Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Mathias Gurtner, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1133 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
MERCADO Agustin
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
อินโดนีเซีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Rondal José
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Garrity Dennis
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
อินโดนีเซีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - ฟิลิปปินส์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Romeo Villamin Labios
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
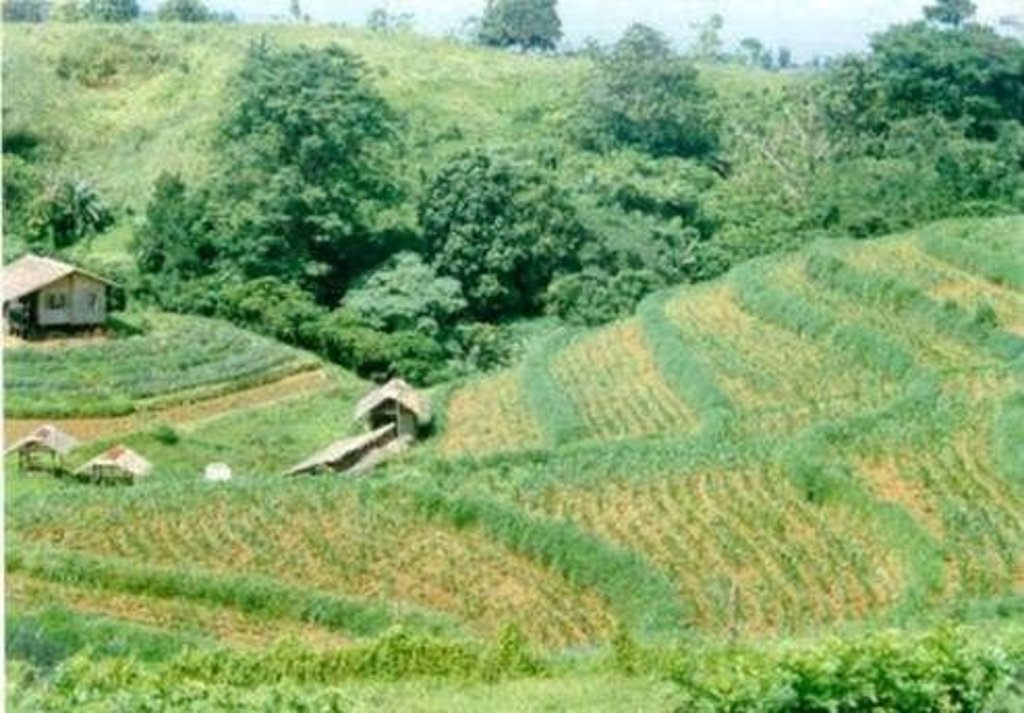
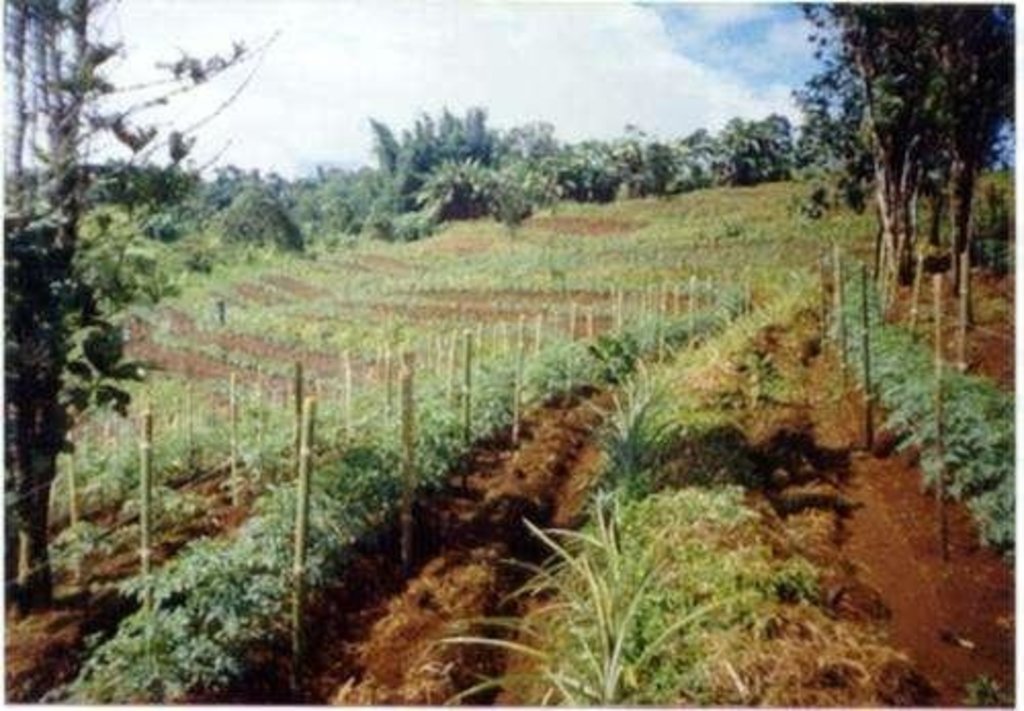
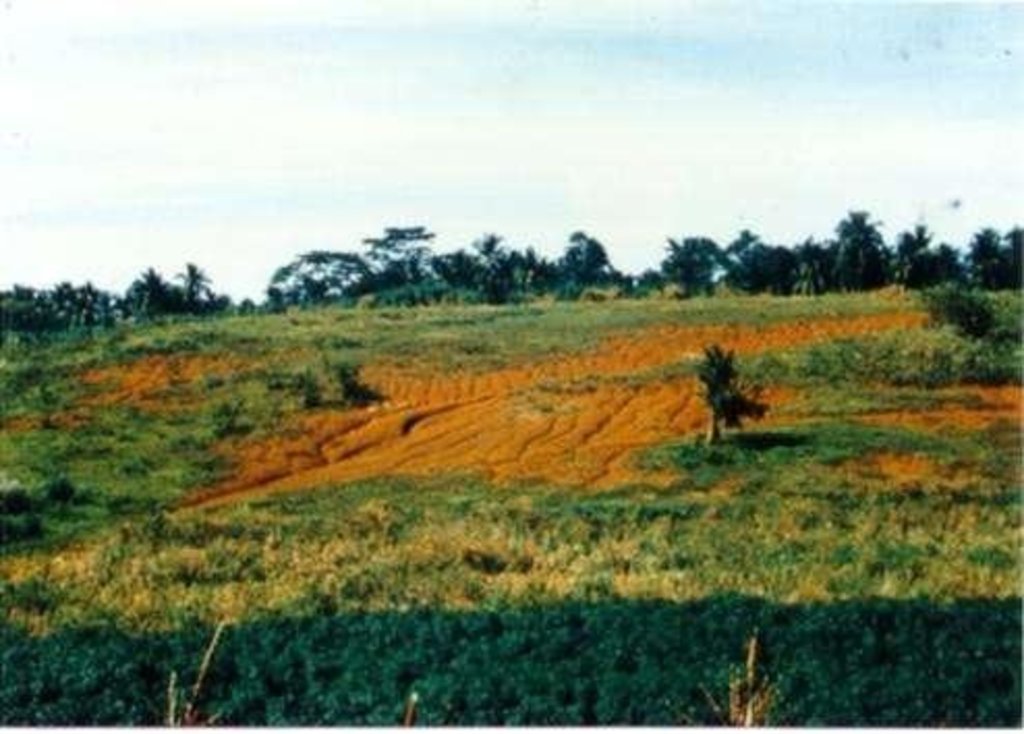
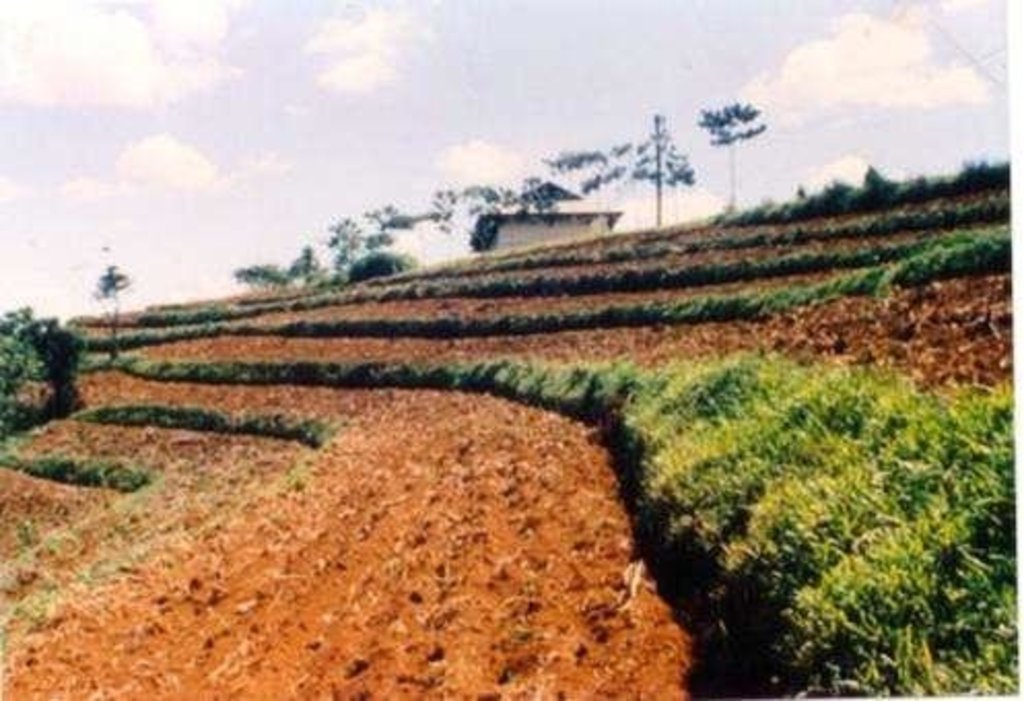
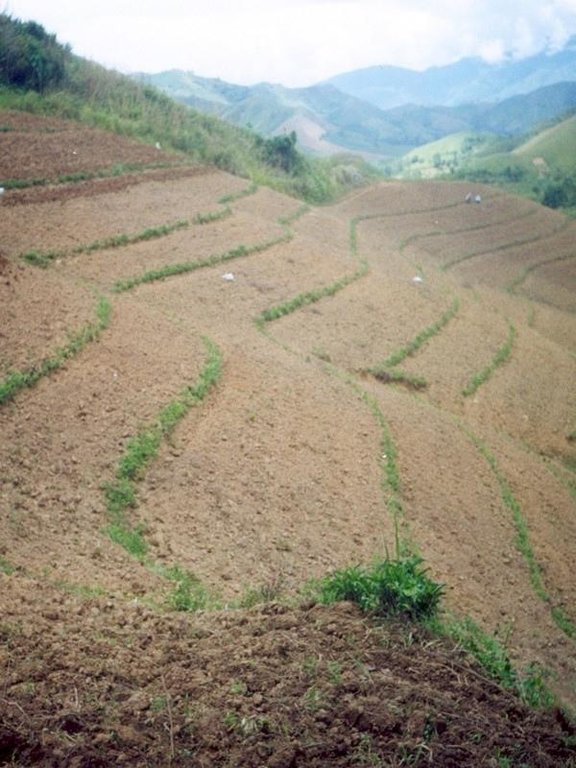
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
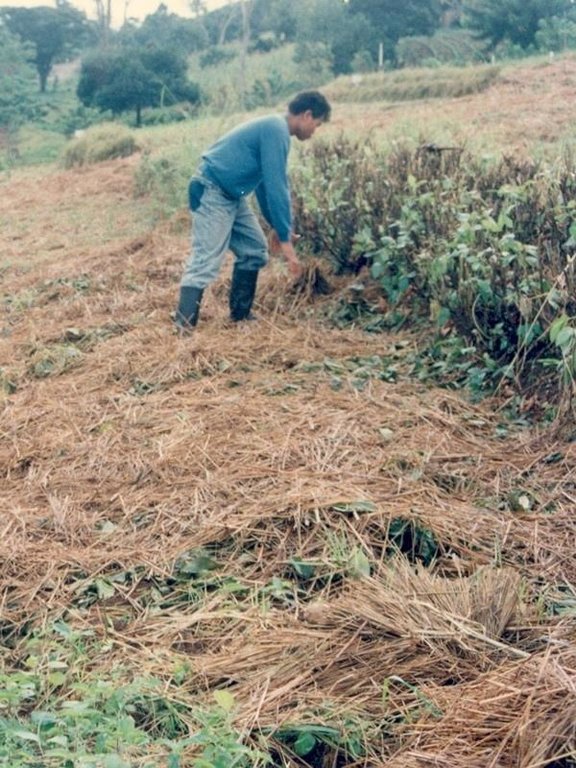
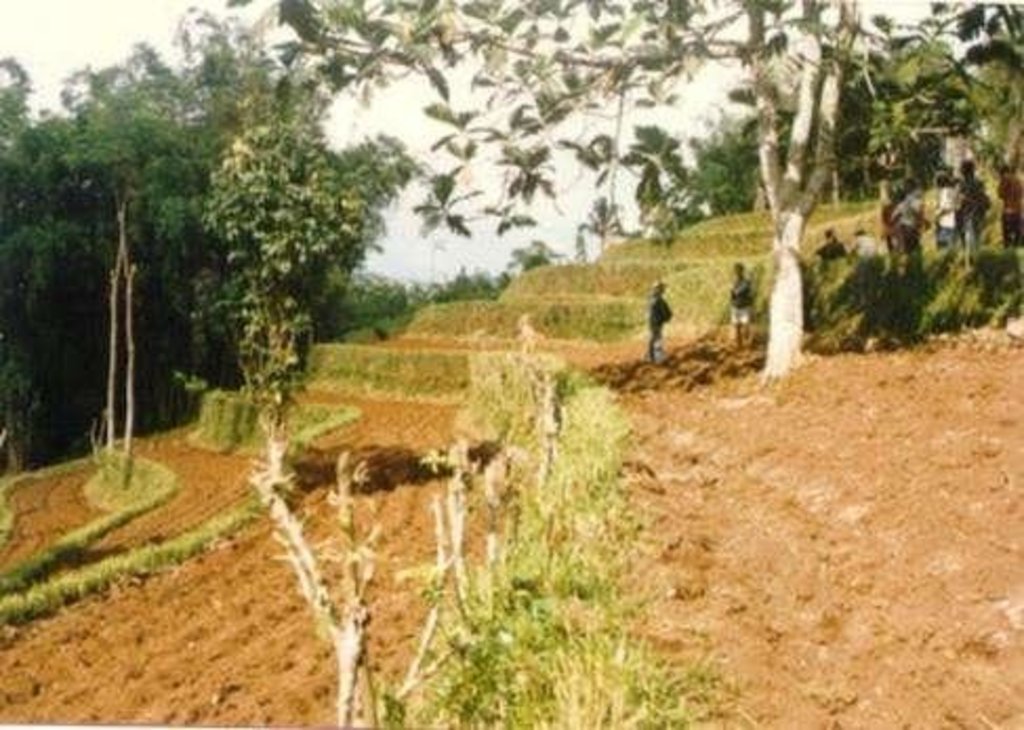
Natural vegetative strips (NVS) are narrow live barriers comprising naturally occurring grasses and herbs. Contour lines are laid out with an A-frame or through the ‘cow's back method’ (a cow is used to walk across the slope: it tends to follow the contour and this is confirmed when its back is seen to be level). The contours are then pegged to serve as an initial guide to ploughing. The 0.3-0.5 m wide strips are left unploughed to allow vegetation to establish. Runoff flowing down the slope during intense rain is slowed, and infiltrates when it reaches the vegetative strips. Eroded soil collects on and above the strips and natural terraces form over time. This levelling is assisted by ploughing along the contour between the NVS - through ‘tillage erosion’ - which also moves soil downslope.
The vegetation on the established NVS needs to be cut back to a height of 5-10 cm: once before planting a crop, and once or twice during the cropping period. The cut material can be incorporated during land preparation, applied to the cropping area as mulch, or used as fodder. This depends on whether the farmer has livestock or not, on personal preference, and on the time of cutting. If the grass is applied as mulch or incorporated, the technology can be considered to be an agronomic, as well as a vegetative, measure.
NVS constitutes a low-cost technique because no planting material is required and only minimal labour is necessary for establishment and maintenance. Some farmers had already practiced the technology for several years before the intervention of the ICRAF (The World Agroforestry Centre) in 1993. ICRAF came to realise that farmers here preferred NVS to the recommended ‘contour barrier hedgerows’ of multipurpose trees- which land users viewed as being too labour intensive. When farmers became organised into ‘Landcare’ groups, NVS began to gain wide acceptance.
Land users appreciate the technique because it effectively controls soil erosion and prevents loss (through surface runoff) of fertilizers applied to the crop. As an option, some farmers plant fruit and timber trees, bananas or pineapples on or above the NVS. This may be during establishment of the contour lines, or later. The trees and other cash perennials provide an additional source of income, at the cost of some shading of the adjacent annual crops.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Misamis Oriental
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Bukidnon
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
110.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 110 km2. The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
1993
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It evolved in the area with some adaptations.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rice (upland)
- vegetables - other
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- fruits, other
- coffee
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period: 240 days (Mar - Dec)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Maize, vegetables; coffee; fruit trees; upland rice
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of topsoil through sheet erosion and rills, leading to rapid soil fertility decline. In turn soil fertility decline results in the need for increasing levels of fertilizer inputs to maintain crop yield. However, these fertilizers are often washed away by surface runoff - a vicious circle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain crop yield.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (caused massive erosion and loss of productivity), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (no clear cut policy and support from LGU). Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (over population of livestock, low land ratio), education, access to knowledge and support services (farmers are not fully aware of simple SWC approach), Agricultural causes (unsustainable practice in farming)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
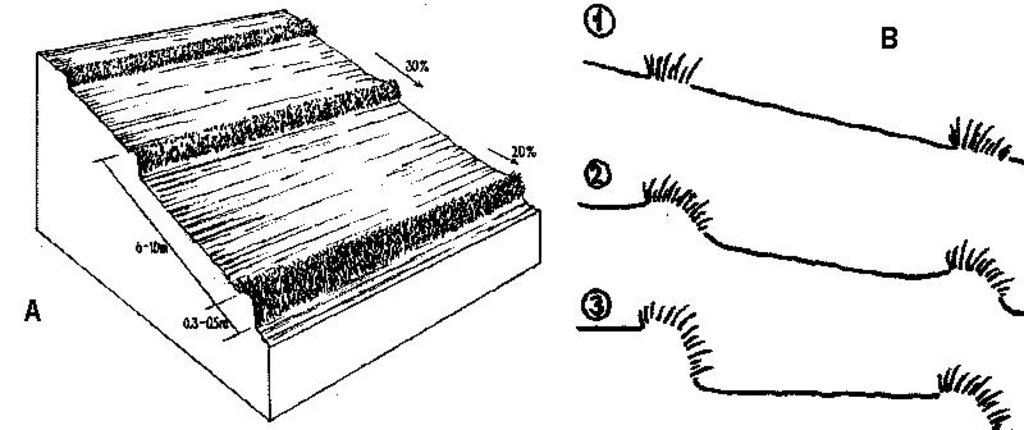
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
A - Spacing of natural vegetative strips depends on the slope.
B - The insert shows the evolution of terraces over time through tillage and soil erosion, leading to accumulation of sediment behind the strips (steps 1-3).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate. Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate.
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, control of dispersed runoff. Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measures:
Mixed cropping / intercropping - Material/ species: annuals/perennials; Remarks: laid out alternately.
Mulching - Material/ species: crop residues; spread on the surface
Legume inter-planting - purpose: for nitrogen fixation
Manure / compost / residues - Material/ species: animal, crop residues
Contour tillage - Material/ species: Contour strips are laid into 6-10 meters apart depending on slope gradient.
Vegetative measures:
Aligned, along contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass, O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Narrow grass barriers
Vegetative material: grass
Number of plants per (ha): dense grass
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia mangium, Eucalyptus deglupta, Gmelina arbarea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Durian, Rambutan, Jackfruit
Perennial crops species: Coffee, rubber, pineappe
Grass species: Bamboo, setara, napier, Panicum spp.
Other species: Legumes
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 20%
ผู้เขียน:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout of contours with the use of an A-frame (or cow’s back method, see Annexe T3)) placing wooden pegs along the contours. | dry season/before land preparation |
| 2. | Seeding (T, F, C) | dry season |
| 3. | Transplanting | onset of rainy season |
| 4. | Land preparation | dry season/before planting |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | animal traction | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | tools | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | stakes (pegs) | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 84.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 84.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial ploughing along the contour: leaving unploughed strips. | onset of rainy season / before each season |
| 2. | Planting | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Mulching | dry season / only whensufficient crop residues |
| 4. | Fertilization | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 5. | Interim cultivation/weeding | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 6. | Ploughing mulch into the soil during normal land cultivation. | |
| 7. | Weeding (T, F, C), Slashing grass | rainy season /2 times |
| 8. | Spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys (between strips) as | rainy season /2 times (weeded materials) |
| 9. | Pruning | before and during cropping /2 times per cropping |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | animal traction | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | tools | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 78.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 78.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: plough, harrow
Costs of establishing contours and maintenance by slashing are calculated by total length of NVS. This example is from a typical field with an 18% slope: at an NVS spacing of 5 m, the approximate total linear distance for one hectare is 2,000 m. In this example, the farmer has paid for everything him/herself (see section on acceptance/adoption). Note that the establishment cost is more or less equivalent to the cost of standard land preparation by ploughing. When 'enrichment planting’ of the strips is carried out, extra cost for seedlings (of fruit trees for example) and associated labour for planting are incurred.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Slope is the dominant factor in cost calculation. The steeper the slope, the more difficult the mobility is and the more closely-spaced the contours are .
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soils are developed from fine-grained igeneous rocks. Soil fertility: strongly acid and with high P fixing capacity. Rapid organic matter mineralisation due to high temperature. Soil drainage is generally good except in isolated depressions.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2; Annual population growth: > 4%
and own 20% of the land (5).
and own 40% of the land (30).
and own 30% of the land (65).
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, trade, business, labour for neighbouring farms and other labour intensive agricultural activities (e.g. vegetable production)
Market orientation of production system: Upland rice is grown as subsistence. Maize is sold to feed millers.
Level of mechanization: The terrain limits the extensive use of machineries.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Subdivision of inheritance lands. High population growth rate attributed to natural birth and envigoration of lowland population create pressure to farm site.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
area competition
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
crop area loss, before NVS evolved to cash perennials or fodder grasses
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
during establishment
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
biomass was given value
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
regular pruning
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
very low inputs required
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
government line agencies and educational institutions
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
negligible socio-cultural conflicts
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
45
หลังจาก SLM:
8
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
partly increased water-logging (negligible)
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
important for sustainability
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
pest sanctuary
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil structure
soil fertility
weed infestation due to seed dispersion and grass roots
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
spreading from the NVS to nearby areas (especially with cogon grass: Imperata cylindrica)
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
no actual measurement
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support (2000 families)
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology spontaneously (without external material support) (2000 families)
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Factor that helped was the formation of Landcare associations which have benefited their members in various ways. There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption, especially where Landcare associations are in operation.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improve soil fertility |
| Prevent soil erosion |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain (How to sustain: Transform farmers associations into cooperative which serve as conduits in marketing. Intensify information and education campaign.) |
| Less competition for space, sunlight, moisture and nutrient. (How to sustain: Ensure continued regular trimming of vegetative strips and use of these as fodder or mulch.) |
| Low labor and external inputs requirement |
| Effective in reducing soil erosion (by 90%) (How to sustain: Adopt other supportive technologies like mulching, zero tillage/minimum tillage, etc.) |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High initial establishment cost | Subsidy/assistance from government |
| Effect of technology is not readily seen | Education about what long term sustainability means |
| High gestation period for some component of the system | Proper mix of annual and perennial crops |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
|
Effect on yield and income is not readily felt, since reduced erosion is not easily translated into increased income or yield |
Farmers should have supplementary sources of income (eg livestock). Education about what long-term sustainability means. |
| Reduction of productive area by approx 10% |
Optimum fertilization to offset production loss. Nutrients are conserved under NVS and this will result in the reduction of fertilizer requirement after some years. |
|
Creation of a fertility gradient within the alley (soil is lost from the top of the alley and accumulates above the NVS where fertility then concentrates) |
Increased application of fertilizer on the upper part of alley. |
| Overall increase of production value is low | Land users could ask for subsidy/assistance from Government: eg for fertilizers, establishment of nurseries, free seedlings (for higher value fruit trees). |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Managing soil fertility on terraces forming behind vegetative filter strips: An assessment of farmer strategies
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Crop productivity using forage legumes and grasses as contour hedgerows species in an acid upland soils
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Garrity DP, Stark M and Mercado Jr A: Natural Vegetative Strips: a bioengineering innovation to help transform smallholderconservation. pp 263–270. 2004.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
in Barker DH, Watson AJ, Sombatpanit S, Northcutt B and Maglinao AR Ground and Water Bioengineering for ErosionControl and Slope Stabilisation.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Science Publishers inc. Enfield, USA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Stark M, Itumay J and Nulla S Assessment of Natural VegetativeContour Strips for Soil Conservation on Shallow Calcareous Soil in the Central Philippines.. 2003.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF), Nairobi, Kenya
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Romeo Villamin Labios
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล