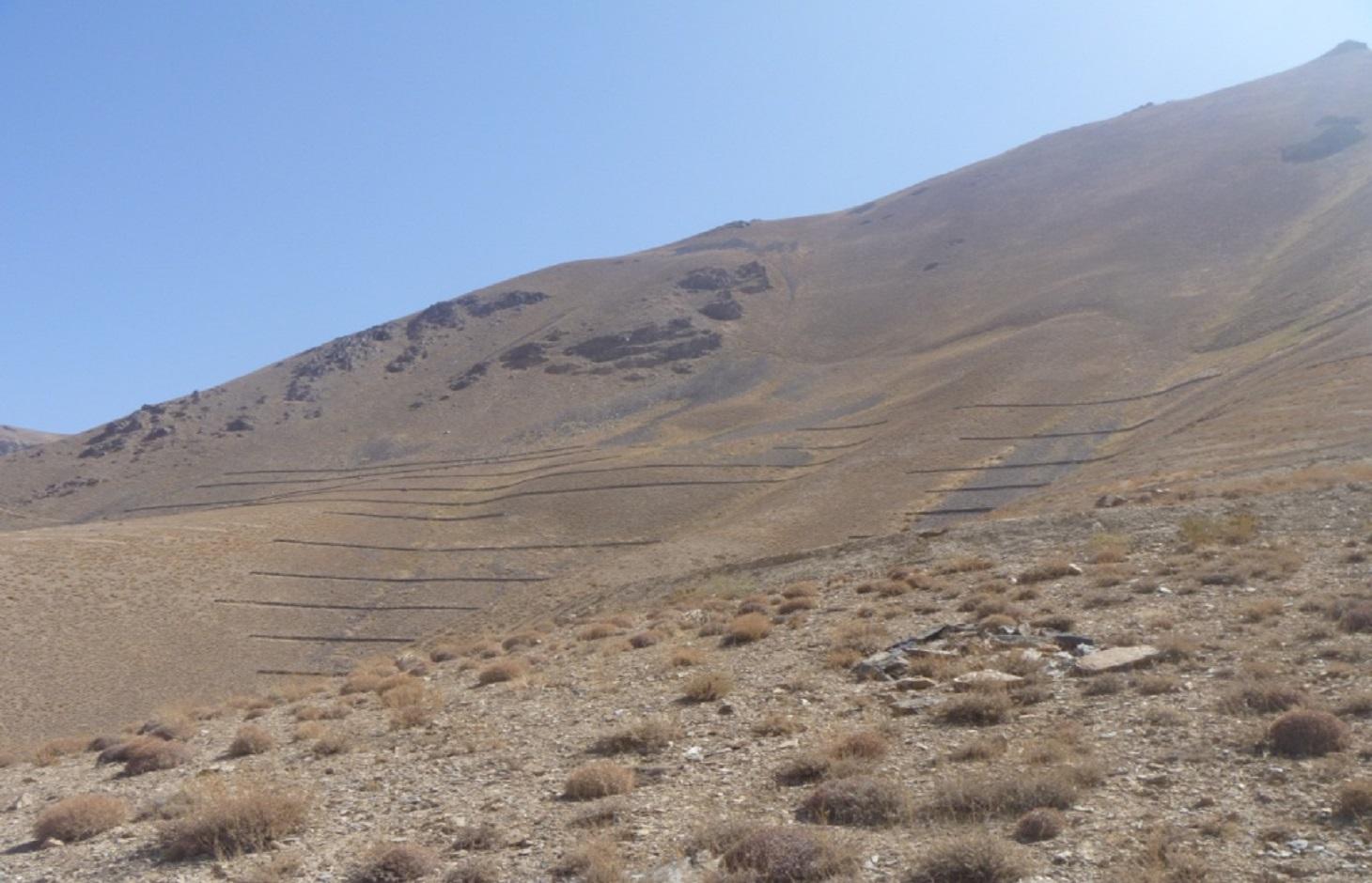
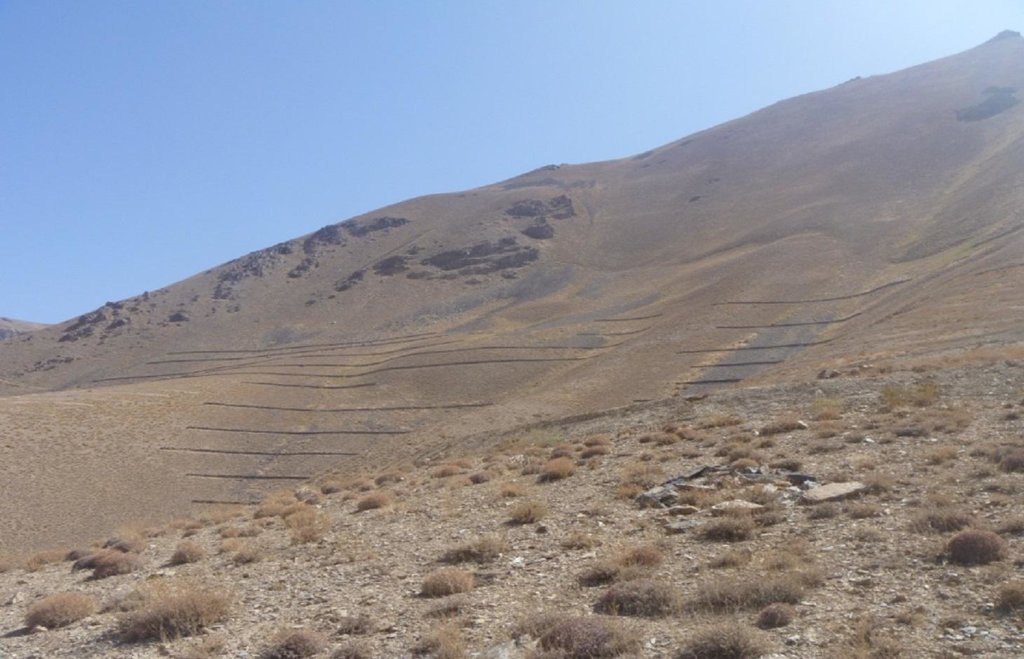
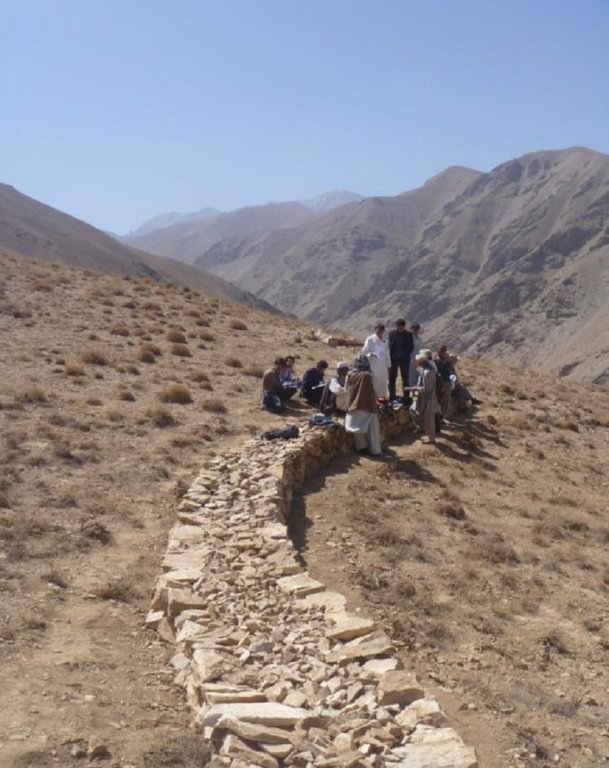
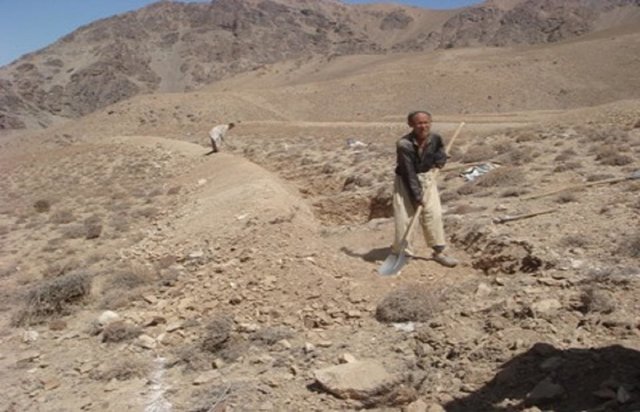
Stone wall [Afghanistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Aqila Haidery
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Alexandra Gavilano
Diwar Sangi (Dari)
technologies_1723 - Afghanistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Burger Sieger
Spécialiste GDT:
Saadat Alemi
Spécialiste GDT:
Zainullah Hazem
Spécialiste GDT:
Hussein Muhammadi
Spécialiste GDT:
Zekrullah Ahmedi
Spécialiste GDT:
Reza Ahmedi
Spécialiste GDT:
Ershad Mustafa
Catholic Relief Service
Afghanistan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Catholic Relief Services/East Africa (Catholic Relief Services/East Africa) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Community-Based Watershed Management [Afghanistan]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- Compilateur : Aqila Haidery
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Contour stone walls constructed on moderate to steep slopes to retain water and sediments and trap snow.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The Stone wall technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation with financial support of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation(SDC) and close support and cooperation of the Catholic Relief Service (CRS). The technology was applied in community land in Sar e Ahangaran (Siakhar Toghai) watershed which drains into the main Bamyan valley forming part of the Kunduz watershed of the Amu Darya river basin. The project was initiated by CRS (Catholic Relief Services) in October 2009 and the participating families were involved in each stage of intervention, including surveys, design, and implementation and monitoring.
Purpose of the Technology: The main function of stone wall is to trap snow and control run-off. Through construction work, many families received income through cash for work. About 21,519 USD were spent on the technology, with 90% contribution from CRS and 10% from the participating community. The cost for implementing Stone Wall technology was about 2,390 USD/ha.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology was applied in extensive grazing land. The stone wall technology is not new to the farmers of Sar e Ahangaran (Siakhar Toghai) as they have applied it in their private croplands as well. CRS built on this traditional technology and improved it by applying it along contour lines demarcated with A-frame and establishing it a more technically sound manner. The technology is effective in reducing snow avalanches, surface run-off, sediments, and downstream flooding leading to more crop production and less destruction of property and crops. It is tolerant to increasing or decreasing temperature and droughts. If constructed properly along the contour, the technology is not impacted by heavy rainfall or severe flash floods.
Natural / human environment: The technology was applied on hill and mountain slopes at 3000-3500 m elevation. The average annual rainfall in the area is 250-500 mm. The longest growing period is 6 months, i.e. from April to September. Due to its proximity to the Koh-i-Baba mountains, the area experiences long, severe winters of around 6 months (Mid-October to mid-April).
The participating families are poor; 10-50 % of their income is from off-farm activities, e.g. labour, migration. The villagers have moderate access to health, education, technical assistance, drinking water and sanitation facilities. Accessibility to employment, markets, energy, good roads and financial services is poor. The production system is subsistence-oriented and non-subsidized.
The effectiveness of stone wall technology was strengthened through other SLM measures, including contour trench bund, gully plugs, shrub cutting and grazing control, planting trees below the walls, and re-sowing with improved fodder species.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afghanistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sar-e-Ahangaran, Bamyan, Afghanistan
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Degradation of slopes due to biotic pressures such as overgrazing, extraction of bushes for fuel and cultivation leading to snow avalanche, flash floods and decrease in spring water quantity. Lack of soil and water conservation measures on slopes contribute to low production from agriculture and pasture lands.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Pâturages
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, Contamination of water due to floods
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
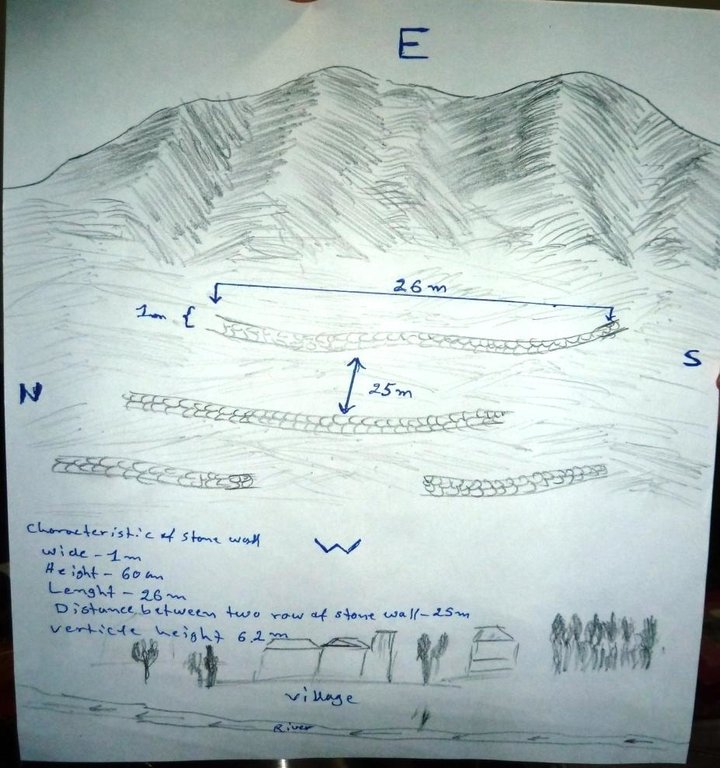
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The hand drawing shows the dimensions of the technology, spacing, area’s borders and as well as the downstream area.
Stone wall dimensions are as follows:
length: 26 m; width: 1m; height: 60 cm; foundation: 30cm in depth.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, Reduction of snow avalanches
Secondary technical functions: Improvement of ground cover due to less soil erosion
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 25
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 26
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (stone): Dry stone masonry
Auteur:
Homayoun Afshar
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
6
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundation | |
| 2. | Construction of the stone wall |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Excavation of the foundation | persons/day/ha | 13,75 | 6,0 | 82,5 | 10,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of the stone wall (skilled labour) | persons/day/ha | 39,73 | 12,0 | 476,76 | 10,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of the stone wall (unskilled labour) | persons/day/ha | 132,43 | 6,0 | 794,58 | 10,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | m3 | 132,43 | 7,82 | 1035,6 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2389,44 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 2389,44 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 10 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | No information on maintenance available. |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Duration of the establishment phase in 0.9 square kilometer in 10 months.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Bamyan has a very harsh 6 months winter with a heavy snow fall. Most of its villages face with scarcity of water during the summer
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil drainage / infiltration is good due to sandy soils
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are not going to the site culturally.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better management measures
risque d'échec de la production
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Decreased area for grazing and shrub cutting
Revenus et coûts
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As it has decreased the requirement of cleaning the field after the floods
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The project was implemented through watershed/NRM committee
apaisement des conflits
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Extra income from cash for work; less floods and hence more crop and fodder production, more spring discharge
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
And velocity
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to reduced run off velocity
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to less run off velocity
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to better soil moisture and area protection
Autres impacts écologiques
soil disturbance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to stone removal
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In spring located downstream
inondations en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to less flash floods
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
No more information is available in this regard.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Appropriate information is not available.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some of the involved farmers who have applied this technology have as well implemented this technology on their private annual croplands by their own initiative, not as technically precise as executed in the projects.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a growing trend towards the adoption of the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Reduces flash flood and sediments How can they be sustained / enhanced? combine the existing structural with vegetative measures |
|
Downstream spring water quantity improved How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetation around the spring catchment |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Less foundation of the structure | Combination of the structure with vegetation; foundation should be better |
| Stone avalanche if heavy rainfall happens | Combination of the structure with vegetation |
| In some areas, stones are not available, hence, the technology cannot be applied | Option for other measures |
| Compared with contour trench, stone wall cannot absorb much runoff | Combine with vegetative measures |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Community-Based Watershed Management [Afghanistan]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- Compilateur : Aqila Haidery
Modules
Aucun module trouvé