African market gardens [ប្រទេសសេណេហ្គាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Julie Zähringer
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_944 - ប្រទេសសេណេហ្គាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Dov Pasternak
International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICRISAT (ICRISAT) - ប្រទេសនីហ្សេ1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
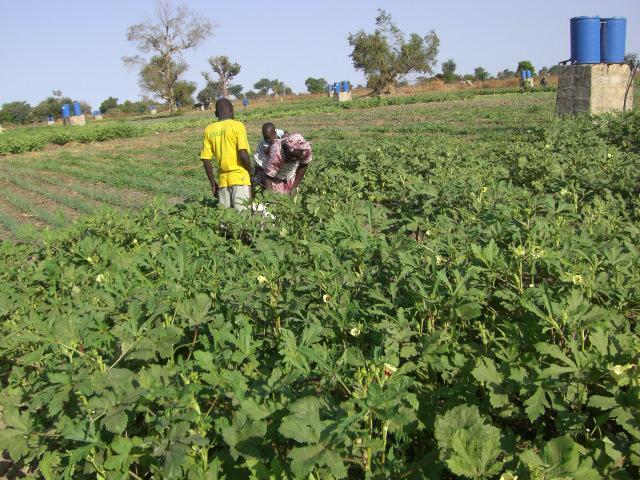
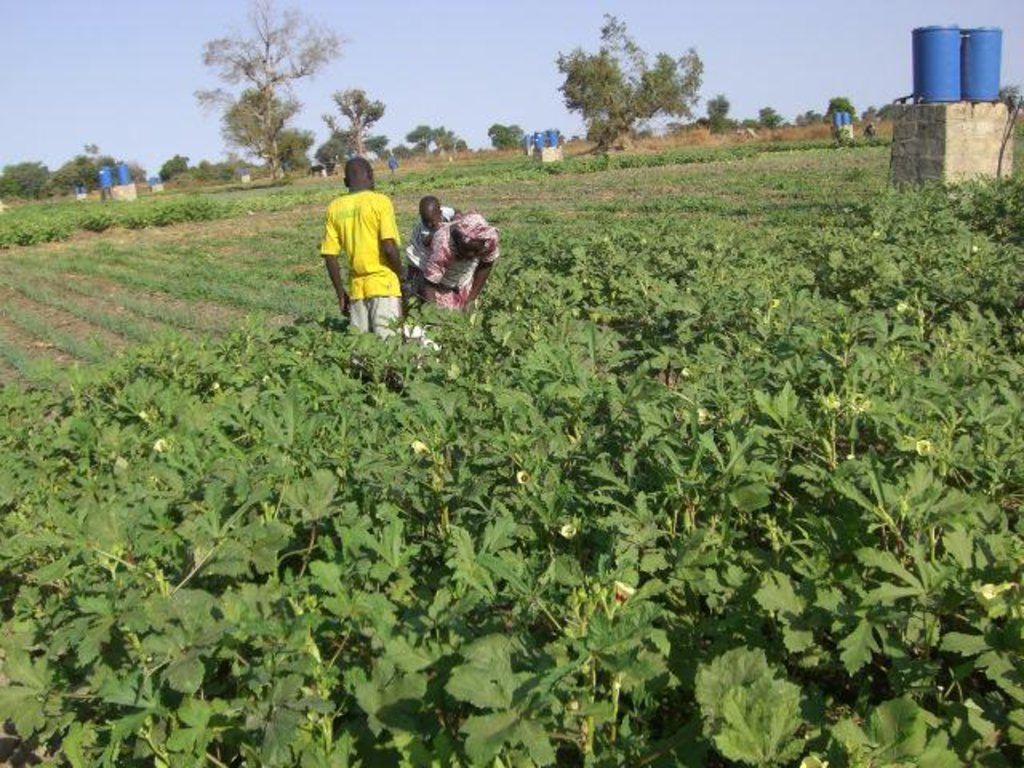
The African Market Garden (AMG) is a horticultural production system based on low-pressure drip irrigation.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
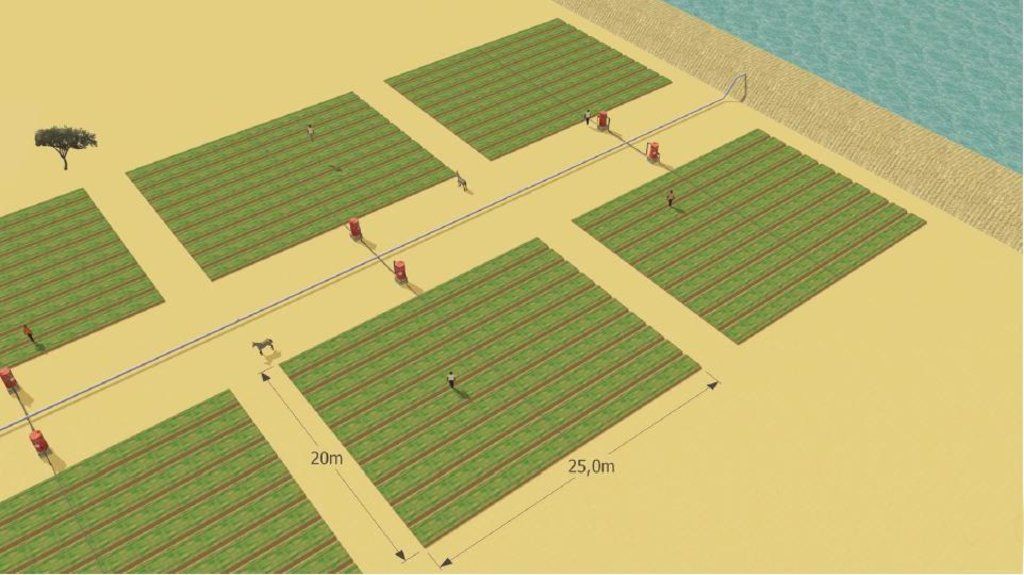
According to the level of experience, market orientation or social structure of the land users, four different AMG models have been developed. This case study focuses on the “Cluster System” which is suitable for an organized group of independent vegetable producers sharing a common water delivery system. From a central source, water is distributed through a pipe network to a cluster of plots. Each farmer operates a 1,000 m2 unit, and each is equipped with an elevated 200 litre barrel and a standard irrigation kit, including a tap, filter and thick-tube drip laterals. Minimal size of an AMG unit should be 500 m2. Affordable high-quality material is used and the design and operation is simple. The barrel also serves as a fertilizer tank. A float ensures a constant pressure head. Water supply is calculated by the time needed for delivery of the daily water dosage, or through the use of water dosing valves. Producers have individual control of water use. Since the AMG requires only 1 meter pressure for operation, it can draw on low-capacity renewable energy sources such as elevated dams, solar pumps or reservoirs. To supply an area of 50,000 m2 with 8 mm/day in the hot season a 400 m3-reservoir is required. The crops are planted on elevated beds. Water mixed with urea as fertilizer is applied daily. Drip irrigation improves growing conditions for crops while at the same time saving labor, water and other inputs. AMG is promoted as a holistic management package, integrating all aspects of production, post-harvest and marketing in one system. This includes the use of improved vegetable varieties, improved crop husbandry, integrated pest management, as well as improved storage, processing and marketing of products, and improved access to inputs.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The following establishment activities are connected to this technology: 1. Build concrete reservoir. 2. Drill borehole (110 mm diameter; 12 m deep, hand drilled). 3. Install motor pump and tubes to connect well with reservoir. 4. Install drip kit with tap, filter and drip laterals (8-16 mm in diameter). 5. Establish a fence to protect the garden.
For maintenance the following activities are required: 1. Prepare elevated beds with a basic dressing of 4 kg/m2 manure and 0.1 kg/m2 NPK fertilizer biannually. 2.Add urea to irrigation water (concentration: 50-100 ppm N). 3. Operate water supply system.
Natural / human environment: AMG is spreading fast in Senegal and Burkina Faso. Up-scaling of AMG in dry West Africa will depend on access to technology, inputs, knowledge and organization, and a conducive institutional environment.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសសេណេហ្គាល់
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Ngoyé Ndioffogor and Mbassis Tadadem
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
មតិយោបល់:
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: AMG is suitable for urban/peri¬urban areas where producers have access to credit, markets, technical support
Strong organisation in groups is important for the maintenance of the system and for access to training/backstopping
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
- វិធានការក្រោយការប្រមូលផល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A7: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Cluster system with several AMG plots connected to a central water source - in this case a small elevated dam
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading
Agronomic measure: drip irrigation
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
ICRISAT, Niamey, Niger
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
2.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Get inputs |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Tools | Unit | 1,0 | 65,0 | 65,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Drip system | Unit | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Oil drum | Unit | 1,0 | 56,0 | 56,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Well/borehole | Unit | 1,0 | 16,0 | 16,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Motor pump | Unit | 1,0 | 34,0 | 34,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Fence | Unit | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | PVC connections | Unit | 1,0 | 79,0 | 79,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 575,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 575,0 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare elevated beds with a basic dressing of 4 kg/m2 manure and 0.1 kg/m2 NPK fertilizer biannually | biannually |
| 2. | Add urea to irrigation water (concentration: 50-100 ppm N) | |
| 3. | Operate water supply system |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | Unit | 1,0 | 510,0 | 510,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 510,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 510,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
A unit corresponds to the area irrigated by one producer (=500 m2). Establishment costs include labour inputs (2 US$ per person-day). Annual maintenance costs include labour, fuel and agricultural inputs (e.g. fertilizer, seeds; based on ICRISAT recommended rates). For a 1000m2-unit prices are doubled (except for tools and fence)
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Effective application of fertilizer with the water
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to doubled profits from vegetable production (compared to traditional irrigation methods)
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced workload: total workload for AMG is 11.5 man-days compared to 30 man-days in traditional irrigation system (allows people to engage in other activities or education)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Production cost
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Costs for drip irrigated gardens are 50% lower than for traditional irrigated gardens due to savings in labour, water and consequently in fuel
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved organisation (farmer associations, user groups)
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved knowledge on irrigation techniques /horticulture
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Water availability / reduced pressure on water resources
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Effective use of water due to accurate and equal distribution of water at optimal rates
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Payback period is only 6 months. Net income per farmer after all deduction is about US$ 1,000 per year. The profitability of the AMG is around double that of vegetable gardens irrigated with traditional methods
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: AMG is spreading fast in Senegal and Burkina Faso. Cost reduction (e.g. alternative energy sources), collective action and intensive training / back¬stopping are very important provisions for successful adoption. Adoption trend: Up-scaling of AMG in dry West Africa will depend on access to technology, inputs, knowledge and organization, and a conducive institutional environment.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| AMG is a holistic management package, integrating all aspects of production, post-harvest and marketing in one system |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Irrigated vegetable production is a capital intensive undertaking | sharing infrastructure, land and water through producer groups can cut investment costs by 60% per unit area. Set-up and operation costs further decrease if producer groups can use communally owned infrastructure and/or alternative energy sources (e.g. elevated dams, solar pumps, artesian well). |
| The AMG system is not suitable for farmers with limited access to knowledge, marketing and services | improve access to markets and training programs (for extensionists and farmers); guarantee technical assistance during 2-3 years; target the system to educated producers who make a living out of vegetable production. Set up AMG service and demonstration centres offering credit, farm inputs, marketing support, training and technical advice. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Woltering L., D. Pasternak and J. Ndjeunga. 2009. The African Market Garden: Development of an Integrated Horticultural Production System for Smallholder Producers in West Africa – Draft Submitted to Irrigation and Drainage 21-10-2009
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
ICRISAT. 2009. The African Market Garden - Advanced Horticulture for the Poor (Flyer)
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល