The 4-Wheels Approach for sustainable scaling [Тунис]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_6885 - Тунис
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Арга барилыг баримтжуулах болон үнэлгээ хийхэд оролцсон хүн эсвэл байгууллагын холбоо барих хаяг
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн(с)
Agricultural Economist:
Aymen Frija
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Тунис
Specialist on Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Тунис
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Тунис
Арга барилыг баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management InitiativeАрга барилыг баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Ливан1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
2022
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 ГТМ-ийн технологийн асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл(д)

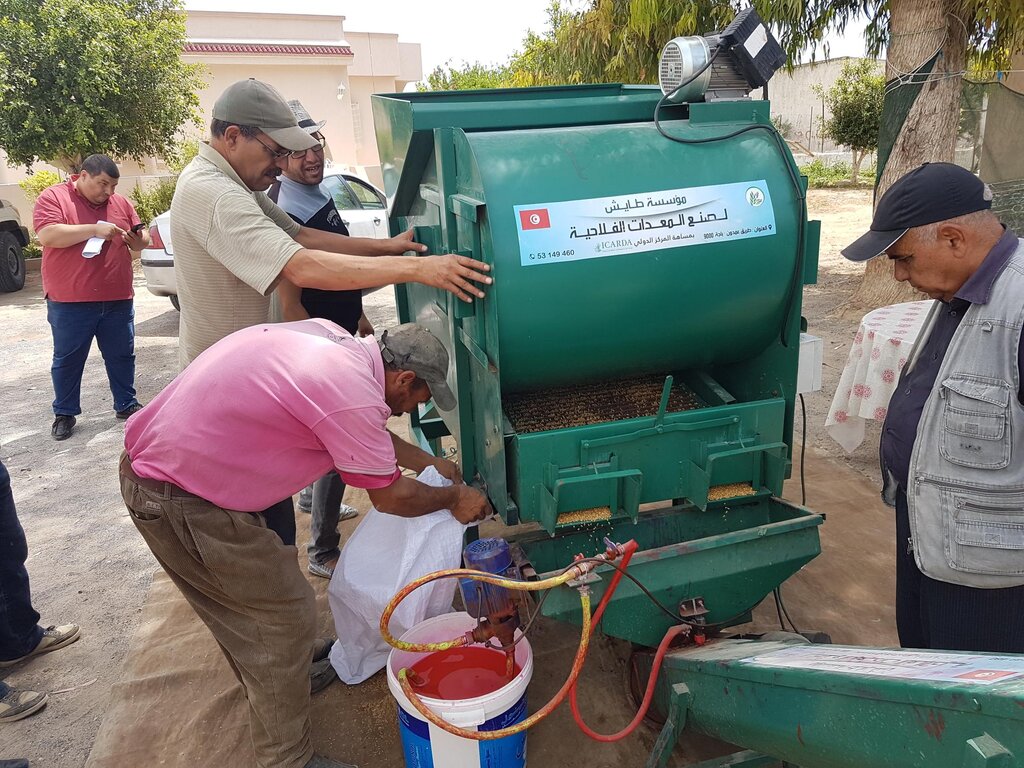
Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [Тунис]
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist

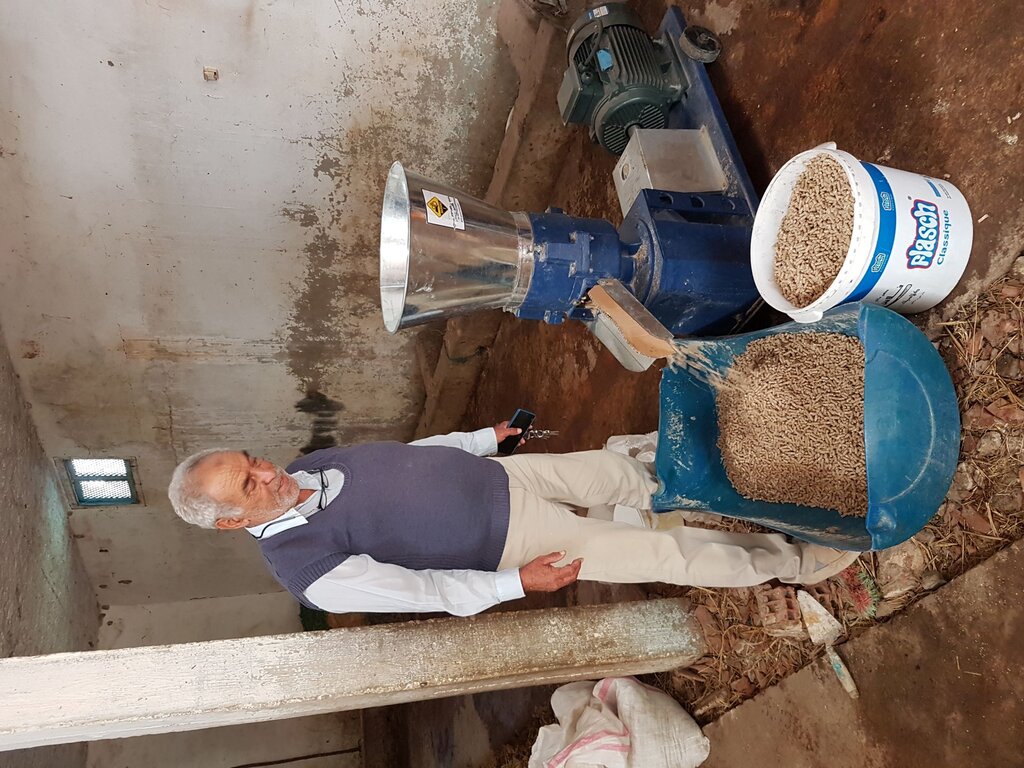
Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [Тунис]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist
2. ГТМ Арга барилын тодорхойлолт
2.1 Арга барилын товч тодорхойлолт
The 4-Wheels Approach addresses the challenge of slow adoption of agricultural innovations among smallholder farmers by establishing Knowledge Hubs and partnerships with diverse stakeholders. The focus is on income-generating technologies and essential factors behind successful scaling up of innovations, ultimately driving agricultural modernization and sustainability.
2.2 Арга барилын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Арга барилын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
The challenge of low and slow adoption of innovations from agricultural research by smallholder farmers is difficult, complex, and is impeding the progress of agricultural modernization in many developing countries. This issue has negative consequences on farm productivity and farmers' livelihoods. Furthermore, it influences the outcomes of investments made by both national and international agricultural research and development initiatives. The problem is exacerbated by evolving climatic and social conditions, which makes more urgent the need for systemic transformation and modernization to enhance food production - while ensuring sustainability.
To confront this challenge of low rates of scaling up and adoption, the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) introduced and validated the “4-Wheels Approach” in countries where ICARDA is active, including Algeria and Tunisia. Among other innovations, two types of machinery are being scaled up this way: (a) the pelletizer (which creates feed pellets from by-products) and (b) the seed cleaning machine (for mechanical seed cleaning, substantially reducing workload). Both technologies have been documented in WOCAT’s global database.
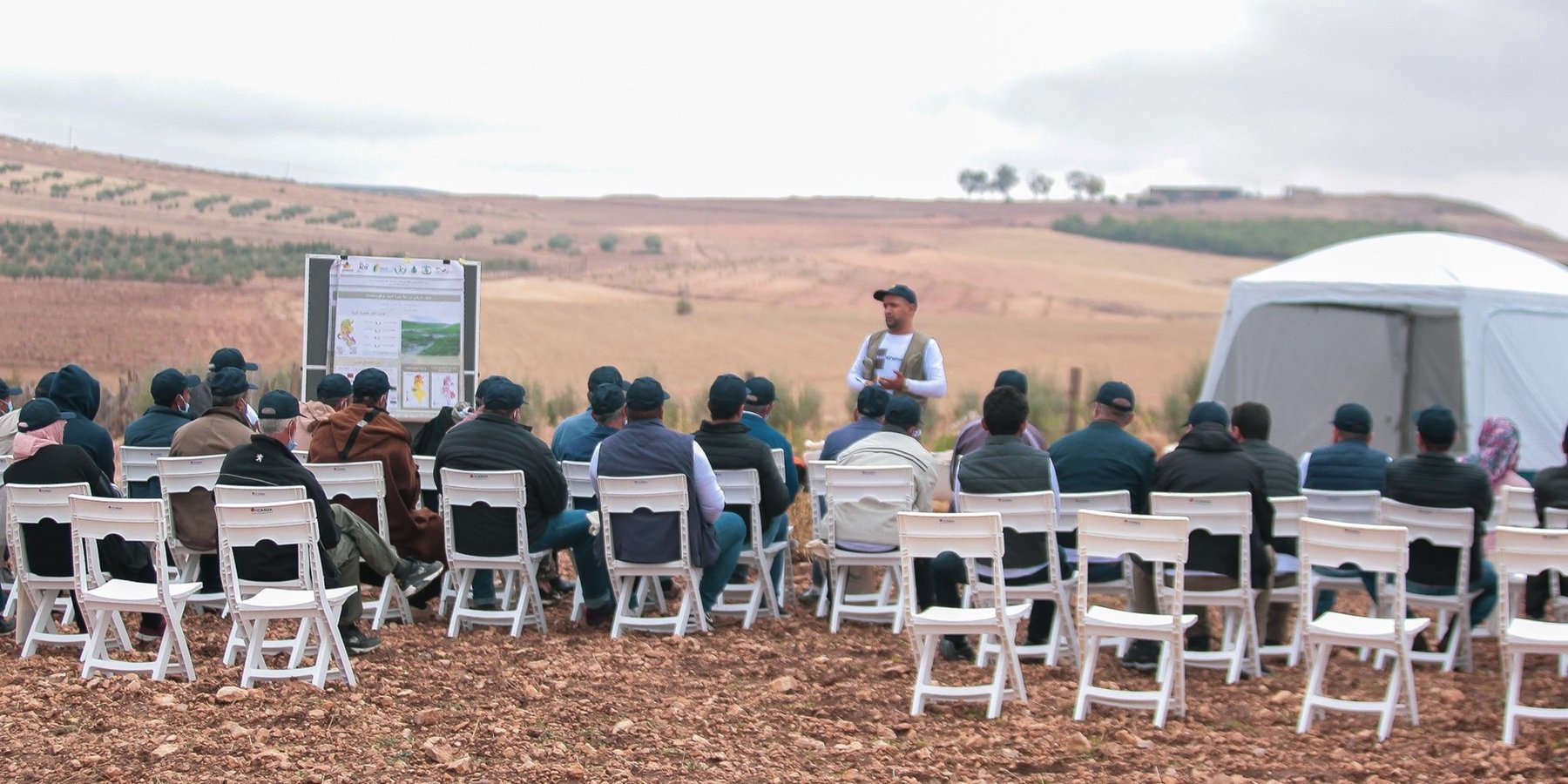
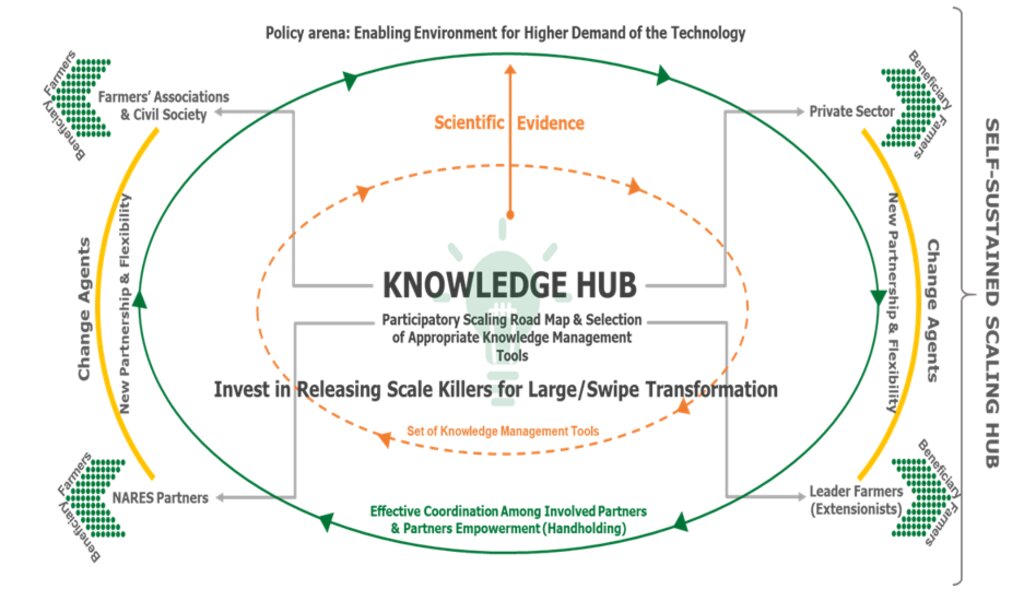
The 4-Wheels Approach is built upon Knowledge Hubs and dynamic partnerships. Knowledge Hubs encompass physical structures, such as (informal) training centres, which usually belong to local farmers’ associations and cooperatives. The purpose of these hubs is to refine and disseminate knowledge locally in a self-sustained way, potentially through established partnerships with key local and regional stakeholders and scaling partners. Four categories of stakeholders, also referred to as change-agents and facilitators of technology dissemination, are identified: i) farmers’ groups and various other local associations, ii) civil society (including non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and the private sector), iii) national public development partners, and iv) lead farmers and extensionists, all of whom play a pivotal role in holding the key knowledge about the technology and spreading it locally. Consequently, these Knowledge Hubs serve to further adapt and mainstream technical knowledge through intermediary beneficiaries (also called proxies or “ambassadors” of the technology), who in turn facilitate dissemination to the ultimate users and beneficiaries, namely the farmers. Viewing the approach’s scaling and Knowledge Hubs through this lens underscores the necessity of investing in continuous and comprehensive networking, which doesn’t overlook any of the possible and relevant scaling partners.
The implementation of the 4-Wheels Approach via Knowledge Hubs and collaborative partnerships has emerged as a compelling strategy for challenges in the uptake of agricultural innovations, fostering a sustainable pathway towards modernization, and thus uplifting the well-being of smallholder farmers in developing areas. The concepts of 4-Wheels Approach and Knowledge Hubs are closely related and interlinked/integrated. The participation of the four types of partners who are engaged through the 4-Wheels Approach within the Knowledge Hub activities allows them to better understand, participate and advocate for relevant local innovations. The 4-Wheels Approach ensures the concentrated involvement of scaling partners of different background within the same landscape, and thus efforts to engage innovation actors become more fruitful by being more accessible and inclusive.
Acknowledgement: This research was funded by the CLCA project (funded by IFAD), PROSOL (funded by GIZ), and OneCGIAR initiative on agroecology. All of the previous projects and initiatives are implemented and coordinated by the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA). The projects partnered with national partners including the OEP (Office de l’elevage et des pâturages) for the training of the cooperatives, as well as Tunisia’s National Agricultural Research Institute (Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique en Tunisi, INRAT) and the National Institute of Field Crops (Institut National des Grands Cultures, INGC) which selected the cooperatives, and the Regional Department for Agricultural Development (Commissariat Regional de Développement Agricole, CRDA) which facilitated the access to farmers communities and creation of knowledge hubs. We would like to thank all partners for their contributions and collaboration.
2.3 Арга барилын зурагууд
2.5 Арга барил нэвтрүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс:
Тунис
Map
×2.6 Арга барилыг эхлэх, дуусах огноо
Хэрэв арга барилыг хэрэгжүүлэх жил тодорхойгүй бол ойролцоогоор эхлэх огноог зааж өгнө үү:
<10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Арга барилын төрөл
- төсөл / хөтөлбөр дээр үндэслэсэн
2.8 Арга барилын үндсэн зорилго, зорилтууд
The aim of this approach is to achieve sustainable scaling and foster greater adoption of innovations. This is pursued through the establishment of Knowledge Hubs (as spaces of innovation) where, the formation of partnerships (based on the 4-Wheels Approach), and the research into viable business models is carefully and step-wise implemented (in reference list see the protocol for implementation in Frija & Idoudi 2020).
2.9 Арга барилын хүрээнд хэрэгжсэн Технологи/Технологиудад дэмжсэн эсвэл саад учруулсан нөхцлүүд
санхүүгийн нөөц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж / боломж
- Хазаарлалт
A minimum of financial resources are needed to create and establish the knowledge hub in the form of informal training center at the cooperative and farmers association level. These fees aims at creating a local space for the community which can be “pedagogically” relevant for further exchange, discussions, trainings, and joint decision making by the community. Such spaces are material investments which can partly enhance the social capital and support the process of building collective cognitive capacity of farmers.
Бүтэц зохион байгуулалт
- Хазаарлалт
The 4-Wheels Approach supports the process of technology transfers in countries where there is a lack of connections and collaboration between research and development. Under such institutional conditions where extension services are low and unavailable, and where research programs are disconnected from the real concrete problems and development bottlenecks, the 4-Wheels approach can be instrumental to leverage the public investments in technology transfers by creating local performing knowledge hubs which would remain sustainable thanks to the mobilization of all relevant innovation and scaling partners (as identified in the 4-wheel partners typology – see above
талуудыг хамтын ажиллагаа/зохицуулалт
- Идэвхижүүлэх
This was rather enabling as different actors like OEP (livestock agency) on the regional level as well as national level were always willing to collaborate with ICARDA and the different beneficiary communities of our different projects (listed in the acknowledgement). This is also especially relevant given that the early technologies for which we built and started piloting the concept of knowledge hubs and partnership for scaling were focusing on forage crops and forage mixtures . Also INRAT was happy to collaborate in the development of the concepts and to also facilitate the overall process of partners mobilization, including collaboration with private actor such as forage seeds companies, pelletizer or seed cleaning manufacturers etc
ГТМ-ийн талаарх мэдлэг, техникийн дэмжлэг авах боломж
- Идэвхижүүлэх
Technical support was guaranteed by OEP, INRAT and ICARDA and private actor. The whole idea of these partners is to generate knowledge through experimentation and demonstration, and sustain it through capacity development and partnership/networking. Communities and particularly farmers associations were key in this regards as these are supposed to be the main holders of knowledge after the project ending. The whole process of creation of KHs aims at enhancing and sustaining knowledge about key agricultural practices and technologies locally, thus making it more inclusive and accessible.
зах зээл (материал худалдан авах, бүтээгдэхүүн борлуулах), үнэ
- Идэвхижүүлэх
Theoretically, markets and prices are not key aspects since we are talking about knowledge. Currently, the problem is about access to lacking knowledge by smallholder farmers and is not about “price of the knowledge” or who is paying for it. However, scaling of KH themselves would involve the development of a business model in which “payment for knowledge” would be key for its scaling and sustainability.
3. Оролцогч талуудын оролцоо ба үүргүүд
3.1 Арга барилд оролцогч талууд болон тэдгээрийн үүргүүд
- Орон нутгийн газар ашиглагч / орон нутгийн иргэд
Farmer Cooperatives
Farmers communities, cooperatives and members are asked to engage into the participatory innovation process by defining their needs, problems, and helping to identify possible affordable solutions. They are also asked to offer a space of concentration where the overall R4D teams can meet, interact and discuss. This space is meant to be sustainable and will be used by the cooperative after the end of the project.
- Судлаачид
INRAT and OEP
Researchers are asked to facilitate the whole process of community engagement and Knowledge Hub installation. They are also asked to install some local experiments which can provide more contextual knowledge about technologies benefits and impact in specific localities. Researchers are also asked to design and facilitate appropriate networking event thus connecting the cooperatives with all relevant public and private actors who are operating for the considered technologies of the Knowledge Hub.
- Хувийн хэвшил
Manufacturer of the seed cleaning unit and Importer of the Pelletizer machine
Private sector in general, supports the communities with some capacity development activities in case they are providers of the technology to be scaled (object of the Knowledge Hubs).
They also ensure good affordable and reliable access of farmers of the community to the relevant technologies object of the hub.
In this case, they did: design and produce, or import machine; train farmers in use and maintenance; perform after sale services
- Олон улсын байгууллага
ICARDA
Lead and coordination; installation of the hub, facilitation between research and development actors; organize training and demonstration
Хэрэв хэд хэдэн оролцогч талууд оролцсон бол голлох төлөөлөгчийг зааж өгнө үү:
ICARDA
3.2 Арга барилын янз бүрийн үе шатанд орон нутгийн газар ашиглагчид / бүлэглэлүүдийг татан оролцуулах
| Орон нутгийн газар ашиглагч / орон нутгийн иргэдийн оролцоо | Хэн оролцсоныг тодорхойлж, үйл ажиллагааг тайлбарлана уу | |
|---|---|---|
| санаачлага/идэвхжүүлэлт | үгүй | ICARDA and OEP led discussion with the importer and manufacturer. |
| Төлөвлөгөө | үгүй | Discussion between ICARDA, OEP, GIZ, INGC, to identify potential beneficiaries of the machines. |
| Хэрэгжилт | интерактив | ICARDA and OEP discussed with farmer cooperatives their interests in the machines. ICARDA, OEP, and manufacture produced and distributed the machines. Financial contribution of the farmer cooperation was requested to foster ownership. |
| Мониторинг/ үнэлгээ | интерактив | ICARDA and OEP visits the farmer cooperatives every three months to collect business data, see if the machine operates correctly, and to identify constraints. |
3.3 Диаграм (хэрэв боломжтой бол)
Тодорхойлолт:
The 4-Wheels Approach for effective partnership for scaling
Зохиогч:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi. (18/12/2020). Self-Sustained “Scaling Hubs” for Agricultural Technologies: Defnition of Concepts, Protocols, and Implementation. (ICARDA)
3.4 ГТМ-ийн технологи/технологиуд сонгох шийдвэр
Хэрэгжүүлэх Технологи/Технологиудын сонголтыг хийж шийдвэр гаргасан хүнийг тодорхойлно уу:
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн дангаараа
Тайлбар:
ICARDA and partners investigated relevant and suitable technologies. Essential was that the business model is self-sustaining.
Шийдвэрийг юунд үндэслэн гаргасан:
- ГТМ-ийн мэдлэгийг баримтжуулалтын үнэлгээ (нотолгоонд суурилсан шийдвэр гаргах)
- Судалгааны үр дүн, ололтууд
- Хувь хүний туршлага ба санал бодол (баримтжуулаагүй)
4. Техникийн дэмжлэг, чадавхи бүрдүүлэх, мэдлэгийн менежмент
4.1 Чадавхи бэхжүүлэх/сургалт
Газар эзэмшигчид / бусад оролцогч талуудад сургалт явуулсан уу?
Тийм
Хэн сургалтанд хамрагдсан бэ:
- Газар ашиглагчид
Хэрэв шаардлагатай бол хүйс, нас, яс үндэс, гэх мэт. нэмнэ үү:
Farmers of the cooperation were trained
Сургалтын хэлбэр:
- Ажил дээр
- үзүүлэнгийн талбай
- Олон нийтийн уулзалт
- курс дамжаа
Хамрагдсан сэвдүүд:
The use of the machinery, their maintenance and recipes for pellets
4.2 Зөвлөх үйлчилгээ
Газар ашиглагчдад зөвлөх үйлчилгээ авах боломжтой байдаг уу?
Тийм
Зөвлөх үйлчилгээ үзүүлсэн эсэхийг тогтоо:
- Газар ашиглагчийн талбай дээр
4.3 Институцийг бэхжүүлэх (байгууллагын хөгжил)
Арга барилаар дамжуулан институц байгуулагдаж эсвэл бэхжсэн үү?
- Тийм, дунд зэрэг
Байгууллагууд бэхжиж, үүсэн бий болсон түвшин(үүд)-г тодорхойлно уу:
- Орон нутгийн
Байгууллага, үүрэг, хариуцлага, гишүүд гэх мэтийг тайлбарлах:
Farmer cooperation and knowledge hubs were established. The rationale is that because the machines are economically viable on their own, the cooperation will keep on sharing the knowledge using the hubs.
Дэмжлэгийн төрлийг ялга:
- чадавхи бэхжүүлэх / сургалт
- Тоног төхөөрөмж
4.4 Мониторинг ба үнэлгээ
Мониторинг болон үнэлгээ нь арга барилын хэсэг үү?
Тийм
Тайлбар:
By monitoring certain indicators, such as the number of beneficiaries, pellets produced, seed cleaned, etc. In addition, ICARDA is frequently visiting the hubs to see progress and solve problems that occurred.
Хэрэв тийм бол энэ баримт бичиг нь мониторинг, үнэлгээнд ашиглагдахаар зориулагдсан уу?
Тийм
4.5 Судалгаа
Судалгаа арга барилын хэсэг нь байсан уу?
Тийм
Сэдвийг тодруулна уу:
- Социологи
- Эдийн засаг/ зах зээл
- Экологи
- Технологи
5. Санхүүгийн болон гадаад материаллаг дэмжлэг
5.1 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгийн жилийн төсөв
Хэрэв жилийн төсөв тодорхойгүй бол хягаарыг тодруулна уу:
- 10,000-100,000
Тайлбар (жнь: санхүүжилтийн гол эх үүсвэр / гол хандивлагчид):
This includes the machines and trainings.
5.2 Газар ашиглагчдад санхүүгийн / материаллаг дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн
Технологи / технологийг хэрэгжүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчид санхүүгийн / материаллаг дэмжлэг авсан уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол дэмжлэгийн төрөл(үүд), нөхцөл, болон нийлүүлэгч(чид) бичнэ үү:
The land users, organized in farmer cooperation, were supported with machinery
5.3 Тодорхой зардлыг даахад чиглэсэн дэмжлэгт (хөдөлмөрийн хүчийг оролцуулаад)
- Тоног төхөөрөмж
| Ямар хөрөнгө оруулалт татаасаар олгогдсоныг заана уу | Ямар талбайн хэмжээнд | Тэтгэмж, урамшууллыг тодорхойлно уу |
|---|---|---|
| машин төхөөрөмж | хэсэгчлэн санхүүждэг | The farmer cooperatives made a financial contribution. |
5.4 Кредит
Арга барилын хүрээнд ГТМ-ийн үйл ажиллагаанд зориулж зээлд хамрагдсан уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Бусад урамшуулал, хэрэгсэл
ГТМ-ийн технологийг хэрэгжилтийг дэмжихэд ашигласан бусад урамшуулал, хэрэгсэл байсан уу?
Үгүй
6. Нөлөөллийн дүн шинжилгээ ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Арга барилын нөлөөллүүд
Арга барил нь орон нутгийн газар ашиглагчдыг чадваржуулах, оролцогч талуудын оролцоог сайжруулсан уу?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
Land users were empowered because the machines strengthen the cooperatives.
Арга барил нь ГТМ-ийн технологийг хэрэгжүүлж, хадгалахад газар ашиглагчдад тусласан уу?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
Арга барил нь ГТМ хэрэгжүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчдын мэдлэг, чадварыг сайжруулахад хүргэсэн үү?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
Farmers received training on how to operate and maintain the machinery, but they are still struggling with the optimal recipes for the pellets.
Арга барил нь оролцогч талуудын хооронд институци, хамтын ажиллагааг бий болгож, бэхжүүлсэн үү?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
The projects was a successful collaboration between many different organization. Its success has strengthen the relations.
Арга барил нь жендэрийн тэгш байдлыг сайжруулж, эмэгтэйчүүд, охидыг чадавхжуулсан уу?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
Conventionally, the cleaning of seeds was done by hand by women and children. The use of machinery has substantially lowered their workload.
Арга барил нь чанаржуулсан шим тэжээл/ хүнсний аюулгүй байдалд хүргэсэн үү?
- Үгүй
- Тийм, бага зэрэг
- Тийм, зарим
- Тийм, их
The use of the machinery lead to improved food security.
6.2 ГТМ-ийг хэрэгжүүлэх газар ашиглагчидын гол санаачилга
- үйлдвэрлэл нэмэгдсэн
- Ашиг нэмэгдсэн (боломж), зардал-үр ашгийн харьцаа сайжирсан
- Гамшигийн эрсдэл буурсан
- Ажлын ачаалал бууруулсан
6.3 Арга барилын үйл ажиллагааны тогтвортой байдал
Газар ашиглагчид арга барилаар дамжуулан хэрэгжүүлсэн арга хэмжээг тогтвортой хадгалж чадах уу (гадны дэмжлэггүйгээр)?
- Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол яаж гэдгийг тайлбарлана уу:
The machines on their self are economically viable.
6.4 Арга барилын тогтвортой/давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Seed Cleaning Unit: better seeds, improves yield, higher income, less workload |
| Feed Pelletizer: use of agricultural by-products, cheap compound feed, less workload |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Major strength of the 4-Wheels approach is the aspect of the collaboration, between private actor (machine manufacturer or importer), farmer organization, lead farmer of the organization, OEP (extension), INRAT (research for composition). This multi-actor collaboration is key of the 4-wheel approach and key of the success of the scaling of the two technologies |
| Seed Cleaning Unit: better seeds, improves yield, higher income, less workload |
| Feed Pelletizer: use of agricultural by-products, cheap compound feed, less workload |
| The 4-Wheels Approach ensures ownership over the machinery while building capacity |
6.5 Арга барилын дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Feed Pelletizer: Farmers still don’t know the optimum mixture of ingredients to produce pellets for each region and categories of animals (sheep / cow / camel). | Intense collaboration with agricultural research |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| A risk of the approach is the sustainability. It is not sure (yet) if and how the knowledge hub will continue once there is no more support from ICARDA and (national) partners. |
The theoretical idea is that through the income generation with these machines they (farmer organization) will continue training others and sharing their knowledge. But this theory needs to be validated and proven. |
| Seed Cleaning Unit: quite expensive for a small scale farmer (7,000 US$ nowadays) | To buy the unit as a farmer organization (cooperation) and use it by many farmers |
| The Feed Pelletizer can be expensive for individual small scale farmer, availability of spare parts of pelletizing machine only in Tunis (access problem), needs available by-products (they are only seasonable), need access to subsidized barley and wheat bran to produce at competitive prices. Farmer organizations have no quota for subsidized barley and wheat bran, only individual farmers to a limited amount and feed enterprises | To use the feed pelletizer as a group to reduce costs per farmer; transform cooperative into a feed processing enterprise as they have access to subsidized barley and wheat bran |
7. Суурь мэдээлэл болон холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн эх үүсвэр/аргууд
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет дэх нээлттэй холбоосууд
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi. (18/12/2020). Self-Sustained “Scaling Hubs” for Agricultural Technologies: Definition of Concepts, Protocols, and Implementation. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12248
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Mourad Rekik, Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi, Santiago López Ridaura, Nasreddine Louahdi, Boubaker Dhehibi, Dina Najjar, Udo Rudiger, Enrico Bonaiuti, Laura Becker, Zohra Djender Ghallem, Hatem Cheikh M'hamed, Mina Devkota Wasti, Barbara Rischkowsky. (11/3/2021). Use of Conservation Agriculture in Crop-Livestock Systems (CLCA) in the Drylands for Enhanced Water Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility and Productivity in NEN and LAC Countries – Progress Highlights: Year (3) - April 2020 to March 2021. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12703
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi, Udo Rudiger, Jebali Oussama, Hatem Cheikh M'hamed, Haithem Bahri, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mourad Rekik, Imen Hemissi, Salah Ben Youssef, Khouloud Chetoui, Mounir Louhaichi, Mouldi Gamoun, Asma Souissi. (6/12/2022). Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security – ProSol: Towards the Effective Scaling of Soil and Water Conservation Technologies under Different Agroecosystems in North and Central West Tunisia – SWC@Scale/ProSol: Technical Progress Report/ January – August 2022. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67835
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [Тунис]
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [Тунис]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна