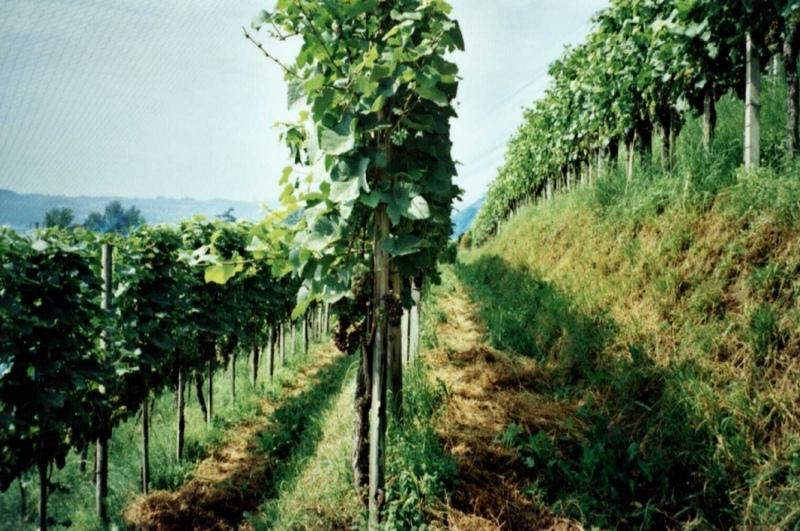
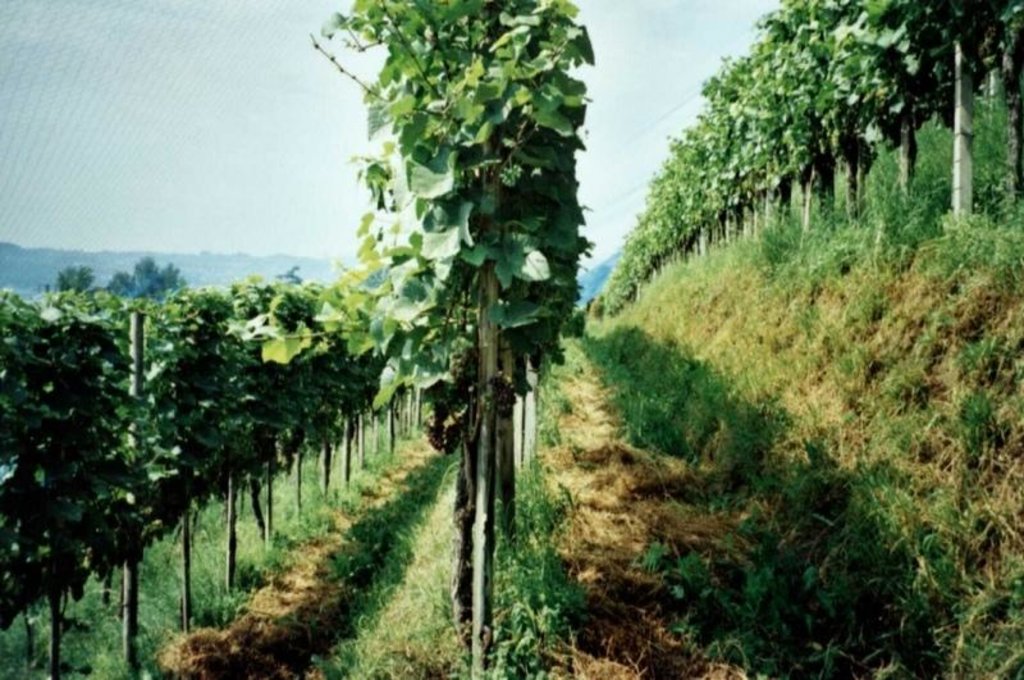
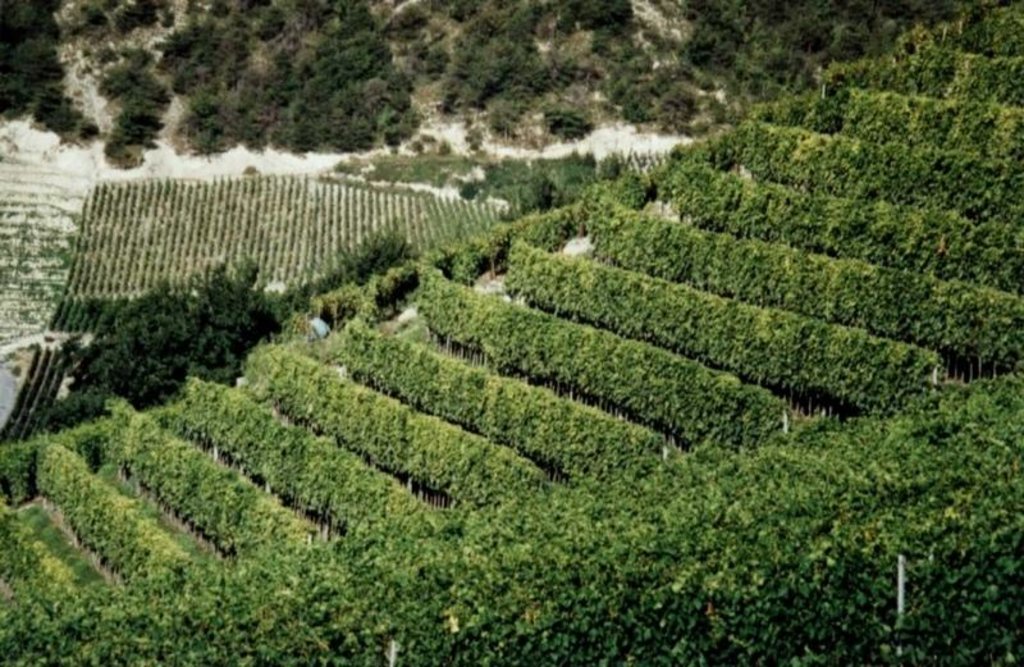
Contour small bench terraces with permanent green cover in vineyards [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
Ganzjährig begrünte Kleinterrassen im Rebbau
technologies_1011 - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Weissenbach Peter
+41 (0)43 783 61 11
info@faw.admin.ch
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture-FAW
Postfach 185, 8820 Wädenswil, Switzerland
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Spring Jean-Laurent
+41(0)22 363 44 44
info@rac.admin.ch
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture-RAC
CP 254 1260 Nyon 1, Switzerland
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Louis Hannes
+41 (32) 315 14 41
johannes.louis@schafiser.com
Louis Weinbau
Schafisweg 37a, 2514 Schafis, Switzerland
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Hasler Lukas
Hasler Weinbau
Moos 43, 2513 Twann, Switzerland
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture (FAW/RAC) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
27/01/2004
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Farmer initiative within enabling environment [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Initiative and innovation of land users, stimulated by government's technical and financial support.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Contour small bench terraces with stabilising permanent green cover in steep sloping vineyards.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Description: The vineyards of the region are all, for micro-climatc reasons, more or less sloped. The technology is applied on steep to very steep slopes. It ist characterised by two elements: 1) small bench terrace with one contour-oriented vine row per terrace and 2) an initially sown all-year green cover of the soil surface for stabilisation reasons (green cover is also used between vine rows which are oriented up and down the slope, eg not terraced, see SWI01).
Purpose: Main purpose of the terrace construction is a possible mechanisation on steep to very steep slopes. Direct purpose of the green cover is the stabilisation of the small terraces, indirect but important purpose is the prevention of soil degradation, especially soil erosion by water and - secondary - to protect soil surface from compactation when using mechanised equipment.
Establishment: The terraces are constructed by external specialists and heavy machinery (walking excavator, type "Menzi Muck") and are considered to serve for a whole life cycle of the vine (20-40 years). The green cover is sown since stabilisation is needed from the very beginning on. The duration of the establishment is 3 years. Because of insufficient root length of young vines agronomic and vegetative measures differ from the "normal" measures: For reasons of competition the space around the freshly planted vines is kept free from vegetation with a hoe.
Maintenance: the topsoil is ripped from time to time with fuel driven machine (spade machine tracked by tractor). Cover vegetation is either cut or chopped and serves as mulching . Herbicides are applied around the vines. Minimum tillage and cutting / mulching may additionally serve to mobilise nutrients and to increase organic matter content or to eliminate competition of cover vegetation.
Natural environment: the vineyards are mainly placed on mountain or hill slopes, below 600 m a.s.l., annual rainfall is around 1000 mm with at least one erosive storm per year. The geological underground is limy, locally layered by Molasse (type of conglomerate). Soil properties are strongly influenced by anthropogenic activities (viticulture). Main degradation problem without green cover is erosion by water.
Human environment / land use: the region has a strong wine growing tradition (several centuries), belongs to the important Swiss wine growing regions and is not very densly populated.
First experiments with green cover in Switzerland were done in the 70ies around Zürich on contour small bench terraces, in the region of the lake of Biel contour small bench terraces with green cover started to be implemented in the 80ies
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Canton of Berne
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Lake of Biel
មតិយោបល់:
The technology is applied in all winegrowing regions of Switzerland, but under different conditions.
2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The development of contour small bench terraces with green cover in vineyards was (also on the international level) essentially promoted and supported by the Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture in Wädenswil (Canton of Zürich) and Changins (Canton of Vaud)
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Major cash crop perennial tree/shrub cropping: Vine grape
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problem was decreasing soil fertility, especially throug soil erosion by water with negative off-site effects like sand- /sediment deposition and contamination of groundwater by nutrients. It became a serious problem since the 60ies when the fact became visible that the traditional labour-intensive cultivation system, which was strongly dependent on external inputss, could no longer be sustained within an industrialised agriculture system.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: a vine plantation is established for a period of 20-40 years (lifetime of a vine). Some farmers make one year of fallow between the destruction of the old and the establishment of a new plantation.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
- Stabilisation of terraces
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
The technology is applied in all winegrowing regions of Switzerland, but under different conditions. The technology described (SWI02) is based on a case study of one region
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
- Cp: ការបំពុលដី

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Cp: soil pollution, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes: fast changing basic conditions of viticulture in the last 100 years), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), fast changing basic conditions of viticulture (economy, laws)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
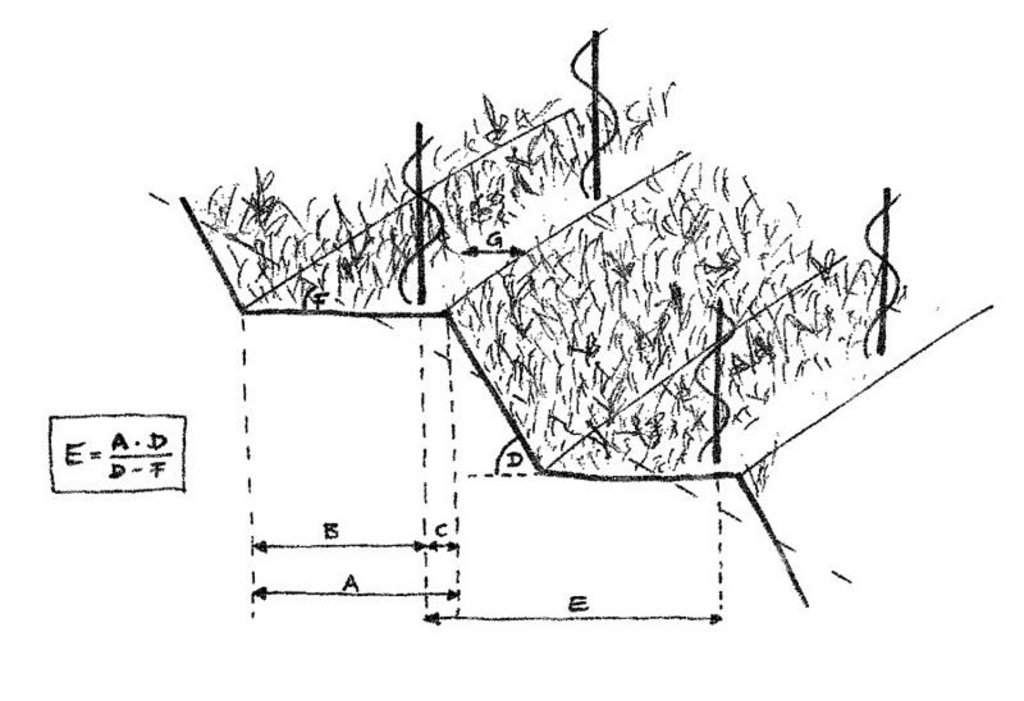
Technical drawing of small contour bench terraces with permanent green cover. A = width of terrace, B = tractor area, C = distance between vine plant and terrace edge, D = gradient of terrace riser, E = distance of vine rows, F = orignal slope, G = zone of application of herbicides (10-40 cm).
Date: June 2003
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: cut or chopped cover vegetation
Remarks: dispersed over the whole surface; if possible cutting/chopping (alternating)
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover
Material/ species: cut or chopped cover vegetation, vine leaves and cut branches
Remarks: between vine rows
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost
Remarks: only sporadically (every 5-10 year or less)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen
Quantity/ density: 0-50 kg/ha
Remarks: normally rather little nitrogen
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: potassium
Quantity/ density: 0-20 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: magnesium
Quantity/ density: 0-25 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: phosphorus
Quantity/ density: 0-20 kg/ha
Breaking compacted subsoil
Remarks: only on terrace, if possible only every second row/terrace (alternating)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: different grass species, taraxacum, veronica, legumes, calystegia, geranium...
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3 m
Spacing between structures (m): 2.5 m
Construction material (earth): only earth of parcel
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | sowing cover vegetation on the terrace riser (for stabilisation) (nonrecurring) | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | winter/spring, usually at the same time as a new plantation is established |
| 2. | letting grow natural cover vegetation on terrace (nonrecurring) | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | winter/spring, usually at the same time as a new plantation is established |
| 3. | Removing vegetation around vines (diameter of vegetation-free zone: 10 - 40 cm) | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | during season (Mai – October), 2 - 4 times, when necessary. |
| 4. | removing old vines | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring |
| 5. | deep tillage | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring |
| 6. | construction of terraces | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring |
| 7. | support of construction of terraces | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cuting and not removing vine leaves and branches | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | winter / annual |
| 2. | fertilising (mineral or manure/compost) | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | April/May / annual |
| 3. | cutting / chopping and then mulcihng cover vegetation | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | during cropping season (first time April/May) / each row 2-4 times during cropping season |
| 4. | cuting and not removing vine leaves and branches | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | during cropping season / several times during cropping season |
| 5. | breaking compacted topsoil | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | April/May / each row every 4-8 years |
| 6. | application of herbicides (glyphosates) | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | beginning of season (May), if necessary second time in Aug./Sept /once (if necessary twice) during s |
| 7. | putting back earth which war fallen from the terrace riser to the terrace | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring/if necessary |
| 8. | slightly reshaping terraces | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | winter/spring/if necessary |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: e.g.: walking excavator, hoe, mower with tracked vehicle or portable motor scythe, spading machine with tracked vehicle; knapsack sprayer or biocide t
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
(manual) labour
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Average: Biel: 1200 mm. Region of Bielersee: 1000 - 1200 mm. Neuchâtel: 930 mm.
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (For climatic reasons vines grow hardly above 600 m a.s.l. in Switzerland)
Landforms: Hill slopes (most of them southeastward sloping hills (part of the Jura mountain range))
Slopes on average: Steep (31-60%) (Vines are planted on different slopes. But contour small bench terraces are applied at steep slopes)
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil depth: From shallow to very deep (Soil depth is very irregular, at some places limestone rocks appear at the surface, at other places soil can be quite deep.But if soil is very shallow for the whole parcel contour small bench terraces)
Soil fertilits is medium (Vines are normally grown on rather marginal spots. Compared to the general productivity these soils have a medium fertility. (If measured at the vine itself, soil fertility is sufficient/high))
Topsoil organic matter is medium (loamy,silty) (without / before SWC (green cover))
Soil drainage/infiltration is mostly good, at some spots medium (depressions; when high percentage of clay)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (without / before SWC (green cover)), high (without / before SWC (green cover)) or low (without / before SWC (green cover). Depressions; when high percentage of clay)
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: This is representative for the full time winegrowers. The majority of winegrowers do winegrowing beside a regular off-farm job as a hobby. Nearly all winegrowers have implementeted the SWC technology. Probably there is no difference in hobby-winegrowers and full-time-winegrowers concernring implementation of the SWC technology.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (most of the work in the vineyard is done by hand (especially harvest)) or mechanised (some of the activities are carried out with fuel driven equipment. But mechanisation is moderate since big and heavy machines cannot been applied in these vineyards).
Market orientation is commercial/market (in the region of the lake of Biel the majority of grapes are pressed to wine an then and sold directly from the farm's wine cellar)
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha (only winegrowing land!)
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
maximum production capacity is reduced due to 1. Plantation density is smaller and 2. Capacity per vine is reduced due to slight competition of water and nutrients, intensified in the terrace riser under dry conditions
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced quality of wine occurs when strong competition of water and nutrients happen and nothing is done against it.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher susceptibility to fungal decay due to higher evapotranspiration rate with green cover and therefore humid microclimatic conditions. Other problems are competition over water and nutrients or danger of frost - negligible - only in depressions or plains (due to higher evapotranspiration rate)
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Primarily due to less costs, especially resulting from less erosion damages in the long term (because of green cover). Secondary due to marketing argument "ecological agricultural production", subsidies related to green cover (direct payment which is only
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
More and specific knowledge necessary
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Inputs for mechanisation
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Special machines needed, mechanisation is almost a must to be economically successful in the long term
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Healthier than without SWC, less application of biocides and more comfortable and healty posture of body.
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased exchange of knowledge and contacts in winegrowers society
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Research stations gained new knowledge and attention
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Among winegrowers, but perhaps also slightly among consumers (through an ecological marketing argument) or walkers (walking through a green vineyard may arise interest in green cover).
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Between generations or between farmers applying green cover and others. Reason: farmers are differently attached to traditional values and norms (i.e.: traditionally every plant was seen as unuseful weed and fought with a hoe).
Personal satisfaction / challenge
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Many farmers apply green cover see green cover as a personal satisfaction or challenge for an ecologically and economically sustainable viticulture
Acceptance by society
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Landscape and appearance of Landscape & appearance of vineyard as cultural heritage. Different values an norms of "how a vineyard should look like". Traditionally vines were planted very dense with no vegetation cover in between. Contour small bench terraces are quite new to the area (20-30 years)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially through improved water retention capacity (due to improved soil structure)
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mainly due to green cover (rather than terraces)
ដីហាប់
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Undesirable plant and animal species (i.e. mice (can hamper stability of terrace riser and terrace itself))
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Through beneficial animals
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
Biodiversity
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
High diversity due to different habitats (extensively managed terrace riser and terrace)
Soil fertility
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 90-100%
មតិយោបល់:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Contour small bench terraces with green cover are seen as good opportunity for viticulture in steep slopes. Adoption is done mainly spontaneous
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Farmer initiative within enabling environment [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
Initiative and innovation of land users, stimulated by government's technical and financial support.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល