Water retention polders with adapted land use (North Sea region) [ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Martin Maier
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Polder mit angepasster Nutzung zur Verbesserung des Wassermanagement (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1660 - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Kleyer Michael
University of Oldenburg
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Sustainable Coastal Land Management (COMTESS / GLUES)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Martin Maier
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk from heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in coastal lowlands. Alternative production systems will be viable within thesepolders.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 3,000 ha will be able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occa-sional flooding.
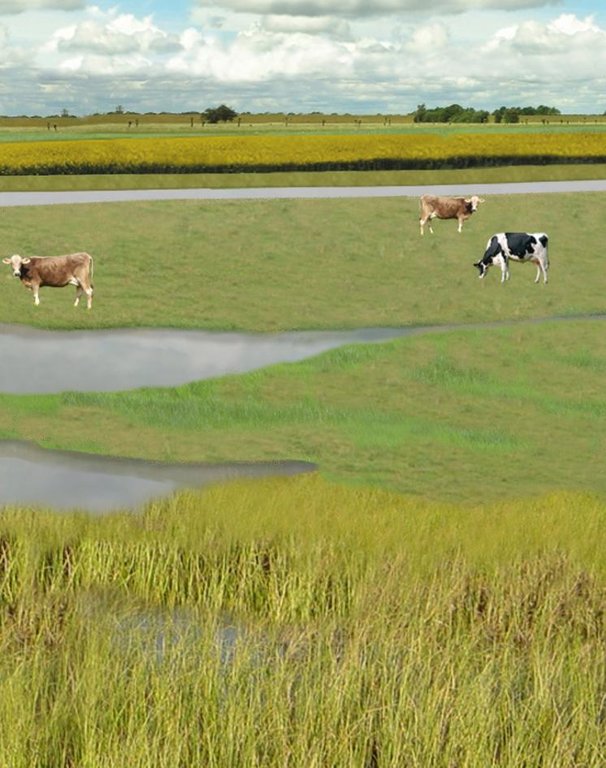
Natural / human environment: However within the proposed retention polders – the areas enclosed by the em-bankment - a change from the current intensive grazing for dairy farming and cropland to extensive grazing, open waters and wetlands covered with reeds will take place. The reeds can be harvested for their commercial value as biomass for renewable energy generation, or for other applications (e.g. thatching of roofs or industrial raw material). According to recent investigations, natural reeds growing in brackish water produce as much biomass as maize cultivated for biogas use. In con-trast to maize, no investments in tillage, fertilizer or biocides are necessary for these naturally growing reed stands. Thus the proposed land use provides an economic alternative to the current production system.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Germany, Lower Saxony
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Landkreis Aurich
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 km2.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- Agro-pastoralism ( រួមបញ្ចូលទាំងដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- wheat
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅតូចៗ/ ផលិតកម្មចំណី:
- កាត់ និងជញ្ជូន/ គ្មានវាលស្មៅសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- បង្កើនវាលស្មៅ
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមយកទឹកដោះ
- សត្វពាហនៈ - សត្វចិញ្ចឹមមិនយកទឹកដោះតែសម្រាប់យកសាច់
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- សាច់
- ទឹកដោះគោ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the current land use system in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This will reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
មតិយោបល់:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការបែងចែកទឹក និងប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកលើដី (ទឹកធ្លាក់ ទន្លេ បឹង សមុទ្រ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cs: សារធាតុប្រៃ/អាល់កាឡាំង

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
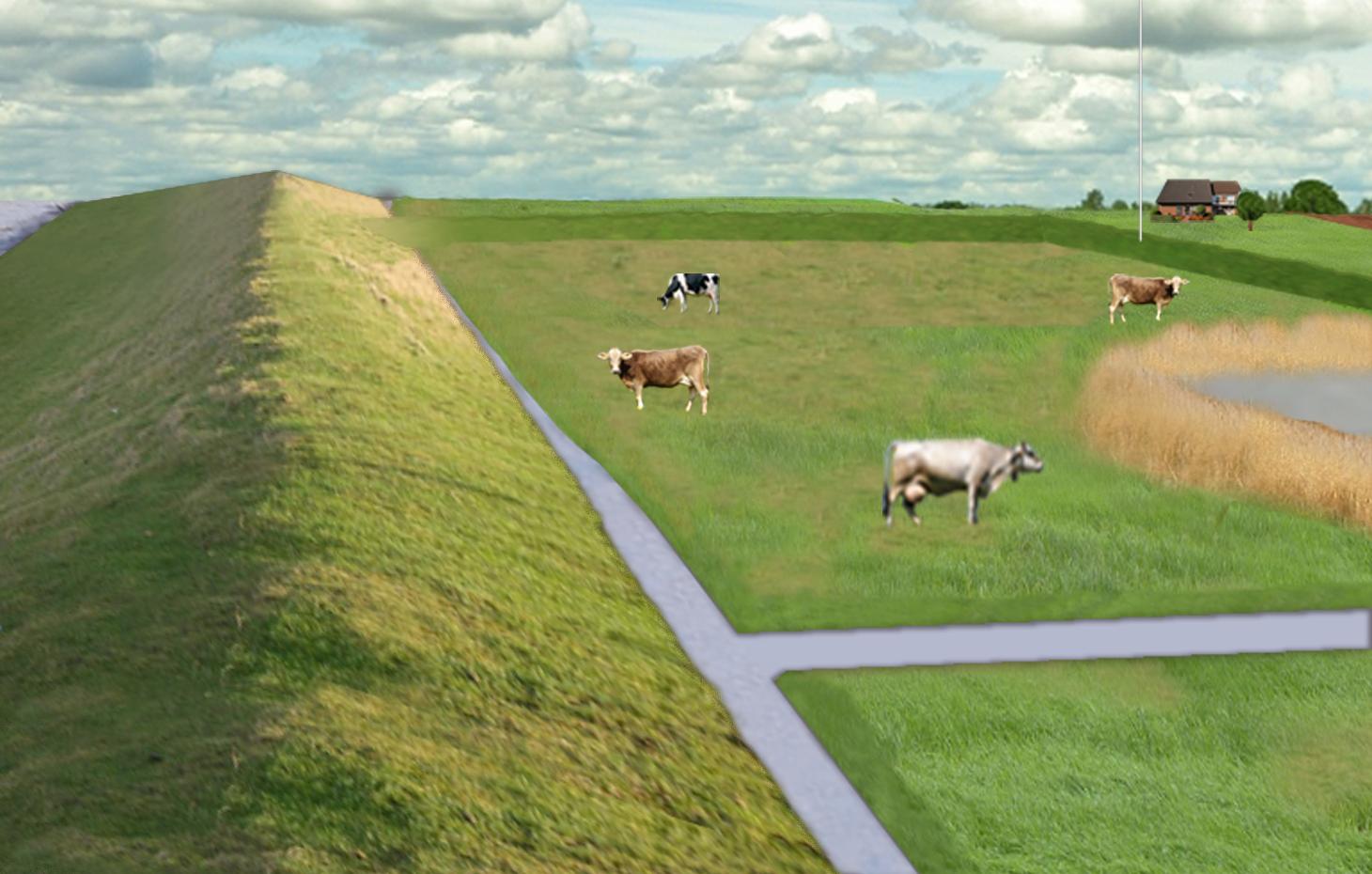
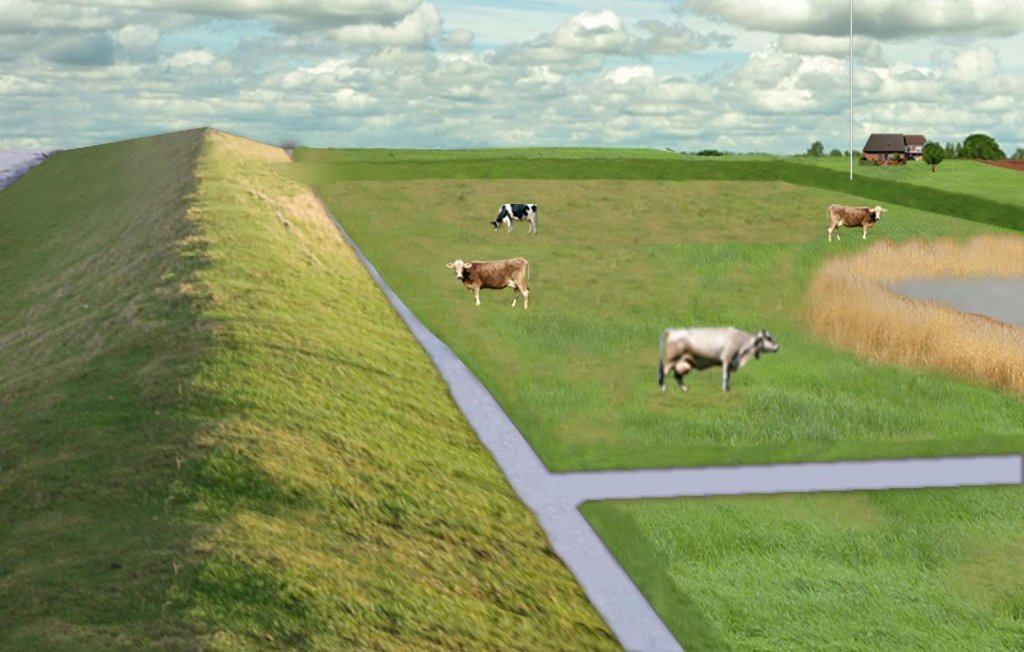
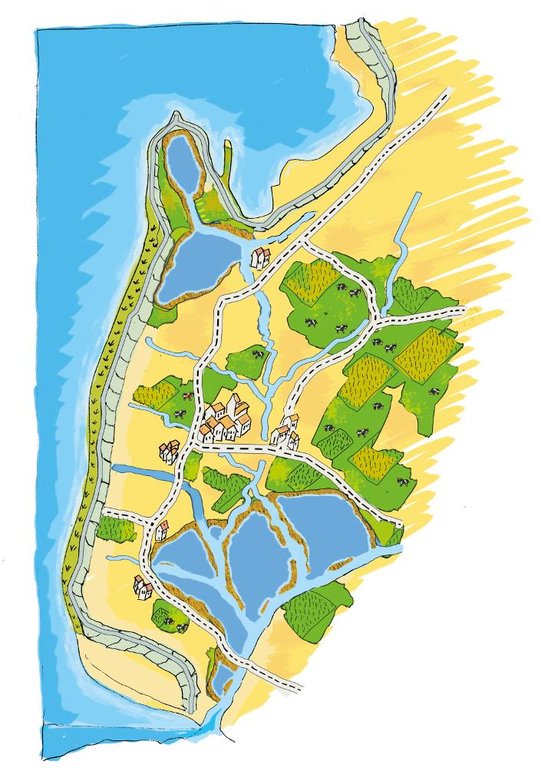
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. Large water bodies (blue) sur-rounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Extensive grazing and reed farming re-places current production systems within the reten-tion polders. The land around the retention area (higher parts of the landscape) profits from the retention areas as the risk of flooding is reduced and can be used for cropland and intensive graz-ing. Depending on the size of the retention polder a huge amount of excess water can be contained. Retention areas of 3,000 ha are able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ water. The height of the dams de-pends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for Water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 25000000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 3,000.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be adapted to hydrological conditions.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensitive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Udo Schotten
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Euro
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,94
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
100.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | during winter months |
មតិយោបល់:
Labour medium: 1 person 1 day, 1m dam, 700USD
Machine hours: 8h, 1m dam, 300 USD
Earth: 10000 M3 (Sand), whole retention area, 22000 USD
Earth: 23000 M3 (Klei), whole retention area, 53000 USD
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | 1,0 | 21000000,0 | 21000000,0 | ||
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | 1,0 | 9000000,0 | 9000000,0 | ||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | 750000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 30000000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 31914893,62 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | once a year |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | 800,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | 300,0 | ||||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Earth | 100,0 |
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The establishment costs are for a dam length of 30 km and the enclosed retention area of 3,000 ha. The establishment period will be half a year. The slope in the region determines the costs as the height of the embankments depend on this. Typical heights are from 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3. . The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of the drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.70 Euro per km including pumping costs. The maintenance cost for the whole retention area will amount to a total of US$ 2,576,200.00.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity high
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកសម្រាប់តែការធ្វើកសិកម្ម (ស្រោចស្រព)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
50% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in industry or servicing sector
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
49000 ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
46000 ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
For the whole catchment area a loss of approx. 3,000 ha (size of retention area).
ការបង្កើតថាមពល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reeds in the retention area are very productive plants and will be used for bio energy generation.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to reduction of saline influx
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Only adjusted land use takes place within retention area, therefore the expenses are reduced.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Intrusion by saline groundwater
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
គុណភាពទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
ភាពប្រៃ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Growth of reeds
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Water from retention area.
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
The benefits will be visible in the longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by local land users but this SLM technology needs to be implemented by spatial planning of the county / federal state.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology is not yet implemented by land users but first it needs to be considered in spatial planning of the county and the federal state. Land users and local experts showed during participatory workshops that there may be a chance for implementation.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
The retention area will support the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding (including strengthening of the ditch system and in-creasing pumping capacity). |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored. |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention polders prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endangered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention areas the very expensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is not necessary anymore How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractivity for touristic use in the retention area benefits for land owner can be generated and the probability to build up retention areas instead of strengthening the existing drainage system is increased. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Retention polders in an important tourism region will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism. | Include tourism concerns in the retention area (access, infor-mation, attractiveness). |
| Loss of land for agricultural production (highly productive arable land) | Establish retention area in low elevated parts, where there is not a high interest for agricultural production. |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention area | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live. |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High water levels (especially with changing water levels) may generate high emission of greenhouse gas | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Martin Maier
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល