No tillage operations, plastic nets permanently on the soil surface [ប្រទេសក្រិក]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Costas Kosmas
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Κάλυψη με πλαστικά (Greek)
technologies_1087 - ប្រទេសក្រិក
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Mentzidakis Ioannis
National Agricultural Research Foundation - NAGREF - Institute of Olive
ប្រទេសក្រិក
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUAb) - ប្រទេសក្រិកឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Agricultural Research Foundation (NAGREF) - ប្រទេសក្រិក1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
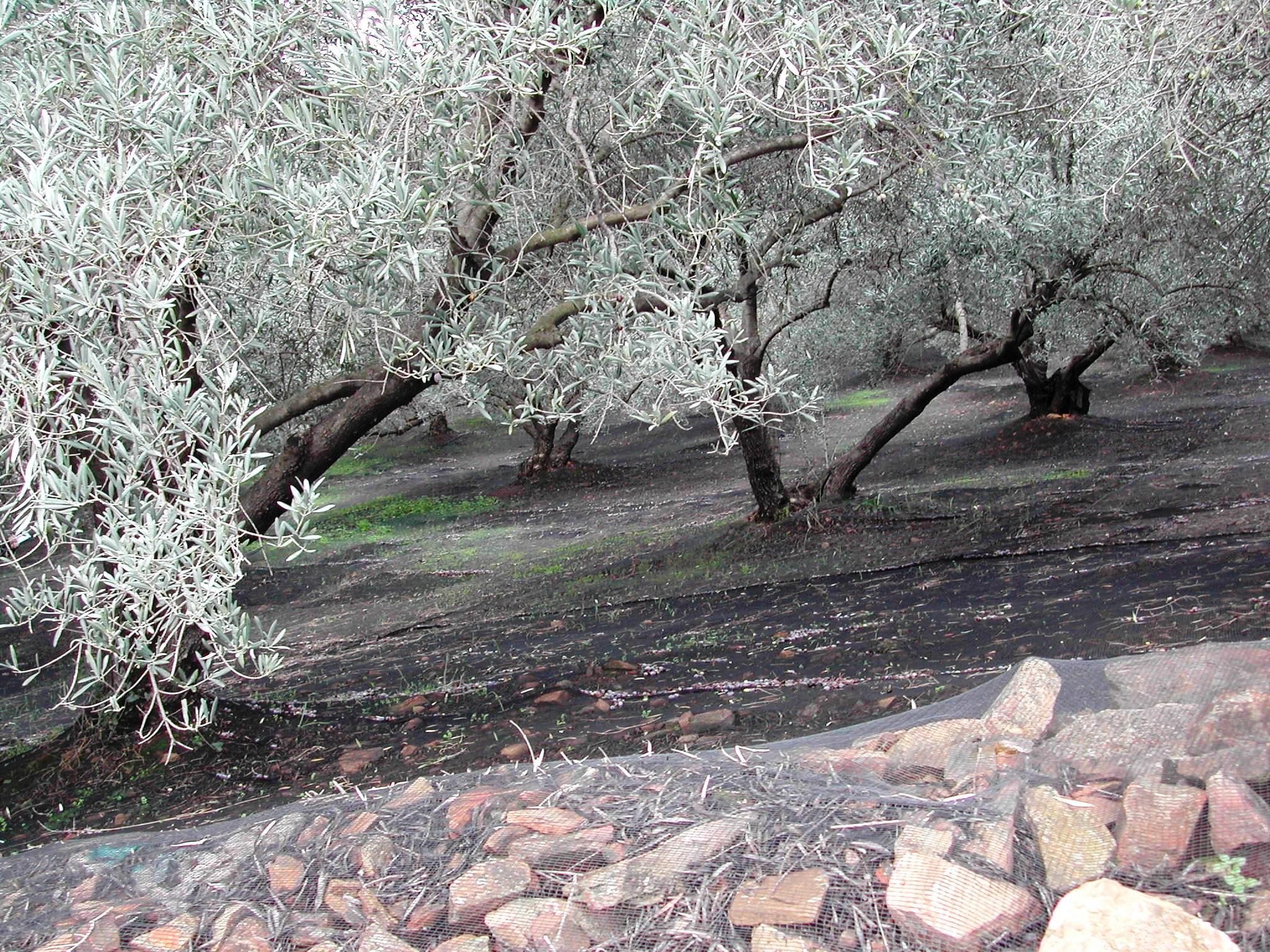
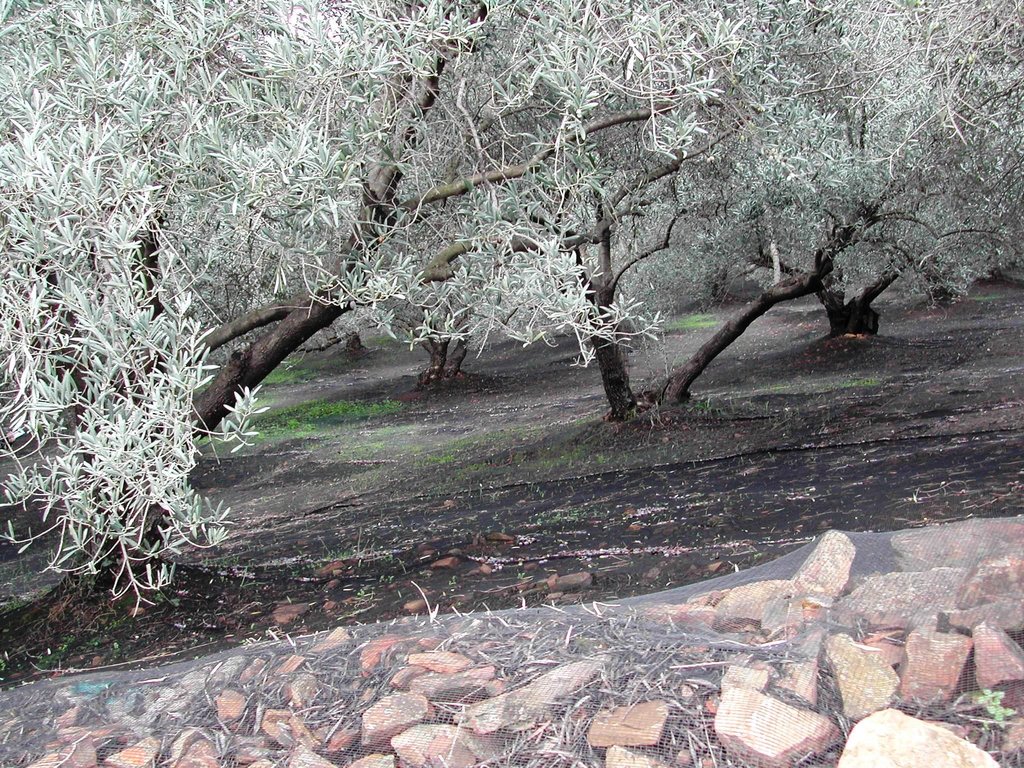
A technology which combines no tillage operations and the cover of the ground with plastic nets
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
This technology has the same main advantages and characteristics as no tillage operation against soil erosion and water lconservation. Soil erosion is drastically reduced since soil surface is protected from raindrop splashing by the existing annual vegetation and the plastic nets. Soil water evaporation is also reduced due to the mulching provided by the plant residues and the nets. Furthermore, higher amount of rain water is infiltrating into the soil compared with other traditional LMPs. The specific technique has emerged as a need to overcome obstacles to the collection of olive fruits and protection of the nets from animals. Nets are spread in the whole field (intensive cultivation) covering completely the soil surface or part of the field (extensive cultivation), so olive fruits falling down can be periodocally collected by the farmer. Furthermore, a problem arises if nets are removed from the ground and stored. Animals, like mice, prefer to go in and make their nets by destroying them. Therefore, by keeping nets in the field during the whole year they are protected from such damages. Nets are installed in the field by stones or using metallic pins of about 15 cm long which are entered into the soil. Nets can remain in the field at least 10 years. Referring to the map showing areas undergoing tillage and non-tillage operations in the study area of Chania, it can be noted that the combined technique using cover nets is applied mainly in areas with high altitude and at a rate of approximately 15% of the no tillage area.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសក្រិក
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kissamos province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Chania-Crete
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 km2.
Map
×3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- អូលីវ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 150Second longest growing period from month to month: March to June
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high soil erosion rates and lack of water for irrigation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Hig cost of olive oil production
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (soil erosion), poverty / wealth (loss in farm income)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: oxalis sp
Mulching
Material/ species: plastics
Quantity/ density: plastics a
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green manure, oxalis sp
Remarks: natural growing plant
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: tillage is not allowed since nets will be destroyed
In blocks
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Perennial crops species: olives
Other species: existing vegetation
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Euro
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1,49
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
80.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy the nets |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Installation | ha | 1,0 | 320,0 | 320,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Nets | ha | 1,0 | 2700,0 | 2700,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 3020,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 2026,85 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | replacing destroyed nets | 0.2 days/ha/year |
| 2. | reinstalling nets removed by winds or other reason | 0.5 days/ha/year |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: no tools
the cost has been calculated for the year 2009
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
the purchase of materials
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
With 6 months of dry period
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Water quality (untreated): good drinking water, for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Yes women are used to work mainly in the house
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich.
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Problem if a minimum tillage LMP is applied since nets must be removed
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
1800 Euro/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
3200 Euro/ha
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increase in farmers income and reduction the off-site effects
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
គុណភាពទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ដី
សំណើមដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
protection of the area from flooding or from animal passing over
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
Reduction of labor and protection of of harvesting materials
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- > 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
500
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Reduce cost production but create problems to the cultivation of olive groves. The major cost in olive production is labour for harvesting. By applying this technology harvesting labour is minimized to about one tenth. It can be viable at small to medium scale farms, prone to water erosion, on very steep slopes where harvesting of olive fruits by the traditional methods become very difficult. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Providing financial support |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Technologies on conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete are mainly related to land management. Olive groves can survive under adverse climatic and soil conditions supporting a significant farmer’s income under relatively low labour. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and transfer knowledge by the local institutes and specialists. The no tillage land management practice combined with plastic nets on the soil surface can be considered as an important technique protecting the land from degradation and desertification and increasing farmer’s income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By explaining the advantages and disadvantages of the technology to the farmers |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Difficulties in removing perrenial natural vegetation and spreading the fertilizers. | applying fertilizers by the irrigation system |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Too many plastics spread around in an area. Recycling of plastics is a great problem. | no overcome |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល