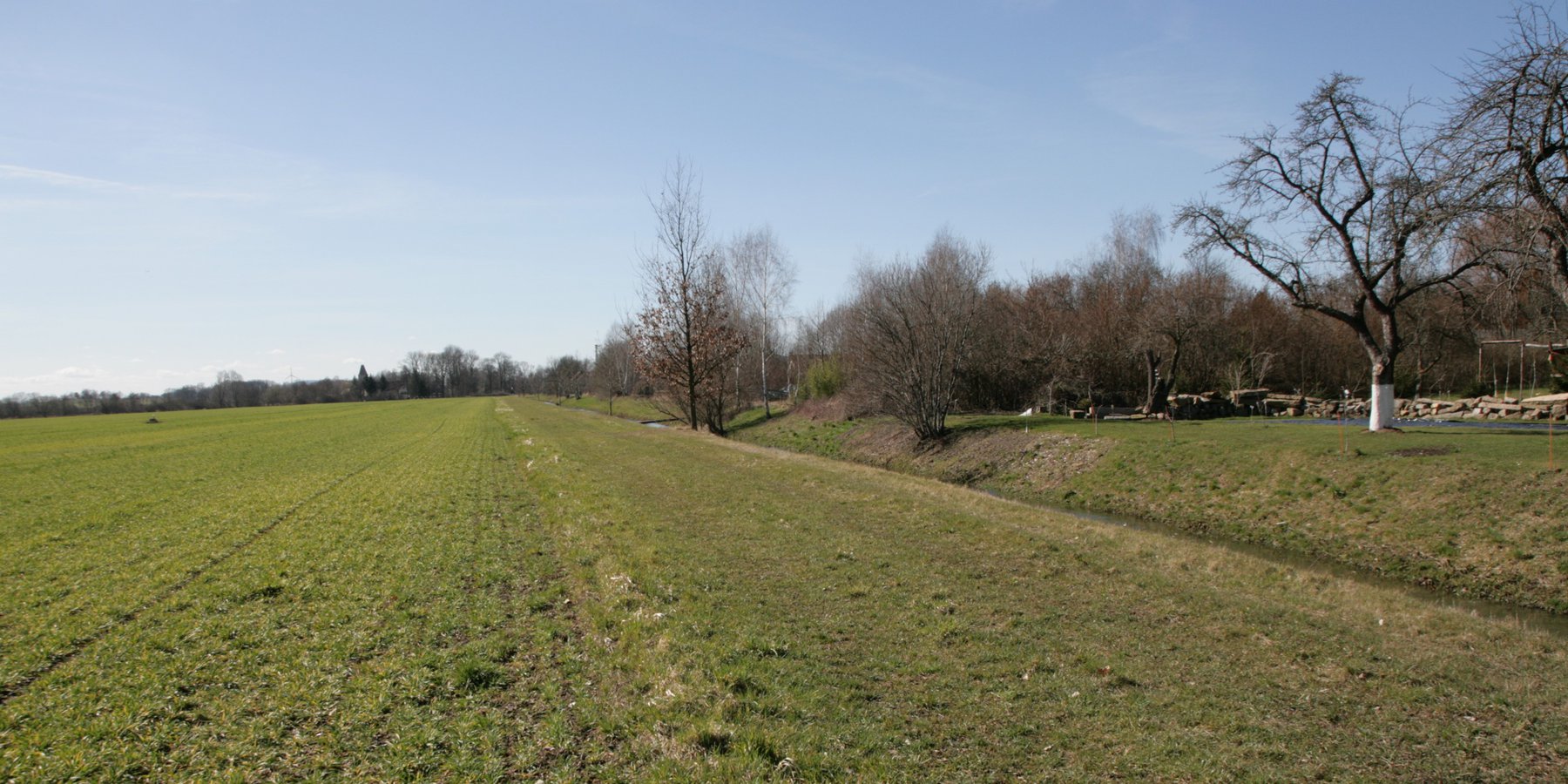
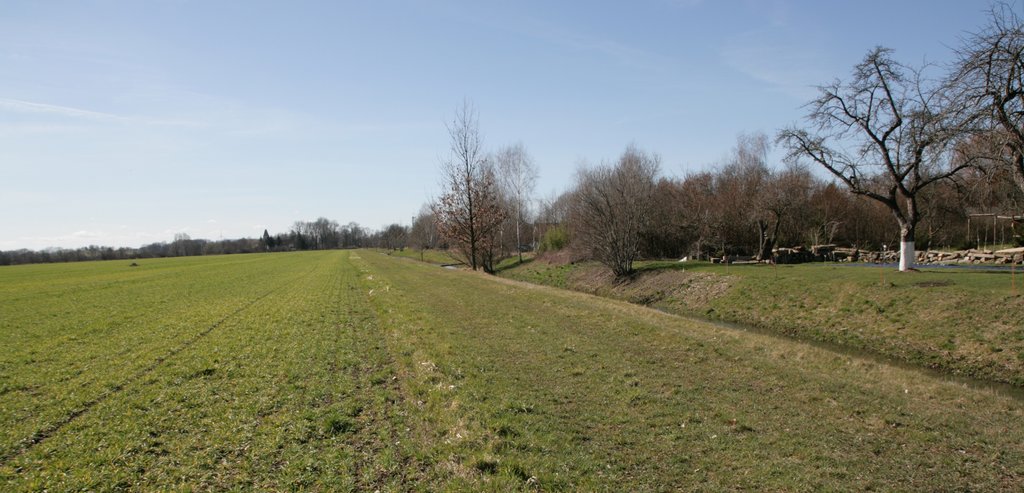
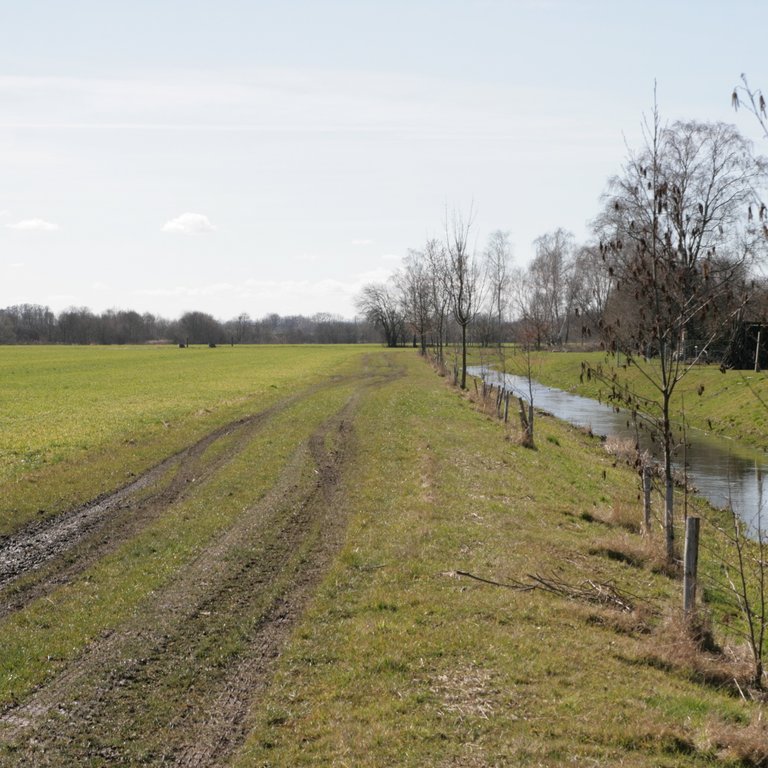
Riparian buffer strip with naturally recovered vegetation [ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Felix Witing
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Michael Strauch, Mona Pauer
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Selbstbegrünte Brache als Gewässerrandstreifen
technologies_6258 - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Riparian buffer strips refer to the permanent greening of arable land alongside streams and other water bodies. By slowing down runoff water from the land, they help to protect water bodies from diffuse pollution. Riparian buffer strips have multiple other environmental benefits, but disadvantages also.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Riparian buffer strips comprise permanent, protective vegetation alongside streams and other water bodies. Our example represents a riparian buffer that evolved from set-aside land with naturally recovered vegetation. For the farmer, this has several advantages in terms of implementation, maintenance and seed costs. The farmer was able to simply leave the buffer strip open after ploughing without seeding or rolling, and maintenance requires only one mowing operation per year.
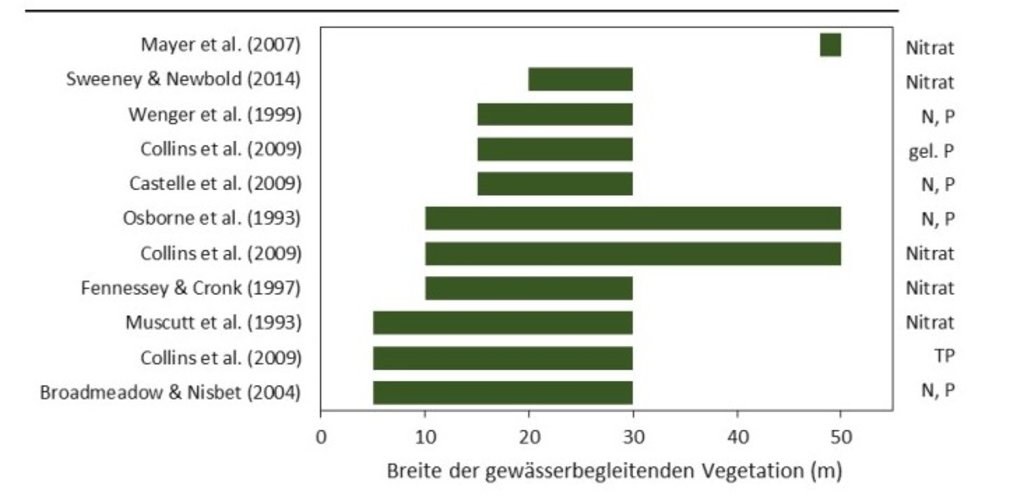
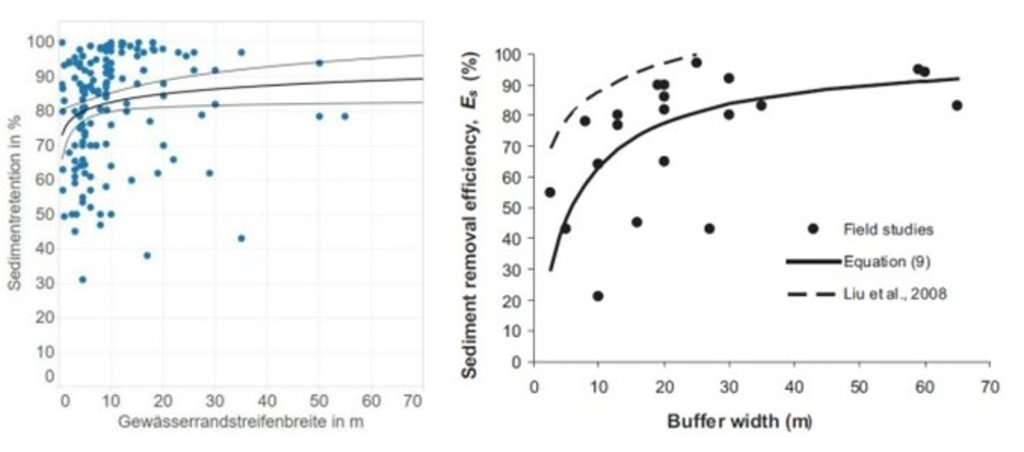
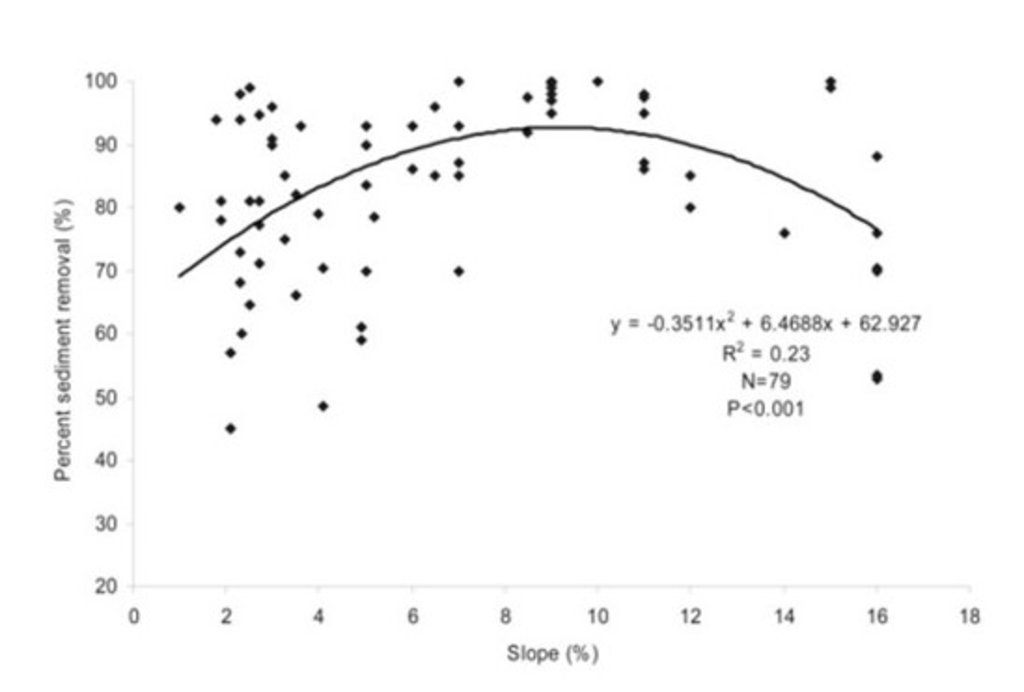
Riparian buffer strips are established at the edge of cultivated areas adjacent to water bodies. The width of the strip should be 5-15 m. In our example, the width of the buffer strip was 6 m, which was defined by working width of the mower. Depending on the type and width of the buffer, the rainfall intensity, the slope and the management, different filtering capacities can be attained by a buffer. An effective strip can retain 70% of the sediment and reduce nutrients in the surface runoff by 50%. However efficient retention of nutrients requires a buffer width of at least 15 m, while efficient retention of fine sediments requires a width of 15-20 m. The slope of the watercourse bank is also important: the optimum slope is 9-10%, and retention performance worsens with increasing slope (Kail et al. 2022).
Grass cover roughens the soil surface, slowing down the flow of water after heavy rainfall events and improving infiltration rates. Additionally, the roots of grasses increase infiltration, the plants absorb nitrate and prevent it from running off into the water bodies. Deeper roots, such as those from trees stabilize river banks, preventing bank erosion during heavy rainfall, as well as increasing shading of the stream. This improves the microclimate and creates better habitats for species native to the watercourse. Moreover, the buffer reduces the siltation of water bodies, preserves gravel bars, and thus preserves habitats. The buffer strip itself provides habitats for flora and fauna. The area adjacent to the buffer strip may experience increased dew formation and soil moisture, reduced evaporation, and wind protection.
The surface roughness of the grassed buffer strip depends on the type of vegetation. Cold-tolerant grasses such as perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) are commonly used, but a mix of grasses and trees is even better. Grassland provides an evenly distributed surface cover and the trees, with their deeper roots, provider higher infiltration capacity. Fast growing, low maintenance and regional species are optimal.
Proper maintenance is important for permanent erosion control. In case of nutrient-rich runoff from adjacent fields, the buffer strip may become saturated after a while and nitrification increases. Nitrous oxide is then produced which is a powerful greenhouse gases. In addition, the soil/vegetation is no longer able to absorb new nutrients, and they are washed into the water body. Mowing once per year removes biomass and can prevent nutrient saturation (Cole et al. 2020).
However, while promoting biodiversity and reducing soil erosion, buffer strips have a major downside for land-users and land-owners. They consume cropland, which leads to a decrease in production. The grass mixture can be used as fodder, but usually this does not compensate for the loss of production, which is why farmers often call for appropriate subsidies.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Saxony
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Nieder Seifersdorf
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2013
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
In order to meet the greening requirements of the CAP, 4% of the total agricultural area of a farm must be used, for example, for crop diversification, maintenance of permanent grassland or creation of ecological priority areas in order to receive direct payments from the state. In this case, a self-vegetated fallow was established as an ecological priority area to fulfill the greening requirements.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
self-vegetated fallow
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
maintenance activity: mowing
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី (សិសិររដូវរងារ)
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
winter rye, winter wheat, silage maize, winter wheat, winter rye, winter barley, silage maize, winter barley, winter rye
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- តំបន់ទ្រនាប់ (បិទការប្រើប្រាស់ គាំទ្រដល់ការស្តារឡើងវិញ)
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wr: សំណឹកដីច្រាំងទន្លេ
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
- Pk: ការបិទរន្ធដី
- Pw: ទឹកនៅដក់ជាប់

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hp: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
- Hw៖ ការថយចុះសមត្ថភាព buffering របស់តំបន់ដីសើមដែលដោះស្រាយជាមួយនឹងទឹកជំនន់ និងការបំពុល
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Widths of the vegetation along the watercourse required for effective nutrient retention (approx. >80%) mentioned in the reviews.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Kail et al. (2022), p.25
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Summary of field studies of sediment retention as a function of buffer strip width under controlled, optimal conditions (left figure) and under realistic, non-optimal conditions (right figure).
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Kail et al. (2022), p.37
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Sediment retention as a function of the slope of a buffer strip.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Kail et al. (2022), p.38
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1 ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
€
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,91
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
18.70€ per hour
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
មតិយោបល់:
There are no establishment activities needed.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mowing | annually at the end of July |
មតិយោបល់:
The farmer in this case study mowed the grass and removed the biomass to prevent nutrient saturation in the riparian buffer. However, the amount of hay yield is small and not relevant according to the farmer.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | mowing | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 25,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 27,47 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
121€/ha were covered by the state of Saxony as a subsidy (AL 5b- self-vegetated perennial needs on arable land; SMUL Sachsen, 2015).
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
A riparian buffer that developed from set-aside land with naturally recovered vegetation is not costly, as it requires only one mowing operation per year and nothing else. However, the buffer consumes agricultural land, leading to a reduction in agricultural production.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
775,00
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
https://whh-kliwes.de/mapview
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Length of growing period (LGP): 209
(https://www.umwelt.sachsen.de/dauer-der-vegetationsperiode-30631.html)
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Gleysol
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ទាប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ទាប
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Normally, a self-vegetated fallow has a high species diversity (depending on the seeds present in the soil) and a medium habitat diversity. Unfortunately, the documented self-vegetated fallow is not properly maintained and the beneficial effects, e.g. species and habitat diversity, are correspondingly low.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
ទេ
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពដំណាំ
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
decreased wind erosion
ដីហាប់
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
The assessment is based on the response of the interviewed farmer and not based on on-site measurements.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
The assessment is based on the expertise of the compilers and not based on measurements in the case study.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុផ្សេងៗ | changing weather conditions | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
No establishment costs. Comment by the farmer: "There is no benefit at all".
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Increased infiltration rates |
| Reduced erosion and nutrient runoff into watercourse |
| Deeper roots, such as those of trees, stabilize river banks against break-off during heavy rainfall. |
| Trees increase shading and microclimate for stream species. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Loss in yield due to loss of arable land. | Accordingly, the yield loss should be offset by subsidies. Use grass mixture as fodder. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
6
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
16/03/2023
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Kail et al. (2022): Ökologische Funktionen von Gewässerrandstreifen. LfULG Broschüre
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://publikationen.sachsen.de/bdb/artikel/40152
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Cole et al. (2020): Managing riparian buffer strips to optimise ecosystem services: A review. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 296
វេបសាយ:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.106891
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
SMUL Sachsen (2015): Förderperiode 2014-2020 - Art. 28 der Verordnung (EU) Nr. 1305/2013 - Richtlinie Agrarumwelt- und Klimamaßnahmen (RL AUK/2015) - Sächsisches Agrarumwelt- und Naturschutzprogramm (AUNaP)
វេបសាយ:
https://www.smul.sachsen.de/lfulg/download/AUK-Massnahmen-Ueberblick.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Hebblethwaite & Somody (2008): Progress in Best Management Practices. In: The Triazine Herbicides. 50 years Revolutionizing Agriculture
វេបសាយ:
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044451167-6.50035-0
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល