Delegating the management of facilities to users [ມາລິ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Dieter Nill
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Laura Ebneter
Délégation de gestion des équipements aux exploitants (French)
approaches_2503 - ມາລິ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ລາຍລະອຽດ ການຕິດຕໍ່ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ຊັບພະຍາກອນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Tamini Jacques
jacques.tamini@helvetas.org
HELVETAS - Swiss Intercooperation
ມາລິ
ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Doumbia Moussa
douballa03@yahoo.fr / bulonbasecom@yahoo.fr
Intercommunalité de Bougouni "Bulonba"
ມາລິ
ຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - ເຢຍລະມັນຊື່ຂອງ ສະຖາບັນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ ຫຼື ປະເມີນແນວທາງ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ຂອງການນໍາໃຊ້ເອກກະສານຂໍ້ມູນ ຂອງ WOCAT
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
01/07/2012
ຜູ້ສັງລວມ ແລະ ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມ ຍອມຮັບໃນເງື່ອນໄຂ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ພັນລະນາ ແນວທາງການຄຸ້ມຄອງນໍາໃຊ້ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ການອະທິບາຍ ໂດຍຫຍໍ້ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
Promote the sustainability and cost effectiveness of schemes by setting up management delegation systems that enable local authorities to entrust infrastructure owned by the territorial community to groups of local farmers.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງວິທີທາງ:
The basic economic infrastructure is usually provided through state or decentralised-authority funding. The building phase of the project is entirely managed by the territorial community (TC). A delegation process ensures that responsibility for managing this infrastructure is transferred to beneficiary actors organised in user associations. Agreements are concluded between the TCs and communities with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities. This agreement makes it possible to extend the ownership of schemes beyond that of the traditional management committee model. It can also increase local tax revenues and prolong the lifespan of facilities when they are well run.
The commune is the owner of the scheme but delegates its management to a user group (an interprofessional farming committee for lowland development projects) by means of a management delegation contract. Member subscription fees and upkeep fees are paid into a bank account opened by the community. The commune has the right to oversee the administrative and financial management of the delegatee and ensures the application of access and farming rules in the scheme. Group managers regularly report on activities to other members and the commune.
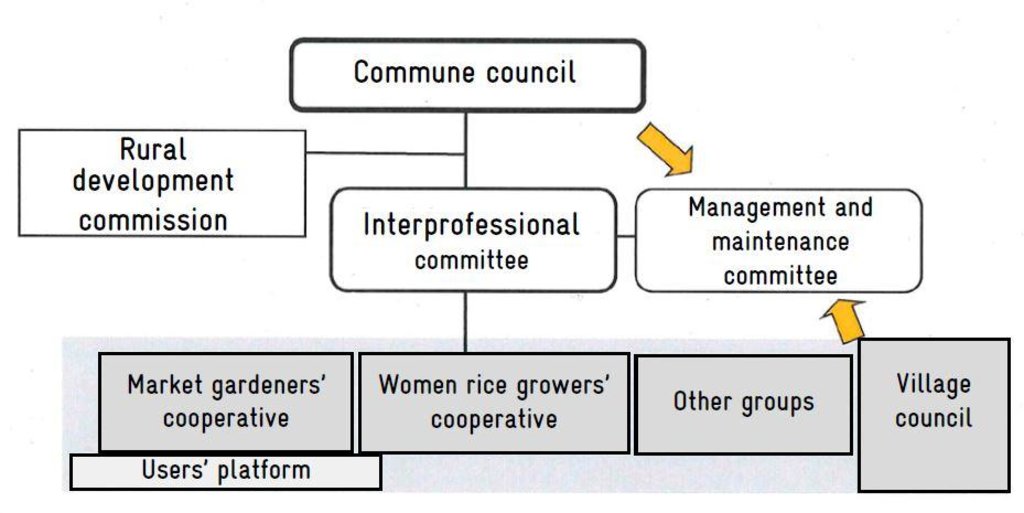
The commune council undertakes the overall project management of the installation works, contributes to funding the developments, provides key guidance on farming matters, delegates the management of the infrastructure to the interprofessional committee (IPC), supports the IPC in recovering fees, and ensures the monitoring and development of the project. The rural development commission of the commune council exists within each council. Its role is to catalogue the issues actors face and propose solutions to the commune council, support cooperatives in their search for partners together with the IPC, research the land titles for schemes on behalf of the council (registration), validate the development plan, support IPC in managing conflicts between cooperatives, and carry out any other tasks that are required of it by the commune council. The interprofessional committee brings together representatives from different cooperatives, associations and groups and takes on the delegated management role. Its role is to: maintain communications between users, the town hall and partners; coordinate activities that affect several local-level cooperatives; ensure the rational use of lowland resources; secure the agreement of the different user groups on the rules for accessing and dividing up the scheme site; assess and validate the cooperatives’ farming plans (individual needs analysis in terms of production capacity); monitor the use of inputs, seed and equipment obtained by the cooperatives; receive the fees collected by each cooperative from its members; manage renovation and maintenance funds; prevent conflicts of interest arising among the cooperatives. The management committee is a sub-committee within IPC and is tasked with managing water supply (opening and closing the distribution gates), carrying out small-scale maintenance and alerting the IPC to any failures to respect the farming code. Consultancies facilitate the process, support the institutional and organisational strengthening of actors and provide training on management tools. Technical services ensure the application of technical and environmental standards and ensure sound financial management (fee collection, financial controls, delegated public procurement). The project team provides advisory support, organises users structurally and delivers training, tools, coordination and monitoring.
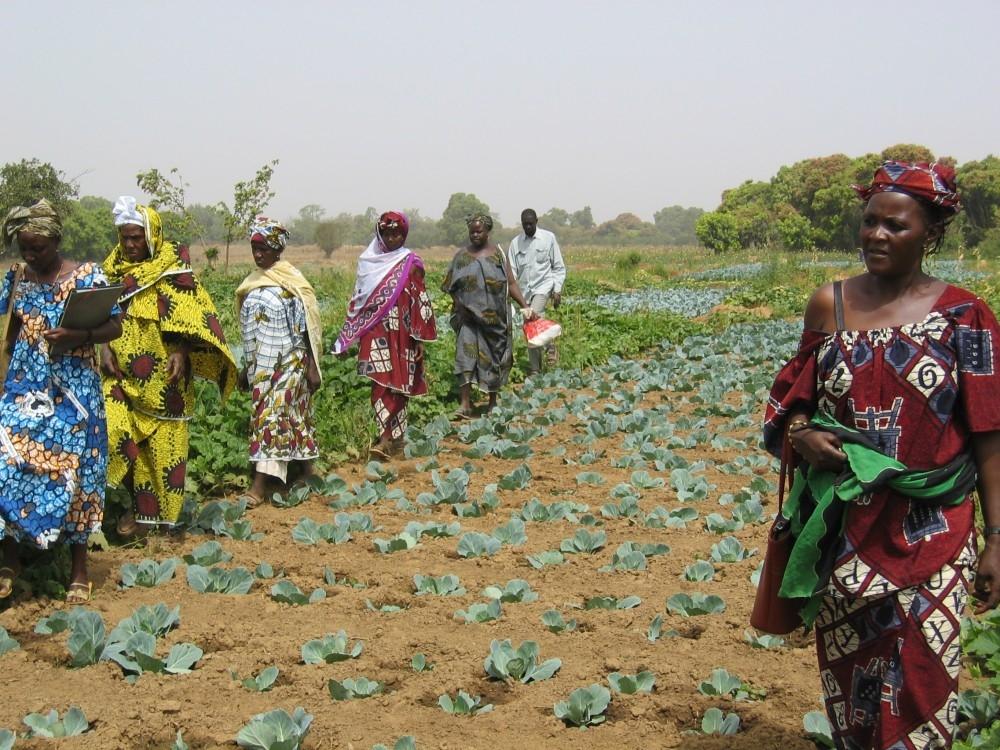
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງແນວທາງ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ແນວທາງໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ປະເທດ:
ມາລິ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Mali
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Sikasso region, circles of Bougouni, Kolondiéba and Yanfolila
2.6 ວັນທີເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ສິ້ນສຸດ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ວິທີທາງ
ສະແດງປີຂອງການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ:
2008
2.8 ເປົ້າໝາຍ / ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ ຂອງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities
The objective of the practice is to promote the sustainability and cost effectiveness of schemes by setting up management delegation systems that enable local authorities to entrust infrastructure owned by the territorial community to groups of local farmers.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: lack of infrastructure for local farmers, low sustainability and cost-effectiveness of schemes
2.9 ເງື່ອນໄຂອໍານວຍ ຫຼື ຂັດຂວາງການປະຕິບັດຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການນໍາໃຊ້ຕາມແນວທາງ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ, ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ
- ເຊື່ອງຊ້ອນ
The basic economic infrastructure is usually provided through state or decentralised-authority funding.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: A delegation process ensures that responsibility for managing this infrastructure is transferred to beneficiary actors organised in user associations with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities.
3. ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ແລະ ບົດບາດຂອງພາກສ່ວນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງທີ່ໄດ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ
3.1 ຜູ້ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນວິທີທາງ ແລະ ພາລະບົດບາດ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
- ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ທີ່ປຶກສາດ້ານກະສິກໍາ
- ອໍານາດ ການປົກຄອງທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
- ພະນັກງານຂັ້ນສູນກາງ (ຜູ້ວາງແຜນ, ຜູ້ສ້າງນະໂຍບາຍ)
3.2 ການມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນຂອງແນວທາງ
| ການລວບລວມ ເອົາຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ / ຊຸມຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຜູ້ໃດທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນແຕ່ລະກິດຈະກໍາ? | |
|---|---|---|
| ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ / ແຮງຈູງໃຈ | ການຮ່ວມມື | |
| ການວາງແຜນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | |
| ການປະຕິບັດ | ການຮ່ວມມື | |
| ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ / ການປະເມີນຜົນ | ການຮ່ວມມື | |
| Research | ການບໍ່ປະຕິບັດ |
3.3 ແຜນວາດ (ຖ້າມີ)
ການອະທິບາຍ:
The measure relies on the direct actors shown in the diagram, who are supported by other stakeholders. From the start of installation works, the commune supports the project in setting up a management system. Installation works are co-funded by the technical and financial partners (TFP), communes and beneficiary villages. It must nevertheless be highlighted that the infrastructure remains the property of the commune and beneficiaries must pay a fee for its upkeep. The commune selects the consultancy (project manager) and chooses the contractor. The commune also Monitors scheme installation and accepts works. A second consultancy is tasked with giving producers guidance on farming and management techniques. The different user groups (market gardeners/planters, women rice growers, livestock farmers, etc.) are formed into interprofessional committees or farming committees. The commune draws up the draft delegated management contract with the interprofessional committee or the cooperative. To this end, it evaluates the potential of the resources that can be mobilised and discusses with its partners the rules for farming the scheme and the methods for its maintenance and repair. Following this, the contract is signed.
3.4 ການຕັດສິນໃຈກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກເຕັກໂນໂລຢີຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ຄົນທີ່ຕັດສິນໃຈ ກ່ຽວກັບການຄັດເລືອກຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ / ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຈະໄດ້ຮັບການປະຕິບັດ:
- ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຫຼັກ, ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ໂດຍຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ອະທິບາຍ:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານວິຊາການ, ການສ້າງຄວາມສາມາດ, ແລະ ການຈັດການຄວາມຮູ້.
4.2 ການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ
ເຮັດຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນມີການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸວ່າການສະໜອງ ການບໍລິການ ໃຫ້ຄໍາປຶກສາ:
- ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ອະທິບາຍ / ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Setting up this system requires ongoing support for two to five years to allow beneficiaries to take ownership of the scheme.
4.3 ສະຖາບັນການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ (ການພັດທະນາອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ຫຼື ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໂດຍການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງບໍ່?
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
ລະບຸ ທາງສະຖາບັນ ໄດ້ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ໃນລະດັບໃດ (ຫຼາຍ):
- ທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
ລະບຸ ປະເພດ ຂອງສະໜັບສະໜູນ:
- ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ
4.4 ຕິດຕາມກວດກາ ແລະ ປະເມີນຜົນ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ໄດ້ມີການປະເມີນຜົນ ແລະ ຕິດຕາມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
ນີ້້ແມ່ນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງ ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ ຂອງວິທີທາງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຫົວຂໍ້:
- ສັງຄົມ
- ເສດຖະສາດ / ການຕະຫຼາດ
- ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
5. ການສະໜັບສະໜູນທາງດ້ານການເງິນ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນຈາກພາຍນອກ
5.1 ງົບປະມານປະຈໍາປີ ສໍາລັບວິທີທາງ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
ຄໍາເຫັນ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນຫຼັກ ຂອງການສະໜອງທຶນ / ຜູ້ໃຫ້ທຶນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: private sector (technical and financial partners (TFP)): 85.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (commune): 10.0%; local community / land user(s) ( village): 5.0%
5.2 ການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ສະໜອງໃຫ້ແກ່ຜູ້ນໍາທີ່ດິນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ທາງດ້ານ ການເງິນ / ອຸປະກອນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າແມ່ນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງການສະໜັບສະໜູນ, ເງື່ອນໄຂ ແລະ ຜູູ້ສະໜອງ (ຫຼາຍ):
Installation works are co-funded by the technical and financial partners (TFP), communes and beneficiary villages. In small-scale irrigation projects, for example, the project provides up to 85% of the funds; the village 5% and the commune 10%. The beneficiaries contribute either in-kind or financially.
5.3 ເງິນສົມທົບສໍາລັບການນໍາໃຊ້ສະເພາະປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລີດກະສິກໍາ (ລວມທັງແຮງງານ)
ຖ້າແຮງງານ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນ ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ, ແມ່ນບໍ່:
- ການອາສາ
6. ວິເຄາະຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ສັງລວມບັນຫາ
6.1 ຜົນກະທົບຂອງແນວທາງ
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດຊ່ວຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງໄດ້ບໍ?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Consensually agreed farming codes and rules are instituted and monitored. Agreements are concluded between the TCs and communities with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities.
ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ວິທີທາງ ສາມາດສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງ ທາງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ເສດຖະກິດບໍ່?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
The system was first initiated and developed at 34 commercial infrastructure trade fairs. Today, it involves 15 farming sites. The practice has been applied since 2008.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
In the Bougouni area, 552 hectares are being farmed by 1,671 rice growers, 80% of whom are women. Production has increased for 70% of growers. The principle of a maintenance fund has been accepted and is now operational, with deposits ranging from 75,000 to 300,000 CFA francs per year
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ບໍ່
- ມີ, ໜ້ອຍໜຶ່ງ
- ມີ, ພໍສົມຄວນ
- ມີ, ຫຼາຍ
6.2 ແຮງຈູງໃຈຫຼັກຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນໃນການປະຕິບັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຜະລິດເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
- ກໍາໄລເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ (ຄວາມສາມາດ), ການປັບປຸງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ, ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ, ອັດຕາສ່ວນ
6.3 ຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງກິດຈະກໍາວິທີທາງ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ ການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຜ່ານວິທີທາງໄດ້ບໍ່ (ໂດຍປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ຈາກພາກສ່ວນພາຍນອກ)?
- ບໍ່ແນ່ນອນ
ຖ້າ ບໍ່ ຫຼື ບໍ່ແນ່ໃຈ, ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ແລະ ຄໍາເຫັນ:
Setting up this system requires ongoing support for two to five years to allow beneficiaries to take ownership of the scheme.
6.4 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ ຂອງວິທີທາງ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Many repairs are already being handled by the delegated management structures. These structures ensure that the consensually agreed rules are appropriately applied. A new kind of partnership has been created between the local authorities and village communities. |
|
It can increase local tax revenues and prolong the lifespan of facilities when they are well run. How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The commune authorities must be willing to promote transparency in communications on works procurement and accept requests for clarification (public audits). The community must have leaders in place who are prepared to lead frank public discussions among key players that are also courteous and respectful. This also applies to the management committee. Monitoring and evaluation of the delegation contract is essential between the commune and platform. It is important to undertake an annual review, the conclusions of which will also be shared with the wider community. To do this, the management committee must be in a position to draw up a balance sheet. The village must be prepared to contribute (with their labour or funds) towards installing the scheme, prior to registering it in the PDESC. It is essential to remove any ambiguity from bylaws for the scheme belonging to the commune. If it is true that actors rarely challenge the old, established rules for accessing rice growing sites, the same cannot be said for market gardens, where the plot allocation rules fall easily into place. Growers must pay the amounts/fees agreed with the commune.) |
| Subscription fees are collected more easily: 84% of members pay their subscription fees for the area in question. Consensually agreed farming codes and rules are instituted and monitored. In the Bougouni area, 552 hectares are being farmed by 1,671 rice growers, 80% of whom are women. Production has increased for 70% of growers. The principle of a maintenance fund has been accepted and is now operational, with deposits ranging from 75,000 to 300,000 CFA francs per year. |
7. ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມໂຍງ
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
7.2 ເອກະສານທົ່ວໄປທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Rapport appui à la valorisation des ouvrages hydroagricoles [Report on supporting the development of small-scale irrigation schemes], GSAD, June 2012
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Annual report: Monitoring lowland areas, BEACIL, June 2012
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ