Holistic demonstration [ອິນເດຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Unknown User
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Samagra Jalanayan Abhivrudhi Pratyakshike (Kannada)
technologies_1084 - ອິນເດຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Holistic demonstration includes integrated cultivation of Agri-Horti-Silvi technologies. Along with the Soil & water Conservation structures suitable to the site.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
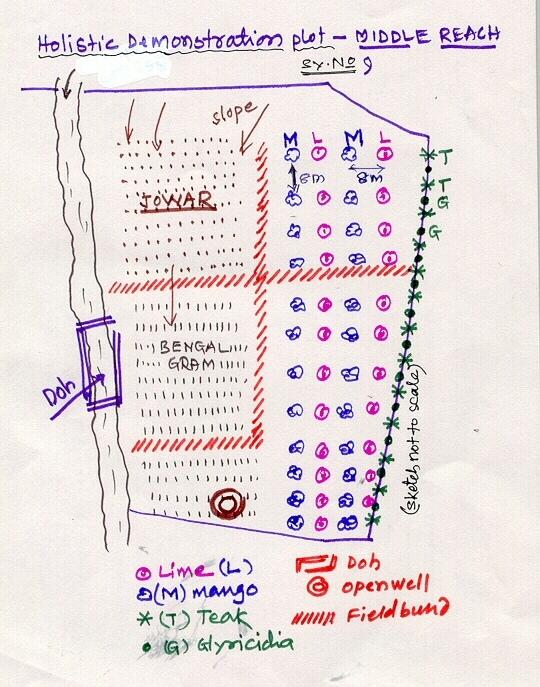
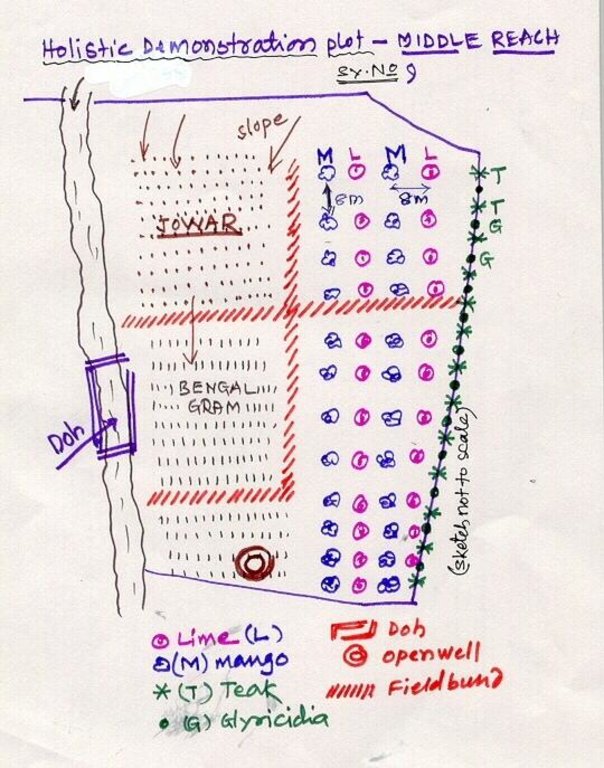
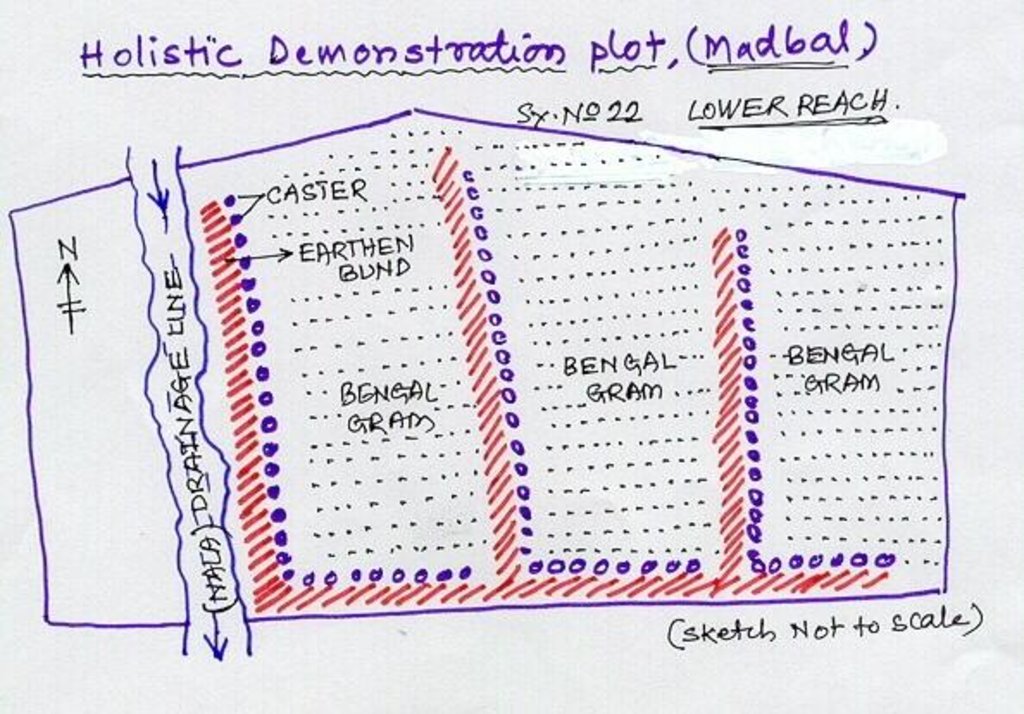
Holistic demonstration was taken in the upper reach, middle reach and lower reach (2 hectares each) in a village in the watershed. The demonstration units includes soil & water consercvation structures also. Crop demonstration with integrated pest management, seed treatment, pitcher irrigation practices, varietal trails were implemented to increase the overall per capita income of the farmer. However, the suitable SWC was according to the site of lower reach/ upper reach or middle reach. The plot was accommodated with suitable field crops, horticultural species either on the bunds or in the fiels itself and some fodder crops, some forestry species etc.
Purpose of the Technology: The demonstration units now serve as the units of awareness brining in understanding the holistic approach and also to encourage the other farmers to replicate the same in their fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: (1) site selection with concerned farmer, (2) design and preparation of estimates by the project staff, (3) discussion with the VWDC and community, (4) discussion regarding contribution with the farmer (5) layout and construction by the project staff with the contribution from the concerned farmers.
Natural / human environment: This technology was taken up in the semi arid condition and in the erratic rainfall condition.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອິນເດຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Karnataka
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Chitapur taluk of Gulbarga district
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ກະຈາຍໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເນື້ອທີ່ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມ (ເປັນ ກິໂລຕາແມັດ):
0.12
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- < 0.1 ກິໂລແມັດ2 (10 ເຮັກຕາ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.12 km2.
The technology area comprises of 2 ha area each in upper reach, middle reach and lower reach in a village of the watershed. In this area cultivation of agri-horti-silvi practices, agronomic trials, in-situ conservation etc were taken with active involvement of the the farmers.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຫຼາຍກ່ອນ 50 ປີຜ່ານມາ (ແບບພື້ນບ້ານ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
Mainly from the SWC specialist
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ທັນຍາພືດ-ເຂົ້າຟາງ
- ພືດອາຫານສັດ-ປະເພດຫຍ້າ
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວປະເພດອື່ນໆ
- ພືດຕະກູນຖົ່ວ ແລະ ຖົ່ວແປກ
- ພືດປະເພດໃຫ້ແກ່ນ-ໝາກງາ, ດອກປອບປີ, ມັດສຕາດ, ອື່ນໆ
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ພືດເປັນຢາ, ກິ່ນຫອມ, ຕົ້ນໄມ້ປາບສັດຕູພືດ-ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
ການປູກພືດທີ່ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກນາວ
- ໝາກໄມ້, ອື່ນໆ
- ໝາກມ່ວງ, ໝາກມັງຄຸດ, ໝາກສີດາ
- ຫມາກໄມ້ນ້ອຍ (ຫມາກໂປມ, ໝາກຊາລີ, ໝາກຈອງ, ແລະອື່ນໆ)
- Tree croppisapota (cf. Sapotaceae family), drumstick (cf. Moringa oleifera), Tamarind, Gliricidia (Gliricidia sepium perennial, medium-sized (2-15 m high) legume tree) pongama (legume)
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
- cattle

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ
ປະເພດຂອງຕົ້ນໄມ້:
- Azadirachta indica
- ໄມ້ໄຜ່
- Tectona grandis
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງ
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ໝາກໄມ້ ແລະ ແກ່ນຖົ່ວ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop land : Low yields due to erosion, less soil moisture, shallow to medium soils. Poor and erratic rainfall, water holding capacity is less.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop land - Uncertain rainfall, more soil loss and poor yields.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: the village cattle are let free for grazing on the common land for some time in the day and they go back and then I is again stall feeding.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: others (scattered)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During kharif (monsoon) season the main crop is redgram (Tur), in addition few cereals were taken, followed by jowar in the major rabi (post-monsoon) crop. No cultivation was o\bserved in summer, farmer are now cultivating vegetable and fruit crop,
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding (both ranked 2)
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ກິດຈະກໍາ ທີ່ລົບກວນດິນ
- ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງພະຍາດ ແລະ ສັດຕູພືດ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ (ລວມທັງກະສິກຳອິນຊີ)
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຊົນລະປະທານ (ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ, ລະບາຍ)
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Lower Reach holistic demonstration plot showing various soil & moisture conservation structures, field crops and bund stabilization by vegetation.
Location: Bennur-B nala watershed Chitapur taluk. Chitapur taluk, Gulbarga District (Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: saplings
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: layout
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: sapplings
Quantity/ density: 360
Remarks: layout
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200
Remarks: layout
Agronomic measure: others (vermicompost)
Material/ species: material
Minimum tillage
Remarks: material
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: pit, sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: other (brushwood dam)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Multidimensional participatory holistic farming system, fallow to cultivable land
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
GK Ron, JPO KWDP Danida Bijapu
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Rupees
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
46.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
0.73
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | Sumer |
| 2. | Procurement of seed/ seedlings | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Sowing of grass, shrub seeds | After first shower |
| 4. | Planting of sappling | After first shower |
| 5. | Survey/ layout | April |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | may |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to the site | May |
| 8. | Construction of bunds, farm pond | may |
| 9. | Construction of brushwood dam, doh | June |
| 10. | Training, capacity building of the farmer | february - March |
| 11. | Establishment of sructural measures | April-June |
| 12. | establishment of vegetative measures | July-September |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 510.0 | 510.0 | 10.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 114.0 | 114.0 | 3.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 169.0 | 169.0 | 74.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 157.0 | 157.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 76.0 | 76.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 3.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 2.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1259.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 27.37 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching | Summer / each cropping season |
| 2. | Across slope ploughing | Summer / each cropping season |
| 3. | In-situ maisture conservation | before sowing / |
| 4. | Watering | summer /once in 10 days |
| 5. | Weeding, mulching | 2-3 months after planting /twice in a year |
| 6. | Re-seeding of grass/ shrub | before first shower /up to 2 years |
| 7. | casualty replacement | before first shower /1, 2, and 3rd years |
| 8. | fencing | during sumer period /every summer season of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year |
| 9. | Repair of breaches in bund | July to september/as required |
| 10. | Desilting of traps | October-November/annual |
| 11. | Refresher interaction with farmer | / seasonally |
| 12. | Rgular meetings | / as and when required |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 51.0 | 51.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 100.0 |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.7 | 15.7 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 7.6 | 7.6 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 100.0 |
| ອື່ນໆ | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 124.1 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 2.7 | |||||
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Non availability of stones, boulders
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
750-800 mm
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (422.8 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateu/plains (3-4% slope, ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (3-4%)
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (60 cm, ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (eroded soils)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high run-off from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກຫຼາຍ
- ທຸກຍາກ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
7% of the land users are average wealthy and own 26% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 58% of the land.
28% of the land users are poor and own 16% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off season employment
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha: Joint farmers, land shared by brothers (ranked 1), 1-2 ha (ranked 2), 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha: Not much grazing land is available in the village.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Drought from last 3 years
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
SWC takes small piece of cultivable land
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Village watershed development committee, users groups etc.
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Project support is expected by most of the farmers at a time.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Area was previously barren
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Good vegetative cover
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Ground cover established with vegetative hedges.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຄວາມຮູນແຮງ ຂອງລົມ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
Soil fertility
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Introduction of legume species (glyricidia)
Biodiversity
Waterlogging
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Not a genereal problem. But only on this plot.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
In-situ conservation
ລົມ ທີ່ພັດເອົາຕະກອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Establishment of ground covers
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ປານກາງ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
452
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
417 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Overall returns fro\m the piece of land is increased owing to horticulture and agriculture crops. Biomass increases. This is seen by other farmers and they are motivated to go for its adaption.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
|
Economic sustainability How can they be sustained / enhanced? vegetative and green manure vermicompost etc. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Effective SWC How can they be sustained / enhanced? maibntenance by the individual farmers |
|
water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting structure |
|
Integrated approach How can they be sustained / enhanced? regular contact |
|
increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated cultivation |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Production (benefits) adversly affected due to drought. | Due to longer dry spel in the area (last three years) |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Non-availability of agricultural improved seed material at local level | by linkage of VWDCs with the Agricultural Research Station and Krishi Vignyan Kendra. |
| conflicts | demands by more number of farmers could not be met by the project at a time. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ