Water retention polders with adapted land use (North Sea region) [Герман]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Martin Maier
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Polder mit angepasster Nutzung zur Verbesserung des Wassermanagement (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1660 - Герман
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Kleyer Michael
University of Oldenburg
Герман
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
Герман
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Sustainable Coastal Land Management (COMTESS / GLUES)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - Герман1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (WOCAT ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [Герман]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Martin Maier
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
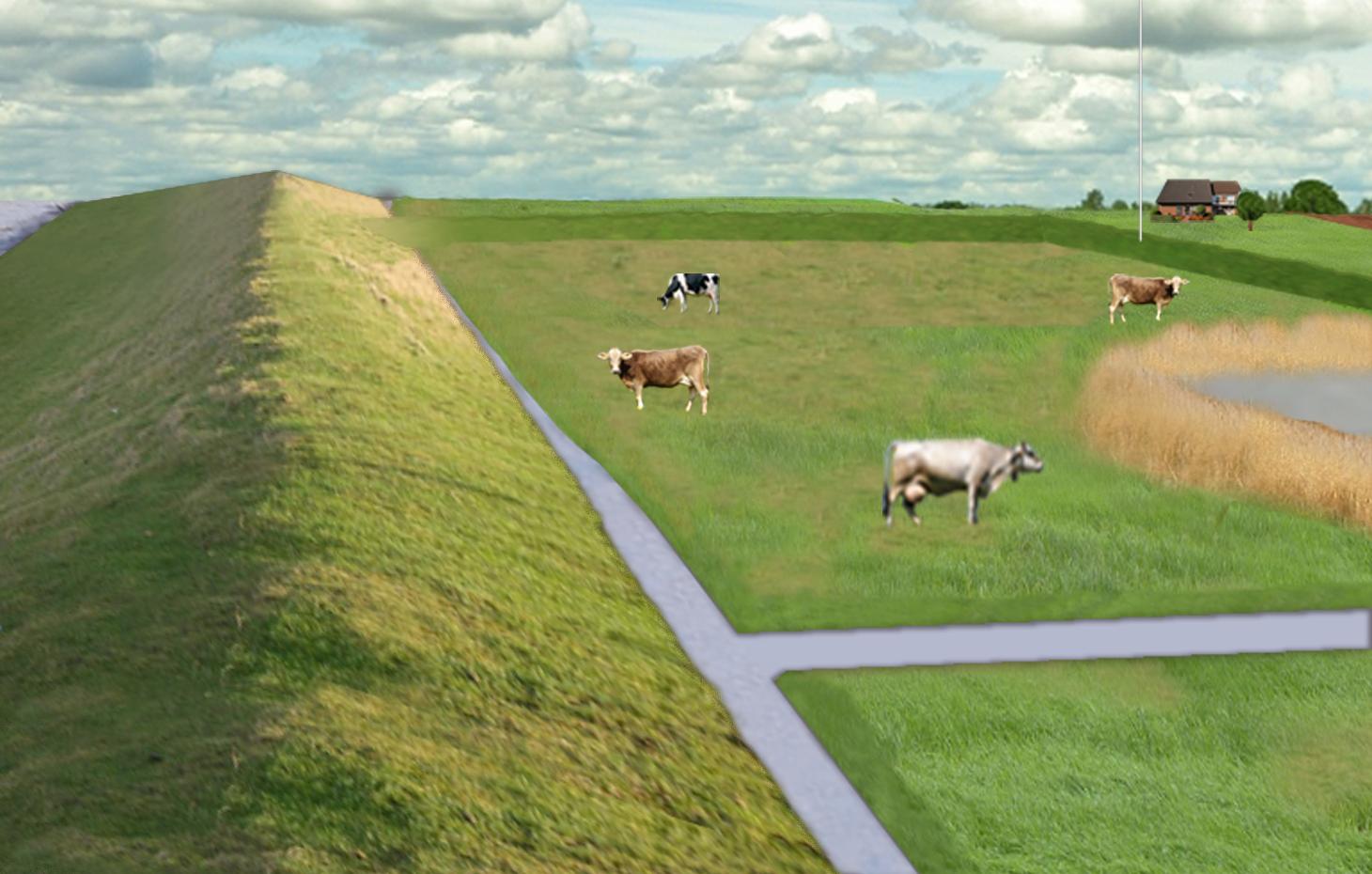
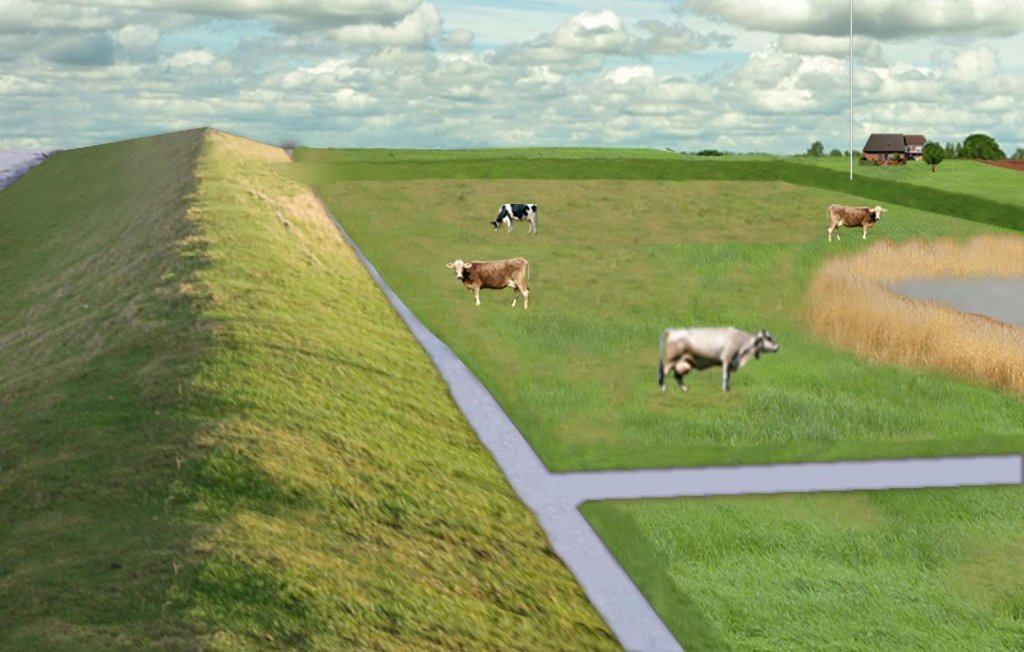
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk from heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in coastal lowlands. Alternative production systems will be viable within thesepolders.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 3,000 ha will be able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occa-sional flooding.
Natural / human environment: However within the proposed retention polders – the areas enclosed by the em-bankment - a change from the current intensive grazing for dairy farming and cropland to extensive grazing, open waters and wetlands covered with reeds will take place. The reeds can be harvested for their commercial value as biomass for renewable energy generation, or for other applications (e.g. thatching of roofs or industrial raw material). According to recent investigations, natural reeds growing in brackish water produce as much biomass as maize cultivated for biogas use. In con-trast to maize, no investments in tillage, fertilizer or biocides are necessary for these naturally growing reed stands. Thus the proposed land use provides an economic alternative to the current production system.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Герман
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Germany, Lower Saxony
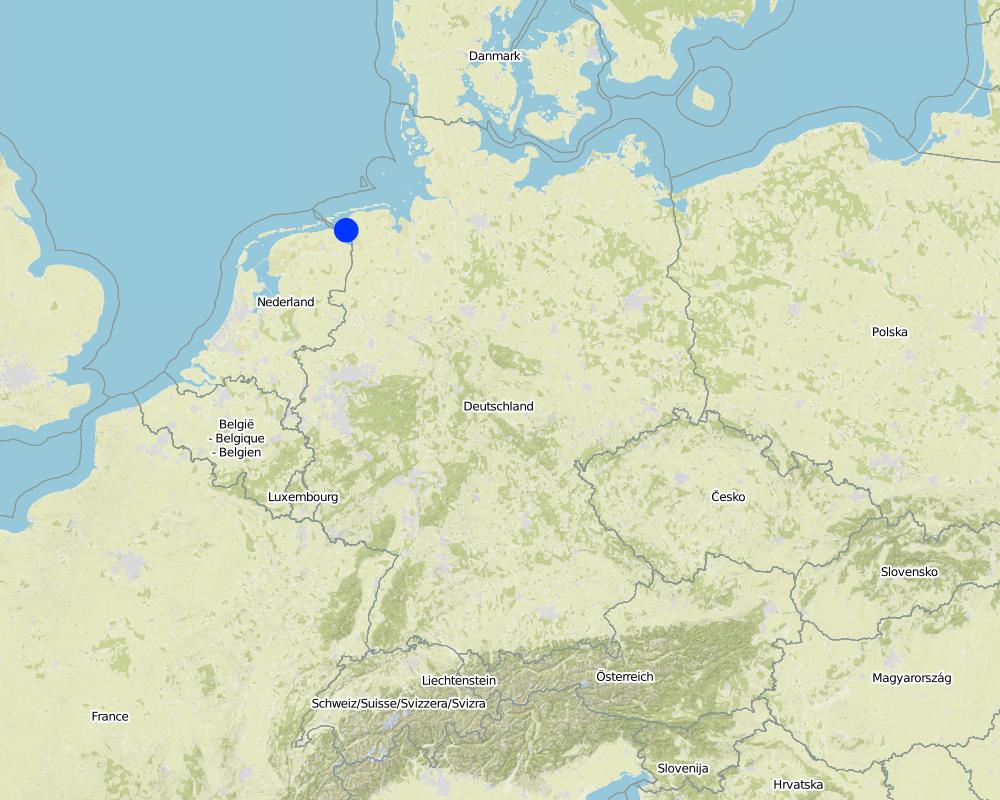
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Landkreis Aurich
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 km2.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - арвай
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- wheat
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн бэлчээр / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
- Сайжруулсан бэлчээр
амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- үхрийн аж ахуй - цагаан идээ
- үхрийн аж ахуй - махны чиглэлийн үхэр
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- мах
- сүү
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the current land use system in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This will reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 хариулт руу шилжинэ үү)
Тайлбар:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.4 Усан хангамж
Тайлбар:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- урсац өөрчлөх ба урсац бүрдүүлэх
- Гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг шанд, гол, нуур, далай)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S5: Далан, хотгор, цөөрөм

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cs: Давсжилт / шүлтжилт

Усны доройтол
- Hs: Гадаргын усны хэмжээ багасах
- Hg: Гүний ус / усан судалт давхаргын түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
- Гүний усны чанар муудах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
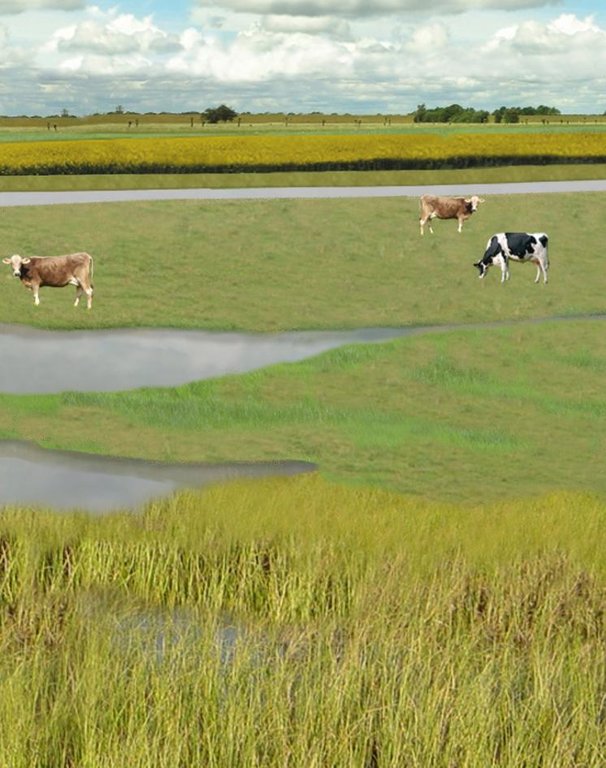
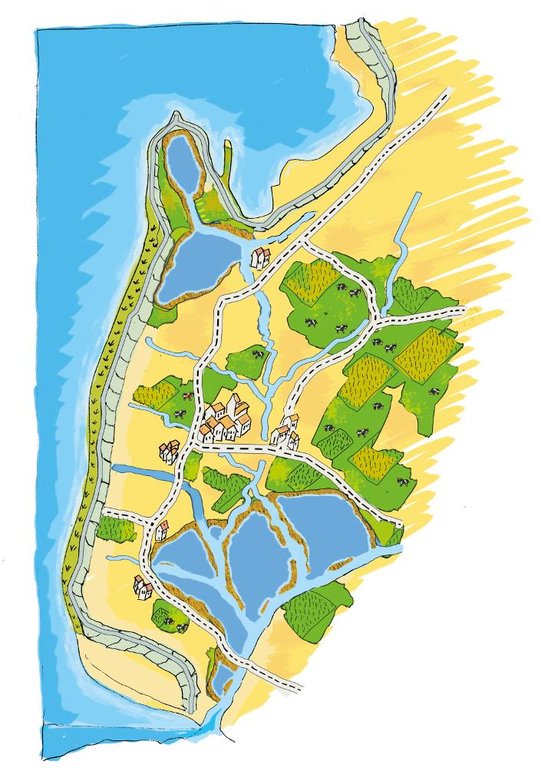
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. Large water bodies (blue) sur-rounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Extensive grazing and reed farming re-places current production systems within the reten-tion polders. The land around the retention area (higher parts of the landscape) profits from the retention areas as the risk of flooding is reduced and can be used for cropland and intensive graz-ing. Depending on the size of the retention polder a huge amount of excess water can be contained. Retention areas of 3,000 ha are able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ water. The height of the dams de-pends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for Water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 25000000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 3,000.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be adapted to hydrological conditions.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensitive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing
Зохиогч:
Udo Schotten
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Euro
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
0.94
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
100.00
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | during winter months |
Тайлбар:
Labour medium: 1 person 1 day, 1m dam, 700USD
Machine hours: 8h, 1m dam, 300 USD
Earth: 10000 M3 (Sand), whole retention area, 22000 USD
Earth: 23000 M3 (Klei), whole retention area, 53000 USD
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | 1.0 | 21000000.0 | 21000000.0 | ||
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | 1.0 | 9000000.0 | 9000000.0 | ||
| Барилгын материал | 750000.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 30000000.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 31914893.62 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | once a year |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | 800.0 | ||||
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | 300.0 | ||||
| Барилгын материал | Earth | 100.0 |
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The establishment costs are for a dam length of 30 km and the enclosed retention area of 3,000 ha. The establishment period will be half a year. The slope in the region determines the costs as the height of the embankments depend on this. Typical heights are from 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3. . The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of the drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.70 Euro per km including pumping costs. The maintenance cost for the whole retention area will amount to a total of US$ 2,576,200.00.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Чийглэг
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Их (>3 %)
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity high
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Сайн
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын % 10-50 хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
50% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in industry or servicing sector
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Том-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, тодорхой цол эргэмгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
ГТМ хэрэгжхээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
49000 ha
ГТМ хэрэгжсэнээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
46000 ha
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
For the whole catchment area a loss of approx. 3,000 ha (size of retention area).
Эрчим хүчний үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reeds in the retention area are very productive plants and will be used for bio energy generation.
Усны хүртээм ба чанар
мал услах усны хүрэлцээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to reduction of saline influx
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н хөрөнгө оруулалтын зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Only adjusted land use takes place within retention area, therefore the expenses are reduced.
тариалангийн газрын орлого
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
Бусад нийгэм-эдийн засгийн нөлөөллүүд
Intrusion by saline groundwater
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
амралт, нөхөн сэргээлтийн боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
усны чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
ууршилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
давсжилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах С
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Growth of reeds
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
Ашигт төрөл зүйл
амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Water from retention area.
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсгал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
Доод урсгалын үер
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учируулах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Орон нутгийн аадар бороо | Сайн |
| Орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Сайн |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Сайн |
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ургалтын хугацаа багасах | Мэдэхгүй |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Дунд зэрэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Дунд зэрэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Тайлбар:
The benefits will be visible in the longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by local land users but this SLM technology needs to be implemented by spatial planning of the county / federal state.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology is not yet implemented by land users but first it needs to be considered in spatial planning of the county and the federal state. Land users and local experts showed during participatory workshops that there may be a chance for implementation.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The retention area will support the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding (including strengthening of the ditch system and in-creasing pumping capacity). |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored. |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention polders prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endangered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention areas the very expensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is not necessary anymore How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractivity for touristic use in the retention area benefits for land owner can be generated and the probability to build up retention areas instead of strengthening the existing drainage system is increased. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Retention polders in an important tourism region will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism. | Include tourism concerns in the retention area (access, infor-mation, attractiveness). |
| Loss of land for agricultural production (highly productive arable land) | Establish retention area in low elevated parts, where there is not a high interest for agricultural production. |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention area | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live. |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| High water levels (especially with changing water levels) may generate high emission of greenhouse gas | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [Герман]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Martin Maier
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна