Improved Dairy Shed [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Tshering Yangzom
- Rédacteur : Haka Drukpa
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Rigsar Gi Nor Khim (རིགས་གསར་གྱི་ནོར་ཁྱིམ།)
technologies_6898 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Zangpo Shacha
Bhoutan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Improved Livestock Farming System [Bhoutan]
The approach involves a group of farmers implementing an improved dairy system. The system incorporates practices and technologies that enhance animal welfare, reduce environmental impact, and increase production.
- Compilateur : Tshering Yangzom

Dairy Cooperatives and KOUFUKU linkage for milk marketing [Bhoutan]
This approach links dairy cooperatives with a dairy plant, KOUFUKU International Limited (KIL), for milk marketing. It is an established dairy value chain that addresses milk and dairy product marketing issues and improves the livelihoods of many small dairy farmers in eastern Bhutan.
- Compilateur : Nima Dolma Tamang
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
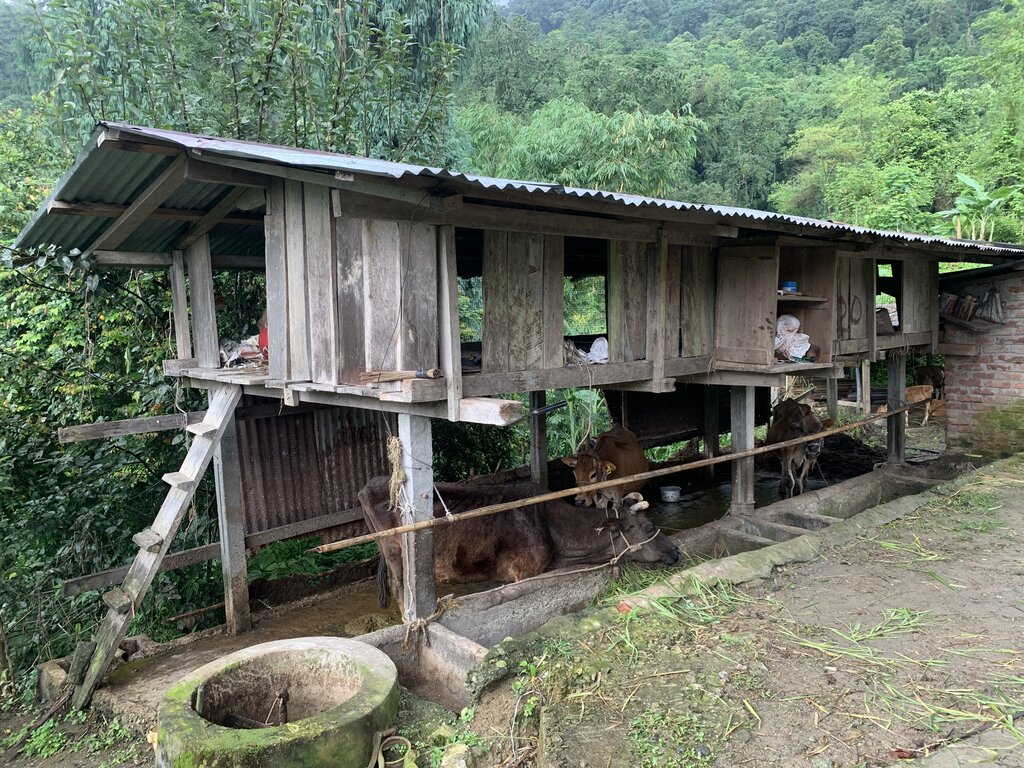
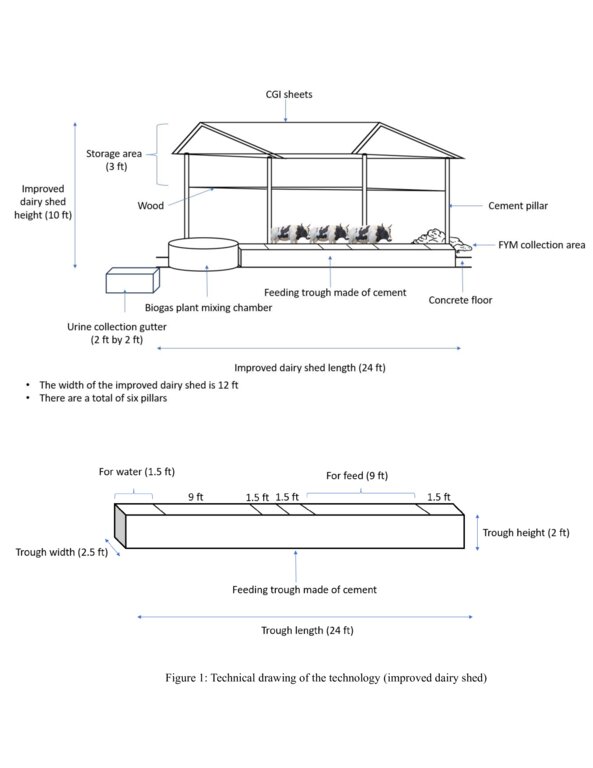
An improved dairy shed in Bhutan is characterized by concrete floors, cement pillars and troughs, enough sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, ample space for cattle movement, as well as urine and dung collection gutters and a farmyard manure collection area.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
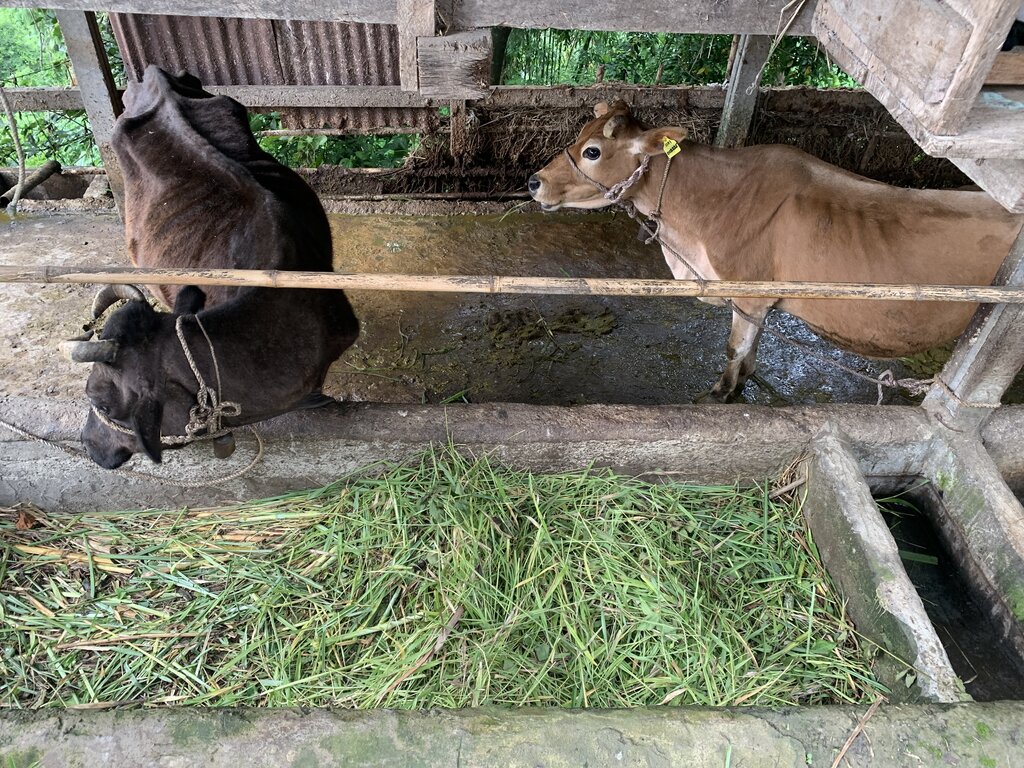
The main characteristics of the improved dairy shed are concrete floors, cement pillars and troughs, enough sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, ample space for cattle movement, urine and dung collection gutters, and a farmyard manure (FYM) collection area. The main purposes are to (a) enhance the overall well-being of animals, (b) optimize animal production, (c) minimize forest grazing and promote stall feeding, (d) increase the availability of FYM and urine for application to croplands, (e) develop pasture with fodder grasses, and (f) provide a comfortable working environment for land users.
The main inputs needed for establishment are cement for concrete floors, pillars, and troughs, and corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) sheets for roofing. The principal activities needed to maintain the technology are undertaking stall feeding instead of forest grazing, developing improved pasture with fodder grasses and trees, replacing low-yielding local cows with improved breeds dairy breeds such as Jerseys through buying or breeding (naturally or through Artificial Insemination [AI]), and better waste management.
The benefits of the technology include (a) the addition of nutrients to fields through the application of FYM and cattle urine, (b) an associated increase in organic matter, (c) better soil moisture retention, (d) availability of good quality fodder and a diverse range of forage options, (e) reduced labour due to less wild fodder collection and herding in the forest, (f) efficient waste utilization, (f) the potential manufacture and use of renewable biogas instead of liquid petroleum gas (LPG), (g) reduced land degradation due to reduction in forest grazing, (h) increased vegetation cover due to improved pasture development, (i) less soil compaction through decreased trampling by animals, (j) more comfortable working environment for land users, (k) improved livestock health and animal welfare, and (l) improved livelihoods of farmers through higher farm income. Besides these benefits, land users like the durability of the new sheds. However, one of the constraints of the technology is that the land users may lack funds to construct the sheds, or for improved cattle breeds, to justify the extra investment. These can hopefully be overcome by government support to land users through cost-sharing measures.
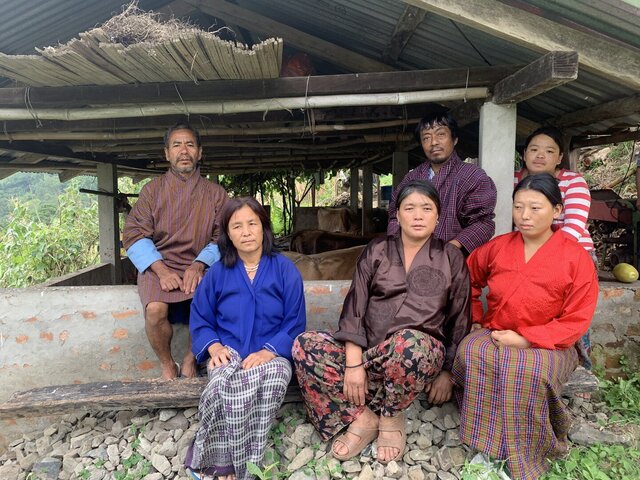
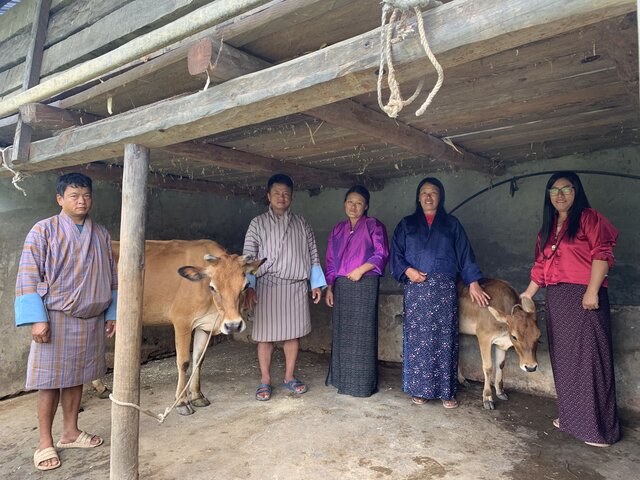
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
Improved dairy shed (a)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ciXnVkJEOZw
Improved dairy shed (b)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-AySt7Bo9Os
Date:
10/07/2023
Lieu:
Martang village, Dewathang gewog, Samdrup Jongkhar Dzongkhag
Nom du vidéaste:
Tshering Yangzom
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Martang village, Dewathang gewog, Samdrup Jongkhar Dzongkhag
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2014
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The land user adopted improved dairy shed partly at the suggestion of the livestock extension officer and partly due to his interest in improving his dairy shed.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- Cole crops, root crops, Solanaceous crops, Mustard Green
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- cultures fourragères - graminées
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- citron
- Mango, pomegranate, jackfruit
Précisez:
Vegetables have one growing season. Maize is grown twice. Fodder grasses and fruit trees have many growing seasons.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
There is intercropping among vegetables and intercropping between vegetables and fruit trees.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Vegetables are grown in rotation.

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
- 7 cattle (Jersey crosses)
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
The crop residues serve as feeds for animals and livestock wastes such as cow dung and urine are used as organic fertlizers for crops. These organic fertlizers enhance soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertlizers.
Produits et services:
- lait
Espèces:
bétail - laitier
Nombre:
7
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S9: Abris pour plantes et animaux
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Application of FYM to the field results in an increase in organic matter and an increase in nutrient availability in fields. There is better soil water retention by an increase in soil organic matter. Cattle urine also adds nutrients to the soil. Stall feeding under an improved dairy shed promotes the cultivation of fodder of good quality and variety. This helps maintain vegetative cover and prevent degradation of arable land. Similarly, stall feeding using crop residues from the field helps maintain vegetative cover and prevent the degradation of arable land. The land user feeds fodder grasses such as Super Napier and Napier that help stabilize soil and provide ground cover. Other feeds provided to cattle include banana stems, mustard cakes, straw, Guatemala grass, and processed feeds (Karma Feeds). The use of organic fertilizers such as cow dung and urine minimizes the need for chemical fertilisers that can cause loss of beneficial soil organisms, reduced organic matter, soil acidification, and nutrient imbalances in the soil.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Nu
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
82,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
500
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Deconstruction of old dairy shed that was made of wood and lacked cemented floor and pillars. | 2013 |
| 2. | Collection of raw materials to construct an improved dairy shed such as sand, stones, cement, and CGI sheets for roofing. | 2013 |
| 3. | Construction of the improved dairy shed (pillars, soling, roofing, storage area) | 2013-2014 |
Commentaires:
The construction of the improved dairy shed took months as the land user was engaged in other farm activities and only worked a few hours some days.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | manpower | person-days | 15,0 | 700,0 | 10500,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | CGI sheet (8", 0.05mm) | No | 31,0 | 900,0 | 27900,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Boulder | Truck load | 1,0 | 7000,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Gravel | Truck load | 0,5 | 17000,0 | 8500,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Sand | Truck load | 0,5 | 22000,0 | 11000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Cement | Bag | 25,0 | 400,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Planks | Cft | 150,0 | 350,0 | 52500,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Iron road | Kg | 150,0 | 75,0 | 11250,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 138650,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1690,85 | |||||
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
140000,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Government
Commentaires:
The government provided 15 bags of cement and 18 CGI sheets.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
Commentaires:
There has been no requirement of maintenance to date. There would not be the need of maintenance unless the technology is destroyed by natural disasters such as earthquake, storm, flood and so on. The technology is durable with concrete floors, pillars and troughs and corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) sheets for roofing.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
There has been no requirement of maintenance to date.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Materials and transportation cost
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
1200-2500 mm
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under. Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Moisture content-21.66%
Organic matter-15.14 %
Organic carbon-8.80%
pH-6.24
Electrical conductivity-521.33 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.44
Phosphorus-2.42
Potassium-223.07 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Clay
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The site has a variety of crops including vegetables, fruit trees, trees, and fodder grasses.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
The total land area owned by the owner is 4.65 acres (1.88 ha) which is large-scale. The average land holding at the national level is 3 acres (1.2 ha)
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop production has increased due to the use of FYM and urine from improved cattle shed.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop quality has increased due to the use of FYM and urine from improved cattle sheds. These organic fertilizers add nutrients to the soil and enhance crop growth and development.
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fodder plantation has been encouraged due to stall feeding under the improved dairy shed technology. The land user has planted fodder grasses on 1.2 acres of land. The fodder grasses grown include Napier, Super Napier, Guatemala grasses.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user has planted fodder grasses (a mix of Super Napier, Napier, and Guatemala) on 1.2 acres of land to be fed to cattle. A variety of fodder grasses are grown for stall feeding of cattle.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Animal production has increased due to improved fodder production and quality. The technology promotes integrated crop-livestock farming whereby the crop residues are fed to the cattle as feeds, another source of nutrients for the animals. Under the improved dairy shed, the animals have access to proper sunlight and ventilation, adequate water, and ample space for their movement resulting in the overall well-being of the animals.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Milk production has increased due to improved fodder production and quality grown for stall feeding. The milk provides raw material to produce a wide variety of dairy products.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production area has increased with the land user growing fodder grasses in 1.2 acres of land. The land user feeds 7 dairy cattle with these fodder grasses.
production d'énergie
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The dung from shed is used in biogas plant to produce biogas. Biogas has reduced the use of LPG gas.
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farm income has increased due to integrated livestock farming that has been promoted by improved dairy shed. Crop production and quality have improved due to the use of FYM and cattle urine. The increased milk production from stall feeding of good quality fodder grasses has enabled the land user to become a member of a milk group where the land user earns some amount every month.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user is now a member of a milk group. The increase in milk has encouraged the land user to join the group.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Food security and self-sufficiency have increased due to increased animal production and crop production.
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Stall feeding has provided an opportunity for the land user to engage in recreational activities. Earlier when there was no stall feeding, the land user had to take cattle to a nearby forest and tend them for hours.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user realizes the benefits of FYM application, stall feeding, fodder production, and biogas plant usage.
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
When stall feeding was not practised, land user had issues with his cattle entering into neighbours' fields and damaging their fields. This problem has been mitigated by the practice of stall feeding.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups has improved due to increased farm production.
Impacts écologiques
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil cover has increased due to fodder grass cultivation on 1.2 acres of land.
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Nutrient cycling has increased due to integrated livestock farming.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil organic matter has increased due to the addition of FYM to fields.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Vegetation cover has increased due to fodder grass plantation on 1.2 acres of land.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Biogas plant has reduced the use of LPG gas and methane emissions.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
There hasn't been notable off-site impacts.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| températures saisonnières | été | augmente | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | augmente | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
25 households out of 28 households have adopted the technology
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| An improved dairy shed made of cement, gravel, and stones is more durable than the old dairy shed made from wood. |
| Addition of nutrients in fields through application of FYM and cattle urine. |
| Increase in organic matter due to FYM application in the field. |
| Availability of good quality fodder and a diverse range of forage options. |
| Reduced labour due to reduced fodder collection and herding in the forest. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Efficient waste utilization. |
| Biogas has reduced the use of LPG gas. |
| Reduced land degradation due to reduction in forest grazing |
| Increased vegetation cover due to improved pasture development and reduction in forest grazing. |
| Stall feeding reduces soil compaction through trampling by animals. |
| Better soil moisture retention by increased soil organic matter. |
| Comfortable working environment for land users. |
| Improved livelihood of farmers through higher farm yields and better household income. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The land user has designed the slurry inlet chamber of the biodigester plant near feeding troughs so the inlet chamber has to be relocated. | Relocate the biodigester. |
| Lack of funds to buy improved breeds. | Government support to land users through cost-sharing measures. |
| Lack of funds for improved dairy shed construction. | Government support to land users through cost-sharing measures. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
1
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
1
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/07/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Thapa, L., Choden, D., & Tamang, N. B. (2019). Adoption of Improved Dairy Production Practices by Dairy and Non- Dairy Farmers’ Groups.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lokey-Thapa/publication/334507972_Adoption_of_Improved_Dairy_Production_Practices_by_Dairy_and_Non-_Dairy_Farmers'_Groups/links/5d2ec146299bf1547cbd248a/Adoption-of-Improved-Dairy-Production-Practices-by-Dairy-and-Non-Dairy-Farmers-Groups.pdf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
National Soil Services Centre. (2011). Bhutan Catalogue of Soil and Water Conservation Approaches and Technologies. National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forests, Royal Government of Bhutan, Thimphu.
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/95/
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
There is a need to increase number of respondents to get realistic data.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Improved Livestock Farming System [Bhoutan]
The approach involves a group of farmers implementing an improved dairy system. The system incorporates practices and technologies that enhance animal welfare, reduce environmental impact, and increase production.
- Compilateur : Tshering Yangzom

Dairy Cooperatives and KOUFUKU linkage for milk marketing [Bhoutan]
This approach links dairy cooperatives with a dairy plant, KOUFUKU International Limited (KIL), for milk marketing. It is an established dairy value chain that addresses milk and dairy product marketing issues and improves the livelihoods of many small dairy farmers in eastern Bhutan.
- Compilateur : Nima Dolma Tamang
Modules
Aucun module trouvé