Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience [Индия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Santosh Gupta
- Редакторы: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Рецензенты: Udo Höggel, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Mishrit kheti
technologies_6724 - Индия
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF для вывода на печать
- Полная аннотация в формате интернет-страницы
- Полная аннотация (неотформатированно)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 5 октября 2023 г. (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 20 ноября 2023 г. (inactive)
- Multilayer Farming Systems For Ensuring Food Diversity And Increasing Resilience: 17 апреля 2024 г. (public)
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - КенияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Индия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
Пояснения:
Multilayer farming is a farming practice that involves cultivating a mix of vegetables and fruits on a small piece of land. Additionally, by growing a variety of crops together, multilayer farming can increase yields and provide a more diverse range of foods for households.
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Multilayer farming, also known as multi-tier farming, is a technique of intercropping crops of different heights, root and shoot patterns, and maturation times in small plots of land. This technique is cost-effective, easily adaptive, and participatory, providing a large number of food groups to farmers to improve their nutritional levels, providing insurance against crop failure, reducing pest and disease incidence, and improving soil properties and soil fertility conditions. Multilayer farming minimizes crop-weed competition, and soil erosion, and optimizes resource utilization resulting in higher returns and better nutritional value. It promotes sustainable agriculture, maintains a balanced diet, increases income per unit area, and reduces the risk of crop failure.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Multilayer farming is an agricultural model that aims at achieving maximum production per unit area by utilizing water, manure, and land resources to their full potential. This method is based on the synergies between the different crops and plants planted on a given piece of land. This method is cost-effective and yields more benefits than other farming systems. By cultivating four to five crops with the same amount of fertilizer and water required for a single crop, farmers can increase their income, and multiple crops can be harvested yearly using the same piece of land.
Multilayer farming is based on scientific, ecological, and economic principles, promoting crop diversification, maximizing productivity, utilizing resources more efficiently, and promoting intensive input use. Moreover, it ensures the sustainability of farm resources and the environment in the long term.
The multilayer farming system mainly consists of an overstory of trees or shrubs with an understory of economic or forage crops. By incorporating these principles, farmers can achieve greater yields and financial success while promoting environmental sustainability.
As a part of the program's approach, WOTR (Watershed Organisation Trust, the project implementing partner trained women change-makers) to spread awareness among villagers about the importance of nutrition and a healthy diet. Since 2018, the active promotion of multilayer farming to address food and nutrition insecurity in Maharashtra is undertaken. As a result, 1124 plots across 150 villages in Maharashtra have adopted this unique farming method to enhance food and nutrition security.
The multilayer farming system involves several steps to ensure maximum productivity from the available resources.
1.The first step is land preparation, which involves applying 300 kg of cow dung or vermicompost along with one kg of Trichoderma powder per 36 x 36 feet plot. Trichoderma is a bio-fungicide that helps to prevent fungal infections in plants and roots.
2.Next, eight beds of 3 x 36 feet are prepared with 1.5 to 2 feet of space left in between. These beds need to be arranged in the North-South direction to ensure that plants receive adequate sunlight.
3.After preparing the bed, 1-foot deep channels are dug to drain excess water so ensuring that the crops are not waterlogged.
4.Finally, in the middle of each bed, vegetable and fruit crops are planted according to a crop planning chart. By planting a variety of crops in the same plot, the multilayer farming system ensures the effective utilization of resources and provides an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year by producing several off-season crops.
The multilayer farming system has numerous benefits that make it an effective and sustainable farming method. It makes effective use of soil, water, and other resources, reducing waste and increasing productivity. Additionally the system reduces climate-specific damage and enhances soil health, helping to maintain an ecological balance in the environment. The soil covered minimizes water loss due to soil evaporation, generating a higher income per unit area with an even distribution of income and employment throughout the year. The multilayer farming system generates jobs and allows for better utilization of labor while reducing the impacts of climate-specific hazards such as high-intensity rainfall, soil erosion, and landslides. Multilayer farming also utilizes soil moisture at different depths and solar energy at different heights, improving soil characteristics and adding organic matter to the soil. It reduces pests and disease infestation and provides micro-climate conditions which ensure better productivity of crops underneath. Overall, multilayer farming is a sustainable and efficient farming method that not only maximizes productivity but also enhances soil and environmental health while promoting economic and social well-being.
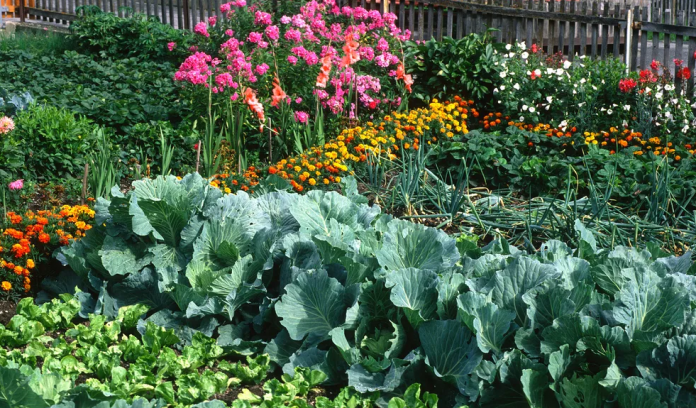
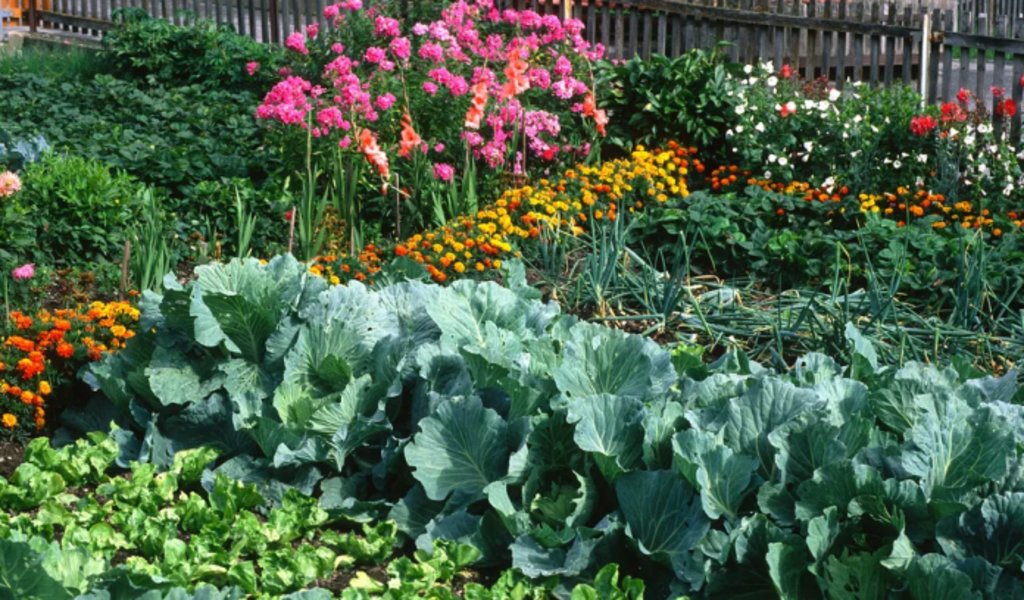
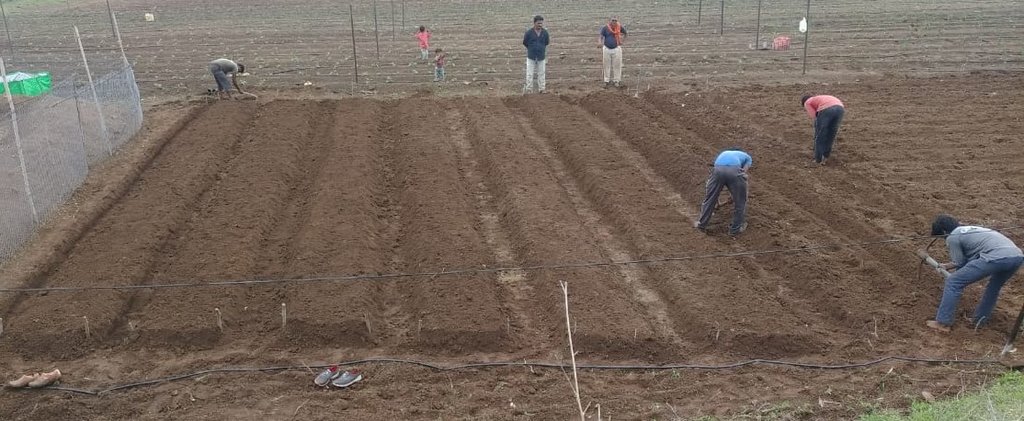
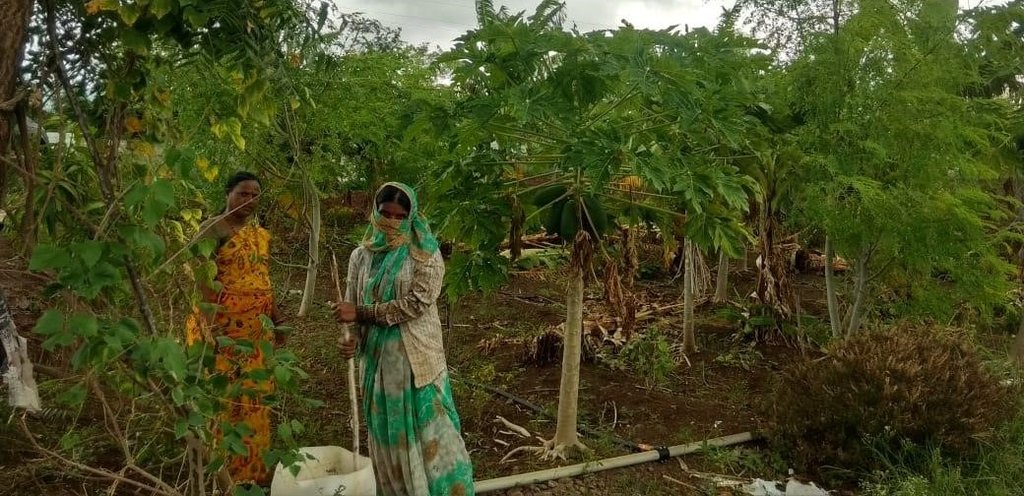
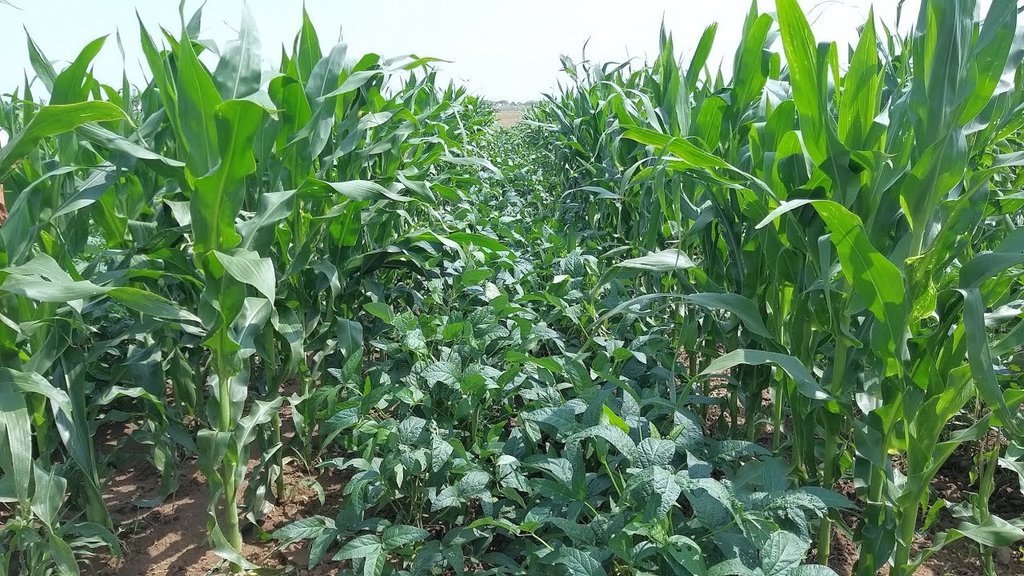
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
Комментарии к фотографиям:
The images provide a visual representation of the essential steps followed by farmers to establish a successful multilayer farming system. These steps include land preparation, bed preparation, and planting a variety of crops in the same plot. The dates mentioned here are the dates of collection of these photos from the project implementing team as the photos were taken by different team members at different times.
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Индия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Maharashtra
Более точная привязка места:
Ahmednagar
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- примененяется точечно/ на небольших участках
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Нет
Пояснения:
In Maharastra State, there are different districts where multilayer farming plots are established such as Ahmednagar, Satara, and Dhule
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2018
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The intervention is a result of experiments and research by WOTR and other agencies at different project locations
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- адаптация к изменению климата / экстремальным погодным явлениям и их последствиям
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
- создание благоприятных социальных условий
- Ensure nutritional security
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Нет

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - пшеница (озимая)
- зерновые культуры - сорго
- Sugarcane, Horticulture crops like Pomegranate, Guava, Mango etc, Onion, pulses
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
In places where irrigation source is availbe the growing seasons vary between 2 to 3
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
In places where irrigation is available, farmers grow Kharif crops (summer crops) followed by Rabi crops (winter crops).
Пояснения:
The majority of farmers in various regions tend to practice mono-cropping due to rainfall variability and less rainfall in the region. However, in places where an irrigation source is available, farmers tend to grow second crops in the Rabi season or go for horticulture crops such as fruits and vegetables.
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Да (Пожалуйста, заполните нижеприведенные вопросы относительно использования земель до внедрения Технологии)
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агролесоводство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
- Horticulture Crops
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- цветочные культуры
- овощи - другие
- drumstick, marigold, radish, dolichos beans, coriander, spinach, fenugreek, dill, okra, brinjal, tomato, red pumpkin, maize, cowpea, castor, ridge gourd
Древесные и кустарниковые культуры - Уточните культуры:
- манго, мангостан, гуава
- папайя
- Sapota
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Если да, укажите, какие посевы применяются:
In multi-cropping systems, fruits and vegetables are planted in a systematically planned manner using crop planning charts. This approach ensures that the growth of plants complements each other, providing adequate nutrition for the family throughout the year.
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
The combination of vegetables is selected based on the suitability to climate conditions as tomatoes are grown during the winter season, beans during the summer seasons etc.
Пояснения:
The land was mostly converted from mono-cropping systems to a multi-cropping system
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
Пояснения:
Multi-cropping systems involve covering the soil with crops throughout the year, which helps to reduce evaporation losses. In addition, irrigation is provided using drip or sprinkler systems to minimize water losses. This approach not only conserves water but also helps to maintain soil moisture levels, leading to higher yields and improved plant health. By adopting these practices, farmers can improve the sustainability and resilience of their agricultural systems.
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
- Управление орошением (включая водоснабжение и дренаж)
- приусадебные участки
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A1: Растительный/ почвенный покров
- A2: Органическое вещество/ почвенное плодородие
- A5: Семенное хозяйство, селекция, применение улучшенных сортов

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров

управленческие мероприятия
- У1: Смена типа землепользования
- У4: Существенные изменения в сроках проведения мероприятий
Пояснения:
1. Effective utilization of natural resources
2. Reduces climate-specific damage & enhances soil health and reduces water loss due to evaporation from the soil
3. The income per unit area increases substantially with this system and multilayer farming ensures the yield of some crops throughout the year
4. Utilizes the soil moisture well at different depths of soil and effectively utilizes solar energy at different heights
5. Improve the soil characteristics and adds organic matter to the soil
6. Provides a partial guarantee against the market glut of a single commodity and the efficient cultivation of a range of products is possible
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фп: сработка органических горизонтов почв, оседание поверхности

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бк: сокращение количества биомассы
- Бв: потеря природного разнообразия
- Бб: рост числа вредителей/болезней
Пояснения:
Multilayer farming covers the soil throughout the year with crops, fruits, and vegetables. The micro-climate enables diversified crops to grow together and provide nutrition to the family through out the year. The year around soil cover reduces soil erosion by wind and flood.
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Multilayer farming improves soil fertility by improving the microbial activities in the soil as the ecosystem of different root zones, plants and organic matter coupled with organic inputs creates a healthy plant environment
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1
Если вы используете местные системы измерения, укажите коэффициент пересчета на один гектар (например, 1 га = 2,47 акров): 1 га =:
ha
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
INR
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
80,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
200
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land Preperation | June |
| 2. | Preperation of beds for seed sowing | June |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds for fruits | Early June |
| 4. | Fencing of the field | Before the sowing |
Пояснения:
Farmers can use local resources such as Bamboo or other crop residues for fencing purposes as well. Land needs to be prepared before the onset of monsoon (during the summer season). Once a multilayer plot is established there is no need to prepare the land as well.
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Land preparation | person days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Preperation of beds for sowing | Person days | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Fencing material | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds for fruit trees (seeds and planting material) | Plant | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Fram yard manure | Tons | 10,0 | 600,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Miscellaneous | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 19000,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 237,5 | |||||
Пояснения:
Costs towards labour, farm yard manure and sometimes seeds are internally arranged by the land users thus there may not be any cost to pay.
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of seeds | June-July/October-November/April/March/April |
| 2. | Application of organic manures | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 3. | Irrigation | Across the year at critical growth stages |
| 4. | Bio-inputs | Based on the plant needs |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fruits, fodder and other produces | Multiple plucking during the year |
| 6. | Sales of farm produces | Multiple times during the year |
Пояснения:
Maintenance activities vary farmers to farmers depending upon the kind of fruits and vegetables planted, availability of resources and land area under cultivation
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 8,0 | 200,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Application of FYM and other inputs | Person days | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Maintenance and monitoring of the field | Person days | 50,0 | 100,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Harvesting | Person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds and planting material | Kg | 0,25 | 1000,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Farm yard manure and other inputs | Tons | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Other cost | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 16600,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 207,5 | |||||
Пояснения:
These farms are mostly managed by the farmers themselves without hiring any additional labour. Thus, labour cost is not something farmers need to pay for.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
1. Availability of family labour to manage the field operations
2. Availability of dairy animals at the household level to meet the FYM needs
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
561,00
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Eco-Region as per the ICAR classification of Ecological Zone
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
https://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/bitstream/123456789/30264/1/MH14.pdf
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Length of growing period: less than 90 days
Rainy days: 44
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Physiographically the district can be broadly divided in four major characteristic landforms viz., hill and ghat section (7.6% area); foothill zone (19.4% area); plateau (3.71% area) and plains (occupy 69.30% area). The intervention has been implemented in different villages of the district.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
The soil types of the district are broadly divided into four categories namely coarse shallow soil; medium black soil; deep black soil and reddish soil occupying about 38, 41, 13 and 8 percent of the cultivated area respectively. In the first two categories, soil moisture is the predominant limiting factor affecting productivity of crops particularly under rainfed condition. (source-http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
> 50 м
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода хорошего качества
Качество воды относится к:
одновременно грунтовые и поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
On an average 26.3 per cent of the cultivated area is under irrigation, out of which 71.5 per cent is under well irrigation (including lift irrigation) and remaining area is under canal irrigation. (http://www.kvk.pravara.com/pages/District%20Profile/District%20Profile.htm)
The overall stage of ground water development for the district is quite high i.e., 79.8%. Further ground water development is not recommended without adhering to the precautionary measures i.e., artificial recharge to augment the ground water resources and adoption of ground water management practices. Ground water quality in the wells
monitored by the concerned authorities in the district is affected because of high NO3 concentrations. (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Maharashtra/Ahmadnagar.pdf)
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
The majority of the area is under farming. Mono cropping is the generally practiced by farmers.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
- группа/ община
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- механизировано/ есть автотранспорт
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- молодёжь
- средний возраст
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Most land users covered during the project are small and marginal farmers with land up to 2 ha. The focus has been on women farmers to ensure the self-consumption of diverse food groups harvested from the multi-layer plots. The land users belong to a heterogeneous group of individuals coming from different social backgrounds and caste segments.
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
Nearly 61% of farmers fall into the category of landholding less than 1 hectare. (https://mahades.maharashtra.gov.in/files/publication/dsa_ahmednagar_2014.pdf)
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
Права на землепользование основаны на традиционной правовой системе?
Нет
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
Пояснения:
The district is one among the progressive districts of Maharashtra and is well connected with a good network of roads and railways.
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Round the year farm, produce of vegetables and fruits is available from multilayer fields. The data is based on the observation of land users, there has not been any study to assess possible qualitative improvements
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Farmers grow multilayer crops in smaller land sizes thus increasing the diversity of the products and the nutrition quality at the household level
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Efficient use of land by growing Multilayer Farming led to efficient utilization of the small farm plots
Доступность и качество воды
доступность оросительных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The use of micro irrigation led to a more efficient use of the same quantity of water allowing for the irrigation of land for a longer duration
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Organic inputs such as cow dung, cow urine, etc were used. This reduced the cost of the inputs.
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Income from farms increased as farm yields increased. Excess produce of vegetables and fruits is sold in the market.
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
As the farmers shift from mono-crop to multilayer cropping. This reduces the risk of crop failure faced by mono-crop farmers.
Другое социально-экономическое воздействие
Intake of Nutritional Food
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Intake of nutritional food increased as the availability of fruits and vegetables no longer depended exclusively on markets
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
состояние здоровья
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Nutritional food available for consumption
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Crop cover for a longer duration over the soil, reducing evaporation losses
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Use of organic practices and covering the soil with crop and dry crop litter for a longer duration increased the soil moisture retention capacity
почвенный покров
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Bio-inputs and dry crop litter added to the soil increased the soil organic matter
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Crop diversity: vegetables and fruit crops are grown
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
As multiple crops are grown, pest and disease infestation is reduced
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений):
The impact areas indicated in the document are based on the experience and observations of the land users and field-level workers of implementing agencies. There has not been any scientific study to measure the quantitative impact of the intervention.
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Пояснения:
The micro-climate of the multilayered farm is maintained, enabling the crops to grow well
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- 1-10%
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 91-100%
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Да
Если да, укажите, по отношению к каким именно изменяющимся условиям среды произведена адаптация?
- изменяющиеся условия рынка
Укажите, что именно изменилось в Технологии (дизайн, используемые материалы или виды растений/животных и т.д.):
The Vegetable and fruits crops are modified based on the Household requirement
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Diversified vegetables and fruits available for household consumption |
| Increase in household income, as the excess produce is sold in the market and also reduced dependency on markets to purchase fruits and vegetables |
| Small farm plot (1300 sq. ft) is utilized under multilayer farming, remaining farmland is available for cereal, etc |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Water use efficiency because of the use of micro irrigation and reduction of evaporation as the crops and dry matter cover the soil |
| A good micro-climate of the multilayer farm plot is maintained |
| Availability of a good range of food groups to farmers may lead to improvement in nutritional parameters especially for women and children |
| Improved soil health due to mixed cropping system and enhancement soil microbial activities |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Labor engagement throughout the year | Mechanization suitable for small farm plots |
| Availability of farm yard manure to ensure cultivation following natural farming practices | Promotion of animal husbandry (dairy) in convergence with the government departments |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The produce from multilayer farming is diversified and comes in small quantities. Therefore the selling of these small quantities of produce is done in the local market. | Creation of farmers' collectives for selling larger amounts of produce in the market |
| Availability of irrigation is important to ensure the sustainability of intervention | Some water based enterprises can be developed to support the farmers not have irrigation facilities |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- опросы землепользователей
5
- данные, собранные из отчетов и достоверных документов
4
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
09/04/2023
7.3 Ссылки на соответствующую онлайн-информацию
Название/ описание:
How is multilayer farming done?
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://wotr.org/2020/07/18/how-multilayer-farming-is-done/
Название/ описание:
Enhancing Household Food and Nutrition Security With Multilayer Farming
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://www.csrmandate.org/enhancing-household-food-and-nutrition-security-with-multilayer-farming/
Название/ описание:
Kitchen Garden, Multilayer Farming Boost Food Security in Maharashtra
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://wotr.org/2020/05/07/kitchen-garden-multilayer-farming-boost-food-security-in-maharashtra-2/
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей