Dugout Sunken Pond with Catchment Treatment [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Bandha/ Pokhari (Oriya)
technologies_1475 - Índia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Patnaik Kishore Chandra
Índia
Especialista em GST:
Pradhan Gandhi
Índia
Especialista em GST:
Tripathy Dasarathi
Índia
Especialista em GST:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Índia
Especialista em GST:
Mohanty K.C
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society
Índia
Especialista em GST:
Mishra BIJAYALAXMI
IDCWDP
Índia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute - ÍndiaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society - ÍndiaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
IDCWDP (IDCWDP) - Índia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Índia]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilador/a: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
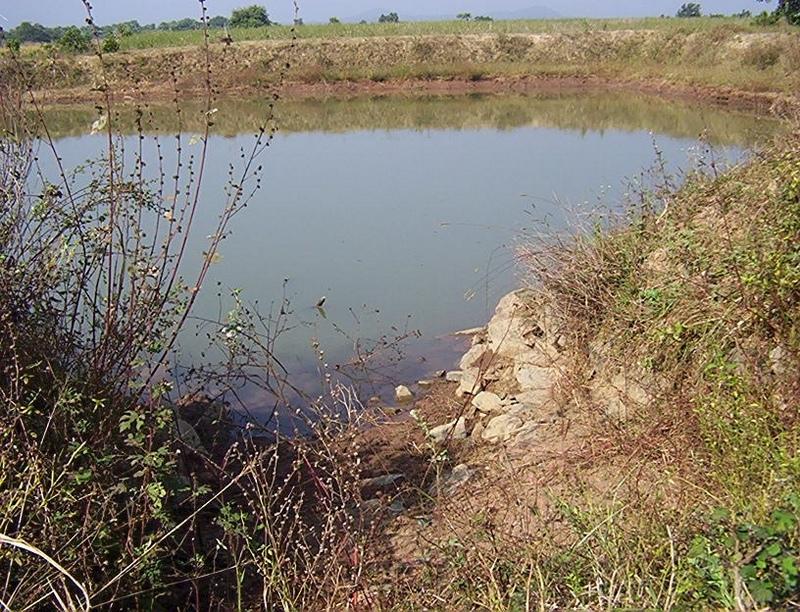
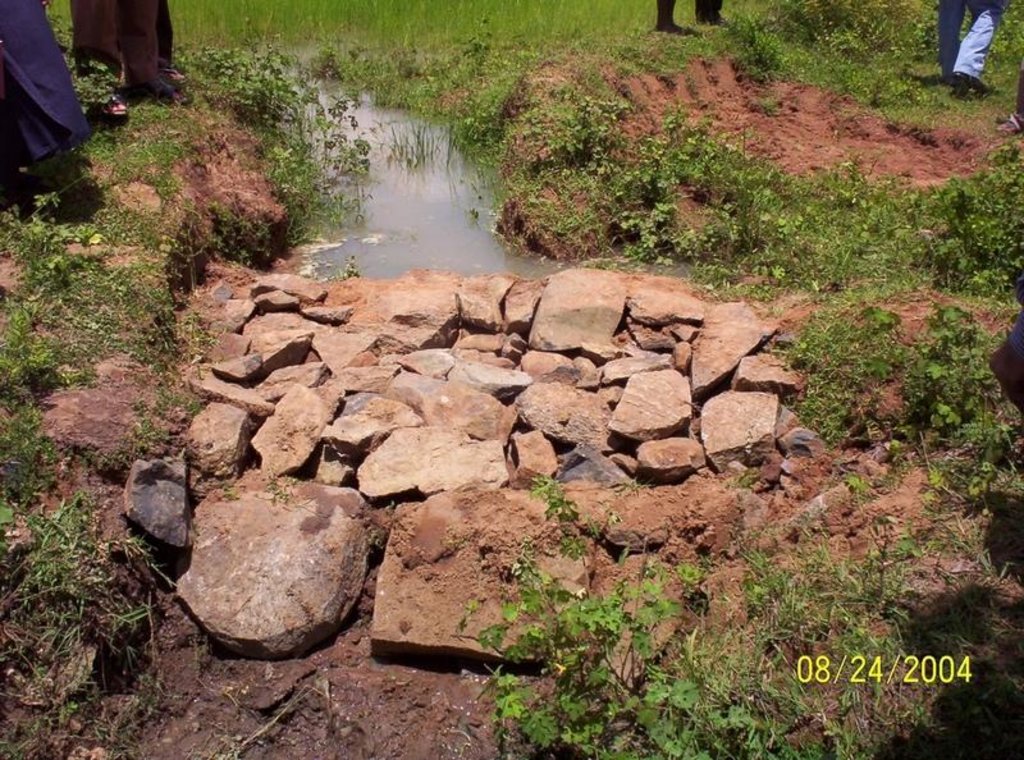
Dugout sunken pond with catchment treatment.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
(1) Total size of the project area = 4.75 Ha.
(2) Different structures taken up in the project area are
(i) Brushwood check dam- 6 Nos.
(ii) Drop structure- 8 Nos.
(iii) Dugout sunken pond - 1 No.
(3) All the above structures were positioned to ridge to valley treatment
(Ref.QT-6/2.1.2/a)
Purpose of the Technology: 1) Storage of runoff for cattle and human use.
2) Construction of structures to check soil erosion and sand casting.
3) Pisciculture.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment :-
1) SWC specialist selected sites for dugout sunken pond, layout the design.
2) SWC specialist also selected sites for drop structures, brushwood check
dams in gullied portion of project area with reference to vertical interval
of slope gradient and space between structures.
3) The execution of work were done by concerned villagers on payment basis.
4) During execution, 20% of the total cost of the dugout sunken pond was
contributed by the villagers in shape of labour.
5) Training on technical know how imparted to the villagrs during execution
of pond, bund, drop structure and brush wood check dam.
Maintenance:-
1) The dugout sunken pond requires (a) Desiltation once in two years (b)
Repair of earthern bund around inlet and outlet every year.
2) The drop structure & brushwood check dams requires little maintenance when
ever requires.
3) One management group has formed in the same village & funds has been
raised by doing pisciculture in the pond.
4) The management group is taking major reponsibility for its maintenance.
Natural / human environment: (1) Drainage line stablilized (2) Adjuscant area cultivated (3) Users group
formed and pisciculture taken up for the Ist time in the village.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
Orissa
Especificação adicional de localização:
Orissa/ Malkangiri
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
0,0475
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0475 km2.
A fellow, understanding, gullied piece ofland selected for the technology which suffers from sand casting and uncertainity of rain.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Area (NWDPRA)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- rice
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov

Pastagem
- cattle
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
1) A fellow, undulating, gullied piece of land.
2) Acute sand casting at the down stream cropland.
3) About 40% of the project area were practicing local paddy which suffers from erratic rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): A piece of land which depends upon the mercy of the Rain God for annual production.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
- apicultura, aquacultura, avicultura, cunicultura, sericicultura, etc.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Erosion problem), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Common social practices
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Aerial view of dugout sunken pond
Location: Siadimal, Korkonda. Malkangiri/Orissa/ India
Date: 15.3.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, water harvesting / increase water supply, Control of sand casting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.45
Vegetative measure: In earthern bund slope
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Compact
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.7
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vertivera and local grass slods
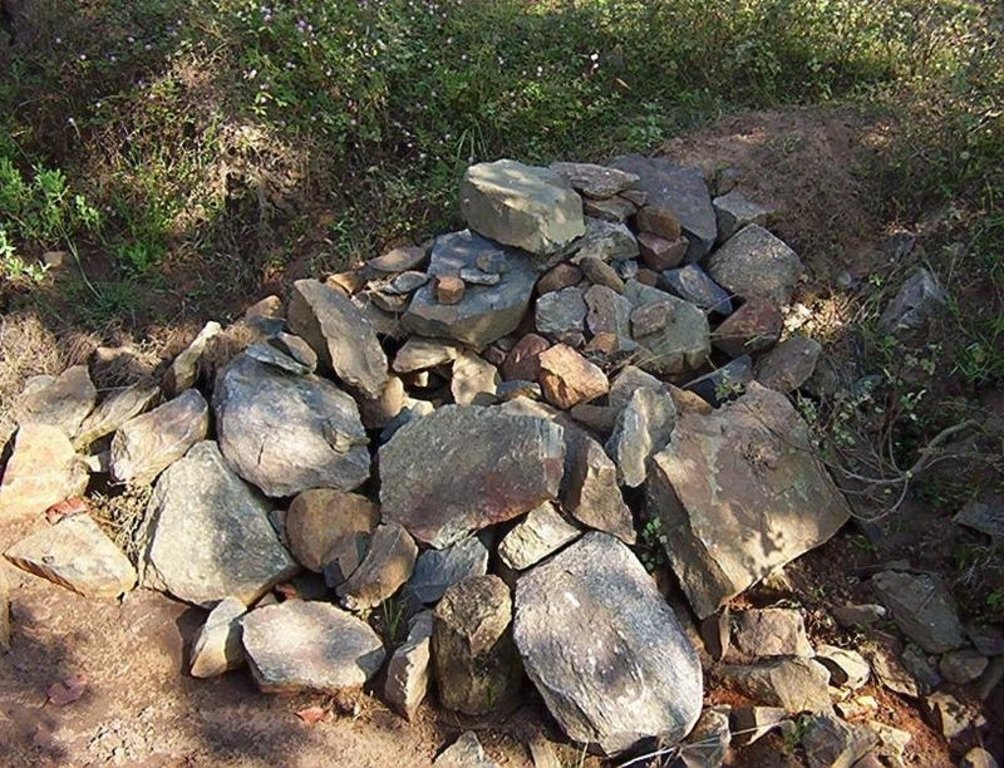
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/brushwood check dam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.6
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/ drop structure
Vertical interval between structures (m): 9
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.05
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 5.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Dam/Pan/Dugout sunken pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Structural measure: Bund/Trapizoidal
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.85
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.50+8.9/2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 157
Construction material (earth): Soil excavated from pond is used to built bund around pond.
Construction material (stone): Inlet and outlet of pond and drop structure are made up of stone
Construction material (wood): Brush wood check dams are made up of wooden poles and bush wood.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:41
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Patnaik K.C, Malkangiri, Oriss
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Rupee
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
45,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
0.89
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection grass sods and vertivera slips | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Transporting grass sods on established banks | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Watering | When dry in Ist. Season |
| 4. | Dugout sunken pond-Surveying | Summer season |
| 5. | Dugout sunken pond- soil excavated from pondage area used in trapizodical bund around leaving inlet & outlet portion. | Summer season |
| 6. | Dugout sunken pond- Collection and transporting stone to inlet & outlet site | Summer season |
| 7. | Dugout sunken pond- construction of inlet & outlet with stone | Summer season |
| 8. | Dugout sunken pond- collection of local grass sods & vertiver slops | Onset of rain |
| 9. | Dugout sunken pond- turfing the bund slopes and planting of vertiver slips in rows at up stream and down steam side of inlet and outlet | On set of rain |
| 10. | Brushwood check dam- surveying | Summer season |
| 11. | Brushwood check dam- collection of wooden poles and brush wood | Summer season |
| 12. | Brushwood check dam- collection of picked up stones | Summer season |
| 13. | Brushwood check dam- fixing of wooden pole, weiving with brush wood, filling up the gaps with picked up stones | Summer season |
| 14. | Brushwood check dam- collection of vertiver slips and planting in upstream and downstream of each structure | On set of rain |
| 15. | Drop structure- surveying | Summer season |
| 16. | Drop structure- collection & transportation of stones to work spot | Summer season |
| 17. | Drop structure- construction of drop structure with stones | Summer season |
| 18. | Drop structure- collection of vertiver slips and planting at up stream and down stream of structure | On set of rain |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 225,0 | 225,0 | 14,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 49,0 | 49,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| Outros | Royalty charges for stones | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| Outros | Fishery and feed | ha | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | |
| Outros | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 73,0 | 73,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 372,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 8,27 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting vertiver slips & grass sods for gap filling | Onset of rain /annual |
| 2. | Collection of grass sods and gap fillling to bund layers | On set of rain/Annualy |
| 3. | Desiltation | Before on set of rain/Biannualy |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 21,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 0,47 | |||||
Comentários:
The above calculation is based on the total establishment/ recurring cost both born by the project and land users is devided by the total project area i.e 4.75 ha. To get average hect. cost.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Availability of stone affects the cost from implementing SWC
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1760,00
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
South Eastern Ghat Agro Climatic Zone
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (423 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (2-7% slope)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users from SWC technology area proctise contour plough, line sowing and using HYV paddy have increased their income significantly.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour and aniaml traction (bullock plough, both ranked 1)
Market orientation of production system: Pisciculture (Selling at village level)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Fish add to their income
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Closure of land by pondage area
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Pisciculture support to live stock, dirnking water for cattle
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Management group formed and strengthened due to continurous income from pisciculture.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Training conducted
Linkage with other institutions
Comentários/especificar:
Due to different activities in the pond linkage to other institution has increased like Horticulture, Fishery etc.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
90
Quantidade posterior à GST:
40
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to water storage
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
87
Quantidade posterior à GST:
45
Outros impactos ecológicos
Biodiversity
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentação a jusante
Soil moisture regime
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If the community find the technology is low cost to teke up and gets eye catching benefits, then the treand of adoption is good.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Water problem for human and cattle solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of pond needed |
|
Damage of crops reduced by construction of series of structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? More field bunding, vegetative cover should be imparted. |
|
Users group brings villagers closure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manageent group to be reorganised annuly |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Water scarcity of the area partly solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular desilting shound be done. |
|
Heavy sand casting and soil loss controled How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative cover required for catchement area |
|
Crop production increased in the project area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Should be replicated by the people. |
|
Pisciculture added extra income to the villagers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hybrid fingerlings to be adopted |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Sand casting could not be checked fully | By full vegetative cover and more structural measures it can be checked. |
| Sediment deposit in down stream area decreased | The loss can be over come by increasing crop yield. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Disponível de onde? Custos?
-do-
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Índia]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilador/a: Srikanta Kumar Parida
Módulos
Não há módulos