Water retention polders with adapted land use (North Sea region) [เยอรมนี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Martin Maier
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Polder mit angepasster Nutzung zur Verbesserung des Wassermanagement (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1660 - เยอรมนี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kleyer Michael
University of Oldenburg
เยอรมนี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
เยอรมนี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Sustainable Coastal Land Management (COMTESS / GLUES)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [เยอรมนี]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Martin Maier
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
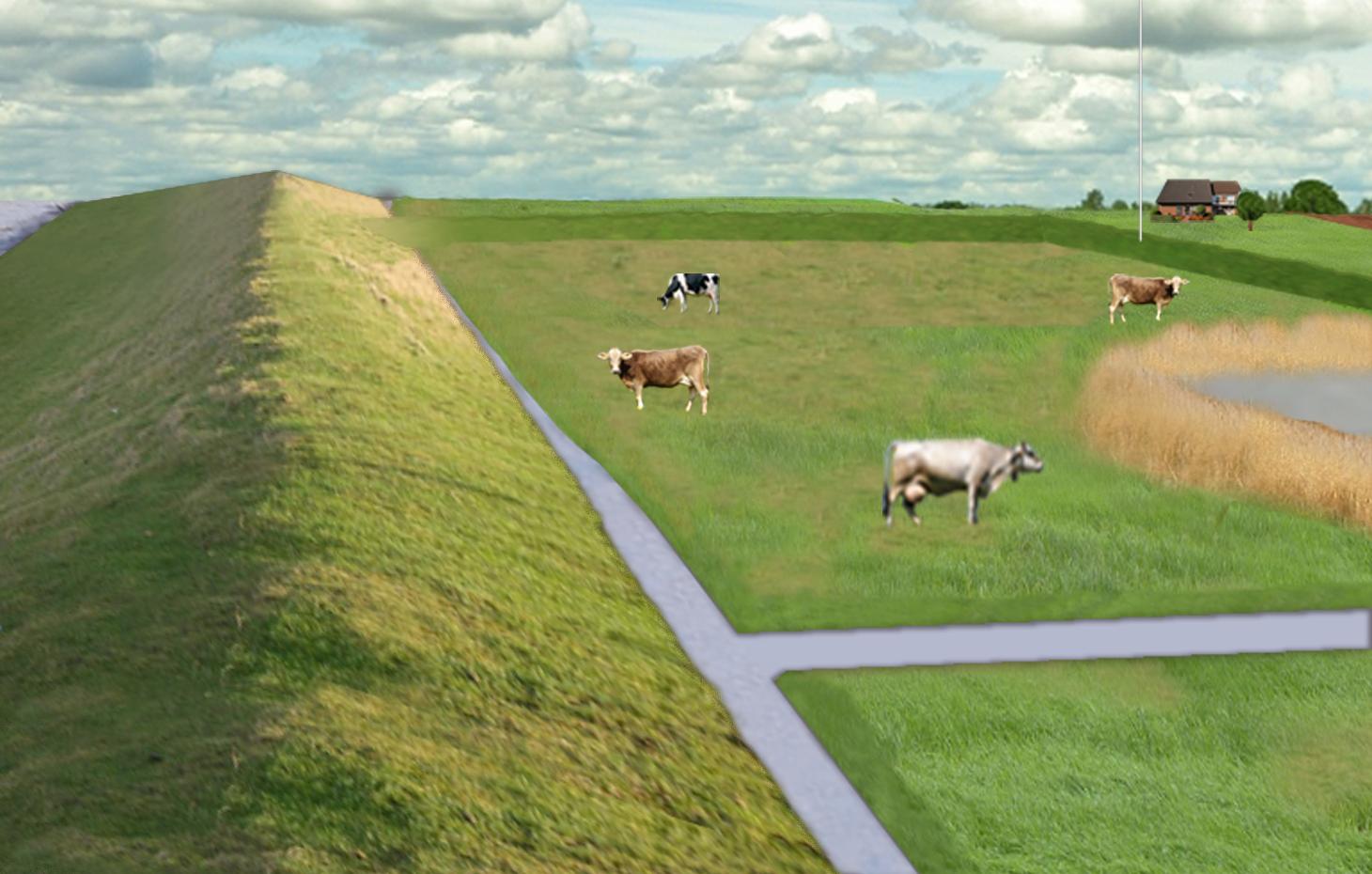
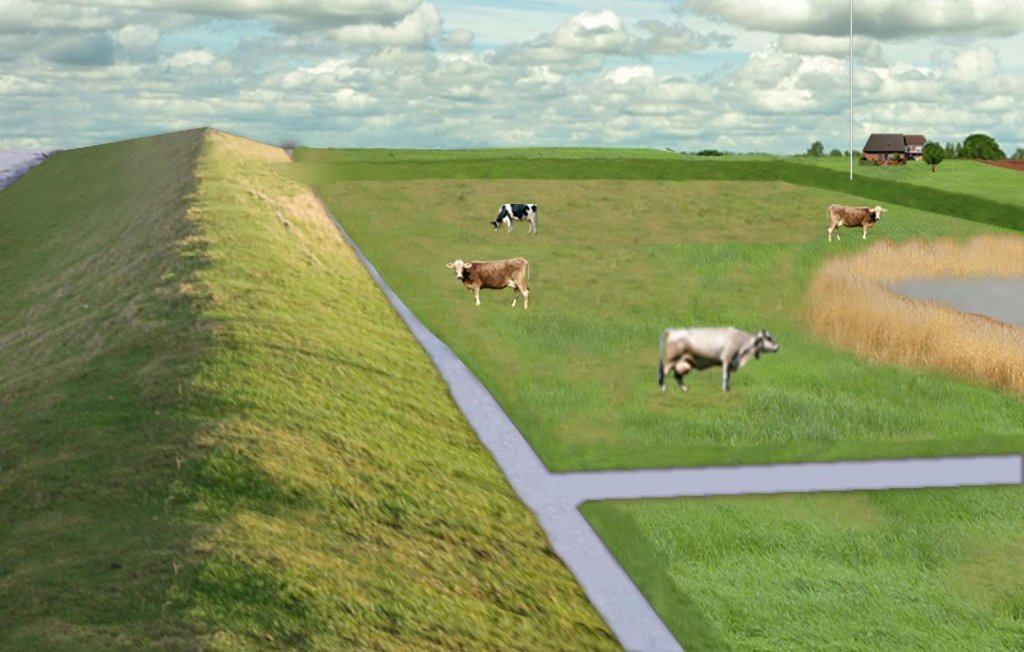
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk from heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in coastal lowlands. Alternative production systems will be viable within thesepolders.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 3,000 ha will be able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occa-sional flooding.
Natural / human environment: However within the proposed retention polders – the areas enclosed by the em-bankment - a change from the current intensive grazing for dairy farming and cropland to extensive grazing, open waters and wetlands covered with reeds will take place. The reeds can be harvested for their commercial value as biomass for renewable energy generation, or for other applications (e.g. thatching of roofs or industrial raw material). According to recent investigations, natural reeds growing in brackish water produce as much biomass as maize cultivated for biogas use. In con-trast to maize, no investments in tillage, fertilizer or biocides are necessary for these naturally growing reed stands. Thus the proposed land use provides an economic alternative to the current production system.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เยอรมนี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Germany, Lower Saxony
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Landkreis Aurich
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- wheat
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- cattle - non-dairy beef
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the current land use system in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This will reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
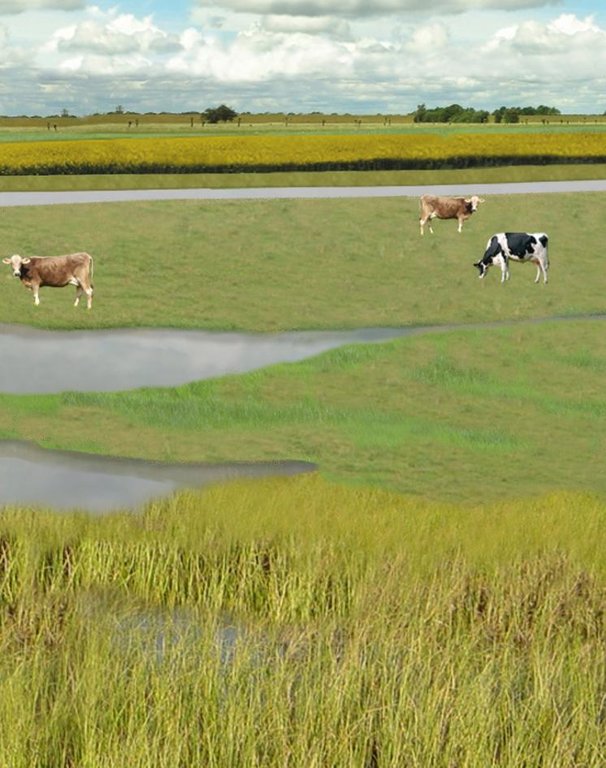
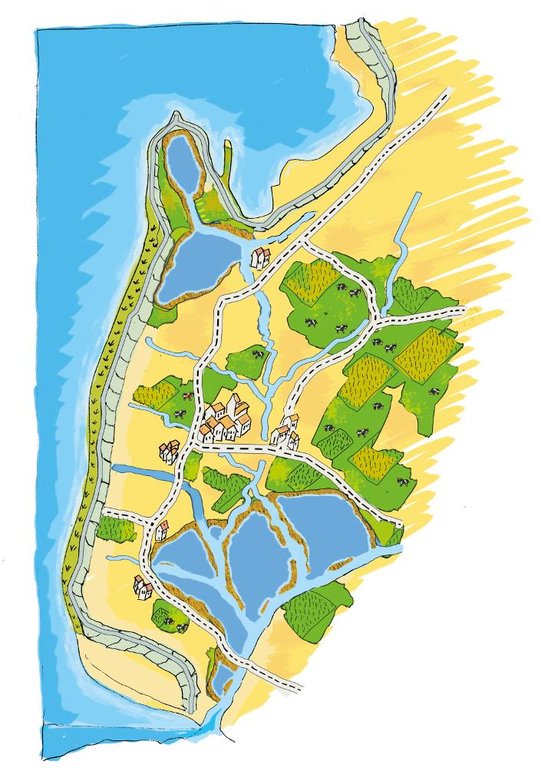
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. Large water bodies (blue) sur-rounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Extensive grazing and reed farming re-places current production systems within the reten-tion polders. The land around the retention area (higher parts of the landscape) profits from the retention areas as the risk of flooding is reduced and can be used for cropland and intensive graz-ing. Depending on the size of the retention polder a huge amount of excess water can be contained. Retention areas of 3,000 ha are able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ water. The height of the dams de-pends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for Water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 25000000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 3,000.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be adapted to hydrological conditions.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensitive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing
ผู้เขียน:
Udo Schotten
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.94
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
100.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | during winter months |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Labour medium: 1 person 1 day, 1m dam, 700USD
Machine hours: 8h, 1m dam, 300 USD
Earth: 10000 M3 (Sand), whole retention area, 22000 USD
Earth: 23000 M3 (Klei), whole retention area, 53000 USD
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | 1.0 | 21000000.0 | 21000000.0 | ||
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | 1.0 | 9000000.0 | 9000000.0 | ||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | 750000.0 | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 30000000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 31914893.62 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | once a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | 800.0 | ||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | 300.0 | ||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | 100.0 |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The establishment costs are for a dam length of 30 km and the enclosed retention area of 3,000 ha. The establishment period will be half a year. The slope in the region determines the costs as the height of the embankments depend on this. Typical heights are from 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3. . The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of the drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.70 Euro per km including pumping costs. The maintenance cost for the whole retention area will amount to a total of US$ 2,576,200.00.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity high
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
50% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in industry or servicing sector
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
49000 ha
หลังจาก SLM:
46000 ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
For the whole catchment area a loss of approx. 3,000 ha (size of retention area).
การผลิตพลังงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reeds in the retention area are very productive plants and will be used for bio energy generation.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to reduction of saline influx
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Only adjusted land use takes place within retention area, therefore the expenses are reduced.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Intrusion by saline groundwater
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
ความเค็ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Growth of reeds
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water from retention area.
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The benefits will be visible in the longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by local land users but this SLM technology needs to be implemented by spatial planning of the county / federal state.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology is not yet implemented by land users but first it needs to be considered in spatial planning of the county and the federal state. Land users and local experts showed during participatory workshops that there may be a chance for implementation.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
The retention area will support the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding (including strengthening of the ditch system and in-creasing pumping capacity). |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored. |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention polders prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endangered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention areas the very expensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is not necessary anymore How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractivity for touristic use in the retention area benefits for land owner can be generated and the probability to build up retention areas instead of strengthening the existing drainage system is increased. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Retention polders in an important tourism region will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism. | Include tourism concerns in the retention area (access, infor-mation, attractiveness). |
| Loss of land for agricultural production (highly productive arable land) | Establish retention area in low elevated parts, where there is not a high interest for agricultural production. |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention area | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live. |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High water levels (especially with changing water levels) may generate high emission of greenhouse gas | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [เยอรมนี]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Martin Maier
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล