Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS) [Филлипин]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Mathias Gurtner, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1133 - Филлипин
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
MERCADO Agustin
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
Индонез
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Rondal José
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Филлипин
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Garrity Dennis
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
Индонез
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - ФиллипинТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - Кени1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [Филлипин]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Romeo Villamin Labios
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
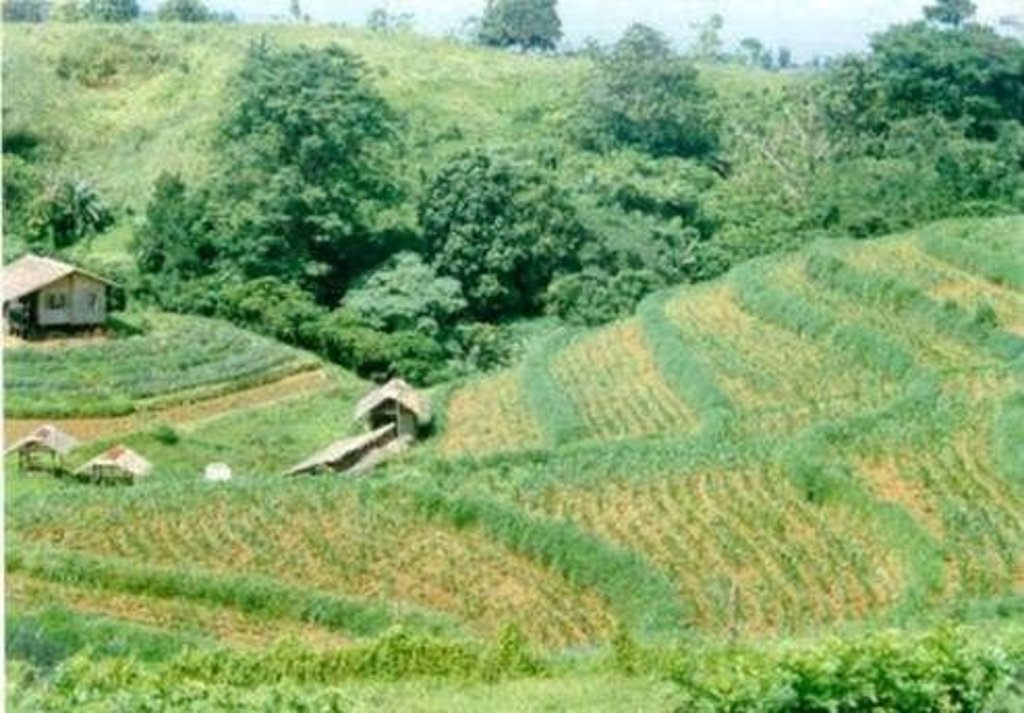
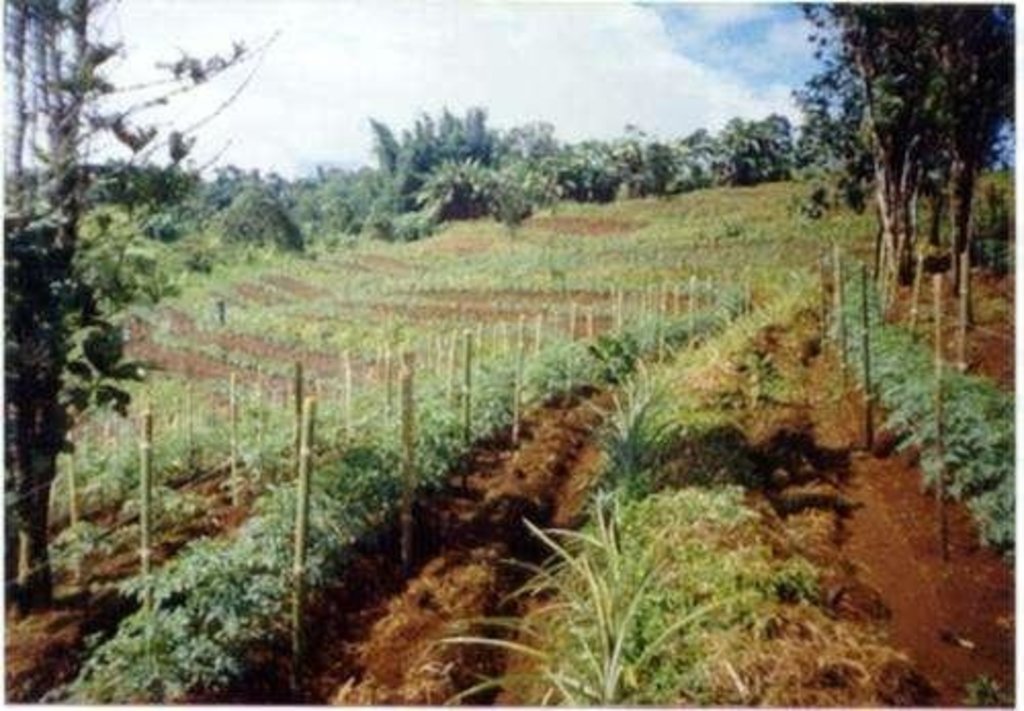
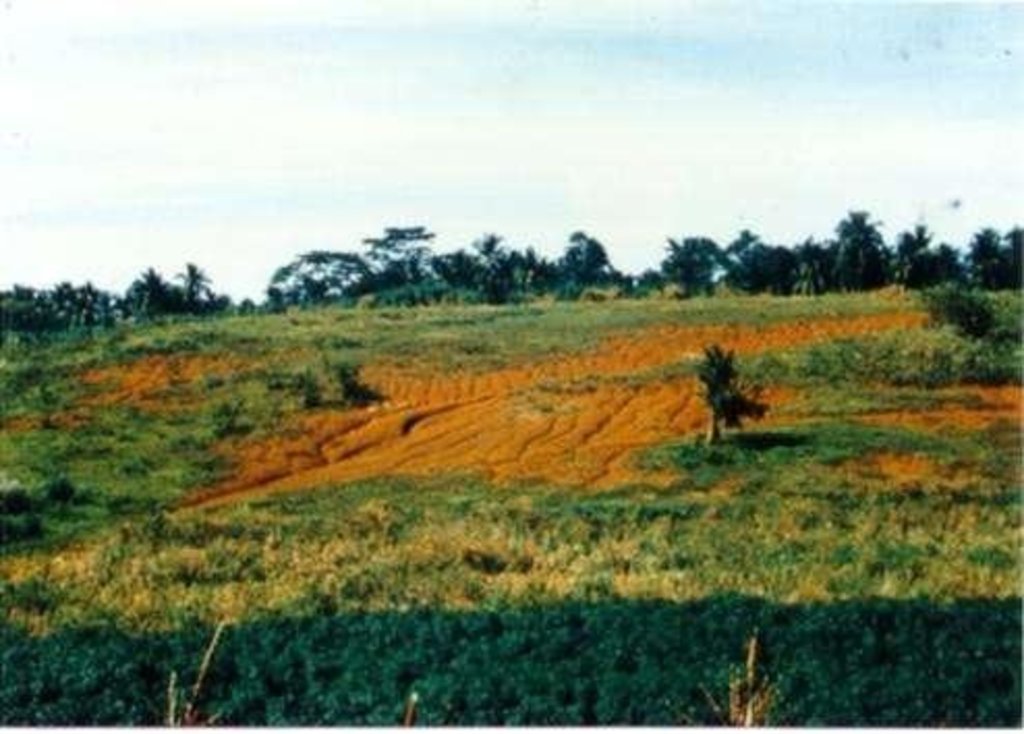
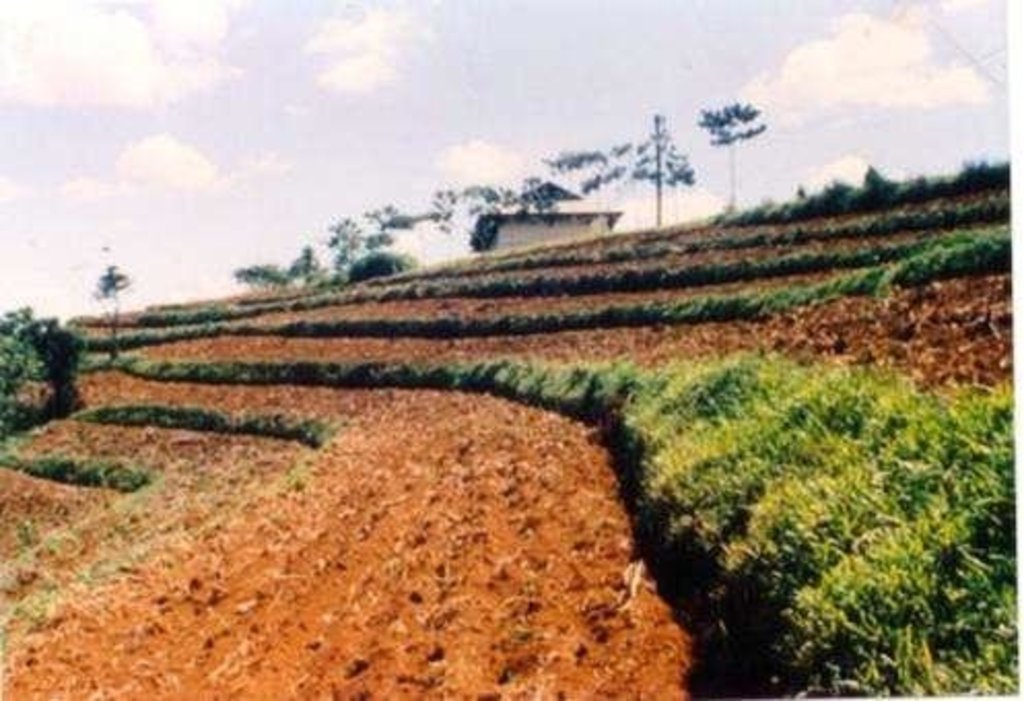
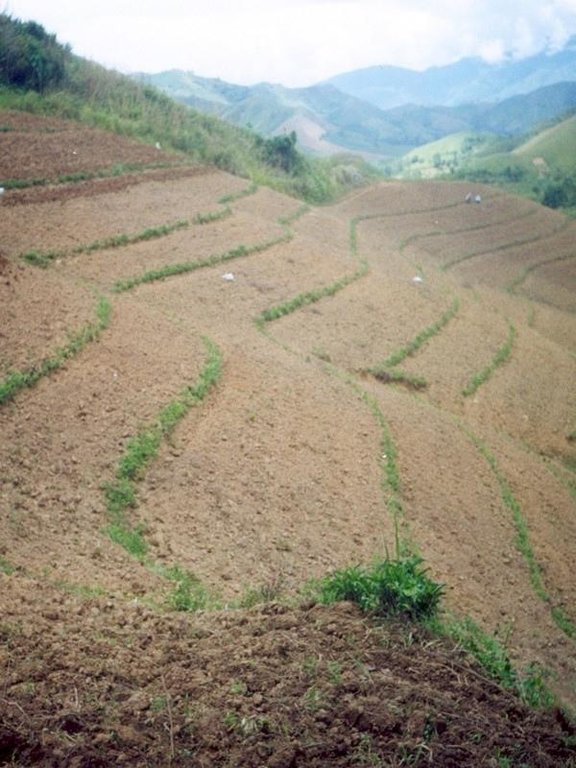
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
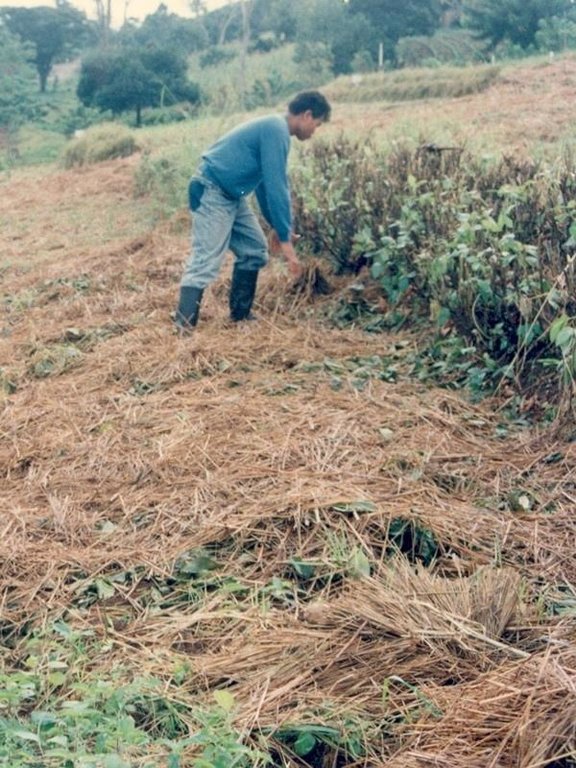
Natural vegetative strips (NVS) are narrow live barriers comprising naturally occurring grasses and herbs. Contour lines are laid out with an A-frame or through the ‘cow's back method’ (a cow is used to walk across the slope: it tends to follow the contour and this is confirmed when its back is seen to be level). The contours are then pegged to serve as an initial guide to ploughing. The 0.3-0.5 m wide strips are left unploughed to allow vegetation to establish. Runoff flowing down the slope during intense rain is slowed, and infiltrates when it reaches the vegetative strips. Eroded soil collects on and above the strips and natural terraces form over time. This levelling is assisted by ploughing along the contour between the NVS - through ‘tillage erosion’ - which also moves soil downslope.
The vegetation on the established NVS needs to be cut back to a height of 5-10 cm: once before planting a crop, and once or twice during the cropping period. The cut material can be incorporated during land preparation, applied to the cropping area as mulch, or used as fodder. This depends on whether the farmer has livestock or not, on personal preference, and on the time of cutting. If the grass is applied as mulch or incorporated, the technology can be considered to be an agronomic, as well as a vegetative, measure.
NVS constitutes a low-cost technique because no planting material is required and only minimal labour is necessary for establishment and maintenance. Some farmers had already practiced the technology for several years before the intervention of the ICRAF (The World Agroforestry Centre) in 1993. ICRAF came to realise that farmers here preferred NVS to the recommended ‘contour barrier hedgerows’ of multipurpose trees- which land users viewed as being too labour intensive. When farmers became organised into ‘Landcare’ groups, NVS began to gain wide acceptance.
Land users appreciate the technique because it effectively controls soil erosion and prevents loss (through surface runoff) of fertilizers applied to the crop. As an option, some farmers plant fruit and timber trees, bananas or pineapples on or above the NVS. This may be during establishment of the contour lines, or later. The trees and other cash perennials provide an additional source of income, at the cost of some shading of the adjacent annual crops.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Филлипин
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Misamis Oriental
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Bukidnon
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
110.0
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 100-1,000 км2
Тайлбар:
The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 110 km2. The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
1993
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
It evolved in the area with some adaptations.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- үр тариа - цагаан будаа (өндөр газрын)
- хүнсний ногоо - бусад
Мод, бут тариалах - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- бусад төрлийн жимс
- coffee
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period: 240 days (Mar - Dec)
Тайлбар:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Maize, vegetables; coffee; fruit trees; upland rice
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of topsoil through sheet erosion and rills, leading to rapid soil fertility decline. In turn soil fertility decline results in the need for increasing levels of fertilizer inputs to maintain crop yield. However, these fertilizers are often washed away by surface runoff - a vicious circle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain crop yield.
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал
Тайлбар:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (caused massive erosion and loss of productivity), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (no clear cut policy and support from LGU). Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (over population of livestock, low land ratio), education, access to knowledge and support services (farmers are not fully aware of simple SWC approach), Agricultural causes (unsustainable practice in farming)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
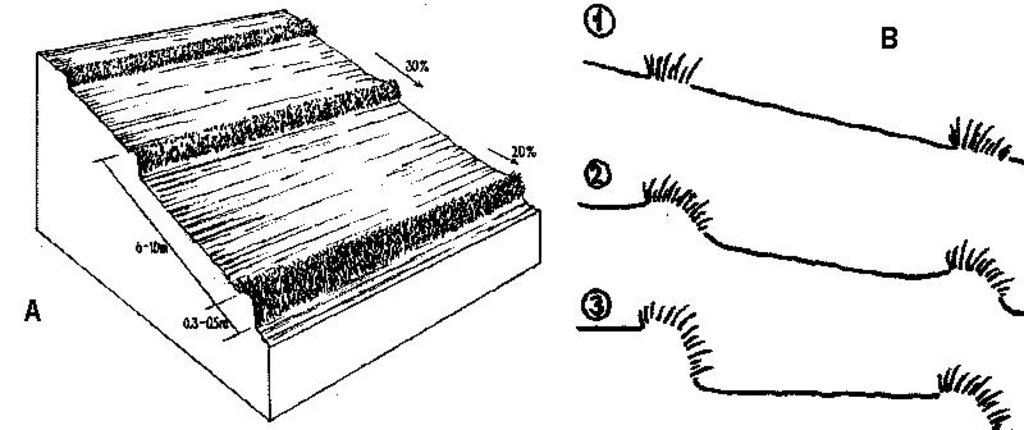
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
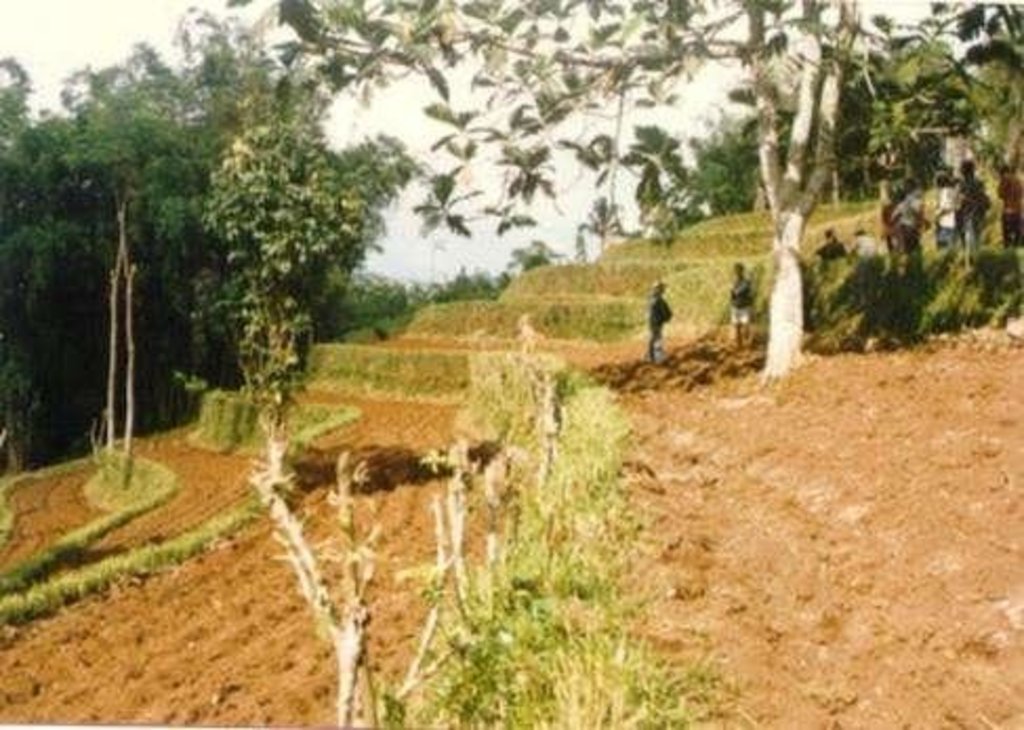
A - Spacing of natural vegetative strips depends on the slope.
B - The insert shows the evolution of terraces over time through tillage and soil erosion, leading to accumulation of sediment behind the strips (steps 1-3).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate. Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate.
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, control of dispersed runoff. Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measures:
Mixed cropping / intercropping - Material/ species: annuals/perennials; Remarks: laid out alternately.
Mulching - Material/ species: crop residues; spread on the surface
Legume inter-planting - purpose: for nitrogen fixation
Manure / compost / residues - Material/ species: animal, crop residues
Contour tillage - Material/ species: Contour strips are laid into 6-10 meters apart depending on slope gradient.
Vegetative measures:
Aligned, along contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass, O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Narrow grass barriers
Vegetative material: grass
Number of plants per (ha): dense grass
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia mangium, Eucalyptus deglupta, Gmelina arbarea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Durian, Rambutan, Jackfruit
Perennial crops species: Coffee, rubber, pineappe
Grass species: Bamboo, setara, napier, Panicum spp.
Other species: Legumes
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 20%
Зохиогч:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
1 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout of contours with the use of an A-frame (or cow’s back method, see Annexe T3)) placing wooden pegs along the contours. | dry season/before land preparation |
| 2. | Seeding (T, F, C) | dry season |
| 3. | Transplanting | onset of rainy season |
| 4. | Land preparation | dry season/before planting |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | animal traction | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | stakes (pegs) | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 84.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 84.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial ploughing along the contour: leaving unploughed strips. | onset of rainy season / before each season |
| 2. | Planting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Mulching | dry season / only whensufficient crop residues |
| 4. | Fertilization | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 5. | Interim cultivation/weeding | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 6. | Ploughing mulch into the soil during normal land cultivation. | |
| 7. | Weeding (T, F, C), Slashing grass | rainy season /2 times |
| 8. | Spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys (between strips) as | rainy season /2 times (weeded materials) |
| 9. | Pruning | before and during cropping /2 times per cropping |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | animal traction | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 78.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 78.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: plough, harrow
Costs of establishing contours and maintenance by slashing are calculated by total length of NVS. This example is from a typical field with an 18% slope: at an NVS spacing of 5 m, the approximate total linear distance for one hectare is 2,000 m. In this example, the farmer has paid for everything him/herself (see section on acceptance/adoption). Note that the establishment cost is more or less equivalent to the cost of standard land preparation by ploughing. When 'enrichment planting’ of the strips is carried out, extra cost for seedlings (of fruit trees for example) and associated labour for planting are incurred.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Slope is the dominant factor in cost calculation. The steeper the slope, the more difficult the mobility is and the more closely-spaced the contours are .
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soils are developed from fine-grained igeneous rocks. Soil fertility: strongly acid and with high P fixing capacity. Rapid organic matter mineralisation due to high temperature. Soil drainage is generally good except in isolated depressions.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
- чинээлэг
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- ердийн хөсөг
- механикжсан / мотортой
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2; Annual population growth: > 4%
and own 20% of the land (5).
and own 40% of the land (30).
and own 30% of the land (65).
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, trade, business, labour for neighbouring farms and other labour intensive agricultural activities (e.g. vegetable production)
Market orientation of production system: Upland rice is grown as subsistence. Maize is sold to feed millers.
Level of mechanization: The terrain limits the extensive use of machineries.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Тайлбар:
Subdivision of inheritance lands. High population growth rate attributed to natural birth and envigoration of lowland population create pressure to farm site.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
area competition
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
crop area loss, before NVS evolved to cash perennials or fodder grasses
газрын менежмент
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
during establishment
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
biomass was given value
эдийн засгийн ялгаат байдал
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
regular pruning
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
very low inputs required
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
үндэсний институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
government line agencies and educational institutions
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
negligible socio-cultural conflicts
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
45
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
8
усны урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
partly increased water-logging (negligible)
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
40
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
2
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
important for sustainability
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
pest sanctuary
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
soil structure
soil fertility
weed infestation due to seed dispersion and grass roots
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
spreading from the NVS to nearby areas (especially with cogon grass: Imperata cylindrica)
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
no actual measurement
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 51-90%
Тайлбар:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support (2000 families)
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology spontaneously (without external material support) (2000 families)
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Factor that helped was the formation of Landcare associations which have benefited their members in various ways. There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption, especially where Landcare associations are in operation.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improve soil fertility |
| Prevent soil erosion |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain (How to sustain: Transform farmers associations into cooperative which serve as conduits in marketing. Intensify information and education campaign.) |
| Less competition for space, sunlight, moisture and nutrient. (How to sustain: Ensure continued regular trimming of vegetative strips and use of these as fodder or mulch.) |
| Low labor and external inputs requirement |
| Effective in reducing soil erosion (by 90%) (How to sustain: Adopt other supportive technologies like mulching, zero tillage/minimum tillage, etc.) |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| High initial establishment cost | Subsidy/assistance from government |
| Effect of technology is not readily seen | Education about what long term sustainability means |
| High gestation period for some component of the system | Proper mix of annual and perennial crops |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
|
Effect on yield and income is not readily felt, since reduced erosion is not easily translated into increased income or yield |
Farmers should have supplementary sources of income (eg livestock). Education about what long-term sustainability means. |
| Reduction of productive area by approx 10% |
Optimum fertilization to offset production loss. Nutrients are conserved under NVS and this will result in the reduction of fertilizer requirement after some years. |
|
Creation of a fertility gradient within the alley (soil is lost from the top of the alley and accumulates above the NVS where fertility then concentrates) |
Increased application of fertilizer on the upper part of alley. |
| Overall increase of production value is low | Land users could ask for subsidy/assistance from Government: eg for fertilizers, establishment of nurseries, free seedlings (for higher value fruit trees). |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Managing soil fertility on terraces forming behind vegetative filter strips: An assessment of farmer strategies
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Crop productivity using forage legumes and grasses as contour hedgerows species in an acid upland soils
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Garrity DP, Stark M and Mercado Jr A: Natural Vegetative Strips: a bioengineering innovation to help transform smallholderconservation. pp 263–270. 2004.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
in Barker DH, Watson AJ, Sombatpanit S, Northcutt B and Maglinao AR Ground and Water Bioengineering for ErosionControl and Slope Stabilisation.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Science Publishers inc. Enfield, USA
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Stark M, Itumay J and Nulla S Assessment of Natural VegetativeContour Strips for Soil Conservation on Shallow Calcareous Soil in the Central Philippines.. 2003.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF), Nairobi, Kenya
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [Филлипин]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Romeo Villamin Labios
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна