No-tillage [ប្រទេសអេស្តូនី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Endla Reintam
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Otsekülv
technologies_3089 - ប្រទេសអេស្តូនី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Tobreluts Toomas
Pirmastu OÜ
ប្រទេសអេស្តូនី
researcher:
Penu Priit
Estonian Agricultural Research Centre
ប្រទេសអេស្តូនី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
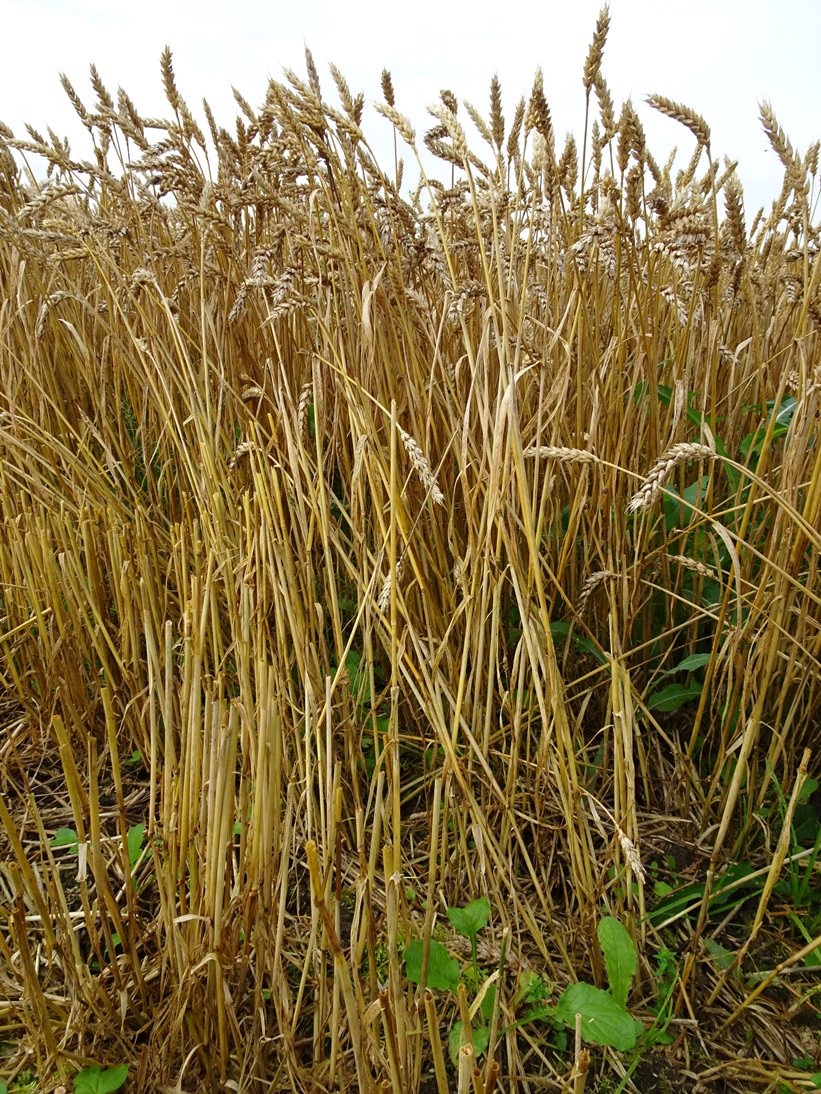
No-till farming (also called zero tillage or direct drilling) is a way of growing crops or pasture from year to year without disturbing the soil through tillage.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat, the southern part is hilly with slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) in the north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. In the agricultural area the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) to high (>5%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater is near the surface in wet soils and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity varies from high to low depending on soil and landscape. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income is less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users, but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 100 ha).
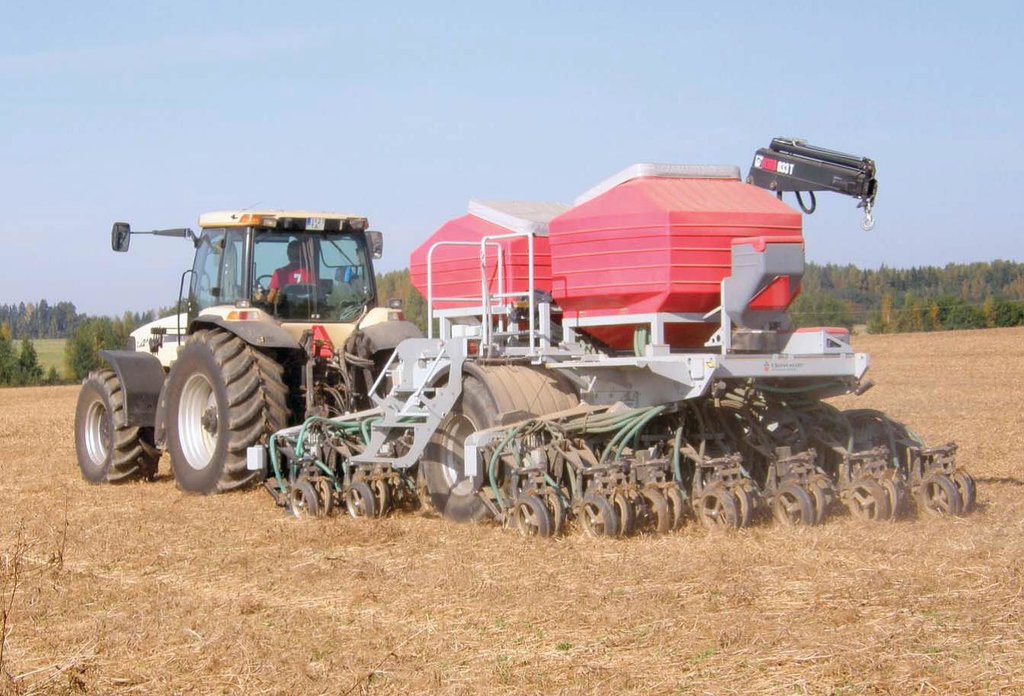
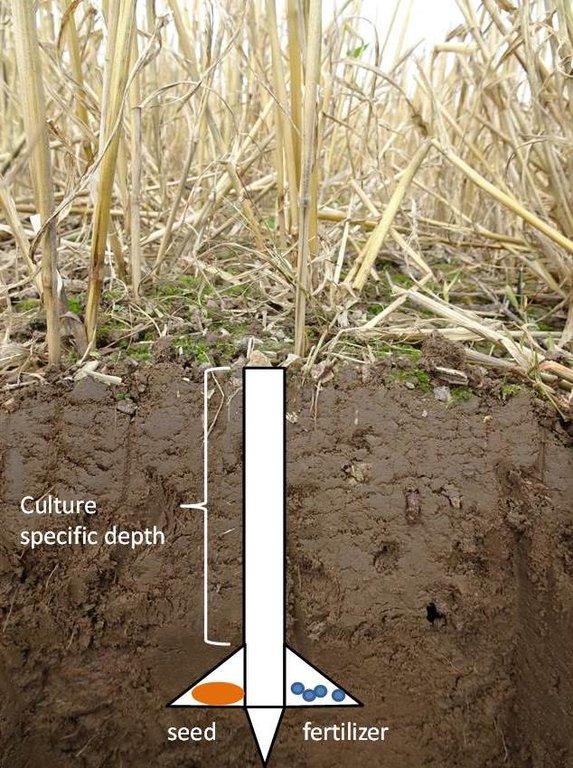
The purpose of the technology is to reduce soil disturbance and with that to reduce erosion and leaching, increase carbon storage, water infiltration and biological activity. Only 5-10% of the soil surface is disturbed during sowing. The drilling is made by special machinery and thus no-till farming requires specialized seeding equipment designed to plant seeds into undisturbed crop residues and soil. Drilling depth depends on the specific needs of the culture. If the straw remains on the field, it should be chopped to smaller pieces (25-40 mm). For direct seeding it is good if the previous culture was seeded with wider spacing, for example 25 cm and harvest height is 15-20 cm. New sowing will be done between previous crop rows. The highest investment to this technology is the new drilling machine. At the same time there is no need for special tillage machines. In order to help eliminate weed, pest and disease problems, crop rotations and pesticides are used. The system is not suitable for root crops. The no-till system is suitable for cereal based cropping systems as well as for renewing grasslands. The suitable crop rotation, for exampe, is: winter oilseed rape - winter wheat - pea (or bean) - winter wheat - spring barley undersown with red clover - red clover. The main benefit is the reduced working time, fuel costs and with that the lower net-cost of the product, but also the better soil structure. The adoption of the technology may increase weediness and pests and decrease the yield due to the preliminar soil compaction of upper 10-20 cm soil layer. If the soil surface of the field is not enough levelled out, the uniformity of the depth of the seedlings can suffer. There is also increased use of pesticides to control weeds, pests and diseases compared to minimum and conventional tillage. The technology is most suitable for medium-texture soils.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអេស្តូនី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Tartu county, Põlva county
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Tartu county, Meeri; Põlva county, Puuri
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 1-10 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
The total area of no-till in Estonia is ca 42 000 ha. On the farm near Tartu it is 1700 ha of land, of which 300 ha are grasslands. The farm near Põlva encompasses an area of 850 ha of which 330 ha are grasslands. The whole area of both farms is managed by no-tillage.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- reduce tillage cost
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី
- wheat
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
One harvest of cereals.
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
មតិយោបល់:
Before implementation of the no-tillage the conventional and/or reduced tillage was used.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
The agrotechnology in case of no-tillage depends on available equipments (drill). If the straw remains on the field, it should be chopped to smaller pieces of 25-40 mm. For direct seeding it is good if the previous culture was seeded with wider spacing, for example 25 cm. Harvest height is 15-20 cm. New seeding will be done between previous crop rows.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Endla Reintam
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
14/08/2017
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
per hectare
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
EUR
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
1,18
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | New direct seeder |
មតិយោបល់:
If you are already active in agriculture, the investment is the new seeder. You also need to have machinery to spread fertilizers and pesticides.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Direct seeder (3m) | piece | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 25000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 21186,44 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
It is possible to apply for an investment support up to 50% of the total price (governmental tool till the year 2020).
មតិយោបល់:
The cost of the direct seeder depends on the farmers prefererences regarding the technology. The cheapest direct seeder can be purchased for ca. 25 000 EUR. Better quality of a cross slot seeder that places seeds under the soil (technical drawing and picture) costs ca 200 000 EUR (working width 4.6 m).
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing together with fertilization | before drilling (spring crops in spring (April), winter crops in autumn (August)) |
| 2. | Plant protection | in spring 2 weeks before sowing, herbicides, during growth period depending on the needs ca 3 times |
| 3. | Fertilization during growth period | For winter crops in spring after snowmelt in the beginning of growth, for spring crops in the beginning of intensive growth |
| 4. | Harvest and grain transport | At the end of season (end of July to beginning of September depending of the crop) |
| 5. | Drying of grain and soil tillage | after harvest |
មតិយោបល់:
The need of plant protection depends on the field conditions. Less pesticides are needed if proper crop rotation with break crops is established and weeds are thus suppressed.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Sowing with fertilization | times | 1,0 | 55,9 | 55,9 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Plant protection | times | 4,0 | 11,2 | 44,8 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Fertilization during growth period | times | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Harvest and grain transport | times | 1,0 | 118,4 | 118,4 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Drying and after harvest activities | times | 1,0 | 132,1 | 132,1 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | kg | 200,0 | 0,28 | 56,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Ammonium nitrate (2x per season) | kg | 147,0 | 0,84 | 123,48 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Complex fertilizer (27 kg N, 40 kg P and 112 kg K per ha) (450 kg of fertilizer per ha) | kg | 179,0 | 0,74 | 132,46 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Herbicides (2 times) | times | 2,0 | 27,0 | 54,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Fungicides (1 time) | times | 1,0 | 33,2 | 33,2 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Insecticides (1 time) | times | 1,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Retartants | times | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 784,14 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 664,53 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The labour costs are included to the machinery work costs. On average the labour cost for a driver is 15-18 EUR/ha.
The average machinery work costs to produce 6 t of winter wheat were 432 EUR/ha, 400 EUR/ha and 780 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively in 2016. Cost of production in this case was 137 EUR/t, 132 EUR/t and 128 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively.
To produce the same amount of spring barley, the cost of machinery was 431 EUR/ha, 411 EUR/ha and 366 EUR/ha in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. Cost of production in this case was 123 EUR/t, 121 EUR/t and 114 EUR/t in conventional, minimum and no-tillage, respectively. It means that the cost of production is 8-11 EUR less than compared with plough based production.
Fuel cost is ca 50% less than in conventional plough based farming.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Fuel price, labour costs.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
696,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Tartu Tõravere
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil type: sandy loam Stagnic Luvisol; N 0.12%, Corg 1.15%; C:N 9.97, P 4.35 mg/100g, K 10.19mg/100g, Ca 49.61mg/100g, Mg 12.19mg/100g, pH 6.0
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Soil biodiversity is higher compared to conventional tillage.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
- សហករ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
The farm near Tatu owns 1700 ha of land, of which 300 ha are grasslands. The farm near Põlva encompasses a total of 850 ha of which 330 ha are grasslands. All soils of both farms are managed by no-tillage.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In different years the crop production may be higher than by ploughing, but another year lower. There has been decrease of spring barley yield by 0.1 t/ha. Winter wheat yield has been ca 1.4 t/ha higher than by ploughing.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No statistically significant difference has been found. However, winter wheat 1000 grain weight was reported 39.6 g by no-tillage and 38.5 g by ploughing.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No need for soil tillage. Instead of several machinery to till the soil, one compact sowing machine is needed.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Less cost for fuel because 50% less fuel is needed compared with ploughing.
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Even if the yield is a little bit lower or the same as with ploughing, the unit cost to produce barley or winter wheat is 8-11 EUR less than with ploughing.
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No time to be spent for tillage. Even extra spreading of pesticides takes less time than ploughing and other tillage operations.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Unit cost of the production is lower and thus it is possible to sell production cheaper.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Residues remaining on the soil surface help to catch more snow during the winter.
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Plant residues protect soil surface structure from raindrop effects, allowing water to infiltrate quicker in the soil.
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Undisturbed soil pore structure allows water quicker to drain in the deeper soil layers. Water permeability of long-term no-till soil is 2 times higher than under conventional management.
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Residues on the soil surface do not allow quick evaporation, protecting soil surface.
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Soil moisture content was 3% higher than by ploughing, but not significantly.
គម្របដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The soil is covered by plants or by plant residues during the whole year.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Residues and plant cover stop both wind and water erosion.
ការកើនឡើងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced decomposition of organic matter increases organic carbon content by 0.1-0.2%.
ដីប្រេះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No crust after applying no-tillage as plant residues protect the soil surface.
ដីហាប់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased from the top (by 0.04 g/cm3) but decreased deeper in the soil by 0.08 g/cm3) compared to the ploughing. No plough pan. Soil penetration resistance was 1 MPa lower between 20-40 cm under no-tillage compared to ploughing.
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the decreased decomposition of organic matter and the increase of organic carbon, more nitrogen remains in the soil.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
It was found that there was slight increase of organic carbon (Corg) by 0.1-0.2% in upper 5 cm of soil compared to ploughing.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Plant/residue cover is during the whole year.
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As there is no tillage, all residues remain on the soil surface.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the need of changes in crop rotation, more diverse rotations instead of monoculture to suppress weeds. Weeds diversity might increase and change due to the reduced tillage intensity.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
More spiders, beetles, ants compared with ploughing.
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
2 species of earthworms
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
3-4 species of earthworms
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
More earthworm species and higher abundance compared with ploughing.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No-till areas create different pattern to the landscape.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Some diseases and pests are surpressed, but there is increase of slugs and snails.
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the reduced use of fuels for tillage, less greenhouse gases will be released. 0.05 kg/ha less greenhouse gases per kg yield is reported by no-tillage compared to ploughing.
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Dry plant residues are a high risk in spring.
អាកាសធាតុ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the residue cover the soil temperature and water content fluctuations are smaller.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the higher amount of organic matter, the nutrients and water holding capacity is higher.
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No wind erosion after applying no-tillage.
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No sediments from the field to the neighbours fields.
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the reduced use of fuels for tillage, less greenhouse gases will be released. 0.05 kg/ha less greenhouse gases per kg yield is reported by no-tillage compared to ploughing.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវរងា | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | និទាឃរដូវ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវរងា | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវស្លឹកឈើជ្រុះ | កើនឡើង | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ព្យុះរន្ទះតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ព្យុះទឹកកកតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ព្យុះព្រិលតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រលកត្រជាក់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ស្ថានភាពខ្យល់ខ្លាំង | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ភ្លើងឆេះ | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
7% from agricultural land
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 51-90%
មតិយោបល់:
It is possible to get investment support from the governmental agricultural tools up to 50% from the total cost of equipment.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Decreases work load and time, also fuel consumption, increases income. |
| Increases soil biological activity, soil organic matter content, better structure and infiltration, decreases erosion. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Decrease of soil organic carbon decomposition, decrease of erosion, increase of soil biological activity. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| High preliminary investment (seeder), increase of weediness and pests, | Investment support, better crop rotation. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Higher use of pesticides and therefore risk to soil and water pollution. | Suggestion of changes in crop rotation, cover crops. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
2 during the iSQAPER project, more than 5 in total with other projects
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
2, more than 5 in total with other projects
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
6
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
04/06/2017
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut. ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ISBN 978-9949-9742-2-1
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
វេបសាយ:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Statistics Estonia
វេបសាយ:
https://www.stat.ee/en
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Erinevate viljelusmeetodite ( sh. otsekülv) rakendusteaduslik kompleksuuring. Riikliku programmi “Põllumajanduslikud rakendusuuringud ja arendustegevus aastatel 2009–2014” projekti lõpparuanne. 2015. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut, Eesti Maaülikool, Põllumajandusuuringute keskus.
វេបសាយ:
http://www.pikk.ee/upload/files/Erinevad_viljelusviisid_pikk_aruanne.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Minimeeritud harimine ja otsekülv. 2017. P. Viil. Eesti Taimekasvatuse Instituut.
វេបសាយ:
http://taim.etki.ee/taim/public/pdf/Trukised/Otseklv-minimeeritud-mullaharimine.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi meetmete ja 3. prioriteedi loomade heaolu meetme püsihindamisaruanne 2015. aasta kohta ja Lisad 1-30
វេបសាយ:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/avaleht/
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
វេបសាយ:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល