Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience [India]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Santosh Gupta
- Editores: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: Udo Höggel, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Mishrit kheti
technologies_6724 - India
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 5 de octubre de 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 20 de noviembre de 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 17 de abril de 2024 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - KeniaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - India1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
Comentarios:
Multilayer farming is a farming practice that involves cultivating a mix of vegetables and fruits on a small piece of land. Additionally, by growing a variety of crops together, multilayer farming can increase yields and provide a more diverse range of foods for households.
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Multilayer farming, also known as multi-tier farming, is a technique of intercropping crops of different heights, root and shoot patterns, and maturation times in small plots of land. This technique is cost-effective, easily adaptive, and participatory, providing a large number of food groups to farmers to improve their nutritional levels, providing insurance against crop failure, reducing pest and disease incidence, and improving soil properties and soil fertility conditions. Multilayer farming minimizes crop-weed competition, and soil erosion, and optimizes resource utilization resulting in higher returns and better nutritional value. It promotes sustainable agriculture, maintains a balanced diet, increases income per unit area, and reduces the risk of crop failure.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Multilayer farming is an agricultural model that aims at achieving maximum production per unit area by utilizing water, manure, and land resources to their full potential. This method is based on the synergies between the different crops and plants planted on a given piece of land. This method is cost-effective and yields more benefits than other farming systems. By cultivating four to five crops with the same amount of fertilizer and water required for a single crop, farmers can increase their income, and multiple crops can be harvested yearly using the same piece of land.
Multilayer farming is based on scientific, ecological, and economic principles, promoting crop diversification, maximizing productivity, utilizing resources more efficiently, and promoting intensive input use. Moreover, it ensures the sustainability of farm resources and the environment in the long term.
The multilayer farming system mainly consists of an overstory of trees or shrubs with an understory of economic or forage crops. By incorporating these principles, farmers can achieve greater yields and financial success while promoting environmental sustainability.
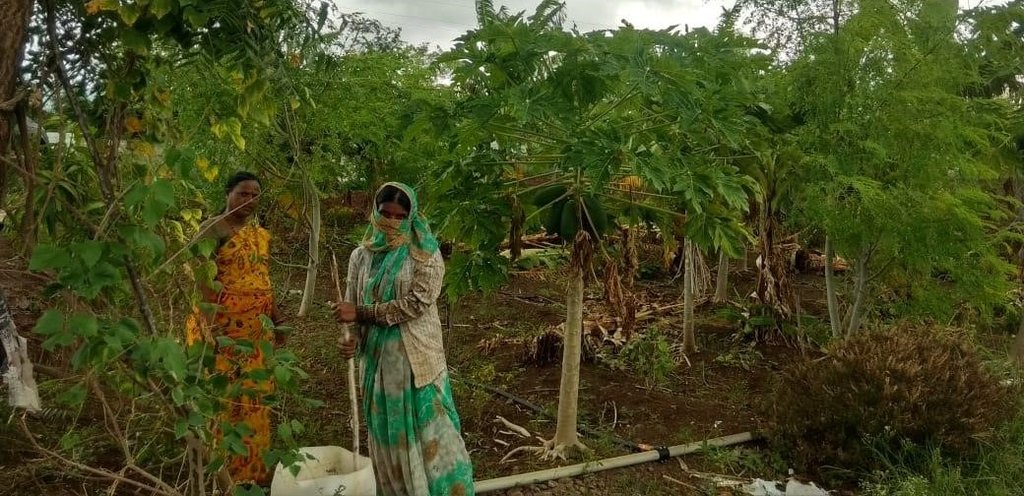
As a part of the program's approach, WOTR (Watershed Organisation Trust, the project implementing partner trained women change-makers) to spread awareness among villagers about the importance of nutrition and a healthy diet. Since 2018, the active promotion of multilayer farming to address food and nutrition insecurity in Maharashtra is undertaken. As a result, 1124 plots across 150 villages in Maharashtra have adopted this unique farming method to enhance food and nutrition security.
The multilayer farming system involves several steps to ensure maximum productivity from the available resources.
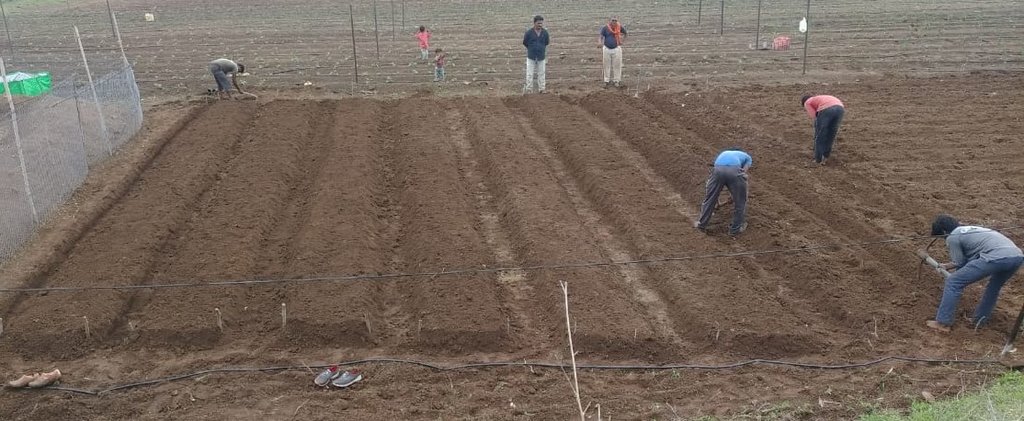
1.The first step is land preparation, which involves applying 300 kg of cow dung or vermicompost along with one kg of Trichoderma powder per 36 x 36 feet plot. Trichoderma is a bio-fungicide that helps to prevent fungal infections in plants and roots.
2.Next, eight beds of 3 x 36 feet are prepared with 1.5 to 2 feet of space left in between. These beds need to be arranged in the North-South direction to ensure that plants receive adequate sunlight.
3.After preparing the bed, 1-foot deep channels are dug to drain excess water so ensuring that the crops are not waterlogged.
4.Finally, in the middle of each bed, vegetable and fruit crops are planted according to a crop planning chart. By planting a variety of crops in the same plot, the multilayer farming system ensures the effective utilization of resources and provides an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year by producing several off-season crops.
The multilayer farming system has numerous benefits that make it an effective and sustainable farming method. It makes effective use of soil, water, and other resources, reducing waste and increasing productivity. Additionally the system reduces climate-specific damage and enhances soil health, helping to maintain an ecological balance in the environment. The soil covered minimizes water loss due to soil evaporation, generating a higher income per unit area with an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year. The multilayer farming system generates jobs and allows for better utilization of labor while reducing the impacts of climate-specific hazards such as high-intensity rainfall, soil erosion, and landslides. Multilayer farming also utilizes soil moisture at different depths and solar energy at different heights, improving soil characteristics and adding organic matter to the soil. It reduces pests and disease infestation and provides micro-climate conditions which ensure better productivity of crops underneath. Overall, multilayer farming is a sustainable and efficient farming method that not only maximizes productivity but also enhances soil and environmental health while promoting economic and social well-being.
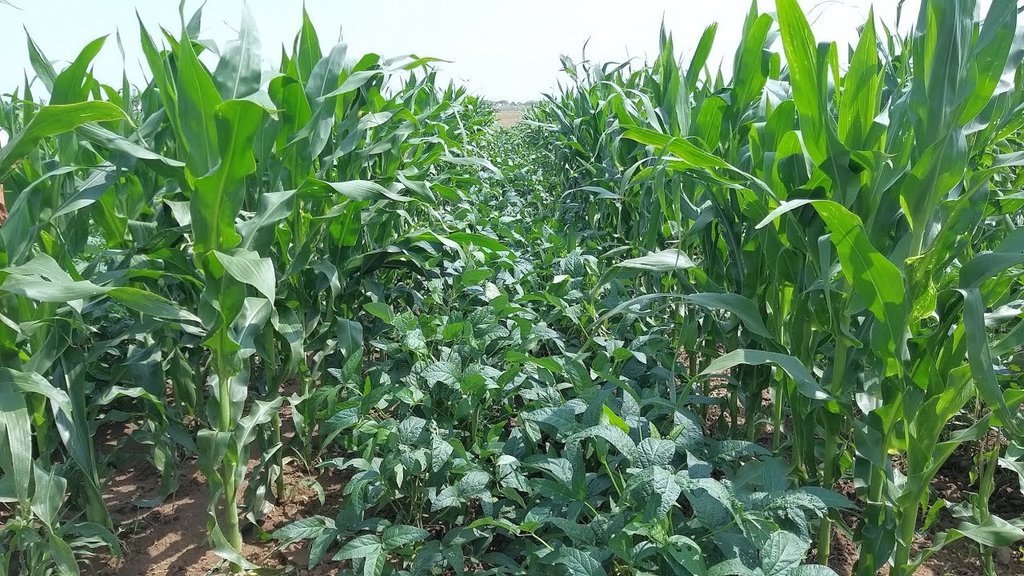
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
The images provide a visual representation of the essential steps followed by farmers to establish a successful multilayer farming system. These steps include land preparation, bed preparation, and planting a variety of crops in the same plot. The dates mentioned here are the dates of collection of these photos from the project implementing team as the photos were taken by different team members at different times.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
India
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Maharashtra
Especifique más el lugar :
Ahmednagar
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿El/los sitio(s) de la Tecnología se ubica(n) en un área de protección permanente?
No
Comentarios:
In Maharastra State, there are different districts where multilayer farming plots are established such as Ahmednagar, Satara, and Dhule
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Indique año de implementación:
2018
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The intervention is a result of experiments and research by WOTR and other agencies at different project locations
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- mejorar la producción
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación del suelo
- adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
- crear impacto económico benéfico
- crear impacto social benéfico
- Ensure nutritional security
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
No

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - trigo (invierno)
- cereales - sorgo
- Sugarcane, Horticulture crops like Pomegranate, Guava, Mango etc, Onion, pulses
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
In places where irrigation source is availbe the growing seasons vary between 2 to 3
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
In places where irrigation is available, farmers grow Kharif crops (summer crops) followed by Rabi crops (winter crops).
Comentarios:
The majority of farmers in various regions tend to practice mono-cropping due to rainfall variability and less rainfall in the region. However, in places where an irrigation source is available, farmers tend to grow second crops in the Rabi season or go for horticulture crops such as fruits and vegetables.
3.3 ¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
¿Cambió el uso de tierras debido a la implementación de la Tecnología?
- Sí (Por favor responda las preguntas de abajo referidas al uso de la tierra antes de implementar la Tecnología)
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: :
Sí
Especifique el uso combinado de tierras (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles):
- Agroforestería

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos
- Horticulture Crops
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cultivos florales
- vegetales - otros
- drumstick, marigold, radish, dolichos beans, coriander, spinach, fenugreek, dill, okra, brinjal, tomato, red pumpkin, maize, cowpea, castor, ridge gourd
Cultivos de matorrales y arbustos - Especifique cultivos:
- mango, mangostán, guayaba
- papaya
- Sapota
¿Se practica el intercultivo?
Sí
Si respondió que sí, especifique qué cultivos son intercultivados:
In multi-cropping systems, fruits and vegetables are planted in a systematically planned manner using crop planning charts. This approach ensures that the growth of plants complements each other, providing adequate nutrition for the family throughout the year.
¿Se practica la rotación de cultivos?
Sí
Si fuera el caso, especifique :
The combination of vegetables is selected based on the suitability to climate conditions as tomatoes are grown during the winter season, beans during the summer seasons etc.
Comentarios:
The land was mostly converted from mono-cropping systems to a multi-cropping system
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- mixta de secano – irrigada
Comentarios:
Multi-cropping systems involve covering the soil with crops throughout the year, which helps to reduce evaporation losses. In addition, irrigation is provided using drip or sprinkler systems to minimize water losses. This approach not only conserves water but also helps to maintain soil moisture levels, leading to higher yields and improved plant health. By adopting these practices, farmers can improve the sustainability and resilience of their agricultural systems.
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- Manejo de irrigación: (incl. provisión de agua, invernaderos)
- jardines domésticos
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo
- A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
- A5: Manejo de semillas, variedades mejoradas

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M4: Cambios significativos en la programación de las actividades
Comentarios:
1. Effective utilization of natural resources
2. Reduces climate-specific damage & enhances soil health and reduces water loss due to evaporation from the soil
3. The income per unit area increases substantially with this system and multilayer farming ensures the yield of some crops throughout the year
4. Utilizes the soil moisture well at different depths of soil and effectively utilizes solar energy at different heights
5. Improve the soil characteristics and adds organic matter to the soil
6. Provides a partial guarantee against the market glut of a single commodity and the efficient cultivation of a range of products is possible
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro físico del suelo
- Ps: hundimiento de suelos orgánicos, asentamiento del suelo

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bq: reducción de la cantidad/ biomasa
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
Comentarios:
Multilayer farming covers the soil throughout the year with crops, fruits, and vegetables. The micro-climate enables diversified crops to grow together and provide nutrition to the family through out the year. The year around soil cover reduces soil erosion by wind and flood.
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
- reducir la degradación del suelo
Comentarios:
Multilayer farming improves soil fertility by improving the microbial activities in the soil as the ecosystem of different root zones, plants and organic matter coupled with organic inputs creates a healthy plant environment
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
1
Si usa una unidad de área local, indique el factor de conversión a una hectárea (ej. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
ha
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
INR
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
80,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
200
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preperation | June |
| 2. | Preperation of beds for seed sowing | June |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds for fruits | Early June |
| 4. | Fencing of the field | Before the sowing |
Comentarios:
Farmers can use local resources such as Bamboo or other crop residues for fencing purposes as well. Land needs to be prepared before the onset of monsoon (during the summer season). Once a multilayer plot is established there is no need to prepare the land as well.
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Land preparation | person days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Preperation of beds for sowing | Person days | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Fencing material | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds for fruit trees (seeds and planting material) | Plant | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fram yard manure | Tons | 10,0 | 600,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Miscellaneous | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 19000,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 237,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
Costs towards labour, farm yard manure and sometimes seeds are internally arranged by the land users thus there may not be any cost to pay.
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of seeds | June-July/October-November/April/March/April |
| 2. | Application of organic manures | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 3. | Irrigation | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 4. | Bio-inputs | Based on the plant needs |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fruits, fodder and other produces | Multiple plucking during the year |
| 6. | Sales of farm produces | Multiple times during the year |
Comentarios:
Maintenance activities vary farmers to farmers depending upon the kind of fruits and vegetables planted, availability of resources and land area under cultivation
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 8,0 | 200,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Application of FYM and other inputs | Person days | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Maintenance and monitoring of the field | Person days | 50,0 | 100,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Harvesting | Person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds and planting material | Kg | 0,25 | 1000,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Farm yard manure and other inputs | Tons | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | Other cost | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 16600,0 | |||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 207,5 | |||||
Comentarios:
These farms are mostly managed by the farmers themselves without hiring any additional labour. Thus, labour cost is not something farmers need to pay for.
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
1. Availability of family labour to manage the field operations
2. Availability of dairy animals at the household level to meet the FYM needs
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
561,00
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Eco-Region as per the ICAR classification of Ecological Zone
Indique el nombre de la estación metereológica de referencia considerada:
https://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/bitstream/123456789/30264/1/MH14.pdf
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Length of growing period: less than 90 days
Rainy days: 44
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- no relevante
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Physiographically the district can be broadly divided in four major characteristic landforms viz., hill and ghat section (7.6% area); foothill zone (19.4% area); plateau (3.71% area) and plains (occupy 69.30% area). The intervention has been implemented in different villages of the district.
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
The soil types of the district are broadly divided into four categories namely coarse shallow soil; medium black soil; deep black soil and reddish soil occupying about 38, 41, 13 and 8 percent of the cultivated area respectively. In the first two categories, soil moisture is the predominant limiting factor affecting productivity of crops particularly under rainfed condition. (source-http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
La calidad de agua se refiere a:
agua subterránea y superficial
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
No
¿Se está llevando a cabo la inundación del área? :
No
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
On an average 26.3 per cent of the cultivated area is under irrigation, out of which 71.5 per cent is under well irrigation (including lift irrigation) and remaining area is under canal irrigation. (http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
The overall stage of ground water development for the district is quite high i.e., 79.8%. Further ground water development is not recommended without adhering to the precautionary measures i.e., artificial recharge to augment the ground water resources and adoption of ground water management practices. Ground water quality in the wells
monitored by the concerned authorities in the district is affected because of high NO3 concentrations. (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Maharashtra/Ahmadnagar.pdf)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Diversidad de hábitats:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
The majority of the area is under farming. Mono cropping is the generally practiced by farmers.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Sedentario o nómada:
- Sedentario
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- pobre
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Edad de los usuarios de la tierra:
- jóvenes
- personas de mediana edad
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Most land users covered during the project are small and marginal farmers with land up to 2 ha. The focus has been on women farmers to ensure the self-consumption of diverse food groups harvested from the multi-layer plots. The land users belong to a heterogeneous group of individuals coming from different social backgrounds and caste segments.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Nearly 61% of farmers fall into the category of landholding less than 1 hectare. (https://mahades.maharashtra.gov.in/files/publication/dsa_ahmednagar_2014.pdf)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
¿Los derechos del uso de la tierra se basan en un sistema legal tradicional?
No
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Comentarios:
The district is one among the progressive districts of Maharashtra and is well connected with a good network of roads and railways.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Round the year farm, produce of vegetables and fruits is available from multilayer fields. The data is based on the observation of land users, there has not been any study to assess possible qualitative improvements
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Farmers grow multilayer crops in smaller land sizes thus increasing the diversity of the products and the nutrition quality at the household level
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Efficient use of land by growing Multilayer Farming led to efficient utilization of the small farm plots
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
Comentarios/ especifique:
The use of micro irrigation led to a more efficient use of the same quantity of water allowing for the irrigation of land for a longer duration
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Organic inputs such as cow dung, cow urine, etc were used. This reduced the cost of the inputs.
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Income from farms increased as farm yields increased. Excess produce of vegetables and fruits is sold in the market.
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
As the farmers shift from mono-crop to multilayer cropping. This reduces the risk of crop failure faced by mono-crop farmers.
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Intake of Nutritional Food
Comentarios/ especifique:
Intake of nutritional food increased as the availability of fruits and vegetables no longer depended exclusively on markets
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Nutritional food available for consumption
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop cover for a longer duration over the soil, reducing evaporation losses
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Use of organic practices and covering the soil with crop and dry crop litter for a longer duration increased the soil moisture retention capacity
cubierta del suelo
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Bio-inputs and dry crop litter added to the soil increased the soil organic matter
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Crop diversity: vegetables and fruit crops are grown
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
As multiple crops are grown, pest and disease infestation is reduced
Especifique la evaluación de los impactos en el sitio (mediciones):
The impact areas indicated in the document are based on the experience and observations of the land users and field-level workers of implementing agencies. There has not been any scientific study to measure the quantitative impact of the intervention.
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Comentarios:
The micro-climate of the multilayered farm is maintained, enabling the crops to grow well
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- 1-10%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, por ej. sin recibir nada de incentivos/ materiales:
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptación
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
Sí
Si fuera así, indique a qué condiciones cambiantes se adaptó:
- mercados cambiantes
Especifique la adaptación de la Tecnología (diseño, material/ especies, etc.):
The Vegetable and fruits crops are modified based on the Household requirement
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Diversified vegetables and fruits available for household consumption |
| Increase in household income, as the excess produce is sold in the market and also reduced dependency on markets to purchase fruits and vegetables |
| Small farm plot (1300 sq. ft) is utilized under multilayer farming, remaining farmland is available for cereal, etc |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Water use efficiency because of the use of micro irrigation and reduction of evaporation as the crops and dry matter cover the soil |
| A good micro-climate of the multilayer farm plot is maintained |
| Availability of a good range of food groups to farmers may lead to improvement in nutritional parameters especially for women and children |
| Improved soil health due to mixed cropping system and enhancement soil microbial activities |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Labor engagement throughout the year | Mechanization suitable for small farm plots |
| Availability of farm yard manure to ensure cultivation following natural farming practices | Promotion of animal husbandry (dairy) in convergence with the government departments |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The produce from multilayer farming is diversified and comes in small quantities. Therefore the selling of these small quantities of produce is done in the local market. | Creation of farmers' collectives for selling larger amounts of produce in the market |
| Availability of irrigation is important to ensure the sustainability of intervention | Some water based enterprises can be developed to support the farmers not have irrigation facilities |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
5
- compilación de informes y otra documentación existente
4
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
09/04/2023
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
How is multilayer farming done?
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/07/18/how-multilayer-farming-is-done/
Título/ descripción:
Enhancing Household Food and Nutrition Security With Multilayer Farming
URL:
https://www.csrmandate.org/enhancing-household-food-and-nutrition-security-with-multilayer-farming/
Título/ descripción:
Kitchen Garden, Multilayer Farming Boost Food Security in Maharashtra
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/05/07/kitchen-garden-multilayer-farming-boost-food-security-in-maharashtra-2/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos