Wetland in the Stabė River [Lituanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jovita Mėžinė
- Rédacteur : Egle Baltranaite
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Šlapynė at Stabės Terespolis
technologies_5996 - Lituanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
co-compiler:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Klaipeda University (KU) - Lituanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The installation of this wetland contributes to reducing the ecological debt to nature by restoring natural complexes, reaching a balance between environmental and economic interests, and promoting sustainable farming conditions in one of the most important and valuable natural areas of central Lithuania.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
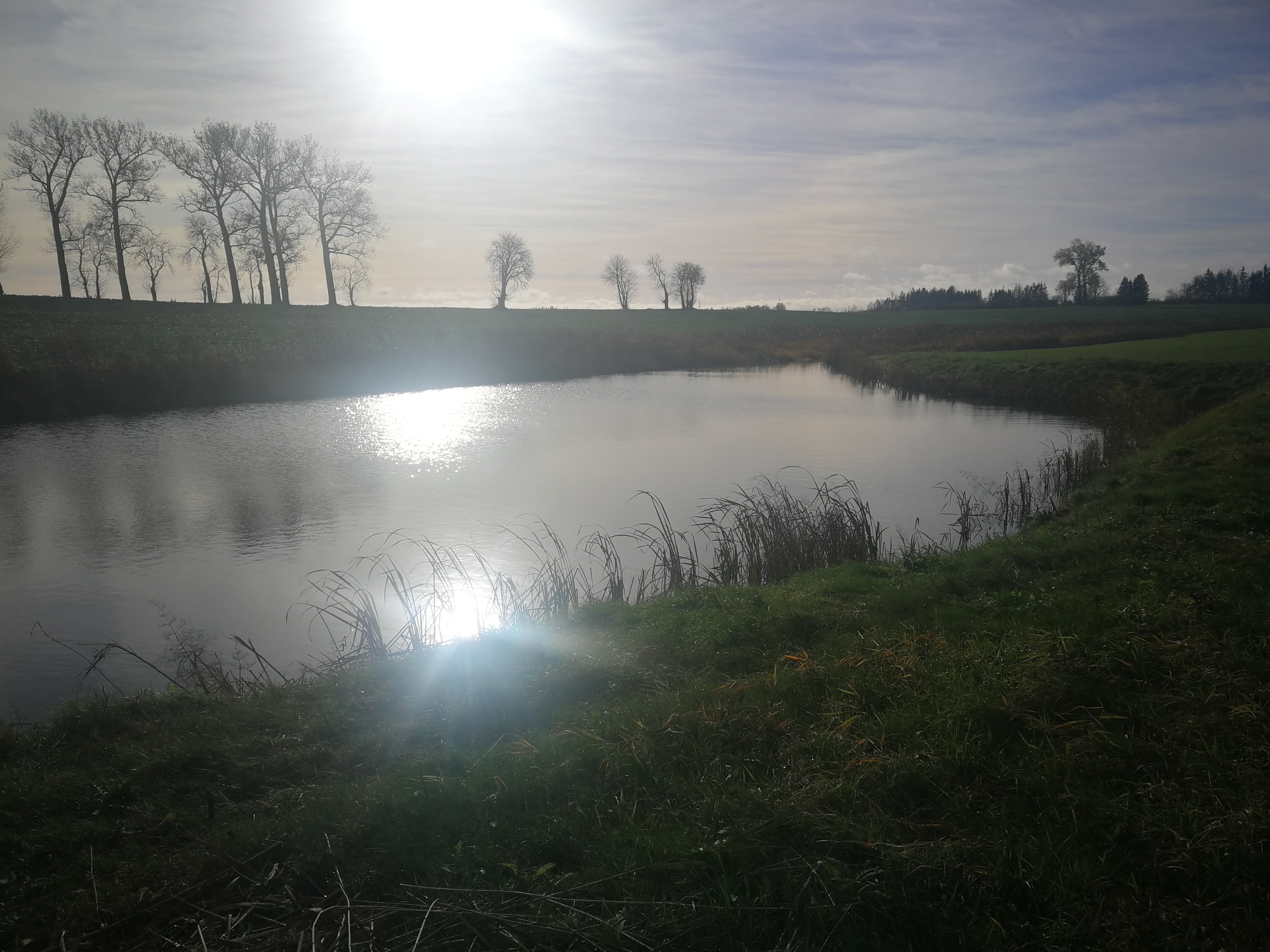
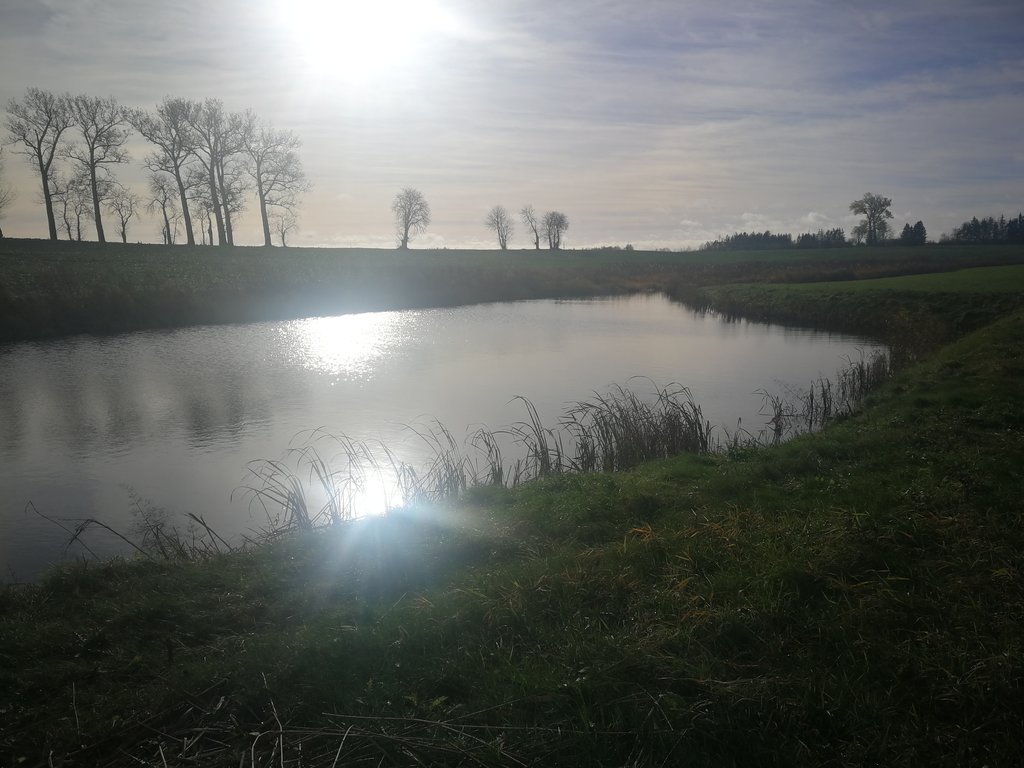
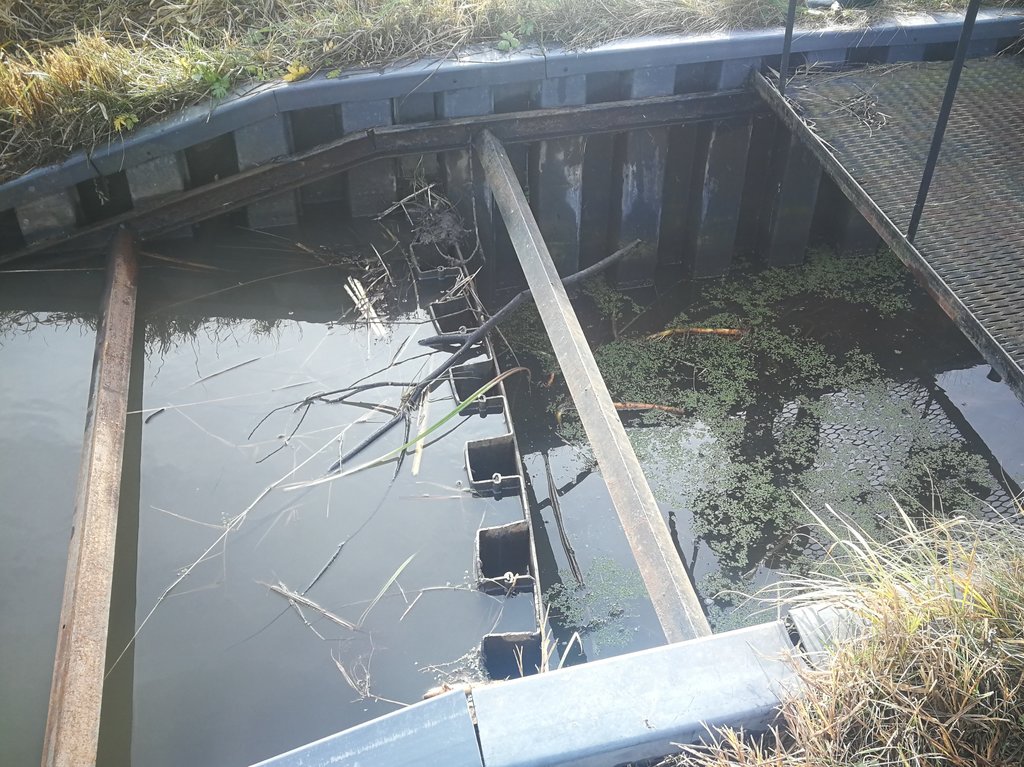
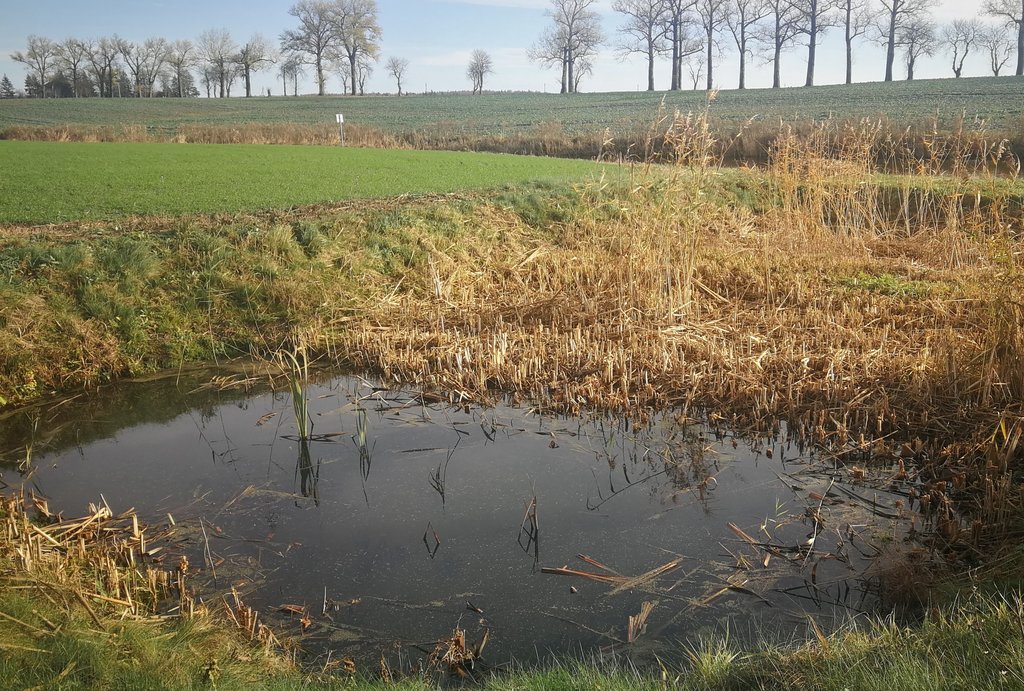
In the lower part of the river Stabė, 1.8 km from its mouth, a wetland of 2.38 ha has been installed. The wetland was constructed by artificially flooding the valley. Corrugated metal plating was used at the inlet and outlet of the wetland to protect the stream banks. While most Lithuanian wetlands are peaty, this one is not. Over time, the surface layer of the wetland has been altered by the hydrophytic wetland-specific plants, their species composition, and the degree of decomposition of these plants. Sediments washed down from the fields accumulate here. The organic matter in these sediments creates the typical habitats of saturated organic soils, which are effective in terms of nitrogen - and especially phosphorus - retention.
The wetland has four main sections. The deepest part covers 0.21 ha and is up to 2.0 m deep. Sediments are deposited here. When there is a decrease in flow, these sediments can then be removed mechanically and transported to fertilize the adjacent fields. The next section covers 0.94 ha and its depth is less than 0.5 m. It is covered with wetland vegetation. The third section works as a filter and the water is aerated. It is protected by a dyke, 6 metres in length, perpendicular to the direction of flow. The dyke is formed from soil and pitched with stone and gravel. The maximum depth of the water in this section is 0.1 metres. The fourth and final section is where the surface water is treated by macropytic vegetation. It covers 1.2 ha and is from 0.2 to 0.5 m deep. Barriers help prolong the period that the water is held.
The wetland was designed to retain nutrients in the spring and reduce their concentrations downstream. Through an ongoing research programme, the impact of the wetland has been monitored from the start. In the first year, vegetation had not become established so there were no impacts. However in 2020 and 2021 there were very positive results in terms of nutrient capture.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Lituanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kėdainiai district
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Terespolis village
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2015
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
EEE Grants. Project implemented by the Environmental Protection Agency at the Ministry of Environment
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Marécages, zones humides

Autre
Précisez:
Land not used for agricultural purposes for a long time
Commentaires:
land use has changed to agriculture because the wetland has helped to drain the farmland area
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres improductives
Commentaires:
Note: the wetland has enabled the surrounding area to become farmland through drainage and fertilization with excavated silt.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion/ protection des zones humides
- New wetlands establishment
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bh: perte d’habitats

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- s'adapter à la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Land owner started using the field for agriculture after the establishment of this wetland.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
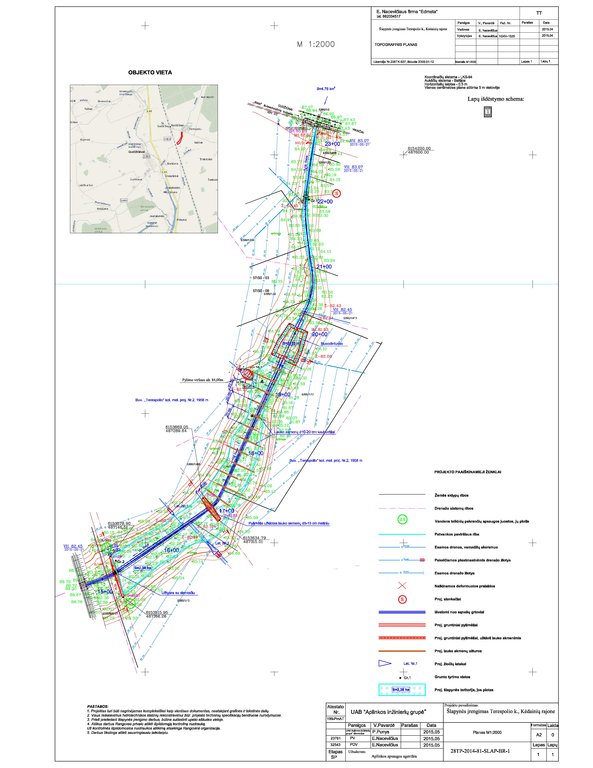
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The wetland is designed from four main parts. The deep part is where sediments are deposited in the event of a sudden decrease in water flow rates. These sediments can then be removed mechanically and transported to appropriate locations.
The shallow part with barriers increases the residence time of surface water in the wetland. In this part, only the artificially induced water level and the loaded strips of field stones that direct the flow of water is loaded, thus increasing the residence time of the surface water.
Completely shallow part up to a depth of 0.1 m. It is a 6.0 m wide underwater embankment with an anti-erosion coating and fieldstone layer, through which the water is aerated and cleared.
The fourth shallow part is where the surface water is treated by macrophyte vegetation.
More technical pictures and detailed description of the technology can be found in the report "Šlapynės įrengimas Terespolio k., Kėdainių rajone (Implementation of wetland in Terespolis village, Kedainiai district) " on https://old.gamta.lt/files/%C5%A1lapyn%C4%97s%20projektas1550671582565.pdf
Auteur:
E. Nacevičiaus firma "Edmeta" and UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė"
Date:
2015
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
wetland
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
2.38 ha
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
EURO
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the river part | autumn |
| 2. | Bank establishment | autumn |
| 3. | Construction of the deep part | autumn |
| 4. | Construction of the shallow parts | autumn |
| 5. | Lower barrier works | autumn |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Preparation of the river part | total costs | 1,0 | 2038,0 | 2038,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Bank establishment | total costs | 1,0 | 2340,0 | 2340,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of the deep part | total costs | 1,0 | 2776,0 | 2776,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of the shallow parts | total costs | 1,0 | 9135,0 | 9135,0 | |
| Equipements | Lower barrier works | total costs | 1,0 | 1053,0 | 1053,0 | |
| Equipements | Preparation of the river part | total costs | 1,0 | 2300,0 | 2300,0 | |
| Equipements | Bank establishment | total costs | 1,0 | 3228,0 | 3228,0 | |
| Equipements | Construction of the deep part | total costs | 1,0 | 11833,0 | 11833,0 | |
| Equipements | Construction of the shallow parts | total costs | 1,0 | 3750,0 | 3750,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Lower barrier works | total costs | 1,0 | 3655,0 | 3655,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Preparation of the river part | total costs | 1,0 | 258,0 | 258,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Bank establishment | total costs | 1,0 | 7336,0 | 7336,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction of the deep part | total costs | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction of the shallow parts | total costs | 1,0 | 34363,0 | 34363,0 | |
| Autre | Lower barrier works | total costs | 1,0 | 5482,0 | 5482,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 89591,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 89591,0 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Total cost covered by the project.
Commentaires:
The price is calculated for the whole wetland (89591.00 EUR). The establishment costs indicate the actual expenses that occurred in 2015.
Project preparation 9,09 %, Labour 43,36 %, Construction materials 31,25 %, Equipment 16,30 %.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Vegetation observations and removal of excess vegetation | once a year |
| 2. | Measurements of sediments and their removal | once a year |
| 3. | N and P measurements and removal of priming | depending on the measurements after fertilization |
| 4. | Animal regulation and removal of damage | depending on the needs and season |
| 5. | Other activities (after floods, vandalism) | after events |
Commentaires:
The maintenance activities depend and differ on the year. Not every year there is a need to remove sediments or excessed plants. Sometimes were is a need of reintegration or replacement of plant material, especially after winter.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
5000,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Since the wetland was established form the project funds, the project team UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė" is responsible for the maintenance of the wetland until the end of the project. After the end of the contract - the successor or authorized person of its results, local farmers or members of rural communities will be responsible for the maintenance of wetland.
Commentaires:
The estimated costs are based on the report "Pasklidosios vandens taršos mažinimo priemonių įrengimo pilotiniame baseine darbai [Establisment of measures to reduce diffuse water pollution in the pilot basin]" presented in 2016.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Inflation is one of the most affecting factors. The real costs of the last years are not publicly available.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Sandy loam with high organic carbon
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production increased by drainage and return of sediment to the cropland.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Impacts écologiques
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
diversité des habitats
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
These are observed impacts by the land owner
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| températures saisonnières | été | augmente | bien |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| orage local | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Land user has no maintenance costs and had no establishment costs.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
No adoption
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| More even seasonality, land more suitable for agriculture. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Biodiversity supported/ sediment capture/ nature-based sustainable solution. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| More nutrients come out of the exit point of the wetland than enter in the entry point. | Accurate details of impact still under assessment |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Land user and maintenance authority (UAB „Aplinkos inžinierių grupė“).
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Project material: application, costs tables, monitoring material.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
2022
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Report about installation of the technology - UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė", 2015. Šlapynės įrengimas Terespolio k., Kėdainių rajone [Installation of wetland in Terespolis village, Kedainiai district], Kaunas
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://old.gamta.lt/files/%C5%A1lapyn%C4%97s%20projektas1550671582565.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Report about implementation of the technology - UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė", 2016. Pasklidosios vandens taršos mažinimo priemonių įrengimo pilotiniame baseine darbai [The installation of diffuse water pollution abatement measures in pilot river basins], Kaunas
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://old.gamta.lt/files/Galutine%20ataskaita%20pakoreguota.pdf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Report about installation of the sedimentation points close to wetland
URL:
https://old.gamta.lt/files/sedimentacijos%20tvenkin%C4%97li%C5%B3%20projektas1550671609855.pdf
Titre/ description:
Report of wetland monitoring in 2021
URL:
https://aaa.lrv.lt/uploads/aaa/documents/files/II%20kasmetin%C4%97%20ataskaita.pdf
Titre/ description:
Report of wetland monitoring in 2022
URL:
https://aaa.lrv.lt/uploads/aaa/documents/files/III%20kasmetine%20%2Bgalutine%20ataskaita(2).pdf
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The questionnaire is well designed, clear and concise with nice explanations and examples that makes it easy to understand what needs to written. However it was difficult to find some material to give a detail answers, especially with the maintenance costs.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé