Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Santosh Gupta
- 编辑者: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- 审查者: Udo Höggel, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Mishrit kheti
technologies_6724 - 印度
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: Oct. 5, 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: Nov. 20, 2023 (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: April 17, 2024 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - 印度1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Multilayer farming is a farming practice that involves cultivating a mix of vegetables and fruits on a small piece of land. Additionally, by growing a variety of crops together, multilayer farming can increase yields and provide a more diverse range of foods for households.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Multilayer farming, also known as multi-tier farming, is a technique of intercropping crops of different heights, root and shoot patterns, and maturation times in small plots of land. This technique is cost-effective, easily adaptive, and participatory, providing a large number of food groups to farmers to improve their nutritional levels, providing insurance against crop failure, reducing pest and disease incidence, and improving soil properties and soil fertility conditions. Multilayer farming minimizes crop-weed competition, and soil erosion, and optimizes resource utilization resulting in higher returns and better nutritional value. It promotes sustainable agriculture, maintains a balanced diet, increases income per unit area, and reduces the risk of crop failure.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Multilayer farming is an agricultural model that aims at achieving maximum production per unit area by utilizing water, manure, and land resources to their full potential. This method is based on the synergies between the different crops and plants planted on a given piece of land. This method is cost-effective and yields more benefits than other farming systems. By cultivating four to five crops with the same amount of fertilizer and water required for a single crop, farmers can increase their income, and multiple crops can be harvested yearly using the same piece of land.
Multilayer farming is based on scientific, ecological, and economic principles, promoting crop diversification, maximizing productivity, utilizing resources more efficiently, and promoting intensive input use. Moreover, it ensures the sustainability of farm resources and the environment in the long term.
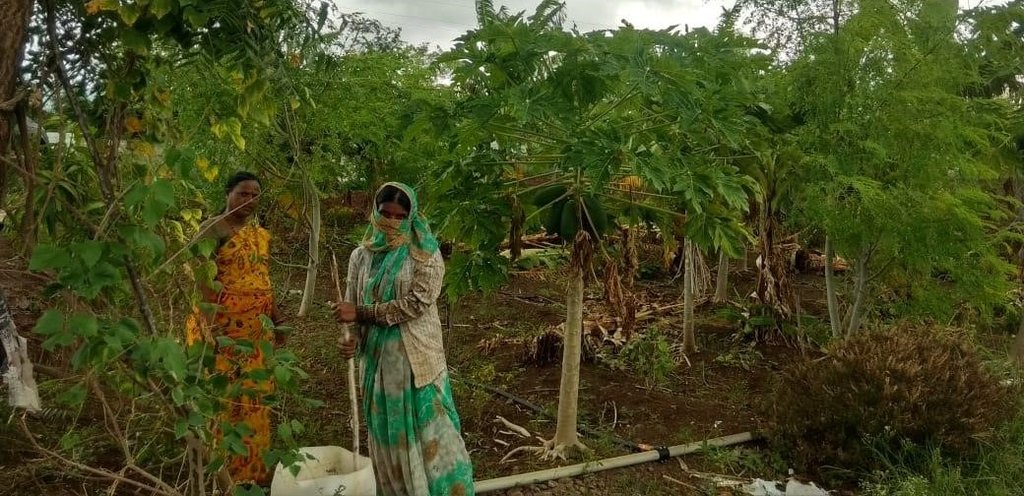
The multilayer farming system mainly consists of an overstory of trees or shrubs with an understory of economic or forage crops. By incorporating these principles, farmers can achieve greater yields and financial success while promoting environmental sustainability.
As a part of the program's approach, WOTR (Watershed Organisation Trust, the project implementing partner trained women change-makers) to spread awareness among villagers about the importance of nutrition and a healthy diet. Since 2018, the active promotion of multilayer farming to address food and nutrition insecurity in Maharashtra is undertaken. As a result, 1124 plots across 150 villages in Maharashtra have adopted this unique farming method to enhance food and nutrition security.
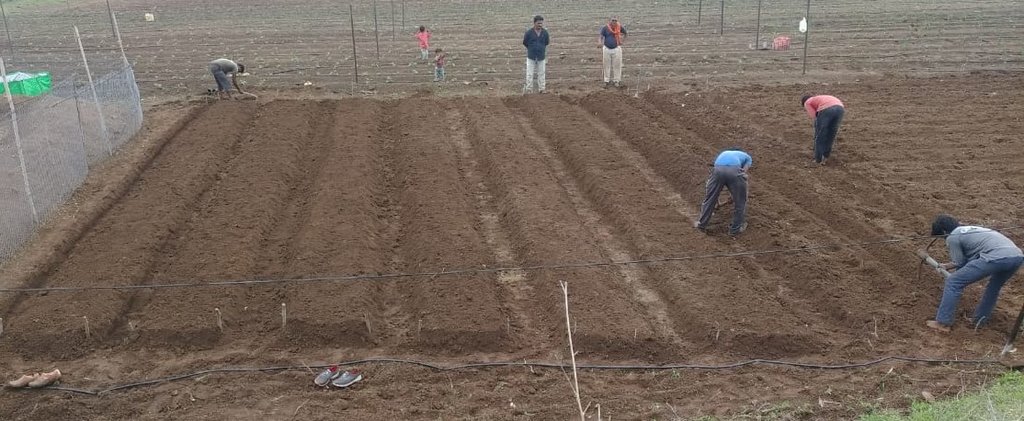
The multilayer farming system involves several steps to ensure maximum productivity from the available resources.
1.The first step is land preparation, which involves applying 300 kg of cow dung or vermicompost along with one kg of Trichoderma powder per 36 x 36 feet plot. Trichoderma is a bio-fungicide that helps to prevent fungal infections in plants and roots.
2.Next, eight beds of 3 x 36 feet are prepared with 1.5 to 2 feet of space left in between. These beds need to be arranged in the North-South direction to ensure that plants receive adequate sunlight.
3.After preparing the bed, 1-foot deep channels are dug to drain excess water so ensuring that the crops are not waterlogged.
4.Finally, in the middle of each bed, vegetable and fruit crops are planted according to a crop planning chart. By planting a variety of crops in the same plot, the multilayer farming system ensures the effective utilization of resources and provides an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year by producing several off-season crops.
The multilayer farming system has numerous benefits that make it an effective and sustainable farming method. It makes effective use of soil, water, and other resources, reducing waste and increasing productivity. Additionally the system reduces climate-specific damage and enhances soil health, helping to maintain an ecological balance in the environment. The soil covered minimizes water loss due to soil evaporation, generating a higher income per unit area with an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year. The multilayer farming system generates jobs and allows for better utilization of labor while reducing the impacts of climate-specific hazards such as high-intensity rainfall, soil erosion, and landslides. Multilayer farming also utilizes soil moisture at different depths and solar energy at different heights, improving soil characteristics and adding organic matter to the soil. It reduces pests and disease infestation and provides micro-climate conditions which ensure better productivity of crops underneath. Overall, multilayer farming is a sustainable and efficient farming method that not only maximizes productivity but also enhances soil and environmental health while promoting economic and social well-being.
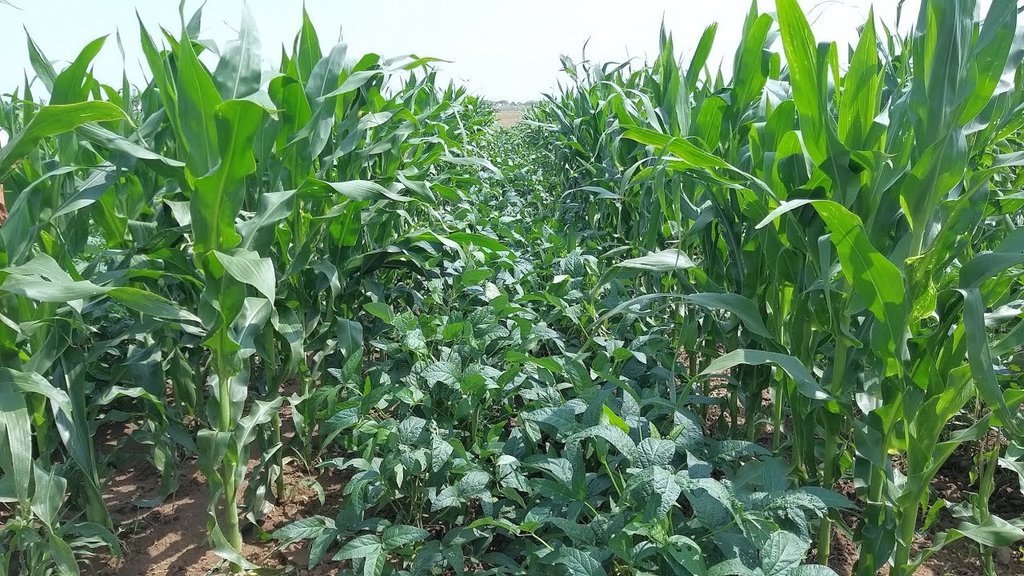
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The images provide a visual representation of the essential steps followed by farmers to establish a successful multilayer farming system. These steps include land preparation, bed preparation, and planting a variety of crops in the same plot. The dates mentioned here are the dates of collection of these photos from the project implementing team as the photos were taken by different team members at different times.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Maharashtra
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ahmednagar
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
In Maharastra State, there are different districts where multilayer farming plots are established such as Ahmednagar, Satara, and Dhule
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The intervention is a result of experiments and research by WOTR and other agencies at different project locations
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
- Ensure nutritional security
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 谷类 - 高粱
- Sugarcane, Horticulture crops like Pomegranate, Guava, Mango etc, Onion, pulses
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
In places where irrigation source is availbe the growing seasons vary between 2 to 3
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
In places where irrigation is available, farmers grow Kharif crops (summer crops) followed by Rabi crops (winter crops).
注释:
The majority of farmers in various regions tend to practice mono-cropping due to rainfall variability and less rainfall in the region. However, in places where an irrigation source is available, farmers tend to grow second crops in the Rabi season or go for horticulture crops such as fruits and vegetables.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Horticulture Crops
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 花卉作物
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- drumstick, marigold, radish, dolichos beans, coriander, spinach, fenugreek, dill, okra, brinjal, tomato, red pumpkin, maize, cowpea, castor, ridge gourd
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- 木瓜
- Sapota
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
In multi-cropping systems, fruits and vegetables are planted in a systematically planned manner using crop planning charts. This approach ensures that the growth of plants complements each other, providing adequate nutrition for the family throughout the year.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The combination of vegetables is selected based on the suitability to climate conditions as tomatoes are grown during the winter season, beans during the summer seasons etc.
注释:
The land was mostly converted from mono-cropping systems to a multi-cropping system
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Multi-cropping systems involve covering the soil with crops throughout the year, which helps to reduce evaporation losses. In addition, irrigation is provided using drip or sprinkler systems to minimize water losses. This approach not only conserves water but also helps to maintain soil moisture levels, leading to higher yields and improved plant health. By adopting these practices, farmers can improve the sustainability and resilience of their agricultural systems.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 家庭花园
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
注释:
1. Effective utilization of natural resources
2. Reduces climate-specific damage & enhances soil health and reduces water loss due to evaporation from the soil
3. The income per unit area increases substantially with this system and multilayer farming ensures the yield of some crops throughout the year
4. Utilizes the soil moisture well at different depths of soil and effectively utilizes solar energy at different heights
5. Improve the soil characteristics and adds organic matter to the soil
6. Provides a partial guarantee against the market glut of a single commodity and the efficient cultivation of a range of products is possible
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
Multilayer farming covers the soil throughout the year with crops, fruits, and vegetables. The micro-climate enables diversified crops to grow together and provide nutrition to the family through out the year. The year around soil cover reduces soil erosion by wind and flood.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Multilayer farming improves soil fertility by improving the microbial activities in the soil as the ecosystem of different root zones, plants and organic matter coupled with organic inputs creates a healthy plant environment
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
INR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
80.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
200
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preperation | June |
| 2. | Preperation of beds for seed sowing | June |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds for fruits | Early June |
| 4. | Fencing of the field | Before the sowing |
注释:
Farmers can use local resources such as Bamboo or other crop residues for fencing purposes as well. Land needs to be prepared before the onset of monsoon (during the summer season). Once a multilayer plot is established there is no need to prepare the land as well.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | person days | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Preperation of beds for sowing | Person days | 3.0 | 200.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Fencing material | Lumpsum | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds for fruit trees (seeds and planting material) | Plant | 100.0 | 50.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fram yard manure | Tons | 10.0 | 600.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Miscellaneous | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 19000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 237.5 | |||||
注释:
Costs towards labour, farm yard manure and sometimes seeds are internally arranged by the land users thus there may not be any cost to pay.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of seeds | June-July/October-November/April/March/April |
| 2. | Application of organic manures | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 3. | Irrigation | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 4. | Bio-inputs | Based on the plant needs |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fruits, fodder and other produces | Multiple plucking during the year |
| 6. | Sales of farm produces | Multiple times during the year |
注释:
Maintenance activities vary farmers to farmers depending upon the kind of fruits and vegetables planted, availability of resources and land area under cultivation
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 8.0 | 200.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Application of FYM and other inputs | Person days | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Maintenance and monitoring of the field | Person days | 50.0 | 100.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting | Person days | 20.0 | 200.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds and planting material | Kg | 0.25 | 1000.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Farm yard manure and other inputs | Tons | 5.0 | 750.0 | 3750.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Other cost | Lumpsum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 16600.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 207.5 | |||||
注释:
These farms are mostly managed by the farmers themselves without hiring any additional labour. Thus, labour cost is not something farmers need to pay for.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1. Availability of family labour to manage the field operations
2. Availability of dairy animals at the household level to meet the FYM needs
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
561.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Eco-Region as per the ICAR classification of Ecological Zone
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
https://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/bitstream/123456789/30264/1/MH14.pdf
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Length of growing period: less than 90 days
Rainy days: 44
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Physiographically the district can be broadly divided in four major characteristic landforms viz., hill and ghat section (7.6% area); foothill zone (19.4% area); plateau (3.71% area) and plains (occupy 69.30% area). The intervention has been implemented in different villages of the district.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The soil types of the district are broadly divided into four categories namely coarse shallow soil; medium black soil; deep black soil and reddish soil occupying about 38, 41, 13 and 8 percent of the cultivated area respectively. In the first two categories, soil moisture is the predominant limiting factor affecting productivity of crops particularly under rainfed condition. (source-http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
On an average 26.3 per cent of the cultivated area is under irrigation, out of which 71.5 per cent is under well irrigation (including lift irrigation) and remaining area is under canal irrigation. (http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
The overall stage of ground water development for the district is quite high i.e., 79.8%. Further ground water development is not recommended without adhering to the precautionary measures i.e., artificial recharge to augment the ground water resources and adoption of ground water management practices. Ground water quality in the wells
monitored by the concerned authorities in the district is affected because of high NO3 concentrations. (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Maharashtra/Ahmadnagar.pdf)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The majority of the area is under farming. Mono cropping is the generally practiced by farmers.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Most land users covered during the project are small and marginal farmers with land up to 2 ha. The focus has been on women farmers to ensure the self-consumption of diverse food groups harvested from the multi-layer plots. The land users belong to a heterogeneous group of individuals coming from different social backgrounds and caste segments.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Nearly 61% of farmers fall into the category of landholding less than 1 hectare. (https://mahades.maharashtra.gov.in/files/publication/dsa_ahmednagar_2014.pdf)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The district is one among the progressive districts of Maharashtra and is well connected with a good network of roads and railways.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Round the year farm, produce of vegetables and fruits is available from multilayer fields. The data is based on the observation of land users, there has not been any study to assess possible qualitative improvements
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Farmers grow multilayer crops in smaller land sizes thus increasing the diversity of the products and the nutrition quality at the household level
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Efficient use of land by growing Multilayer Farming led to efficient utilization of the small farm plots
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
The use of micro irrigation led to a more efficient use of the same quantity of water allowing for the irrigation of land for a longer duration
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Organic inputs such as cow dung, cow urine, etc were used. This reduced the cost of the inputs.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Income from farms increased as farm yields increased. Excess produce of vegetables and fruits is sold in the market.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
As the farmers shift from mono-crop to multilayer cropping. This reduces the risk of crop failure faced by mono-crop farmers.
其它社会经济效应
Intake of Nutritional Food
注释/具体说明:
Intake of nutritional food increased as the availability of fruits and vegetables no longer depended exclusively on markets
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Nutritional food available for consumption
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Crop cover for a longer duration over the soil, reducing evaporation losses
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Use of organic practices and covering the soil with crop and dry crop litter for a longer duration increased the soil moisture retention capacity
土壤覆盖层
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Bio-inputs and dry crop litter added to the soil increased the soil organic matter
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Crop diversity: vegetables and fruit crops are grown
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
As multiple crops are grown, pest and disease infestation is reduced
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The impact areas indicated in the document are based on the experience and observations of the land users and field-level workers of implementing agencies. There has not been any scientific study to measure the quantitative impact of the intervention.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
注释:
The micro-climate of the multilayered farm is maintained, enabling the crops to grow well
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The Vegetable and fruits crops are modified based on the Household requirement
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Diversified vegetables and fruits available for household consumption |
| Increase in household income, as the excess produce is sold in the market and also reduced dependency on markets to purchase fruits and vegetables |
| Small farm plot (1300 sq. ft) is utilized under multilayer farming, remaining farmland is available for cereal, etc |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water use efficiency because of the use of micro irrigation and reduction of evaporation as the crops and dry matter cover the soil |
| A good micro-climate of the multilayer farm plot is maintained |
| Availability of a good range of food groups to farmers may lead to improvement in nutritional parameters especially for women and children |
| Improved soil health due to mixed cropping system and enhancement soil microbial activities |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labor engagement throughout the year | Mechanization suitable for small farm plots |
| Availability of farm yard manure to ensure cultivation following natural farming practices | Promotion of animal husbandry (dairy) in convergence with the government departments |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The produce from multilayer farming is diversified and comes in small quantities. Therefore the selling of these small quantities of produce is done in the local market. | Creation of farmers' collectives for selling larger amounts of produce in the market |
| Availability of irrigation is important to ensure the sustainability of intervention | Some water based enterprises can be developed to support the farmers not have irrigation facilities |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
5
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
4
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/04/2023
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
How is multilayer farming done?
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/07/18/how-multilayer-farming-is-done/
标题/说明:
Enhancing Household Food and Nutrition Security With Multilayer Farming
URL:
https://www.csrmandate.org/enhancing-household-food-and-nutrition-security-with-multilayer-farming/
标题/说明:
Kitchen Garden, Multilayer Farming Boost Food Security in Maharashtra
URL:
https://wotr.org/2020/05/07/kitchen-garden-multilayer-farming-boost-food-security-in-maharashtra-2/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块