Community Based Soil Rehabilitation for Grassland on Common Lands After Erdadication of the Invasive Lantana Camara [ອິນເດຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Santosh Gupta
- ບັນນາທິການ: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Kim Arora, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Udo Höggel, Joana Eichenberger, Sally Bunning
technologies_6689 - ອິນເດຍ
- ສະຫຼຸບສັງລວມຢ່າງທັງໝົດທີ່ເປັນ PDF
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ PDF ເພື່ອສັ່ງພິມ
- ສັງລວມເປັນບົດ ຢູ່ໃນ browser
- ບົດສະຫຼຸບ ສະບັບເຕັມ (ບໍ່ມີແບບຟອມ)
- Community Based Soil Rehabilitation for Grassland on Common Lands After Erdadication of the Invasive Lantana Camara: June 25, 2023 (inactive)
- Community Based Soil Rehabilitation for Grassland on Common Lands After Erdadication of the Invasive Lantana Camara: Sept. 14, 2023 (inactive)
- Community Based Soil Rehabilitation for Grassland on Common Lands After Erdadication of the Invasive Lantana Camara: April 11, 2024 (public)
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit - India (GIZ India) - ອິນເດຍຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - ເຄັນຢາຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - ອິນເດຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology described is aimed at restoring community land by controlling the spread of the invasive plant species known as Lantana Camara
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Community-based soil rehabilitation by eradicating the invasive plant Lantana Camara using the 'cut rootstock' method (refer to WOCAT technology 6660) is an effective, cost-efficient, and sustainable approach to restoring grasslands on common lands in the Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh. The three-tier institutional structure used in this eradication process involved the formation of informal women groups at the hamlet level (village organisational structure), the Village Environment Committee (VEC) at the village level, and an Executive Committee at the cluster level (higher organisational structure) so to ensure community involvement and ownership.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
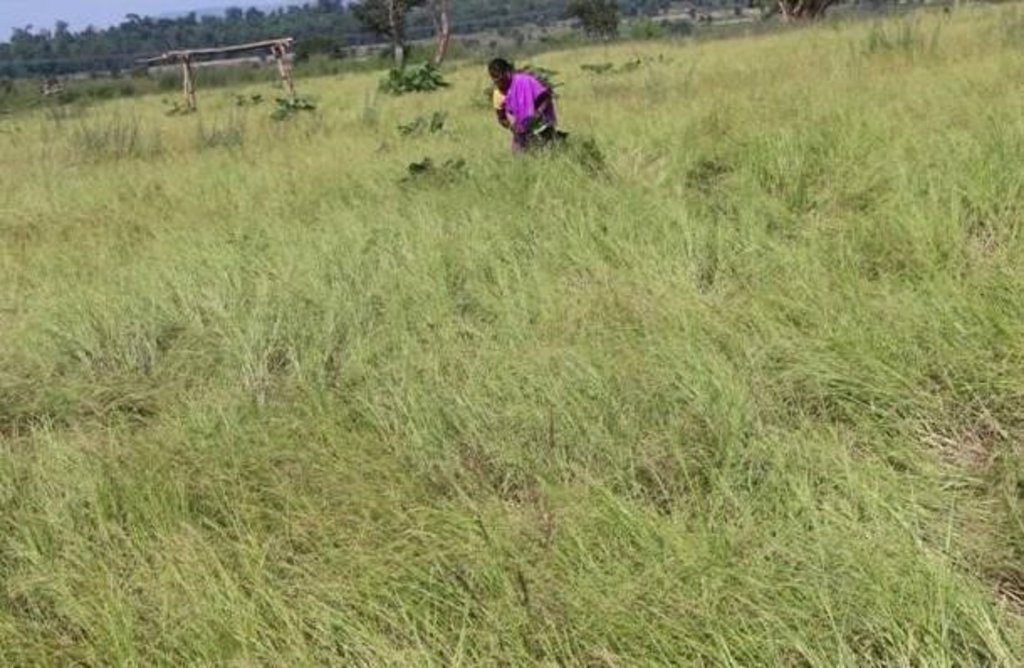
Community-based soil rehabilitation after the eradication of the invasive plant species, Lantana Camara, is an effective technique for restoring grasslands on common lands that had earlier been invaded by this species. The invasion of Lantana Camara can have significant negative impacts on the ecosystem, reducing the diversity of plant life and disrupting the local communities' use of common lands for grazing, for agriculture, and for collecting non-timber forest products.
To address these issues, a three-tier institutional structure is being used by the project-implementing organization Foundation for Ecological Security (FES). This structure includes the formation of informal women groups at the hamlet level, the Village Environment Committee (VEC) at the village level, and an executive committee at the cluster level. The VEC prepares proposals on common issues and plans with budgets that are presented to the executive committee, which is made up of a mix of individuals, with 50% of the seats reserved for women.
The first step in the process is for the village executive committee to take the Gram Sabha (Village Governing Body) into confidence and prepare bylaws for the restoration and conservation of the Lantana-eradicated site. These bylaws are regularly discussed in the village institution meeting to refresh the memory of the community and different stakeholders on how to properly conserve the site. Local resource persons facilitate the implementation of work.
One of the major works undertaken by these communities in the Mandla District is the soil rehabilitation from Lantana Camara for grassland restoration on common lands. The uprooting of Lantana is a tricky process, and improper methods can result in an even more forceful recurrence of the species. Therefore, the "cut rootstock" method is used, which involves cutting the root of the plant three inches below the ground and lifting the bush upside down to prevent it from gaining ground. This method is done between July and September before fruiting to avoid seed fall, which can cause recurrence for up to three years, also this is the time when the soil has enough moisture thus softness to uproot the Lantana plants.
The Cut Rootstock (CRS) method to control the spread of Lantana Camara is cost-effective and sustainable as it does not require the use of chemical herbicides or heavy machinery. In addition to using the CRS method, perching trees are located, and saplings are removed from under their canopies and along the nearby surface runoff zone. Regular monitoring and follow-up actions may be necessary to ensure the long-term success of this method in controlling the spread of Lantana Camara.
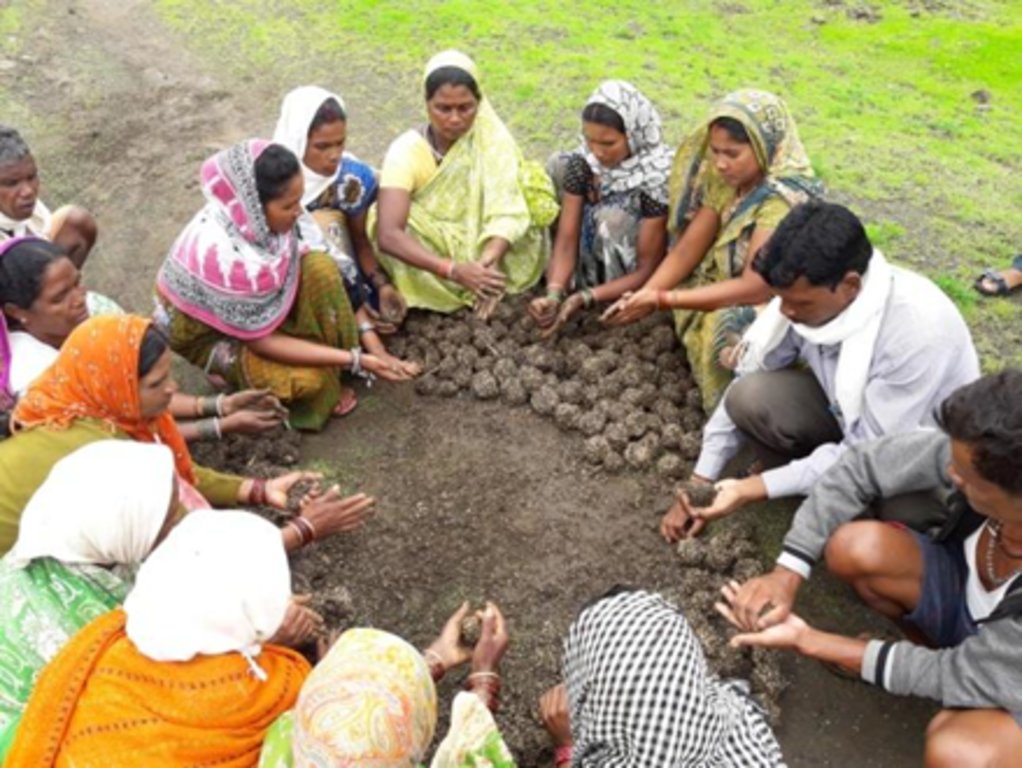
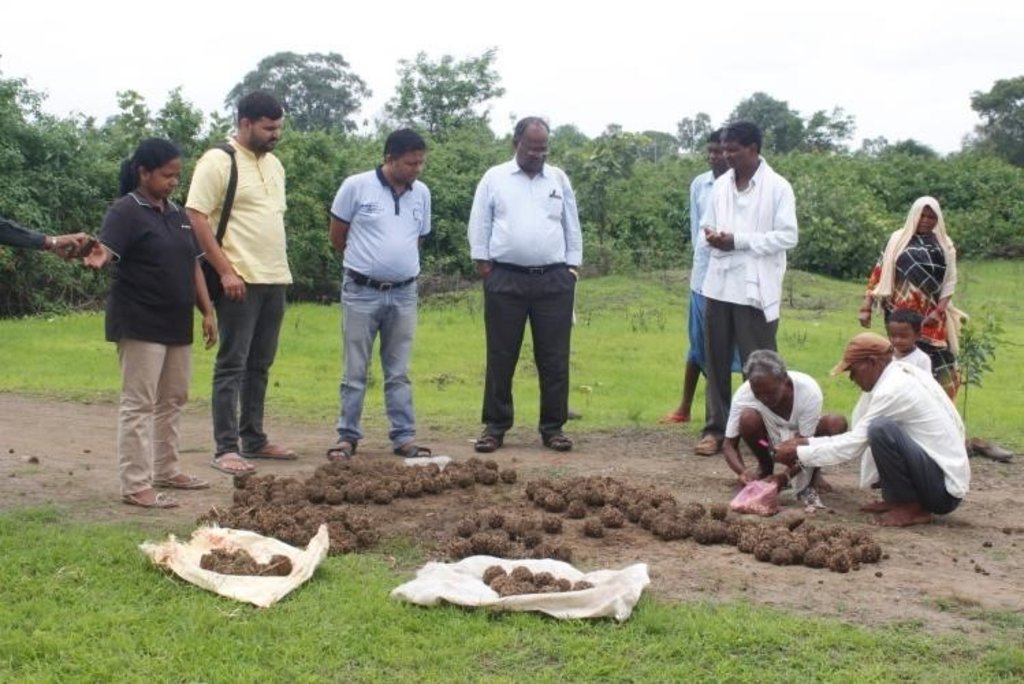
To prevent a recurrence, measures such as mopping for three years continuously, planting and seed sowing in areas where rootstocks seem to be less, and grass seed sowing are executed. The community institution ensures the collection of indigenous grass species, which are made into seed balls and sown before the advent of monsoon. These grass seeds germinate and grow in the rainy season, reducing the suitable environment for Lantana seed germination. Revegetation measures involve selecting and planting grazing hardy, fire hardy, and water hardy tree species such as bamboo, Khameer, Java Plum, Karanj (Pongame oil tree), Aonla, Harra, and other non-timber forest product-producing tree species. These plants are selected to create a three-tiered forest and sustainably provide food, fuel wood, and fodder. Once established, they do not allow Lantana to grow.
Biomass assessment is undertaken every year to assess the improvement in the status of the biomass in the plot, and the findings are shared with the community to motivate them to follow the rules and regulations formulated by the village institution. Cut and carry practices are allowed from the second year, but open grazing is prohibited, and Lantana eradication from nearby areas is required while cutting the grass. This helps to bring Lantana under control while sustainably utilizing the grass resources.
This initiative has ensured access to common lands for the local communities, access to fodder and green grass for livestock and the emergence of biodiversity in the area. This initiative is well recognised by Government institutions and policy makers.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອິນເດຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Madhya Pradesh
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Village: Changaniya, Block- Bichhiya, Mandla
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology is applied on common lands viz. common grazing land, forest, Gram Panchayat land
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸປີ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
2016
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
FES has done extensive research and studies to find out the appropriate technologies and approaches to remove the Lantana plants and rehabilitate the soil by restoring grasslands
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄື່ອນທີ່
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ຕັດຫຍ້າ ແລະ ຂົນຫຍ້າ / ບໍ່ມີທົ່ງຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບປຸງ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
- Eradication of Lantana and restoring the grasslands
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ຄວາຍ
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ
- ແບ້
ແມ່ນການເຝືກຄຸ້ມຄອງ ການປູກພືດປະສົມປະສານ ກັບການລ້ຽງສັດບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- economic security, investment prestige
ສາຍພັນ:
ຄວາຍ
ສາຍພັນ:
ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນນົມ
ສາຍພັນ:
ແບ້

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- (ເຄິ່ງ) ປ່າໄມ້ທໍາມະຊາດ / ປ່າປູກໄມ້
(ເຄີ່ງ) ປ່າທໍາມະຊາດ / ປ່າປູກ: ລະບຸປະເພດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ:
- ການເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍໄມ້ທີ່ຕັດ / ໄມ້ທີ່ຕາຍແລ້ວອອກໄປ
- ການນຳໃຊ້ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງ
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ທີ່ຖືກລະບຸຢູ່ຂ້າງເທິງ ເປັນປ່າຜັດປ່ຽນໃບ ຫລື ປ່າດົງດິບ?
- ການປ່ຽນໃບ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ໝາກໄມ້ ແລະ ແກ່ນຖົ່ວ
- ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The common land in villages which is generally not maintained, so allowing for the growth of invasive species, and unregulated open grazing is restored by the local community in a participatory manner for common benefits.
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ແມ່ນ (ກະລຸນາຕື່ມໃສ່ ຄຳຖາມຂ້າງລຸ່ມນີ້ກ່ຽວກັບການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ກ່ອນການທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ)
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄື່ອນທີ່
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ຕັດຫຍ້າ ແລະ ຂົນຫຍ້າ / ບໍ່ມີທົ່ງຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດ
- After restoration of common land, grasses are allowed to grow
ແມ່ນການເຝືກຄຸ້ມຄອງ ການປູກພືດປະສົມປະສານ ກັບການລ້ຽງສັດບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- Common village land and fringe areas of forests
- Indigenous grass restoration on common lands
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ທີ່ຖືກລະບຸຢູ່ຂ້າງເທິງ ເປັນປ່າຜັດປ່ຽນໃບ ຫລື ປ່າດົງດິບ?
- ການປ່ຽນໃບ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ໝາກໄມ້ ແລະ ແກ່ນຖົ່ວ
- ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ປ່າໄມ້ອື່ນໆ
- ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The common lands are restored to grasslands in a participatory manner
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Mandla is a predominantly rainfed district of Madhya Pradesh, with agriculture being the mainstay of the local economy. The District receives an average annual rainfall of around 1280 mm, with the monsoon season being the primary source of precipitation.
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປິດພື້ນທີ່ (ຢຸດການນໍາໃຊ້, ເພື່ອປູກເປັນປ່າຟື້ນຟູ)
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງສັດລ້ຽງ ແລະ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
- ການປັບປຸງດິນ / ພືດຄຸມດິນ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V4: ການປູກທົດແທນ / ກຳຈັດສາຍພັນ ທີ່ຮຸກຮາມ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- M5: ການຄວບຄຸມ / ການປ່ຽນແປງຂອງອົງປະກອບຂອງຊະນິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Invasive species are removed and the land and soil are rehabilitated by promoting the growth of indigenous grasses. During the first year, no grazing is allowed. In the second year of restoration only manual cutting/carry of grasses is permitted.
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bf: ຜົນກະທົບ ຄວາມເສຍຫາຍ ຈາກໄຟໄໝ້
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Lantana has several disadvantages including being unpalatable, hindering the growth of other species, reducing the collection of NTFPs (non-timber forest products), and causing soil infertility and erosion. It also provides shelter to wild boar and tigers, leading to human and cattle conflict, and catching fire. Additionally, it has a hard seed cover and can remain dormant for up to 30 years, making eradication difficult.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Drawing of this technology does not require as there no technical structure being build as part of the intervention. The images indicated a rehabilitated field after the eradication of Lantana.
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
1
ຖ້ານໍາໃຊ້ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ເນື້ອທີ່ຕາມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ໃຫ້ປ່ຽບເປັນ 1 ເຮັກຕາ (ຕົວຢ່າງ: 1 ເຮັກຕາ = 4 ໄລ່ ): 1 ເຮັກຕາ = :
ha
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
INR (2023 April)
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
82.12
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
204
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of lantana | September-October (After Monsoon) |
| 2. | Preparation of seeds for sowing | Before the onset of Monsoon |
| 3. | Sowing of seeds | Just before the onset of monsoon or during the monsoon (June/July) |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The cost for Lantana eradication is being shared between the community institution and project
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Removal of lantana | ha | 1.0 | 7229.0 | 7229.0 | 20.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Land preparation for plantation | Person day | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ | Sowing of seeds | Person days | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Land preparation for plantation | ha | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seeds or planting material | Ha | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Cow dung and compost material | Ha | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 12329.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 150.13 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The remaining cost is being covered by the project funds routed through community participation.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The cost varies based on the density of lantana in the field. Depending on density, it varies from Rs 7729 per ha to Rs 2808 per ha. The work is done in a participatory manner by the local community. For the removal of the Lantana project funds routed, the plantation of indigenous grass seeds, curbing the regrowth of Lantana Camara, etc work is undertaken by the local community.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Regular monitoring of the plantation area | July to November |
| 2. | Application of compost | June-July |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Lantana Camara is a persistent weed, and even after complete eradication from common lands, its seeds can remain viable in the soil for a prolonged period. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the area regularly and prevent re-growth at the initial stage in the next few years.
Since the community works together on common lands in a participatory manner, there is very little maintenance cost involved in the process.
The density of lantana in the field can be categorized into three levels based on the number of bushes per area. A density of more than 1500 bushes per area is considered high density, while a density between 500-1500 is classified as moderately dense. A density of fewer than 500 bushes per area is known as low density.
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Monitoring of plantation area | Person days | 12.0 | 200.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Application of compost | Ha | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 4400.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 53.58 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The Project and other Government agencies support by providing the planting material
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This being a community-based approach a lot of activities are being done in a participatory way without the involvement of monetary transactions
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The density of lantana in the field is categorized into 3: more than 1500 bushes are considered high density, and between 500-1500 are considered moderately dense, while less than 500 is known as lowly dense. Such categories have a decicive impact on the costs.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1427.70
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Monsoon season is June-September which has the majority of the rainfall
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
District at glance report of Ministry of Water Resources, Central Groundwater Board, North Central Region BHOPAL, 2013
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
The National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning (NBSS&LUP) developed twenty agroecological zones based on the growing period as an integrated criterion of adequate rainfall and soil groups. It delineated boundaries adjusted to District boundaries with a minimal number of regions. Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh lies in a hot subhumid ecoregion with red and black soil.
Precepitation - 1000–1500mm; Potential Evapotranspiration -1300–1500 mm; Lenght of Growing Period-150–180days
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
The project area is hilly and forested (Satpura Hill Range) and highly undulating with narrow strips of cultivated plains in the valley portion of the river. The plateau is in the northern part, formed by basalt and east-west trending hill in the southern region. The highest elevation is 934 m amsl in the northern part, and the lowest elevation is around 400 m amsl in the northwestern part of the area. Protected forest areas cover the majority of the site in the District as part of the Kanha National Park.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil Testing Parameter status (Average) 2017-20 for the project areas is as follows. This data is based on the soil samples tested by the FES in its soil labs from the project villages.
Soil pH:- 5.906548628; EC (electrical conductivity):- 0.122993577; Soil Organic Carbon:- 0.83%; Nitrogen. :- 293.3696598; Phosphorus:- 25.77762582; Potassium (K):- 139.6696636; Sulphur (S):-18.93457993; Zinc (Zn):- 0.955246706; Boron (Bn):- 0.490850376
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ທັງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ແລະ ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
The groundwater status is within the safe limits as per the reports by the Government of Madhya Pradesh. People use water from rivers, streams, and traditional small wells for domestic purposes. In the absence of good vegetative cover, the rainwater washes off the fertile topsoil from the farmlands making the land barren and resulting in the siltation of ponds and other water bodies. Further, a heavy infestation of invasive species such as Lantana Camara compounds the degradation. The studied block Bichhiya is in a better position in terms of stage of groundwater development with 17%, while the average of the district is 7%. (stage of groundwater development refers to the % of groundwater being used for various purposes from the available groundwater in that area e.g. net annual groundwater availability in Bichhiya block is 9087 ham (hectare meters) while the existing annual ground water draft for all usage is 1523 ham, making it a 17% groundwater development stage)
Source: http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/MP/Mandla.pdf
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
The area is surrounded by Kanha National Park and Phen Wildlife Sanctuary, with a good presence of forest area. World famous Kanha Tiger Reserve is situated in the Mandla District. Kanha is famous for Tiger and Barasingha. Kanha has numerous species of insects, butterflies, reptiles, fishes, and other lesser life forms. Important mammals, birds, reptiles, crustaceans, amphibians, insects, mollusks, and fishes are found in Kanha National Park. The faunal diversity of the district represents 32 wild animals, 63 birds, 4 fishes, and 9 reptile species, respectively. Regarding floral diversity, out of 1006 plant species available in the district, 162 are tree species, followed by 71 species of shrubs, 681 species of herbs, 51 species of climbers, 39 species of grasses, and 2 species of parasites. Mandla is richer in herbaceous species than other adjoining districts like Jabalpur and Seoni.
Source:- Documentation of Biodiversity Status in Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh.
https://mpsbb.mp.gov.in/completedProject/MB.pdf
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
The majority of the landusers belong to the tribal community, including some households from an ethnic community called Baiga.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baiga_tribe
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
The concerned authorities have issued landowners the land certificates.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Communities have the legal rights for land ownership and other resources. The mentioned intervention is being undertaken on the commons, having legal rights of local self-governance institutions like Gram Panchayat or Joint Forest Management Committees.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Parts of the District suffer from poor road and transportation network
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
From the second year onwards after the restoration of the grassland, the grass can be made available for cattle through a cut and feed method. This involves cutting the grass in a controlled manner and providing it to the cattle as feed. By using this method, the grass can be harvested at its optimum stage of growth, and the cattle can be provided with high-quality feed throughout the year. Additionally, this method allows for better utilization of the grass, minimizing any waste or overgrazing of the grassland.
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Availability of fodder to villages from common lands
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Lantana Camara is a problematic weed that has many disadvantages. It can reduce biodiversity, decrease soil fertility, and impede the growth of other plant species. Moreover, it can also be toxic to livestock and humans if ingested.
The restoration of grasslands and the eradication of lantana can help in land management. By removing the weed, the growth of other plant species can be promoted, leading to increased biodiversity and improved soil fertility. The removal of lantana can also help to reduce the risk of wildfires, as it is known to be a highly flammable plant.
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
Restoration of grassland and regulating the use of indigenous grasses as fodder for cattle
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The restoration of grassland and regulation of indigenous grasses for cattle fodder can benefit villagers both socially and economically. Socially, it promotes community involvement and ownership of the land, while promoting sustainable land use practices benefit the environment and community. Economically, the restoration provides a sustainable source of income through the sale of milk and meat products, and eco-tourism can help to boost the local economy.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Lantana is known to release allelopathic compounds into the soil, which can inhibit the growth of other plant species. By removing Lantana, the negative impact of these compounds on the soil are reduced, which can promote the growth of a wider range of plants.
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Diversified vegetation cover supports land restoration
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ສາຍພັນຕ່າງຖີ່ນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄຟໄໝ້
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Eradicating Lantana Camara reduces the risk of wildfires as it is highly flammable and provides a significant fuel source. Removing Lantana reduces the fuel source for fires, especially in areas prone to wildfires or near human settlements. Moreover, removing Lantana can promote the growth of more fire-resistant plant species, creating a more resilient ecosystem that can better withstand natural disasters.
ລະບຸ ການປະເມີນຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ສະຖານທີ່ (ການວັດແທກ):
All of the impact areas indicated in the document are based on the discussions with community members, community institutions and project implementing teams. However, a detailed scientific assessment has not taken place so far.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ພື້ນທີ່ທໍາການຜະລິດ ຂອງເພື່ອນບ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນກະທົບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The spread of Lantana Camara seeds was reduced within neighboring fields
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ໄຟໄໝ້ປ່າ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
| ໄຟໄໝ້ດິນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
All of the impact areas indicated in the document are based on the discussions with community members, community institutions and project implementing teams. However, a detailed scientific assessment has not taken place so far.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Overall, this is a very cost effective technology without having any negative impact on the human and the natural environment
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 1-10%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
On more than 100 locations common land locations this work has been undertaken
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 0-10%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
This being a relatively new intervention, spontaneous adoption will take some time
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Eradication of Lantana Camara reduces its spread and provided access into the forest areas |
| The common lands are restored to grasslands |
| Fodder available for cattle |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Rehabilitation of the soil by eradication of Lantana Camara |
| Sustainable use of common resources for the purpose of biodiversity restoration |
| A participatory approach for resolving common issues |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Continuous monitoring of the regrowth of Lantana Camara as the seeds stay dormant in the soil for many years | Monitoring, and promoting growth with indigenous grasses, local trees, etc. so that the land is not kept fallow |
| Conflict among the members of community institutions for the management of the common property resources | Handholding and training of community institutions |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Currently, the program funds the eradication of Lantana Camara undertaken by the local community | Including the work under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 or MGNREGA |
| Mechanism to scale up the program participatory approach to manage common land resources | Integrating it with other government schemes |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
10
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
5
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
2
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
22/02/2023
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
During the field visit along with visiting the sites, discussions were held with community institutions, community members, the project implementing agency and other concerned stakeholders to understand the processes, impacts, challenges and future plans
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Ecological Restoration of Lantana-Invaded Landscapes in Corbett Tiger Reserve, India Suresh Babuy Amit Love and Cherukuri Raghavendra Babu
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://www.jstor.org/stable/43441335
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Impacts of biochar application on upland agriculture: A review Kumuduni Niroshika Palansooriyaa,1, Yong Sik Oka,1, Yasser Mahmoud Awada, Sang Soo Leeb, Jwa-Kyung Sungc, Agamemnon Koutsospyrosd, Deok Hyun Moone,∗
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30616189/
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Lantana Demo Video
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1d80KyKPkDo
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ