Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Santosh Gupta
- Editores: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: Udo Höggel, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Mishrit kheti
technologies_6724 - Índia
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 5 de Outubro de 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 20 de Novembro de 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 17 de Abril de 2024 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - QuêniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Índia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
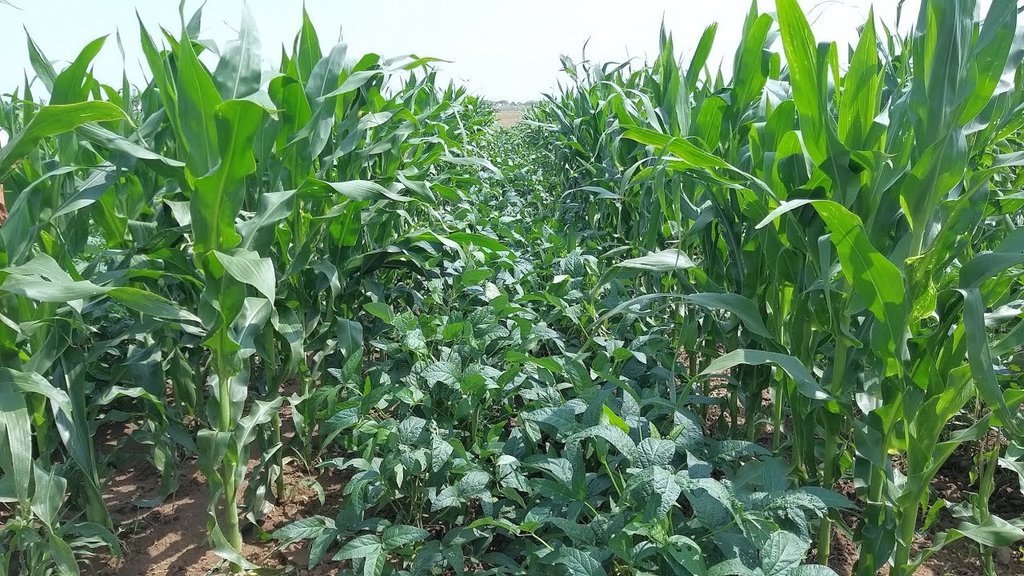
Multilayer farming is a farming practice that involves cultivating a mix of vegetables and fruits on a small piece of land. Additionally, by growing a variety of crops together, multilayer farming can increase yields and provide a more diverse range of foods for households.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Multilayer farming, also known as multi-tier farming, is a technique of intercropping crops of different heights, root and shoot patterns, and maturation times in small plots of land. This technique is cost-effective, easily adaptive, and participatory, providing a large number of food groups to farmers to improve their nutritional levels, providing insurance against crop failure, reducing pest and disease incidence, and improving soil properties and soil fertility conditions. Multilayer farming minimizes crop-weed competition, and soil erosion, and optimizes resource utilization resulting in higher returns and better nutritional value. It promotes sustainable agriculture, maintains a balanced diet, increases income per unit area, and reduces the risk of crop failure.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Multilayer farming is an agricultural model that aims at achieving maximum production per unit area by utilizing water, manure, and land resources to their full potential. This method is based on the synergies between the different crops and plants planted on a given piece of land. This method is cost-effective and yields more benefits than other farming systems. By cultivating four to five crops with the same amount of fertilizer and water required for a single crop, farmers can increase their income, and multiple crops can be harvested yearly using the same piece of land.
Multilayer farming is based on scientific, ecological, and economic principles, promoting crop diversification, maximizing productivity, utilizing resources more efficiently, and promoting intensive input use. Moreover, it ensures the sustainability of farm resources and the environment in the long term.
The multilayer farming system mainly consists of an overstory of trees or shrubs with an understory of economic or forage crops. By incorporating these principles, farmers can achieve greater yields and financial success while promoting environmental sustainability.
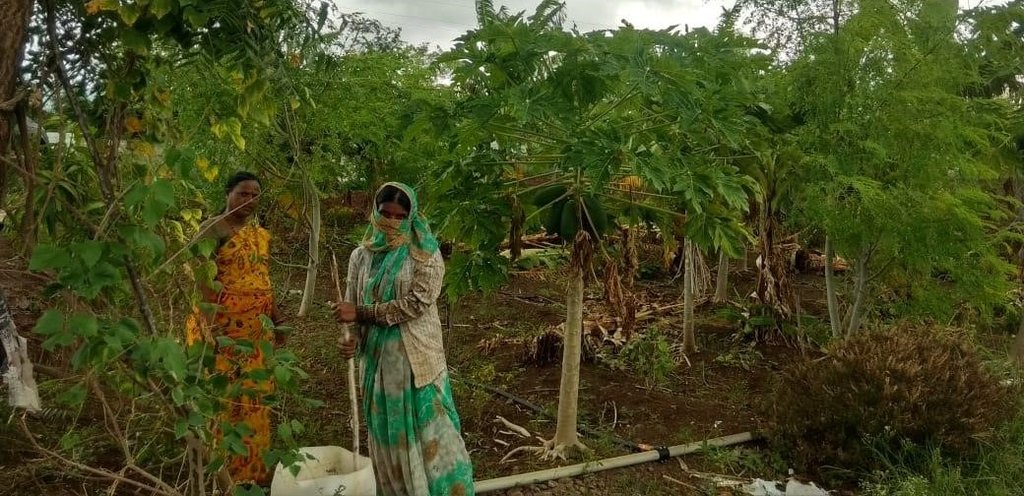
As a part of the program's approach, WOTR (Watershed Organisation Trust, the project implementing partner trained women change-makers) to spread awareness among villagers about the importance of nutrition and a healthy diet. Since 2018, the active promotion of multilayer farming to address food and nutrition insecurity in Maharashtra is undertaken. As a result, 1124 plots across 150 villages in Maharashtra have adopted this unique farming method to enhance food and nutrition security.
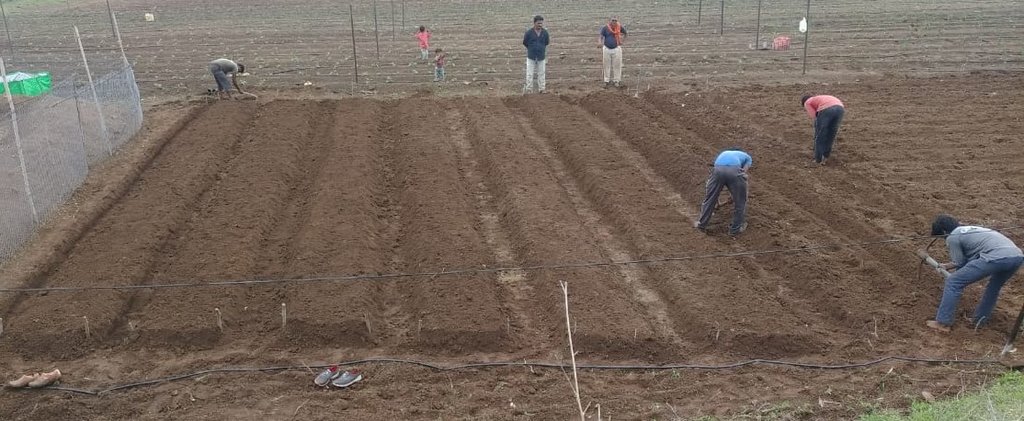
The multilayer farming system involves several steps to ensure maximum productivity from the available resources.
1.The first step is land preparation, which involves applying 300 kg of cow dung or vermicompost along with one kg of Trichoderma powder per 36 x 36 feet plot. Trichoderma is a bio-fungicide that helps to prevent fungal infections in plants and roots.
2.Next, eight beds of 3 x 36 feet are prepared with 1.5 to 2 feet of space left in between. These beds need to be arranged in the North-South direction to ensure that plants receive adequate sunlight.
3.After preparing the bed, 1-foot deep channels are dug to drain excess water so ensuring that the crops are not waterlogged.
4.Finally, in the middle of each bed, vegetable and fruit crops are planted according to a crop planning chart. By planting a variety of crops in the same plot, the multilayer farming system ensures the effective utilization of resources and provides an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year by producing several off-season crops.
The multilayer farming system has numerous benefits that make it an effective and sustainable farming method. It makes effective use of soil, water, and other resources, reducing waste and increasing productivity. Additionally the system reduces climate-specific damage and enhances soil health, helping to maintain an ecological balance in the environment. The soil covered minimizes water loss due to soil evaporation, generating a higher income per unit area with an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year. The multilayer farming system generates jobs and allows for better utilization of labor while reducing the impacts of climate-specific hazards such as high-intensity rainfall, soil erosion, and landslides. Multilayer farming also utilizes soil moisture at different depths and solar energy at different heights, improving soil characteristics and adding organic matter to the soil. It reduces pests and disease infestation and provides micro-climate conditions which ensure better productivity of crops underneath. Overall, multilayer farming is a sustainable and efficient farming method that not only maximizes productivity but also enhances soil and environmental health while promoting economic and social well-being.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The images provide a visual representation of the essential steps followed by farmers to establish a successful multilayer farming system. These steps include land preparation, bed preparation, and planting a variety of crops in the same plot. The dates mentioned here are the dates of collection of these photos from the project implementing team as the photos were taken by different team members at different times.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
Maharashtra
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ahmednagar
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
In Maharastra State, there are different districts where multilayer farming plots are established such as Ahmednagar, Satara, and Dhule
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The intervention is a result of experiments and research by WOTR and other agencies at different project locations
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
- Ensure nutritional security
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- cereais - sorgo
- Sugarcane, Horticulture crops like Pomegranate, Guava, Mango etc, Onion, pulses
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
In places where irrigation source is availbe the growing seasons vary between 2 to 3
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
In places where irrigation is available, farmers grow Kharif crops (summer crops) followed by Rabi crops (winter crops).
Comentários:
The majority of farmers in various regions tend to practice mono-cropping due to rainfall variability and less rainfall in the region. However, in places where an irrigation source is available, farmers tend to grow second crops in the Rabi season or go for horticulture crops such as fruits and vegetables.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
- Horticulture Crops
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- culturas de flores
- legumes - outros
- drumstick, marigold, radish, dolichos beans, coriander, spinach, fenugreek, dill, okra, brinjal, tomato, red pumpkin, maize, cowpea, castor, ridge gourd
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
- mamão
- Sapota
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
In multi-cropping systems, fruits and vegetables are planted in a systematically planned manner using crop planning charts. This approach ensures that the growth of plants complements each other, providing adequate nutrition for the family throughout the year.
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
The combination of vegetables is selected based on the suitability to climate conditions as tomatoes are grown during the winter season, beans during the summer seasons etc.
Comentários:
The land was mostly converted from mono-cropping systems to a multi-cropping system
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Multi-cropping systems involve covering the soil with crops throughout the year, which helps to reduce evaporation losses. In addition, irrigation is provided using drip or sprinkler systems to minimize water losses. This approach not only conserves water but also helps to maintain soil moisture levels, leading to higher yields and improved plant health. By adopting these practices, farmers can improve the sustainability and resilience of their agricultural systems.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Hortas familiares
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A5: Gestão de sementes, variedades melhoradas

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
Comentários:
1. Effective utilization of natural resources
2. Reduces climate-specific damage & enhances soil health and reduces water loss due to evaporation from the soil
3. The income per unit area increases substantially with this system and multilayer farming ensures the yield of some crops throughout the year
4. Utilizes the soil moisture well at different depths of soil and effectively utilizes solar energy at different heights
5. Improve the soil characteristics and adds organic matter to the soil
6. Provides a partial guarantee against the market glut of a single commodity and the efficient cultivation of a range of products is possible
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização física do solo
- Ps: Subsidência de solos orgânico, sedimentação do solo

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
Multilayer farming covers the soil throughout the year with crops, fruits, and vegetables. The micro-climate enables diversified crops to grow together and provide nutrition to the family through out the year. The year around soil cover reduces soil erosion by wind and flood.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Multilayer farming improves soil fertility by improving the microbial activities in the soil as the ecosystem of different root zones, plants and organic matter coupled with organic inputs creates a healthy plant environment
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
ha
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
INR
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
200
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preperation | June |
| 2. | Preperation of beds for seed sowing | June |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds for fruits | Early June |
| 4. | Fencing of the field | Before the sowing |
Comentários:
Farmers can use local resources such as Bamboo or other crop residues for fencing purposes as well. Land needs to be prepared before the onset of monsoon (during the summer season). Once a multilayer plot is established there is no need to prepare the land as well.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land preparation | person days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Preperation of beds for sowing | Person days | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Fencing material | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds for fruit trees (seeds and planting material) | Plant | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fram yard manure | Tons | 10,0 | 600,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Miscellaneous | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 19000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 237,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs towards labour, farm yard manure and sometimes seeds are internally arranged by the land users thus there may not be any cost to pay.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of seeds | June-July/October-November/April/March/April |
| 2. | Application of organic manures | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 3. | Irrigation | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 4. | Bio-inputs | Based on the plant needs |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fruits, fodder and other produces | Multiple plucking during the year |
| 6. | Sales of farm produces | Multiple times during the year |
Comentários:
Maintenance activities vary farmers to farmers depending upon the kind of fruits and vegetables planted, availability of resources and land area under cultivation
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 8,0 | 200,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Application of FYM and other inputs | Person days | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance and monitoring of the field | Person days | 50,0 | 100,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Harvesting | Person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds and planting material | Kg | 0,25 | 1000,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Farm yard manure and other inputs | Tons | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Other cost | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 16600,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 207,5 | |||||
Comentários:
These farms are mostly managed by the farmers themselves without hiring any additional labour. Thus, labour cost is not something farmers need to pay for.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
1. Availability of family labour to manage the field operations
2. Availability of dairy animals at the household level to meet the FYM needs
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
561,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Eco-Region as per the ICAR classification of Ecological Zone
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
https://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/bitstream/123456789/30264/1/MH14.pdf
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Length of growing period: less than 90 days
Rainy days: 44
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Physiographically the district can be broadly divided in four major characteristic landforms viz., hill and ghat section (7.6% area); foothill zone (19.4% area); plateau (3.71% area) and plains (occupy 69.30% area). The intervention has been implemented in different villages of the district.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
The soil types of the district are broadly divided into four categories namely coarse shallow soil; medium black soil; deep black soil and reddish soil occupying about 38, 41, 13 and 8 percent of the cultivated area respectively. In the first two categories, soil moisture is the predominant limiting factor affecting productivity of crops particularly under rainfed condition. (source-http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
On an average 26.3 per cent of the cultivated area is under irrigation, out of which 71.5 per cent is under well irrigation (including lift irrigation) and remaining area is under canal irrigation. (http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
The overall stage of ground water development for the district is quite high i.e., 79.8%. Further ground water development is not recommended without adhering to the precautionary measures i.e., artificial recharge to augment the ground water resources and adoption of ground water management practices. Ground water quality in the wells
monitored by the concerned authorities in the district is affected because of high NO3 concentrations. (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Maharashtra/Ahmadnagar.pdf)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The majority of the area is under farming. Mono cropping is the generally practiced by farmers.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Most land users covered during the project are small and marginal farmers with land up to 2 ha. The focus has been on women farmers to ensure the self-consumption of diverse food groups harvested from the multi-layer plots. The land users belong to a heterogeneous group of individuals coming from different social backgrounds and caste segments.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Nearly 61% of farmers fall into the category of landholding less than 1 hectare. (https://mahades.maharashtra.gov.in/files/publication/dsa_ahmednagar_2014.pdf)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
The district is one among the progressive districts of Maharashtra and is well connected with a good network of roads and railways.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Round the year farm, produce of vegetables and fruits is available from multilayer fields. The data is based on the observation of land users, there has not been any study to assess possible qualitative improvements
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers grow multilayer crops in smaller land sizes thus increasing the diversity of the products and the nutrition quality at the household level
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Efficient use of land by growing Multilayer Farming led to efficient utilization of the small farm plots
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The use of micro irrigation led to a more efficient use of the same quantity of water allowing for the irrigation of land for a longer duration
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Organic inputs such as cow dung, cow urine, etc were used. This reduced the cost of the inputs.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Income from farms increased as farm yields increased. Excess produce of vegetables and fruits is sold in the market.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
As the farmers shift from mono-crop to multilayer cropping. This reduces the risk of crop failure faced by mono-crop farmers.
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Intake of Nutritional Food
Comentários/especificar:
Intake of nutritional food increased as the availability of fruits and vegetables no longer depended exclusively on markets
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Nutritional food available for consumption
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Crop cover for a longer duration over the soil, reducing evaporation losses
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Use of organic practices and covering the soil with crop and dry crop litter for a longer duration increased the soil moisture retention capacity
Cobertura do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Bio-inputs and dry crop litter added to the soil increased the soil organic matter
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Crop diversity: vegetables and fruit crops are grown
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
As multiple crops are grown, pest and disease infestation is reduced
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
The impact areas indicated in the document are based on the experience and observations of the land users and field-level workers of implementing agencies. There has not been any scientific study to measure the quantitative impact of the intervention.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Comentários:
The micro-climate of the multilayered farm is maintained, enabling the crops to grow well
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mercados dinâmicos
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
The Vegetable and fruits crops are modified based on the Household requirement
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Diversified vegetables and fruits available for household consumption |
| Increase in household income, as the excess produce is sold in the market and also reduced dependency on markets to purchase fruits and vegetables |
| Small farm plot (1300 sq. ft) is utilized under multilayer farming, remaining farmland is available for cereal, etc |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Water use efficiency because of the use of micro irrigation and reduction of evaporation as the crops and dry matter cover the soil |
| A good micro-climate of the multilayer farm plot is maintained |
| Availability of a good range of food groups to farmers may lead to improvement in nutritional parameters especially for women and children |
| Improved soil health due to mixed cropping system and enhancement soil microbial activities |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Labor engagement throughout the year | Mechanization suitable for small farm plots |
| Availability of farm yard manure to ensure cultivation following natural farming practices | Promotion of animal husbandry (dairy) in convergence with the government departments |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The produce from multilayer farming is diversified and comes in small quantities. Therefore the selling of these small quantities of produce is done in the local market. | Creation of farmers' collectives for selling larger amounts of produce in the market |
| Availability of irrigation is important to ensure the sustainability of intervention | Some water based enterprises can be developed to support the farmers not have irrigation facilities |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
5
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
4
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
09/04/2023
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
How is multilayer farming done?
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/07/18/how-multilayer-farming-is-done/
Título/ descrição:
Enhancing Household Food and Nutrition Security With Multilayer Farming
URL:
https://www.csrmandate.org/enhancing-household-food-and-nutrition-security-with-multilayer-farming/
Título/ descrição:
Kitchen Garden, Multilayer Farming Boost Food Security in Maharashtra
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/05/07/kitchen-garden-multilayer-farming-boost-food-security-in-maharashtra-2/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos