currently available for the fish species occurring at the reserve.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
其它(具体说明):
Tourists
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Nature reserve - tourism
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- State land
- State land
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
其它社会经济效应
Job creation
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The on-site impact assessment mainly includes a visual assessment of the amount of sediment trapped behind the silt fences and the establishment of vegetation.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地雷暴 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Very important to stabilise landscapes. |
| Helps to improve the habitat for wildlife, biodiversity in the protected area. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Helps to improve the habitat for wildlife, biodiversity in the protected area. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sensitive to floods | Timing of construction crucial - ready before the floods occur |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Same as above |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Revisited the restoration sites by Mr. Van Heerden
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Various discussions with Mr. Van Heerden and Mr. Buckle
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Silt fence report by Mr. Jan van Heerden (Agricultural Research Council) and the Strategic plan for the Potlake Nature Reserve (Limpopo Department of Economic Development, Environment and Tourism - LEDET)
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/09/2021
注释:
Meetings commenced with Mr. Buckle
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Combating erosion with silt fences, Jan van Heerden, 2006, ISBN 1-919849-76-9
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.arc.agric.za/arc-iae/Documents/Publication%20List%20and%20Orderform.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Five-year strategic plan for the Potlake Nature Reserve, Limpopo Province, South Africa
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
LEDET - no cost
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Working for Water [南非]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
模块
无模块