Holistic demonstration [อินเดีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Samagra Jalanayan Abhivrudhi Pratyakshike (Kannada)
technologies_1084 - อินเดีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Holistic demonstration includes integrated cultivation of Agri-Horti-Silvi technologies. Along with the Soil & water Conservation structures suitable to the site.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
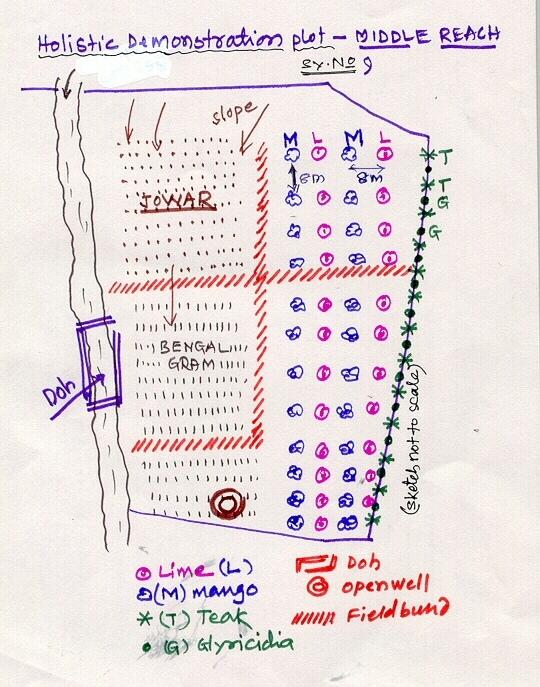
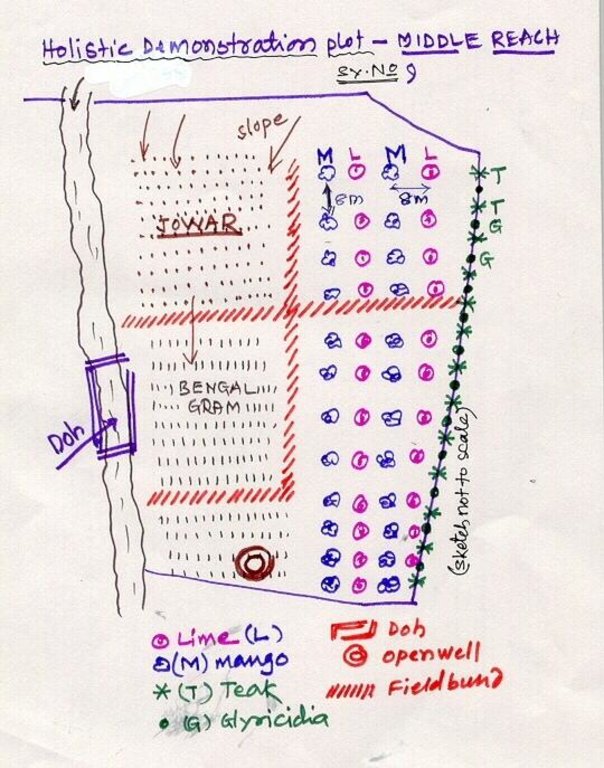
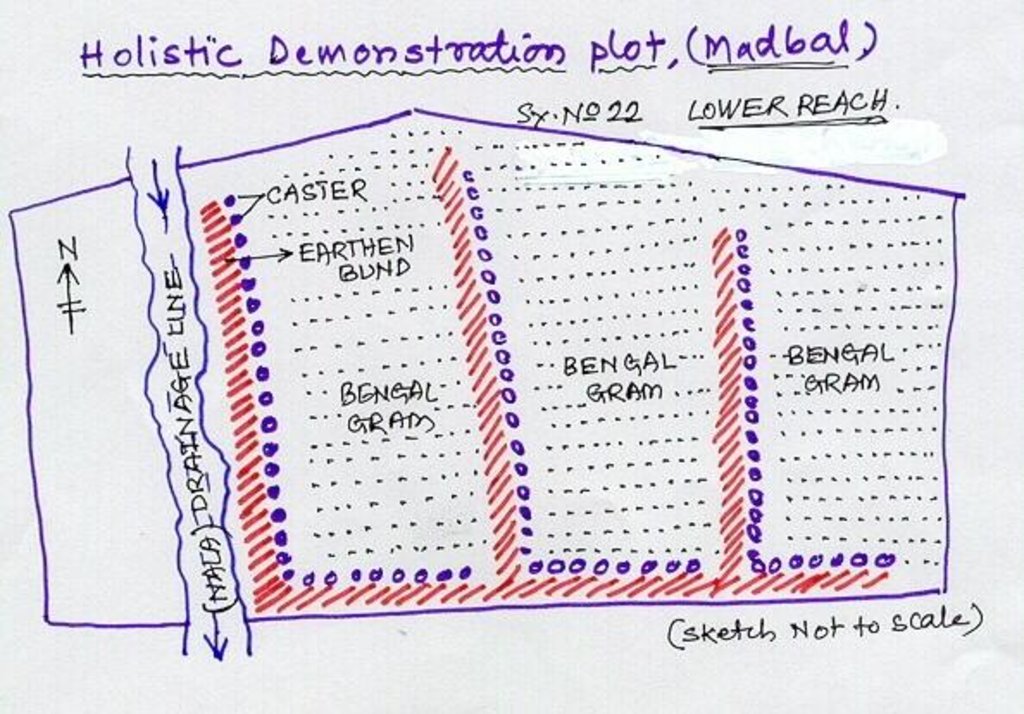
Holistic demonstration was taken in the upper reach, middle reach and lower reach (2 hectares each) in a village in the watershed. The demonstration units includes soil & water consercvation structures also. Crop demonstration with integrated pest management, seed treatment, pitcher irrigation practices, varietal trails were implemented to increase the overall per capita income of the farmer. However, the suitable SWC was according to the site of lower reach/ upper reach or middle reach. The plot was accommodated with suitable field crops, horticultural species either on the bunds or in the fiels itself and some fodder crops, some forestry species etc.
Purpose of the Technology: The demonstration units now serve as the units of awareness brining in understanding the holistic approach and also to encourage the other farmers to replicate the same in their fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: (1) site selection with concerned farmer, (2) design and preparation of estimates by the project staff, (3) discussion with the VWDC and community, (4) discussion regarding contribution with the farmer (5) layout and construction by the project staff with the contribution from the concerned farmers.
Natural / human environment: This technology was taken up in the semi arid condition and in the erratic rainfall condition.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
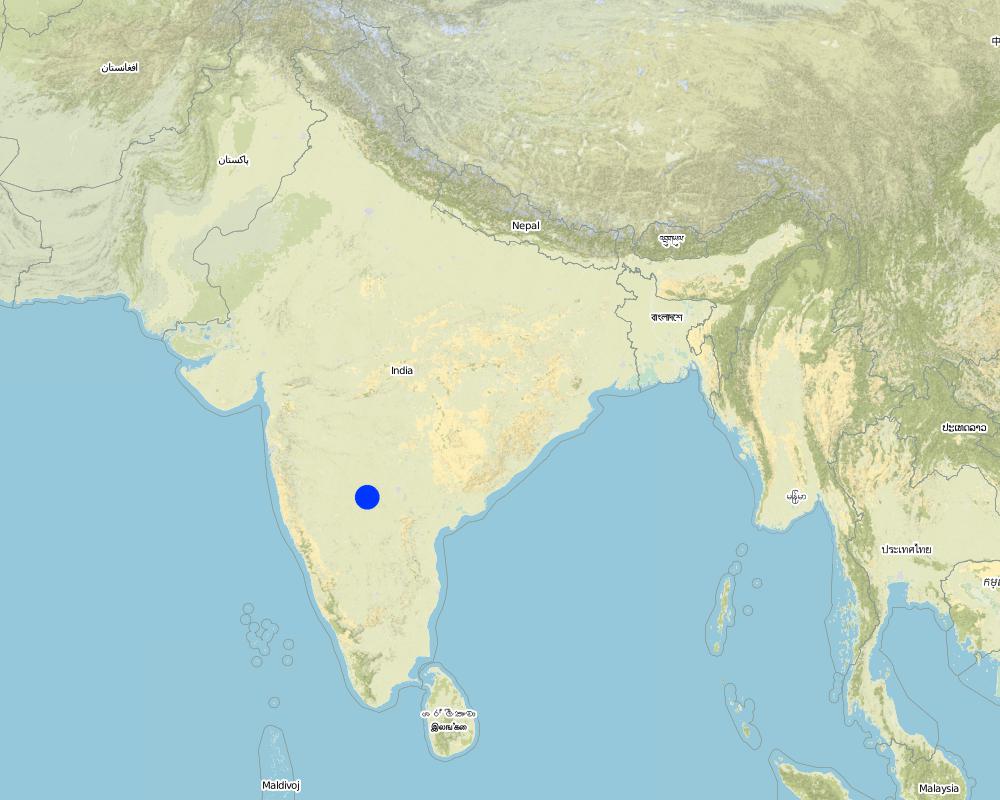
ประเทศ:
อินเดีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Karnataka
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Chitapur taluk of Gulbarga district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.12
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.12 km2.
The technology area comprises of 2 ha area each in upper reach, middle reach and lower reach in a village of the watershed. In this area cultivation of agri-horti-silvi practices, agronomic trials, in-situ conservation etc were taken with active involvement of the the farmers.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Mainly from the SWC specialist
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - sorghum
- fodder crops - grasses
- legumes and pulses - other
- legumes and pulses - peas
- seed crops - sesame, poppy, mustard, other
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal plants - perennial
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- citrus
- fruits, other
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
- Tree croppisapota (cf. Sapotaceae family), drumstick (cf. Moringa oleifera), Tamarind, Gliricidia (Gliricidia sepium perennial, medium-sized (2-15 m high) legume tree) pongama (legume)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
- cattle

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Type of tree:
- Azadirachta indica
- Bamboo bamboo
- Tectona grandis
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop land : Low yields due to erosion, less soil moisture, shallow to medium soils. Poor and erratic rainfall, water holding capacity is less.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop land - Uncertain rainfall, more soil loss and poor yields.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: the village cattle are let free for grazing on the common land for some time in the day and they go back and then I is again stall feeding.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: others (scattered)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: During kharif (monsoon) season the main crop is redgram (Tur), in addition few cereals were taken, followed by jowar in the major rabi (post-monsoon) crop. No cultivation was o\bserved in summer, farmer are now cultivating vegetable and fruit crop,
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding (both ranked 2)
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Lower Reach holistic demonstration plot showing various soil & moisture conservation structures, field crops and bund stabilization by vegetation.
Location: Bennur-B nala watershed Chitapur taluk. Chitapur taluk, Gulbarga District (Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: saplings
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: layout
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: sapplings
Quantity/ density: 360
Remarks: layout
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200
Remarks: layout
Agronomic measure: others (vermicompost)
Material/ species: material
Minimum tillage
Remarks: material
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Trees/ shrubs species: Neem, Glyricdia, Pongamia, Bamboo
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango. Tamarind, Lime, Sapota, Clustard apple
Grass species: Napiar
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 12
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: pit, sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Structural measure: other (brushwood dam)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Multidimensional participatory holistic farming system, fallow to cultivable land
ผู้เขียน:
GK Ron, JPO KWDP Danida Bijapu
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Rupees
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
46.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.73
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | Sumer |
| 2. | Procurement of seed/ seedlings | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Sowing of grass, shrub seeds | After first shower |
| 4. | Planting of sappling | After first shower |
| 5. | Survey/ layout | April |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | may |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to the site | May |
| 8. | Construction of bunds, farm pond | may |
| 9. | Construction of brushwood dam, doh | June |
| 10. | Training, capacity building of the farmer | february - March |
| 11. | Establishment of sructural measures | April-June |
| 12. | establishment of vegetative measures | July-September |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 510.0 | 510.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 114.0 | 114.0 | 3.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 169.0 | 169.0 | 74.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 157.0 | 157.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 76.0 | 76.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 3.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 2.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1259.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 27.37 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching | Summer / each cropping season |
| 2. | Across slope ploughing | Summer / each cropping season |
| 3. | In-situ maisture conservation | before sowing / |
| 4. | Watering | summer /once in 10 days |
| 5. | Weeding, mulching | 2-3 months after planting /twice in a year |
| 6. | Re-seeding of grass/ shrub | before first shower /up to 2 years |
| 7. | casualty replacement | before first shower /1, 2, and 3rd years |
| 8. | fencing | during sumer period /every summer season of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year |
| 9. | Repair of breaches in bund | July to september/as required |
| 10. | Desilting of traps | October-November/annual |
| 11. | Refresher interaction with farmer | / seasonally |
| 12. | Rgular meetings | / as and when required |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 51.0 | 51.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.7 | 15.7 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 7.6 | 7.6 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Pitcher pots | ha | 1.0 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 124.1 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2.7 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Non availability of stones, boulders
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
750-800 mm
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (422.8 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateu/plains (3-4% slope, ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (3-4%)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (60 cm, ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (eroded soils)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high run-off from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
7% of the land users are average wealthy and own 26% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 58% of the land.
28% of the land users are poor and own 16% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off season employment
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha: Joint farmers, land shared by brothers (ranked 1), 1-2 ha (ranked 2), 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha: Not much grazing land is available in the village.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Drought from last 3 years
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SWC takes small piece of cultivable land
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Village watershed development committee, users groups etc.
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Project support is expected by most of the farmers at a time.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Area was previously barren
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good vegetative cover
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Ground cover established with vegetative hedges.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Soil fertility
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Introduction of legume species (glyricidia)
Biodiversity
Waterlogging
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Not a genereal problem. But only on this plot.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In-situ conservation
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Establishment of ground covers
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
452
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
417 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Overall returns fro\m the piece of land is increased owing to horticulture and agriculture crops. Biomass increases. This is seen by other farmers and they are motivated to go for its adaption.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Economic sustainability How can they be sustained / enhanced? vegetative and green manure vermicompost etc. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Effective SWC How can they be sustained / enhanced? maibntenance by the individual farmers |
|
water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting structure |
|
Integrated approach How can they be sustained / enhanced? regular contact |
|
increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated cultivation |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Production (benefits) adversly affected due to drought. | Due to longer dry spel in the area (last three years) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Non-availability of agricultural improved seed material at local level | by linkage of VWDCs with the Agricultural Research Station and Krishi Vignyan Kendra. |
| conflicts | demands by more number of farmers could not be met by the project at a time. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล