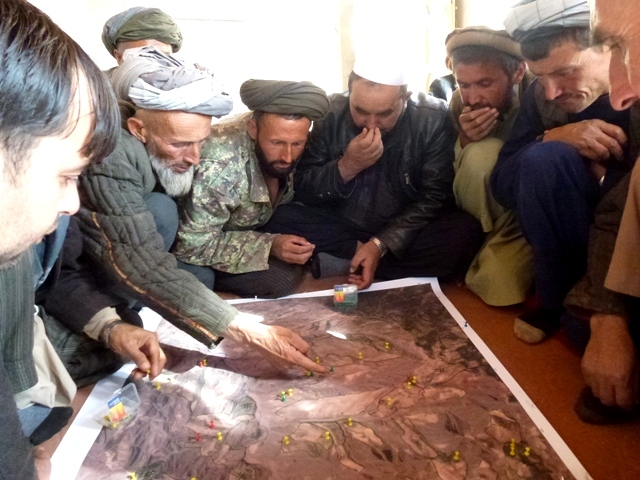
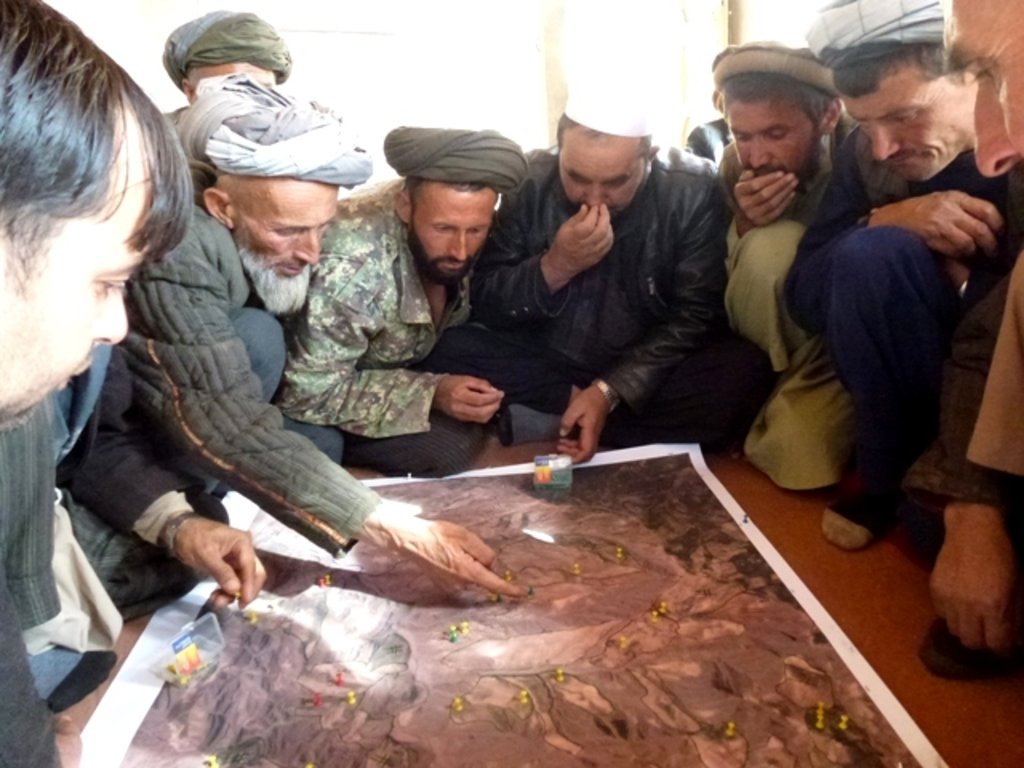
Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees (NRMC) [Afghanistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
- Rédacteurs : Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aqila Haidery
- Examinateur : William Critchley
approaches_545 - Afghanistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
17/10/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Références au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Technologies de GDT

Improved livestock shed for better health and productivity [Afghanistan]
Existing livestock sheds can be improved through interior and exterior refurbishing, and door and window installation. More favourable indoor conditions benefit animal health and the quality of animal products.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm

Rotational grazing to restore degraded pastures [Afghanistan]
A plan for rotational grazing has been developed to control pasture use and prevent overgrazing of rehabilitated pastures.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm

Community fodder bank for sustaining supplies [Afghanistan]
Community fodder banks have been established in villages for the purpose of ensuring supplies of livestock fodder during winter, to prevent loss of livestock and to prevent over-grazing early in spring.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm
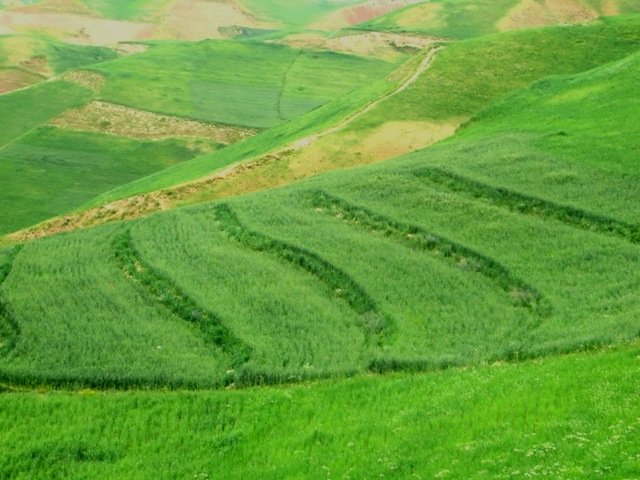

Terraces with improved seed and fertilizer application [Afghanistan]
Terraces are established on mountain slopes used mainly for cropping wheat, with the purpose of soil protection from erosion, preserving runoff, sediments and nutrients on-site. Improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on the terraces for increasing crop yield, but also vegetation cover and biomass production, and thus prevent further land …
- Compilateur : Roziya Kirgizbekova
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support the Natural Resource Management Committees (NRMC) at village level.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
Terre des Hommes (Tdh) has been implementing the Livelihood project (LIPT) in Rustaq district in northern Afghanistan since 2007. The overall aim of the project is to offer the rural population new and improved livelihood options, with capacity building of the rural population, to design and implement their own sustainable development options, and to enhance their resilience to cope with natural and conflict-related stress. For this purpose, capacity of supporting stakeholder institutions is strengthened (LIPT’s boundary partners) to ensure that good development is on-going. Boundary partners are trained and equipped in relevant techniques regarding sustainable natural resource management.
Two Watershed Associations (WSA) and 20 Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) were founded through LIPT. Two WSAs, in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas, are registered at national level within the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL), and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support the NRMCs at village level. Out of their newly established and registered regional offices, the WSAs coordinate the NRMCs, take over responsibilities from Tdh (e.g. the 2014 reforestation campaign) and are getting more involved in planning and monitoring of LIPT’s activities. The 20 NRMCs have "hands and eyes" on all LIPT activities implemented in their communities, and their trained extension workers render valuable services to the farmers in their villages.
Methods: Today, all NRMCs have a strong institutional set-up. Their extension workers have been trained and equipped. Members of NRMCs and WSAs have been trained on group management, planning, documentations, record keeping, IPM, reforestation management, soil protection, mulching, hedgerows and terracing, making fermenters, pruning and budding. WSAs and NRMCs gained further organizational, technical and management capacity building in both watershed areas. As one of biggest challenge at watershed level is soil erosion within hillside agriculture, LIPT III trained the NRMCs and WSAs on terracing and hedgerows to protect the soil from erosion. Furthermore, NRMCs were trained in sustainable irrigation water management, gully treatment, and surface water harvesting. There were also training courses conducted on leadership, finance, proposal writing, documentation, procurement and operations management.
Both WSAs and NRMCs started to get a real understanding of environmental issues and were then able to motivate their communities. WSAs coordinated the NRM intervention with NRMCs including reforestation, soil protection hedgerows, contour lines, terracing, establishment of public nurseries (to produce trees and be an income source for WSAs), establishment of centralized community bakeries (to reduce the demand for firewood and decrease the women’s workload in the watershed areas), irrigation infrastructure, bio-engineering and gully control (to reduce the progression of gullies on both ploughed lands and pastures), livestock value chains at regional (watershed) level, etc., while NRMCs are looking after these interventions and the mobilization of the community at the village level. Farmers and communities have adopted natural resource management practices to maintain/increase soil fertility, rangeland, water resources and forest coverage.
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Afghanistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tahor Province, Rustaq districts
Autres spécifications du lieu :
Dashti Mirzai, Javaz Khana and Sari Joy villages
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2007
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez approximativement quand l'Approche a démarré:
il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The main aim of the project is to offer the rural population new and improved livelihood options and to deliver capacity building for the rural population to design and implement their own sustainable development options and enhance their resilience to cope with natural and conflict related stress.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- favorise
The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within Afghan society, while at the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. However. it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
- entrave
Lack of capacity of the rural population to design and implement sustainable development options; vulnerability to natural and conflict related stress
cadre institutionnel
- favorise
Establishment of Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC)
- entrave
Lack of institutions at the community level to introduce natural resource management options
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- favorise
Training has improved technical knowledge
- entrave
Lack of technical knowledge
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
The overall aim of the project is to offer the rural population new and improved livelihood options and give capacity building to the rural population to design and implement their own sustainable development options, and enhance their resilience to cope with natural and conflict related stress.
- organisations communautaires
Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC)
- organisation internationale
Terre des Hommes , SDC
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | aucun | |
| planification | interactive | |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive |
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- tous les acteurs concernés dans le cadre d'une approche participative
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, modérément
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
- régional
- national
Décrivez l'institution, ses rôles et responsabilités, ses membres, etc.
LIPT III will leave behind successful and strong boundary partners in place to carry out the development options, as main boundary partners (WSAs, NRMCs, as the major boundary partners) will have a source of income for their operation and management.
Précisez le type de soutien:
- financier
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
- équipement
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- économie/ marketing
- technologie
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
On-going research, as well as multiple trials by LIPT to find the best-adapted technical solutions, to communicate and discuss them with local communities and farmers, were the key elements of this success.
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 10 000-100 000
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez le(s) type(s) de soutien, les conditions et les fournisseurs:
Fully supported under project
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Non
5.5 Autres incitations ou instruments
D'autres incitations ou instruments ont-ils été utilisés pour promouvoir la mise en œuvre des Technologies de GDT?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez:
local institution were support with equipment
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
NRM is the area where LIPT III made the most remarkable progress despite the fact that NRM was a completely new approach, and its implementation is highly demanding in terms of manpower, community awareness and mobilization. Profound changes in behaviour, motivation and mobilization both at individual and community levels made this possible. On-going research, as well as multiple trials by LIPT to find the best-adapted technical solutions, and to communicate and discuss them with local communities and farmers, were the key elements of this success. The NRMCs, WSAs as well as individual farmers in both watershed areas increased their knowledge and gained a better understanding of the importance of sustainable management, rehabilitation of farm land, pastures and their main natural resources. Farmers adapt and replicate the innovations once they see the results, farmers interest became high and they are ready to replicate it to protect their land form degradation.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Farmers adapt and replicate the innovations. Once they see the results, farmers' interest became high and they are ready to replicate it to protect their land from degradation.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à des emplois, des opportunités de revenus?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
One Example: Under irrigation water improvement interventions, LIPT in coordination with NRMCs brought more 110 ha land under irrigation and the yield is expected to be doubled in this agricultural land, and NRMCs are trained on sustainable irrigation water management, gully treatment, and surface water harvesting
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- réduire les risques de catastrophe
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
To look to the capacity and institutional strengthening of the project boundary partners, LIPT III will leave behind a successful and strong boundary partner in place to carry out the development options, as main boundary partners will have source of income (nurseries, cooperative shop, etc.) for their operation and management.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The traditional social structures and customary institutions play an important role in problem solving in everyday community life, but traditional problem solving structures may also limit the taking up of new approaches. More effective approaches are needed, for example in the field of the management of common pool resources (water, pastures, trees and shrubs). The newly established Watershed Associations demonstrate how groups addressing specific urgent tasks may be successfully established and functioning within a very short period of time. |
|
NRM is the area where LIPT III made the most remarkable progress despite the fact that NRM was a completely new approach, and its implementation is highly demanding in terms of manpower, community awareness and mobilization. Profound changes in behaviour, motivation and mobilization both at individual and community levels made this possible. The permanent research, as well as multiple trials by LIPT to find the best-adapted technical solutions, to communicate and discuss them with local communities and farmers were the key elements of this success. WSAs and NRMCs are playing an active role in implementation of NRM intervention, even they have become more interested and active when they registered in Department of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock at national and regional level. |
| Farmers adapt and replicate the innovations once they see the results, as soil erosion is the main concern in Rustaq - but nobody in watershed area was ready to protect their agriculture land by implementing barrier hedgerows. After demonstrating of hedgerow by LIPT III, farmers saw its impact on controlling of soil erosion, farmers' interest became high and they are ready to replicate it to protect their land from degradation. |
|
All community extension workers are trained and in place, playing an essential role in supporting the boundary partners in implementing NRM activities that include community mobilization, technical design of orchards and nurseries, reforestation sites, terracing and hedgerow designs. The NRMCs, WSAs as well as individual farmers in both watershed areas increased their knowledge and gained better understanding of the importance of sustainable management, rehabilitation of farmland, pastures and their main natural resources. A high degree of motivation and mobilization of farmers, and adequate technical capacity of CEWs regarding NRM is certainly one of the main outcomes of the LIPT, and an essential step towards the fulfilment of LIPT’s mission. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| A rewarding sign of the development of NRM awareness is how farmers took up the problem of soil erosion.100 ha of cultivable land on hillsides have been terraced since the terracing activity had been initiated in November 2013. And 155 ha of additional land are in the process of being terraced. The biggest success with terracing is that a number of farmers started replication themselves what they had seen. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Improved livestock shed for better health and productivity [Afghanistan]
Existing livestock sheds can be improved through interior and exterior refurbishing, and door and window installation. More favourable indoor conditions benefit animal health and the quality of animal products.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm

Rotational grazing to restore degraded pastures [Afghanistan]
A plan for rotational grazing has been developed to control pasture use and prevent overgrazing of rehabilitated pastures.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm

Community fodder bank for sustaining supplies [Afghanistan]
Community fodder banks have been established in villages for the purpose of ensuring supplies of livestock fodder during winter, to prevent loss of livestock and to prevent over-grazing early in spring.
- Compilateur : Bettina Wolfgramm

Terraces with improved seed and fertilizer application [Afghanistan]
Terraces are established on mountain slopes used mainly for cropping wheat, with the purpose of soil protection from erosion, preserving runoff, sediments and nutrients on-site. Improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on the terraces for increasing crop yield, but also vegetation cover and biomass production, and thus prevent further land …
- Compilateur : Roziya Kirgizbekova
Modules
Aucun module trouvé