Area closure and reforestation with Acacia [ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Maarten De Boever
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1568 - ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Hamdi Lazar
Direction générale des fôrets
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Direction générale des fôrets - ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ីឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Ghent University (UGent) - ប្រទេសបែលហ្ស៊ិក1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Protection and reforestation of degraded arid lands in pre-Saharan Tunisia.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
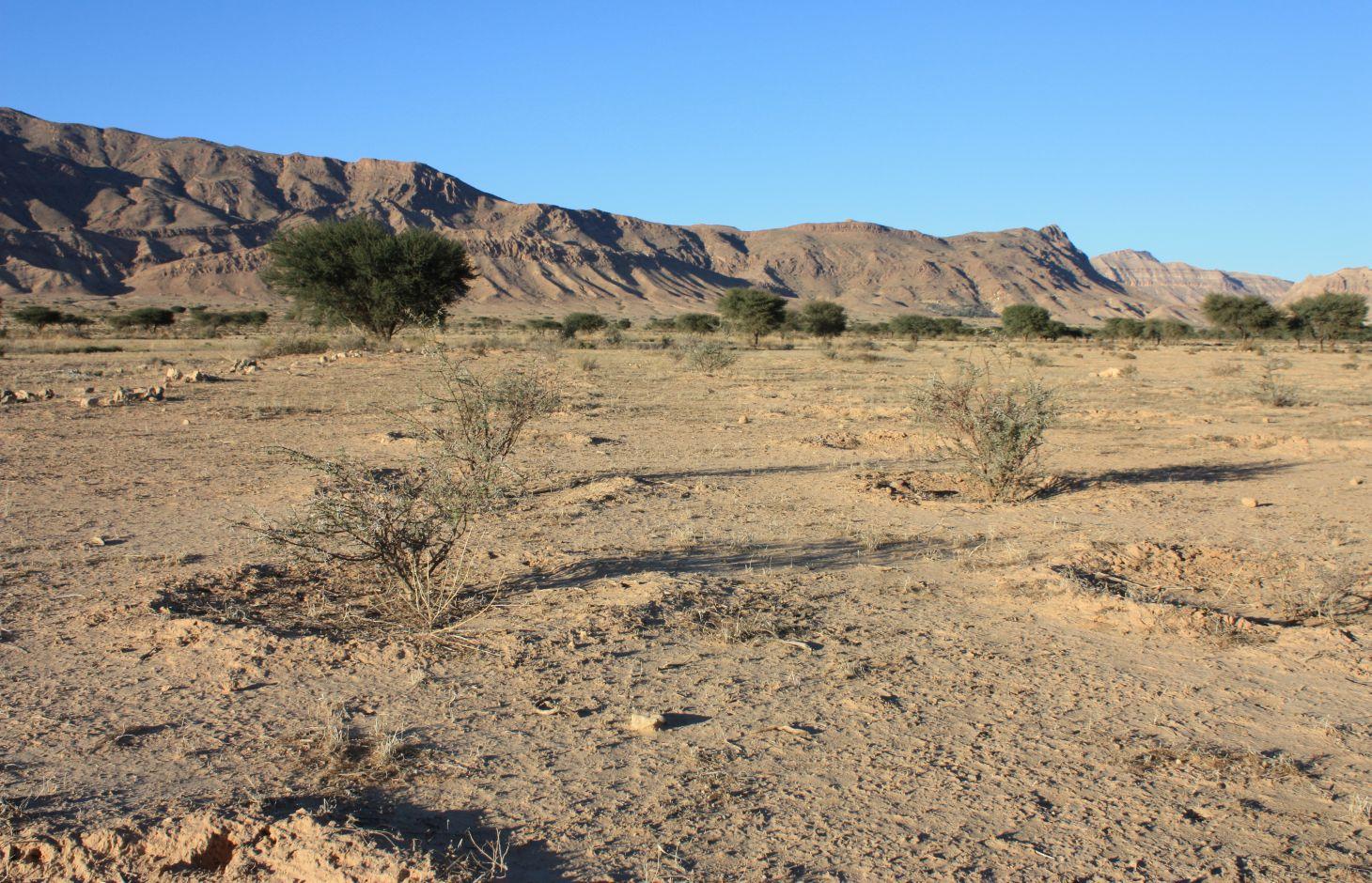
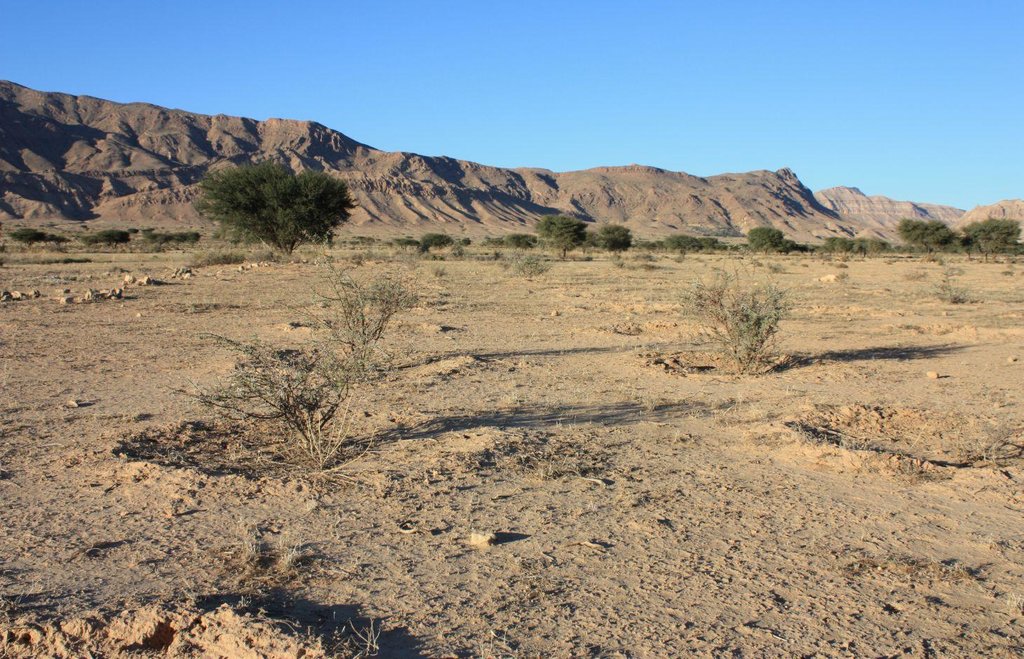
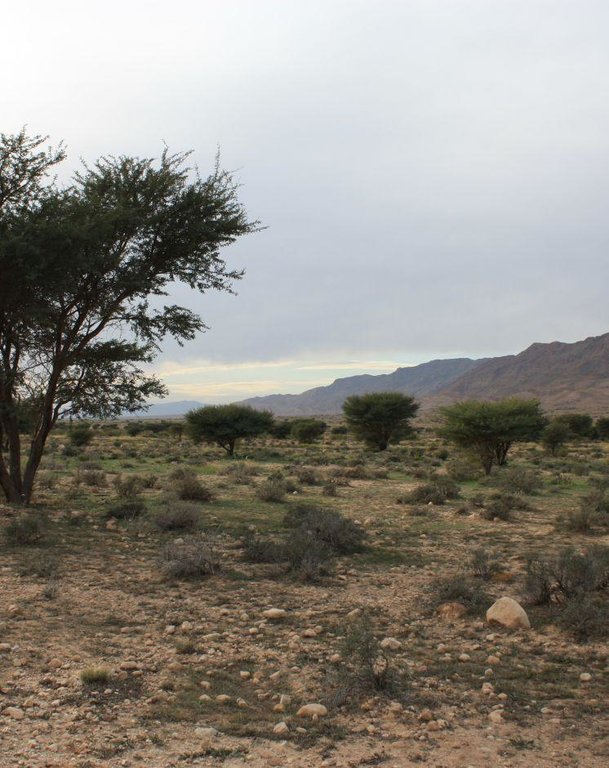
Protection and reforestation of degraded arid lands in central and southern Tunisia (Bled Talah region) with tree species Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana. A. raddiana is a native trees species which is able to tolerate extreme droughts and to persist on the edge of the Sahara desert. Acacia plantations are set up following a 3m x 3m grid using seedlings of A. raddiana. Seedlings are planted in the bottom of infiltration pits which are constructed for rainwater harvesting. Protection of the plantation area is established by means of a fence.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of afforestation is the rehabilitation of degraded drylands and restoration of the original forest-steppe ecosystem in the Bled Talah region, which suffered for over a century from overexploitation of natural resources and intensification of agricultural activities. Focus is put on the synergy between the protection of the natural resources with the involvement of local people and the improvement of their livelihoods.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The protection of the Bled Talah region was initiated in 1936 and from then on several actions were undertaken such as the construction of a tree nursery and the creation of Integral Protection Zones through complete fencing. The Bled Talah area was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1977. Bou Hedma National Park was officially created by the Ministry of Forests in 1980 covering an area of approximately 16.000 ha. The park consists of three Integral Protection Zones or core areas which are completely fenced, two agricultural zones and two buffer zones. Since the 1970s, several reforestation campaigns with A. raddiana are conducted in the Integral Protection Zones.
Natural / human environment: Arid Tunisia, i.e. the central and southern part of Tunisia, is characterized by an extremely irregular spatiotemporal rainfall pattern, a limited amount of rain (350 mm maximum per year), a limited number of days of rain (15 to 40 days a year) and a high average annual temperature (18 to 21 °C).
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសទុយនីស៊ី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Sidi Bouzid/Gafsa
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 165 km2.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- កាប់តែមួយចំនួន
- Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
- វាលស្មៅ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overexploitation of natural resources such as tree cutting for fuelwood and intensification of agriculture such as intensive grazing of cattle lead to increased pressure on the environment causing severe degradation of the orginal ecosystem.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Less arable land and reduced fodder availability in the region.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
មតិយោបល់:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- តំបន់ទ្រនាប់ (បិទការប្រើប្រាស់ គាំទ្រដល់ការស្តារឡើងវិញ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pk: sealing and crusting, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (tree cutting for fuel), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fodder), overgrazing (intensive grazing), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure, poverty / wealth
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Third goals: prevention of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
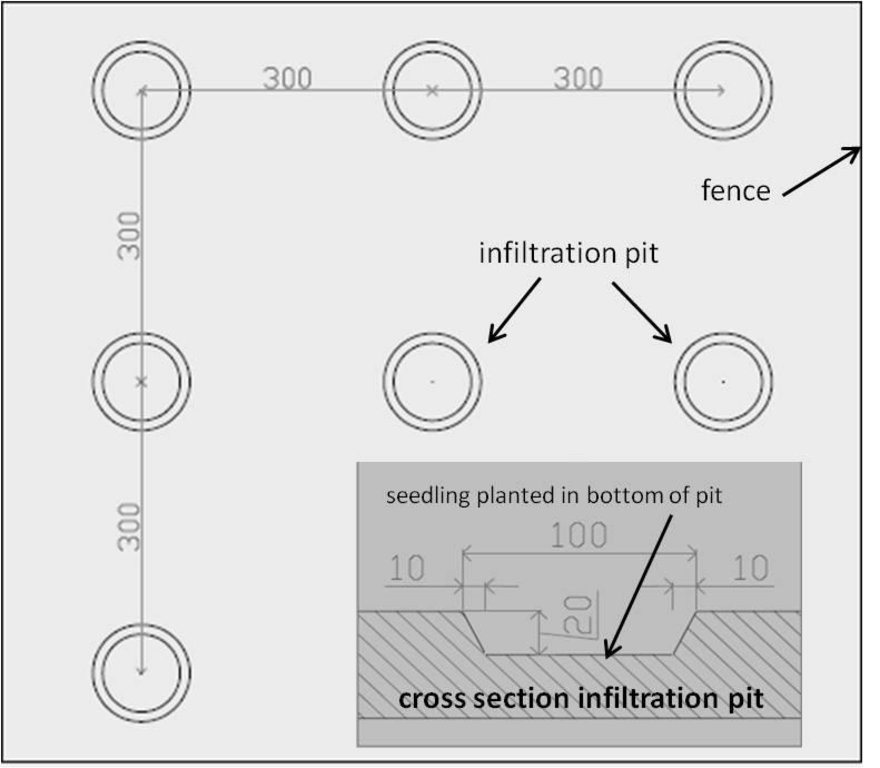
Fenced plantation with Acacia trees on a 3m x 3m grid with cross section of infiltration pit (length given in cm)
Location: National Park Bou Hedma. Sidi Bouzid
Date: 2014-02-04
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia raddiana
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Construction material (other): wire fence
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Maarten De Boever
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Tunisian Dinar
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1,65
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
6.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | seed collection | June/July/August |
| 2. | tree nursery | July/August |
| 3. | plantation | rainy season (sept-->dec) |
| 4. | installation fence | 1 day |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 330,0 | 330,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Iron wire fence | ha | 1,0 | 1600,0 | 1600,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | iron poles | ha | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 2730,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 1654,55 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 8 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | follow up plantation (irrigation) | weekly 1 day by 2 workers for 1 year |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 30,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 18,18 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The above costs were calculated for the establishment of a 1 ha fenced plantation with 1000 seedlings on a 3m x 3m grid. From collecting seeds to planting of the seedlings and fencing the plantation it takes about 8 months. Irrigation through the first year after planting is done to ensure survival of the seedlings.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The most determinate factor affecting the costs is tree nursing. This factor is not only labour intersive but also high in water demand.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Rainy season September-December
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- ស្ងួត
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil texture: coarse/medium (loamy sand/sandy loam)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium - poor
Soil water storage is low - medium
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Mainly men are involved because the establishment of a plantation is labour intensive.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ក្រុម
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The technology improves the livelihoods of local people directly through income generation from employment in the park and indirectly by the improvement of climatological conditions in the neighbourhood of the park.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
រំហួត
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Until now no land users have implemented the technology because the government does not provide any incentives/subsidies.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
protection (less soil degradation) and rehabilitation of the natural ecosystem How can they be sustained / enhanced? involvement of local people |
|
direct and indirect improvement of the livelihoods of local people How can they be sustained / enhanced? awareness raising |
|
improved soil carbon stocks How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of existing and establishment of new plantations |
|
increased biodiversity (trees act as fertility islands facilitating the growth of ground cover plants) How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of existing and establishment of new plantations |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| no tree planting initiatives undertaken by local people | incentives/subsidies from government |
| no public awareness of importance to conserve natural resources | set up of a large educational program with regular activities in the park and further elaboration of the small ecological museum |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល