Lining irrigation canals [Мали ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Dieter Nill
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Revêtement des canaux d’irrigation (French)
technologies_1651 - Мали
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Traore Minamba
IICEM
Мали
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - Герман1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
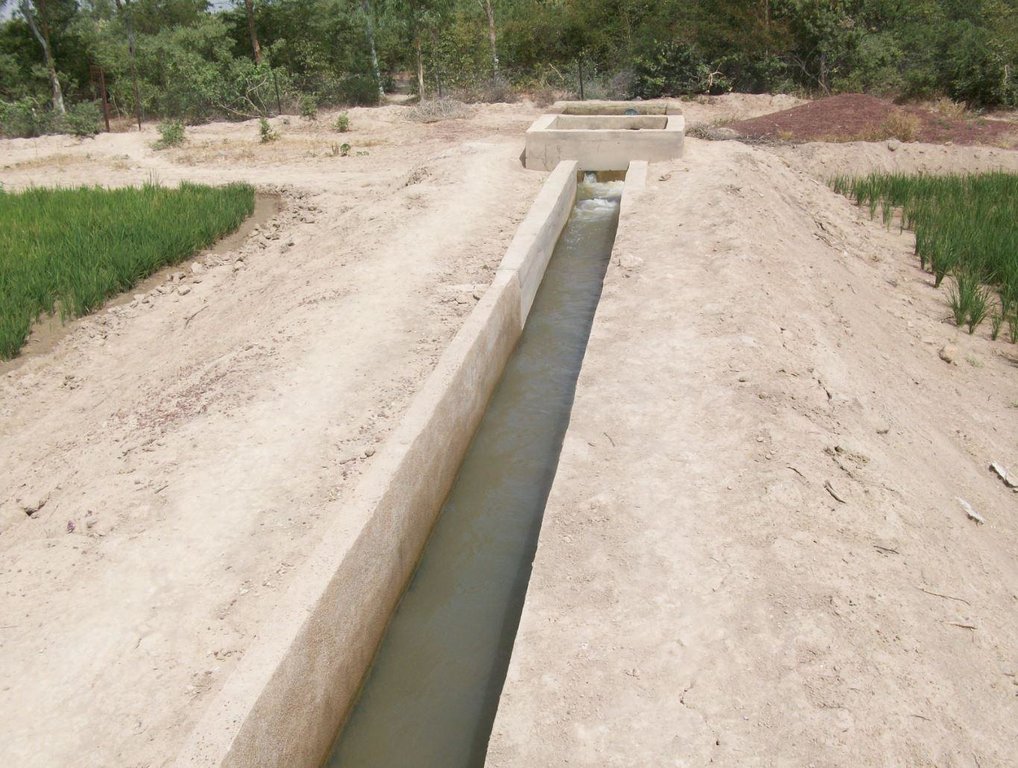
Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses, and to reduce pumping time and costs.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
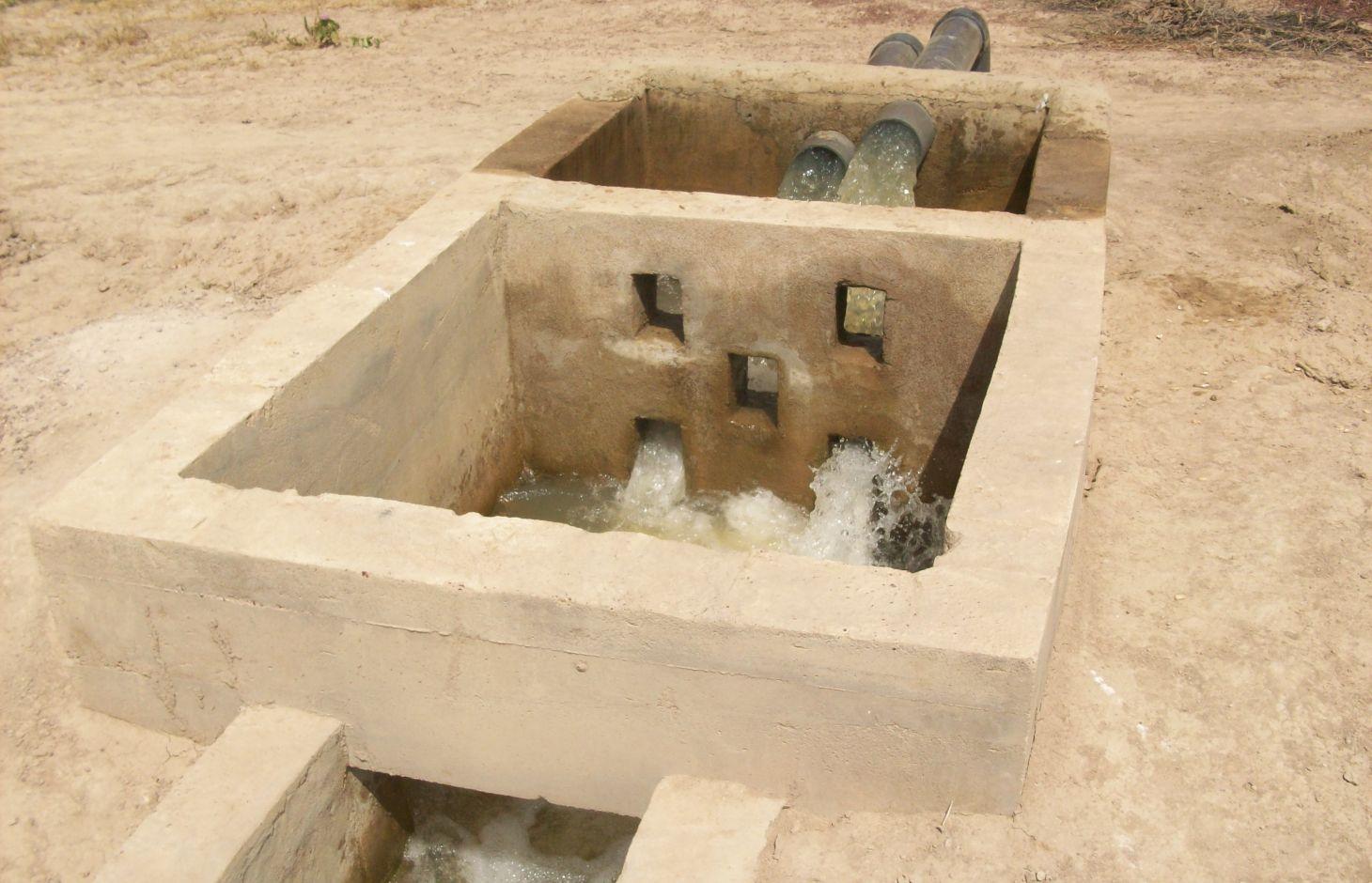
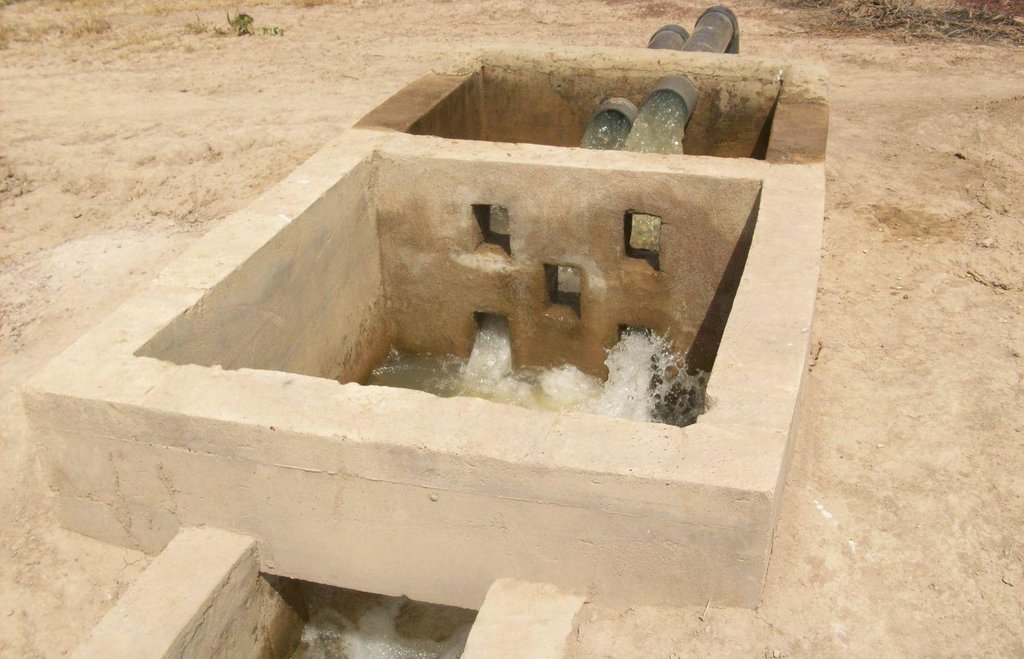
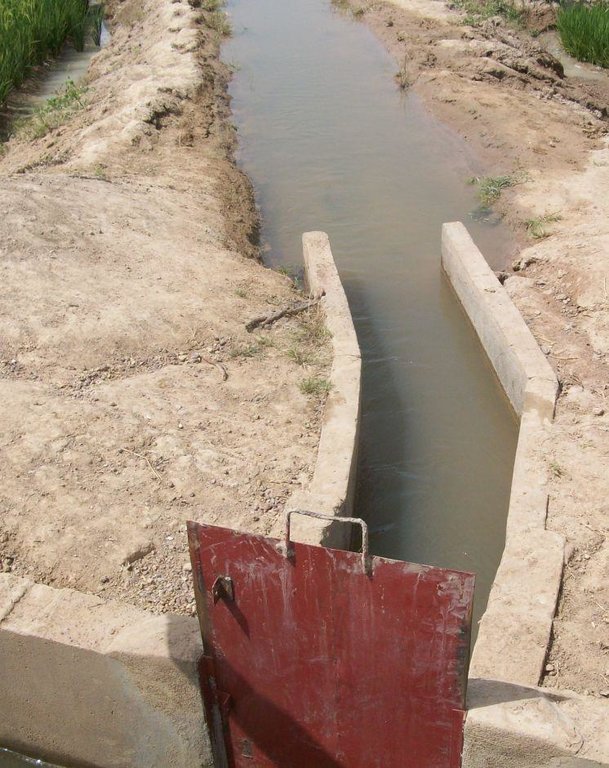
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required.
Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Lining is mainly used to improve the efficiency of existing irrigation systems. Once the canal has been lined, yields increase by between 35% and 80%. This is because crops receive the water they need to ripen as and when it is required. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. Pumping hours per hectare are considerably reduced (by 25% in the rainy season) because the canals ensure the correct distribution of irrigation water. Consequently, irrigation costs per tonne of produce drop due to the reduction in pumping hours and the costs of periodical maintenance and increases in yields.
Together with the growers, a memorandum of understanding was drawn up with IICEM and then signed by the mayor. The memorandum describes all the activities that form part of the collaboration between IICEM and the various beneficiaries. The works were carried out either in-company or constituted part of the highly labour-intensive work (HLIW).
a) Work delivered in-company (turnkey basis): Works are carried out in several stages: 1) Identifying the sites requiring lining. This involves locating the sites to develop and making contact with the NGOs that represent the project in the region, as well as regional directorates of rural engineering and economic operators working with the farming organisations in question. 2) The delimited sites chosen for development must undergo technical studies, which are entrusted to engineering consultancies recruited through an open tender process in accordance with the terms of reference for the studies to be conducted. 3) The technical feasibility studies comprise topographical, geotechnical, soil and environmental studies, as well as the creation of a development plan and quantification of materials required for the construction work. 4) Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses. In lieu of a ToR, an ITT is created by the project according to the requirements of the site. It is then published so that interested consultancies can put forward their bids. 5) Works are carried out under the control and supervision of the oversight office to ensure they adhere to professional standards.
b) Highly labour-intensive work: 1) The same as above. 2) Topographical surveys are carried out by IICEM specialists to calculate the calibration of the canals to ensure they are able to submerge plots over a large area. 3) After calibrating the schemes (energy dissipation basin and division box, main canal and secondary canal turnout, channel), a work plan is drawn up. This uses the measurements calculated to quantify construction material and equipment requirements. 4) Teams of (preferably local) builders are recruited to line the canals. The teams comprise master builders, reinforcing ironworkers, bricklayers and surveyors. 5) The materials and equipment required for each site are provided by an appropriate supplier recruited through a tendering process. 6) Provision of labour and farmer participation. Only the building contractors are paid for working on the project. Labour is supplied by the local community who are provided with lunch to maintain motivation and to prevent lost time caused by workers going off-site. 7) In villages where schemes are proposed, teams of shift workers from the local community are set up and trained in proper conduct for working on a canal lining project and in the keeping of a construction project log book.
Once the canal lining works are complete, IICEM provides a pump unit and subsidises the required fuel and consumables for one growing season. Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee.
The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years if small repairs are regularly undertaken. Ensuring linings are impermeable is of the utmost importance because water penetrating through micro-cracks as it flows through the network can lead to rapid and major water loss. It is therefore essential that producers can maintain installations and repair cracks.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Мали
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Mali
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao, Sikasso
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
12.0
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12 km2.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1200 hectares have had their canals lined
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August-November

Бэлчээрийн газар

Усан зам, усан сан, ус намгархаг газар
- Бохир усны зайлуулах шугам, усан зам
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): unequal distribution of irrigation water, ineffective irrigation systems (water loss)
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаа хосолсон
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
- Усжуулалтын менежмент (усан хангамж, ус зайлуулалт зэрэг.)
- урсац өөрчлөх ба урсац бүрдүүлэх
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S3: Шаталсан суваг, шуувуу, гольдрол
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wr: Голын эргийн эвдрэл

Хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим болон органик агууламж буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах

Усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
The irrigation area’s main earthen canals have their inverts lined in concrete and their sides lined with solid cement blocks. Concrete support posts are set at intervals and capped in concrete. Each lined main canal should be no longer than two kilometres. The main canal’s turnouts into the secondary canals are built in cement and are equipped with gates that can be opened and closed as required. Each turnout’s outflow area is protected by a rockfill structure that is built right up to the top of the canal wall to prevent the canal banks at the head of the secondary canals from becoming degraded.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Зохиогч:
Minamba Traore, IICEM
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
CFA Franc
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
512.0
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identifying the sites requiring lining | |
| 2. | Launching the invitation to tender for the technical studies / Undertaking topographical surveys to calibrate schemes | |
| 3. | Performing the technical studies / Quantifying building material requirements | |
| 4. | Drawing up the invitation to tender (ITT) documents and communicating the tender process to businesses / Recruitment of masons, bricklayers and reinforcing ironworkers | |
| 5. | Delivery of works under the supervision of the oversight office / Invitation to tender for the provision of materials and equipment | |
| 6. | Provision of labour and farmer participation | |
| 7. | Training workers from the local community in building site conduct |
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | small repairs are regularly undertaken |
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. Total costs: 1,587,865.50 US Dollar
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас хуурай
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Дунд (1-3 % )
- Бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын % 10-50 хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Ядуу
- Дундаж
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Хүнд хүчир ажил
Хүйс:
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Тайлбар:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
үйлдвэрлэл зогсох эрсдэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Орлого, зарлага
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийгөө хангах
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
ус хураах / цуглуулах
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсгал
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Орон нутгийн аадар бороо | Сайн биш |
| Орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Сайн |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Сайн биш |
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ургалтын хугацаа багасах | Мэдэхгүй |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Lining of canals is an investment which is generally only feasible with external assistance.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Irrigation system canals in Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao and Sikasso have been lined.
Around 50 sites covering approximately 1,200 hectares have had their canals lined. This kind of practice has been carried out by IICEM since 2009.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Lining canals is a powerful way to save irrigation water by minimising seepage losses. |
| Pumping time and costs are also greatly reduced through the speedy distribution of irrigation water supplies, and reducing the use of motorised pumps lowers maintenance costs. |
| Yields increase by between 35% and 80%. Often, lining also makes it possible to extend the irrigated area. |
| Training in how to run and maintain pump units is provided for the local beneficiaries tasked with their upkeep. Furthermore, training in the management and maintenance of irrigation schemes is delivered to the farming organisations’ steering committee |
| The lifespan of a canal lining ranges from 10 to 20 years |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/07/2012
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
www.iicem.net
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна