Keyhole Garden [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : John Brogan
- Rédacteur : Shahid Kamal
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Alvin Chandra, Joana Eichenberger
PUSTI BAGAN ("Garden for nutrition")
technologies_779 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Varadi Daniel
Greendots
Suisse
Spécialiste GDT:
Taylor Sheila
Send a Cow UK & Greendots
WASH Advisor:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Peer to Peer Pass-on Approach with Women [Bangladesh]
Terre des hommes and Greendots introduced the Peer to Peer pass-on system to enable women's groups in Bangladesh to spread the Keyhole Garden technique within their communities with the aim of enabling year-round homestead vegetable production despite the risk of flooding and tidal surge.
- Compilateur : John Brogan
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
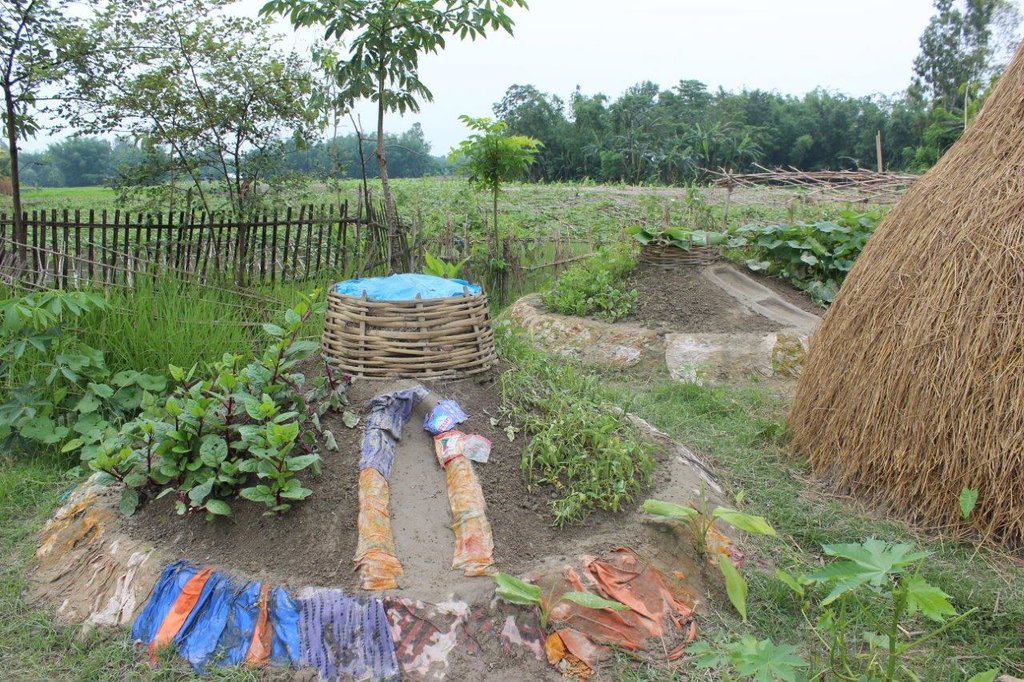
The Keyhole Garden model of homestead vegetable cultivation enhances the resilience of families living in areas with climate-related hazards, such as flooding and drought. Keyhole gardens have been shown to increase vegetable production in all seasons, thereby improving household food autonomy and dietary diversity.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
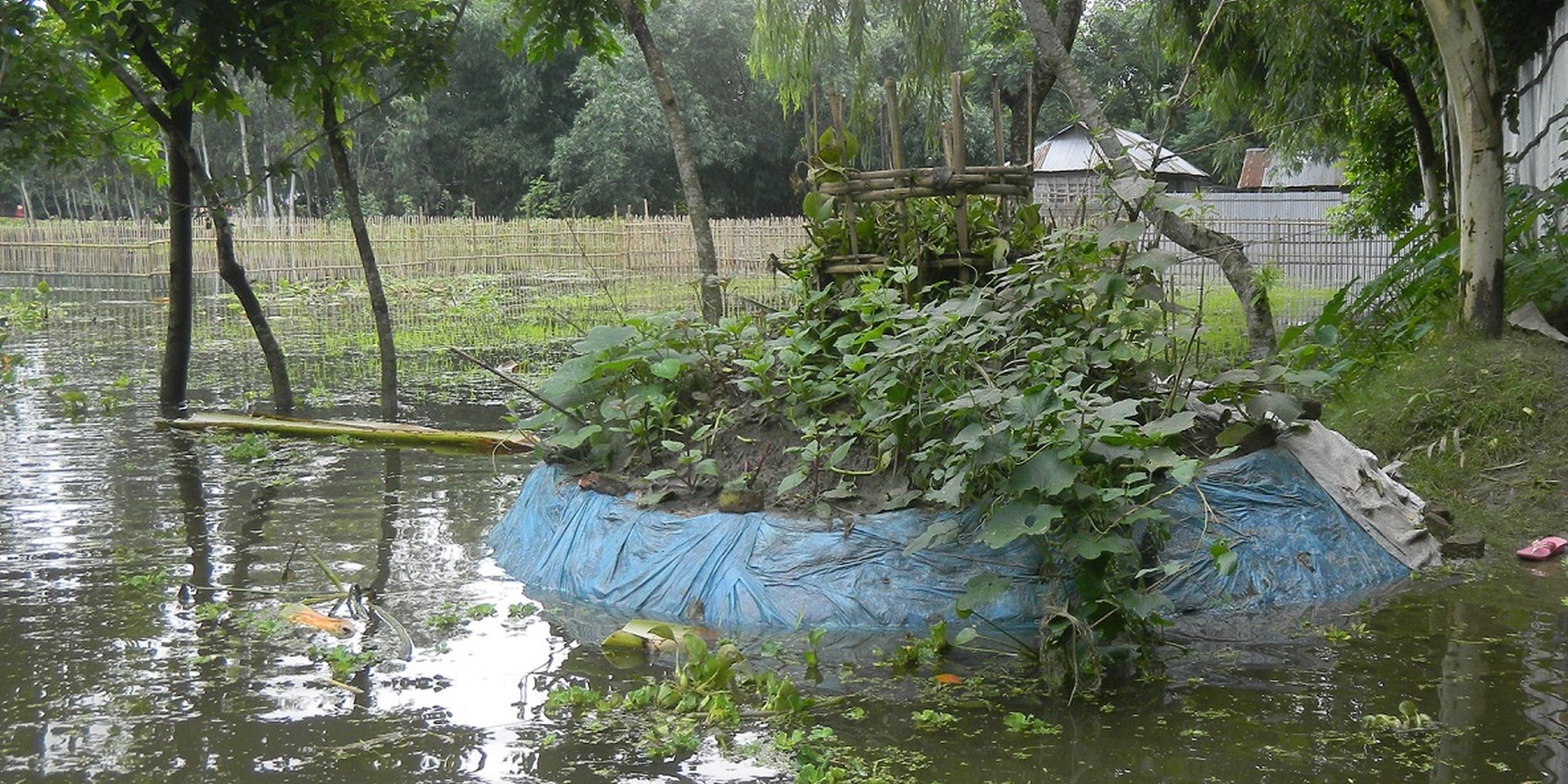
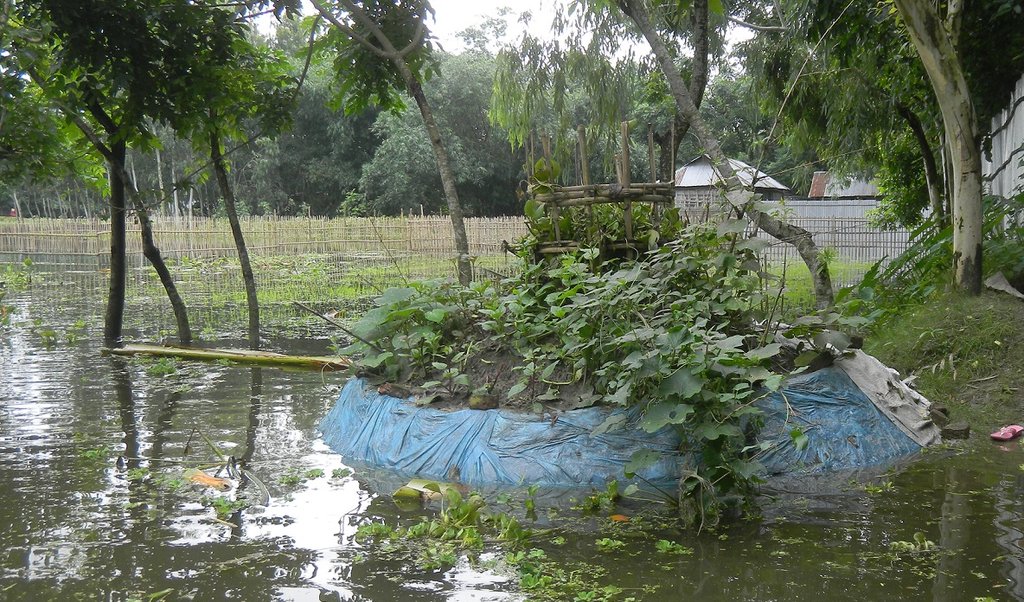
First initiated in Ugandan communities by Send a Cow UK, the keyhole garden technique is widespread in Africa. In 2011, Terre des hommes (Tdh) and Greendots piloted Keyhole Gardens for the first time in Asia, effectively adapting the design and methodology in Africa to the conditions of flood prone areas of Bangladesh, and eventually India. The garden is a good way to enhance dietary diversity, especially for poor/landless families.
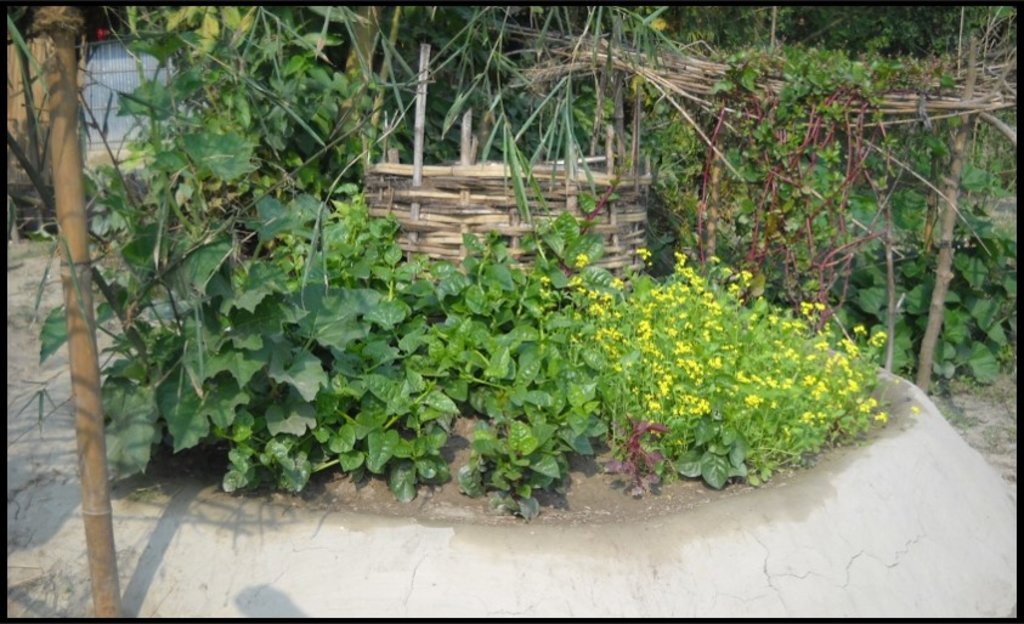
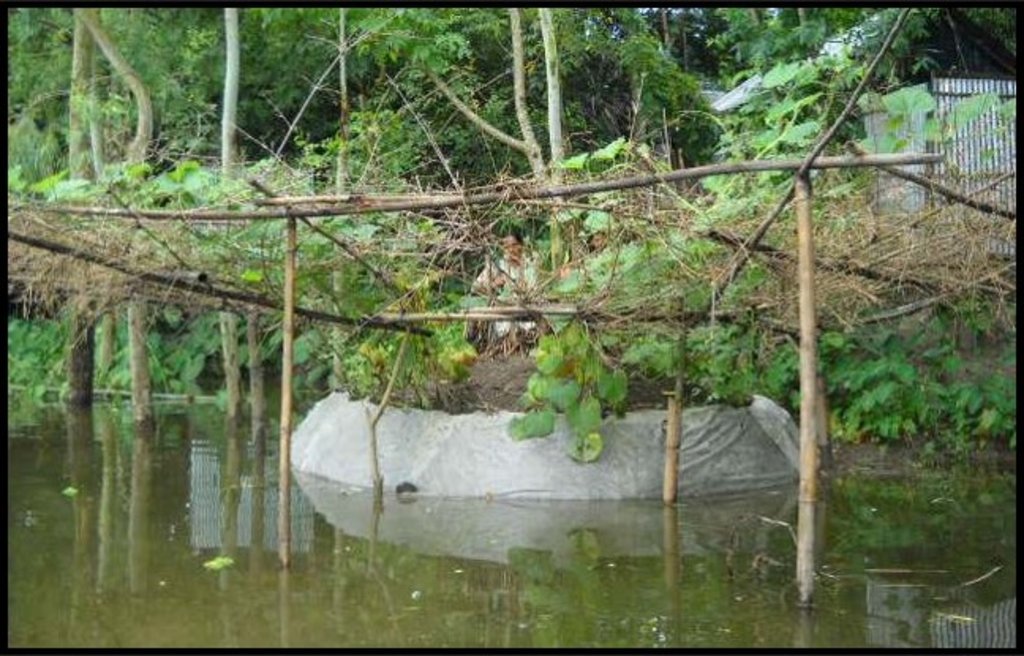
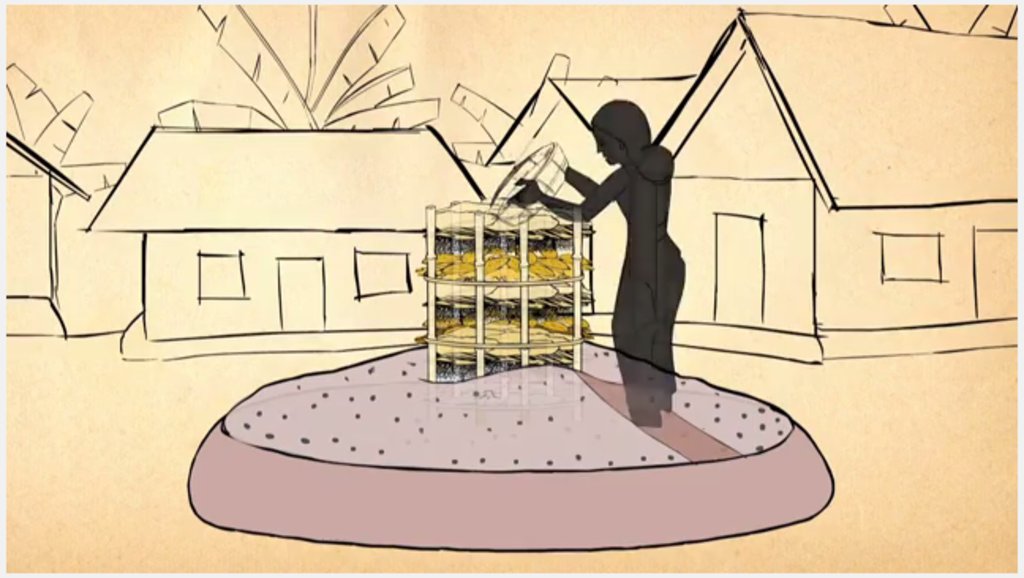
Keyhole gardens consist of a raised circular garden made of clay, shaped like a horseshoe or keyhole, with a maximum diameter of approximately three meters. For flood prone areas in Bangladesh and India, the plinth height depends on the location and is typically the same as the house plinth to resist flooding. A compost basket is built at the center of the garden. Organic matter (kitchen cuttings) and residual water are added on a regular basis through the compost pit. In some countries, bricks or stones are used to make the plinth.
The keyhole garden is a typical Low External Input Sustainable Agriculture (LEISA) approach that includes integrated composting, water retention, use of local materials, natural pest and disease control techniques, natural soil fertility measures, and proximity to the kitchen for both harvesting and care of the garden. In regions with mild conditions of flooding, tidal surge and drought, the garden increases the duration of gardening period during the year thus reducing the risk of disaster. In the aftermath of cyclone Mahasen, keyhole gardens demonstrated DRR utility: although many were partially damaged, none had to be rebuilt entirely. Where plants did not survive the storm, users were able to sow seeds immediately. On the other hand, the traditional ground-level plots used for pit and heap gardening were completely flooded / waterlogged and unusable.
Benefits of the technology include: compact size, proximity to the household for convenient maintenance and harvesting, composting of kitchen cuttings in the basket; and an ergonomic structure (raised, accessible). The small size is also ideal to facilitate training on vegetable growing, soil fertility and pest & disease management to first-time gardeners and students in schools. Keyhole gardens are highly productive—in Lesotho a typical garden can satisfy vegetable needs for a family of eight persons (FAO, 2008). Combined, these factors are scalable as an appropriate technology for landless and marginal farmers. In Bangladesh, the gardens enabled families to produce vegetables even during the monsoon period. As the keyhole garden normally does not need to be rebuilt every year it is a more efficient technique in the long-term than traditional methods such as pit and heap.
Users say that their garden produce tends to be larger and tastier than conventional gardens or market produce; and many indicated that they were able to meet their own vegetable consumption needs and to sell surplus or gift vegetables. For some women it was difficult to access sufficient amounts of soil, which meant that they needed to walk long distances to build the plinth. (Fortunately many received support from other villagers.) Secondly, during the monsoon, while most of the land is flooded, the keyhole garden remains dry. Consequently, it may provide shelter to certain animals (e.g. rats) and attract higher number of pests. Regardless of these two limitations users agree that the benefits greatly
outweigh any observed limitations.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
https://vimeo.com/44042261
The Keyhole garden was originally developed by African farmers to preserve their crops from the wind and the sand. Locally adapted in Bangladesh in Afzal’s vegetables garden with the help of Terre des hommes staff, the Keyhole garden can also protect the crops from the heavy monsoon rain and the salt water brought by flooding and storms. These literally destroy the crops. Widely adopted, it could help in preventing malnutrition by preserving the farmer's crops.
“Two days ago, my vegetable garden was wrecked by salt water and the monsoon rains”, says Afzal, who was the first person to test the new design proposed by Tdh and its technical partner Greendots. “The storm destroyed everything – except the keyhole garden, which is intact.”
Date:
14/06/2012
Lieu:
Patharghata, Barguna District, Barisal Division, Bangladesh
Nom du vidéaste:
Julien Lambert, Image of Dignity
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bangladesh
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kurigram District / Rajshahi and Barguna District / Barisal
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kurigram municipality (Kurigram), Patharghata Union (Barguna)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
Kurigram and Pataharghata, Bangladesh
Applied in homesteads.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2012
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- atténuer le changement climatique et ses impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Homestead Gardening
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - quinoa ou amarante
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- légumes - melon, citrouille, courge ou cucurbitacées
- légumes - autres
- légumes - légumes-racines (carotte, oignon, betterave, autres)
- tomatoes, cauliflower, brocoli, watercress, eggplant, cucumber
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- plantes et herbes médicinales/ aromatiques/ pesticides - pérennes
- chili
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 3
Précisez:
In Bangladesh the gardens produced in all seasons, with most challenges coming in the dry season due to soil salinity in some areas.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Winter/Summer seasons
Commentaires:
Winter Season: red amaranth, spinach, green chilli, tomato, eggplant, carrot, radish, onion, garlic, country bean, pumpkin, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli.
Summer & Rainy Seasons: red amaranth, green amaranth, Indian spinach, Chinese watercress, green chili, okra, eggplant, yard long bean, bitter gourd, ash gourd, cucumber, pumpkin
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
- lutte intégrée contre les ravageurs et les maladies (incluant l'agriculture biologique)
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
See details in section 2.2
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Gardens should be built in close vicinity to the beneficiary’s house, because gardens that are easily accessible and clearly visible are visited more regularly and maintained better.
The design is highly adaptable to local conditions and availability of free construction materials. The radius of the garden is 150CM and the delineated radius of the circular compost basket (in the center of the garden) is 45cm. The diagrams show (1) the location is near to house as an entry point for maintaining the garden; (2) the plinth is built to the same level of the house and a step is included where the plinth is high; (3) mulching to conserve the moisture; (4) interplanting a diversity of vegetables for both good vegetable health and good family nutrition; (5) using interplanted natural repellent plants as pest control for vegetables; (6) covering the basket during times of high sun intensity or heavy rain; (7) using liquid manures and plant teas as top dressing fertilisers.
Establishing what is the best height for your plinth very much depends on the local climatological conditions. In Bangladesh, the plinth is built from subsurface clayey soil, typically 2-3 feet in height - dependent on the location and level of seasonal flooding. The house plinth is a good gauge for how high to build the garden plinth. If the plinth is built too high, the roots of the plant will not be able to access sufficient water; and if built too low the next flood during the monsoon season may destroy the garden. Depending on dryness or soil/groundwater salinity, daily maintenance usually includes irrigating the soil. The outer rim of the plinth is protected with mud (and plastic or cloth) or stones. On top of the plinth is a mixture of soil and compost/manure (ratio 2:1) sloped up to the basket at a 30 - 40 degree angle. The central compost basket is filled with layers of fresh and dried vegetable matter, manure and ash to ensure that the soil fertility of the garden.
Women devised a number of different solutions to protecting the wall of the plinth and garden: Plastic bags, a combination of rice sacks (around the plinth edge) and plastic entrance way because of wear and tear (rice sacks erode faster), palm matting and old cloth. Some women put extra manure in the plinth walls to protect against flooding.
Sam Rich (www.fourthway.co.uk) has produced other technical drawings in addition to "How to Make Liquid Manure" such as: "How to make a Natural Pesticide" and "How to Make Plant Tea". There is also a version of the "How to Make a Keyhole Garden" in English from the experience in Africa.
Auteur:
Sam Rich: www.fourthway.co.uk
Date:
13/05/2012
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Keyhole Garden
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
U.S.$2.50
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear land; mark out basket and external boundary using rope and stick pivoted from the centre) | Anytime |
| 2. | Build plinth (highest monsoon flood level+30cm); | Anytime |
| 3. | Construct basket at the centre from local materials. Fill basket with composting materials; | Anytime |
| 4. | Bring soil and heap it around the central basket. Any available animal dung can also be added into the soil mix for greater initial productivity. | Anytime |
| 5. | Plant vegetable seeds around the garden - a mix for good family nutrition and to stop the spread of pests and diseases; | According to the seasonal varieties |
| 6. | Mulch between plants to protect the soil. | Anytime |
| 7. | Protect the walls with rice sacks or other waterproof protection if neccessary. | Anytime |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Building the garden | person-days | 3,0 | 2,5 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | clay | 20,0 | ||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 7,5 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 7,5 | |||||
Commentaires:
Firstly, building the garden requires an initial investment in terms of labour and (locally available) inputs, such as soil and wood and clayey soil for the plinth (stones and bricks are frequently used for the plinth in Africa). These inputs are available on the homestead or in the community and generally free of cost. In rare cases families paid to have soil carted to their homestead, thus increasing the initial structural costs.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding, harvesting, watering | Daily |
| 2. | Structural maintenance on the garden | Annual |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Maintenance | person-days | 11,0 | 2,5 | 27,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Structural maintenance on the garden | person-days | 1,0 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth Clay -depends on height: ex .4m plinth) | cubic meter | 11,0 | |||
| Matériaux de construction | Manure (quantity depends on design) | cubic meter | 2,0 | |||
| Matériaux de construction | Basket (sticks/bamboo with thin sticks to weave the basket | Sticks | 15,0 | |||
| Matériaux de construction | Protective material, rice bags/stones/plastic | Square meter | 18,0 | |||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 30,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 30,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
In Bangladesh, women referred to the time spent working on the keyhole garden as “leisure time” and that they do this work after they have completed their domestic chores. Women estimated 45 minutes daily of such activity to maintain the garden. Calling it "leisure time" is misleading, but it suggests that most women generally enjoy working in the garden and do not regard it as heavy labour. The daily wage of an agricultural labourer differs per region. In Tdh's project area, wages are relatively low, especially for women. While male labourers may earn 200 BDT ($2.50) per day, women usually earn only 90 to 150 BDT. For the calculation, we applied the principle of equal pay for equal work, taking 200BDT per day.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Over the last few years, people in disaster-affecteed areas of Bangladesh have become familiar to receiving during humanitarian distributions; and expect “hand-outs” if they were to participate in a development project. The Keyhole garden project, however, follows the LEISA approach and does not rely on giving free inputs to the participants. (In a few cases where the local population was lacking seeds and experience in seed production, women's groups were given seeds and training.) A lack of reliance on external inputs or subsidies contributes to the sustainability of the project. The inputs (clay, manure, sticks, rocks, etc.) are locally available and usually do not require additional expenses. This may not be the case in all contexts.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
2666,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Applied in areas with monsoon and drought like conditions in the project areas in Bangladesh.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.PRCP.MM
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
- subhumide
- semi-aride
The technology is adapted to semi-arid areas/countries in Africa like Uganda and Tanzania.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
In project sites along the Bay of Bengal
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
fréquemment
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Using a methodology called the problem tree analysis it is understood that the people living in the two working areas regularly experience health-related problems, economic challenges, and agricultural difficulties.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
The majority of the project beneficiaries are "landless" having access to small homestead areas and without cropland. Most households have access to small (< 16 decimal) or very small (< 6 decimal) homestead areas.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
<5% of pilot families growing vegetables in all 3 seasons
Quantité après la GDT:
50% of the pilot families able to grow vegetables in 3 seasons
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before the project started, the majority of the participants were not able to produce vegetables year round. Especially during the monsoon months, people were dependent on produce available at the local market. The baseline survey indicated that in both regions more than 50% of the households would cultivate vegetables for a maximum of 3 months per year and in Kurigram 30% of the participants were not able to grow vegetables at all.
This situation has changed significantly after the introduction of the keyhole gardens. At least 50% of the households were able to produce vegetables during each season. Where in the past almost no one was able to cultivate during the monsoon period, now on average 63% of the households in Kurigram and 73% of the households in Patharghata were growing vegetables in the wet season.
The summer figures are actually lower than the monsoon figures. Seeds did not germinate well, because participants were not fully prepared to deal with the dry and saline conditions during this season. Learning from this experience, and with adequate support from Tdh, participants should be able to achieve higher cultivation rates in the future.
diversité des produits
Quantité avant la GDT:
Average of 2-4 types of vegetables grown.
Quantité après la GDT:
Average of six types of vegetables grown
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During the field visits and individual interviews in June 2013, the majority of the participants indicated that in the keyhole garden they usually grow 6 or more different types of vegetables at any given time. This is a marked difference from previous years, when the majority of people in Patharghata would only grow 2 types of vegetables. In Kurigram the baseline was somewhat higher (31% cultivated 4 types of vegetables per year on average), but still significantly lower than in 2013. By increasing the different types of vegetables grown, the families have access to a more diversified diet.
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
333
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In addition to the 175 pilot keyhole gardens, an additional 158 gardens were started on homesteads either via peer to peer pass-along system or spontaneous copy/replication of the technology.
Impacts socioculturels
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The Keyhole Garden supports a diversified diet by enabling year-round vegetable production; thus boosting the resilience of homesteads exposed to extreme weather patterns (drought or monsoon/flood seasons).
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Gardens will quickly increase household vegetable production, easing economic burden and providing for the household consumption or surplus to sell or gift. The latter can increase social bonding and benefit peer to peer linkages.
Teaching
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Keyhole garden building and maintenance teaches lessons of good soil, water and vegetable management that can be transferred to field crops or plain large scale vegetable growing.
Impacts écologiques
Sols
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Precious topsoil is not lost during flooding events.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Gardens that are not submerged by floods continue to produce in the monsoon season.
Autres impacts écologiques
Surpluses can be used for selling or gifting; increased vegetables especially at times when they are not usually available enables families to save money on expensive purchases out of the normal vegetable season
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Teaching
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Keyhole garden building and maintenance teaches lessons of good soil, water and vegetable management that can be transferred to field crops or plain large scale vegetable growing.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête tropicale | modérément |
| orage local | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | très bien |
| onde de tempête/ inondation côtière | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
No long term study available.
In most cases no (or very low) investment cost in materials and a low investment cost in labor was necessary. Thus the establishment and maintenance costs are relatively low compared to the benefit of increased homestead vegetable production and access to produce for increasing dietary diversity. The benefit increases when the technology supports resilience to flooding as was the case from flooding (Kurigram), and partially from a cyclone (Patharghata).
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
333 from the pilot study. Subsequent projects by Tdh from 2013-2015 have seen over 3'500 keyhole gardens created in Bangladesh and India.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
All of the adopters did so with training but without inputs. Spontaneous adoption of the Keyhole Garden without training is not easy to measure, but Tdh's experience shows a conservative average of 11% (38 of 333 gardens).
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The technology was adapted from semi-arid zones in Africa (where soil amelioration and water conservation were priorities and materials such as stones and brick are available) to areas of South Asia prone to flood and tidal surge.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Seasonal local agriculturalists reported that gardens yielded high productivity with good vegetable quality and diversity; withstood heavy monsoon rains lasting for several days; and withstood a salt water tidal intrusion that destroyed adjacent traditional gardens. During the FGDs women clearly expressed a lot of enthusiasm for the project and all the participants indicated that they would continue with their garden, even if Tdh would no longer provide any support. One volunteer reported successfully harvesting five common vegetables usually impossible to grow in monsoon conditions: - In plain land we can cultivate once in a year but in keyhole garden we can harvest vegetables in three seasons and they don't go underwater in the rainy season - Save money for the family: don't need to buy fertilizers or vegetables and some people earn money by selling the garden product - We can collect vegetables for the children’s requirements directly from the garden when they need them - In a small space you can have lots of different vegetables and the taste is much better because the garden depends on compost – no chemicals - The cost to make is it very low, but you need labour; by our own labour we can build it - Because of composting the garden can always get nutrients |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
The keyhole garden project has been very successful and has largely achieved its core objective to improve year-round access to nutritious food from the homestead area. These benefits are summarized again as: - Appropriate size for landless homesteads, also ideal to facilitate training on LEISA techniques to first-time gardeners and students in schools. - Proximity to the household for convenient maintenance and harvesting, composting of kitchen cuttings in the basket; - Ergonomic structure (raised, accessible). - Highly adaptable to local conditions that supports resilience to flood and drought conditions. - Highly productive—families produced vegetables even during the monsoon period. - As the keyhole garden normally does not need to be rebuilt every year it is a more efficient technique in the long-term than traditional methods such as pit and heap. Therefore, the reviewer did not suggest any major changes to the technique or project; rather to focus on specific issues that could help making the project more efficient and that could help broaden its impact. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
No major weaknesses in the technology or design were expressed. However for some women it was difficult to access sufficient amounts of soil, which meant that they needed to walk long distances to bring soil to build the plinth. In coastal areas where saline intrusion in groundwater and soils is on the rise, growing and irrigating crops is difficult in the dry season. |
Some women received support from other family members or neighbours; identify a support network for families having challenges to access soil to build the plinths. Continue to look for for alternative irrigation sources and/or groundwater recharge innovations as well as soil conservation techniques to protect against salinity. Likewise, saline resistant vegetable varieties may be available. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
More careful planning of the location for the keyhole garden is needed. In Patharghata 11 women decided to relocate their garden within the first year. This suggests that the women appreciate the benefits of the garden, but having to break down and move the garden is a rather laborious activity. Not surprisingly, women who have less time to work in the homestead area, e.g. due to work or other out-of-home responsibilities, are not able to maintain their keyhole garden so well. |
Spend more time to assist the participants with identifying the most suitable locations to construct the garden for a keyhole garden in the homestead area at the start of the project. While maintaining a focus on women, involve the husband or other family members/ neighbours and ensure that they are also trained and ensure that the garden is clearly visible and can be accessed. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
50: The project evaluation took place from 4 June to 12 June 2013 with field visits in the two project areas, Kurigram and Patharghata. In total 5 Focus Group Discussions (FGD), with approximately 10 participants per FGD, were organized during this period. The core objective of the FGDs was to assess whether keyhole gardens have contributed to increases in vegetable production throughout the year and if this has lead to improved consumption practices. The additional aim of the FGDs was to learn directly from the participants about their nutritional needs and their ideas to further improve the keyhole garden project.
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
8: In addition to the FGDs the consultant carried out eight individual interviews with project
participants from the two regions. The individual interviews provided more detailed
information about production techniques and about the impact of the project at the
household level.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Al-Amin S, 2012 and 2013, Tdh Bangladesh, Monthly Situation Reports for Garden Projects (unpublished)
Taylor S, 2013, Discussion paper for the Agrobiodiversity Conference, Dhaka, 28 January
2013, “Keyhole Gardens – great potential for improving homestead crop diversity and
mother & child nutrition”
Taylor S, 2012, Tdh Bangladesh, Project Report Homestead Garden for Greendots (unpublished)
Van Hout, 2013, Keyhole Gardens: Improved Access to Homestead Vegetables and Dietary Diversification, External Evaluation and Capitalization of the Keyhole Garden Project in Bangladesh (unpublished)
Varadi D, 2011, Tdh Bangladesh Field Visit Report for Greendots (unpublished)
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
02/08/2012
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
"Keyhole Gardens: Improved Access to Homestead Vegetables and Dietary Diversification- External Evaluation and Capitalization of the Keyhole Garden Project in Bangladesh", Van Hout, R., 2013
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Freely available: Terre des hommes Lausanne Asia Desk: info@tdh.ch
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
“Keyhole Gardens – great potential for improving homestead crop diversity and mother & child nutrition”, Taylor S, 2013, Discussion paper for the Agrobiodiversity Conference, Dhaka, 28 January 2013
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Freely available: Terre des hommes Lausanne Asia Desk: info@tdh.ch
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
"Keyhole Gardens in Lesotho", FAO Nutrition and Consumer Protection Divis"ion (AGN), 2008 (with Send a Cow UK)
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.fao.org/ag/agn/nutrition/docs/FSNL%20Fact%20sheet_Keyhole%20gardens.pdf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Greendots - Terre des hommes technical partner for Keyhole Gardens in South Asia
URL:
www.greendots.ch
Titre/ description:
Send a Cow UK: How to make an African style raised bed (YouTube, ex. Uganda)
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ykCXfjzfaco
Titre/ description:
Send a Cow UK - Keyhole Garden resources (Learning from Africa: How to make a Keyhole Garden)
URL:
http://www.sendacow.org.uk/lessonsfromafrica/resources/keyhole-gardens
Titre/ description:
Fourthway's posters online: Smallholder organic agriculture (Uganda, including Keyhole gardens)
URL:
http://www.fourthway.co.uk/posters/
Titre/ description:
Fourthway's posters online: Smallholder organic agriculture (Bangladesh, including Keyhole gardens)
URL:
http://www.fourthway.co.uk/bangladesh/index.html
Titre/ description:
Terre des hommes: First Keyhole Garden in Asia (to resist storm surge/floods in Bangladesh)
URL:
https://vimeo.com/44043929
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Peer to Peer Pass-on Approach with Women [Bangladesh]
Terre des hommes and Greendots introduced the Peer to Peer pass-on system to enable women's groups in Bangladesh to spread the Keyhole Garden technique within their communities with the aim of enabling year-round homestead vegetable production despite the risk of flooding and tidal surge.
- Compilateur : John Brogan
Modules
Aucun module trouvé