Irrigation of uplands through Hydraulic Flange Pump [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Aabyari zamin hai boland Aaba thawasut Pump_e_Aabi_Charkhdar
technologies_1731 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
People in Need (PIN) (People in Need (PIN)) - Afeganistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
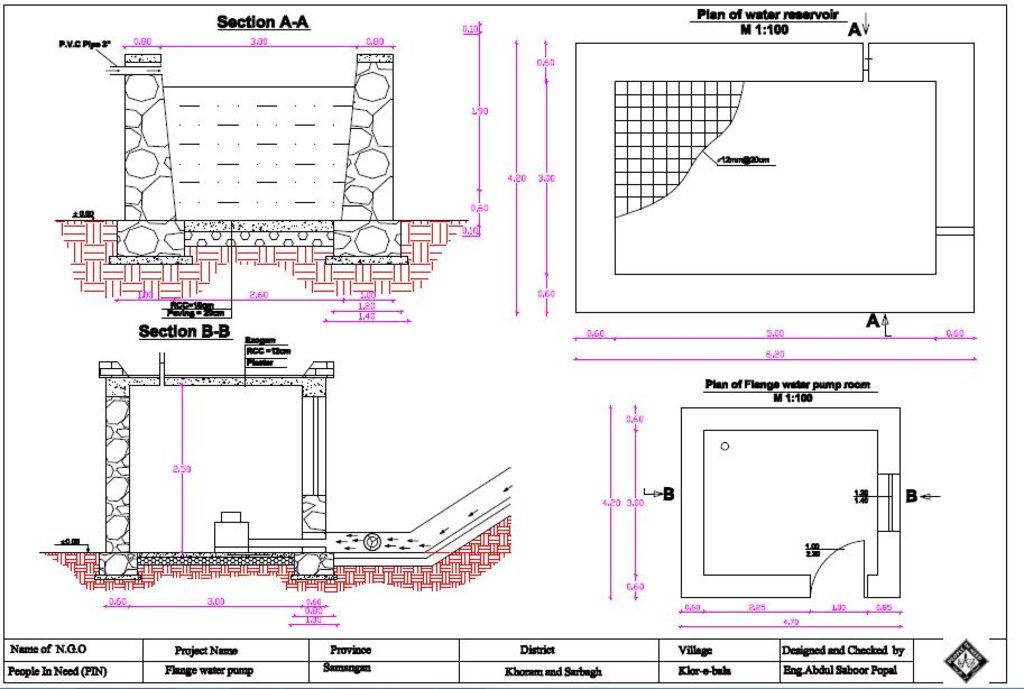
Technology for lifting water to uplands: hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
This technology is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project, implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), with close support and cooperation of People in Need.
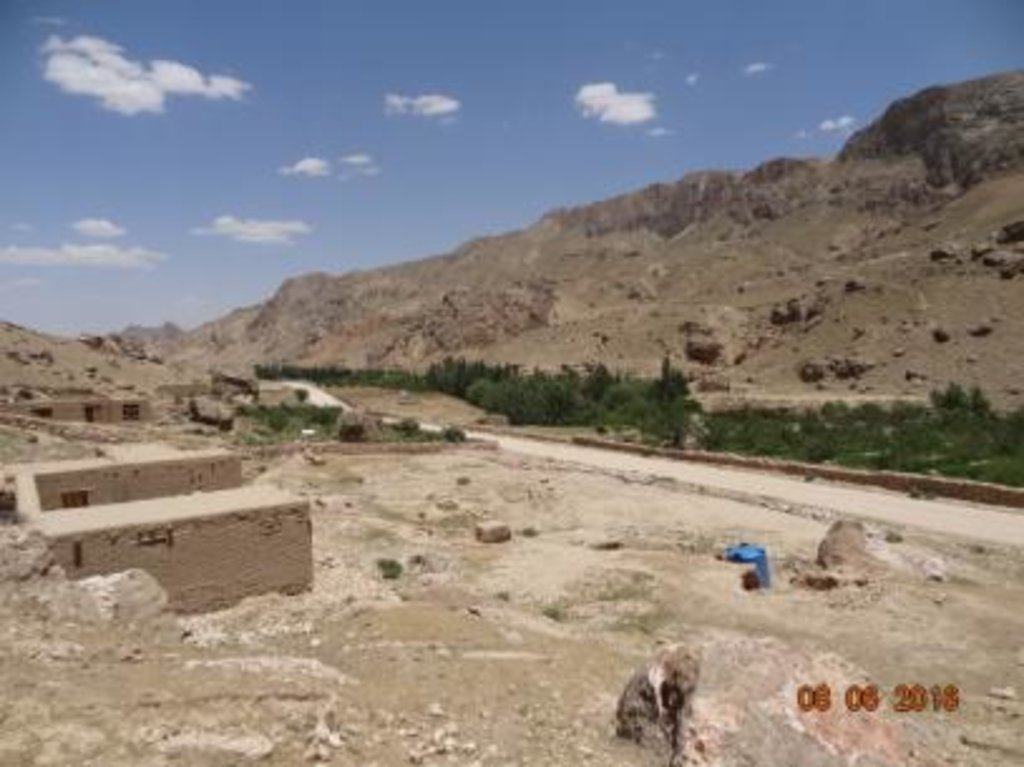
Samangan, Khuram wa Sarbagh district, Klor-e-Bala village is situated in a mountainous region where the greatest limiting factor to agricultural production is water. Arable lands are located far away from water sources. Lack of technology to exploit these lands prohibits villagers to cultivate their land to make a livelihood. Therefore, families are compelled to leave their village during summer.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, People in Need (PIN), with financial support from GIZ and the Czech Embassy (CzDA) introduced irrigation through hydraulic flange pump. The hydraulic flange pump provides water to 30 orchards of Klor-e-Bala village, drinking water to the 43 village households, the mosque and the school of 500 students.
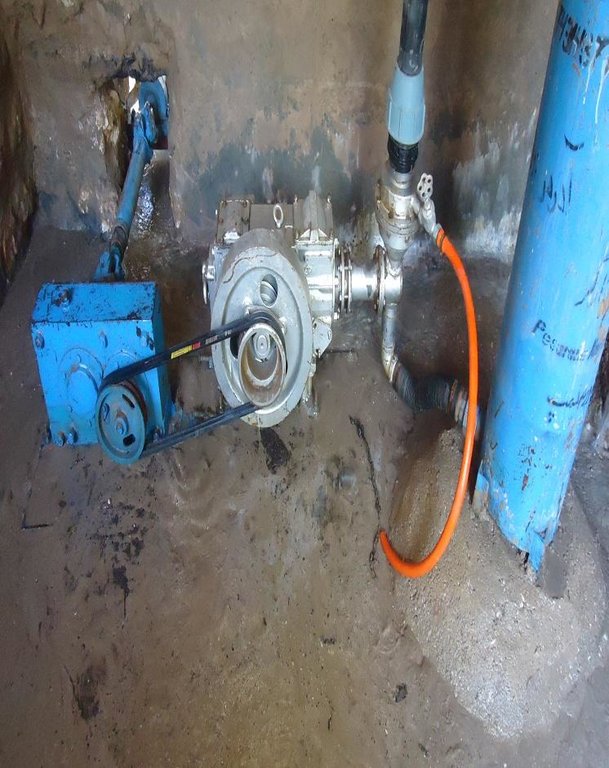
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main water source which starts and runs the hydraulic flange pump is the Khuwaja Hayat spring. The spring water arrives to the hydraulic flange pump from 1.8 meter height on a 12 percent slope in 200 meters distance from the water source. The water flow passes through the intake and moves towards the water wheel which starts/runs the hydraulic flange pump. The water is then pumped through three pipes of one inch to the reservoir. The hydraulic flange pump has the capacity of lifting water up to 250 meters.
The reservoir’s storage capacity is 25,600 liters of water with the dimensions as follows: 4.9 meter length; 2.9 m width; and 1.8 m height. It has two outlets: a spill way fitted with three pipes of one inch at the top of the reservoir and two outlets fitted with two pipes of three inches at the bottom. The lower outlet leads water to the orchards by diverting water after 40 meters into two pipes which are 1,000 meters long. Each orchard is connected to one of these two pipes by a T-connector and the water flows into a tin water tank with the capacity of 1,000 liters for each orchard. The two pipes are extended as far as the school which is located near the orchards and has been equipped with a 2000 liters tin water tank.
The hydraulic flange pump is made locally in Taloqan city, Takhar province of Afghanistan in the Baradaran-e- Kargar workshop. The pump costs 140,000 Afghani/ 2,200 US$, including installment. The estimated cost of the construction of the reservoir and the pump’s room including the hydraulic flange pump is 19,000 US$. The pipe scheme of the project was installed by the Community Development Council (CDC) with technical support from PIN’s engineering team. Community members contributed 10 percent of the costs as labor. As Klor-e-Bala village is situated in flood prone area and flooding is a common occurrence, PIN, with funding from the GIZ, constructed in 2015 two protection walls, 45 m and 55 m in length, on both sides of the river, to minimize erosion and protect the pump’s intake from floods. The protection walls were built through cash for work programme, but community members provided 10 percent contribution through labor and by providing stones for construction. The total estimated cost of the hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme technology amounted to 37,000 US$.
Furthermore, in order to maintain the technology, a caretaker, who lives close to the pump’s room has been appointed. The caretaker was trained by the technician who installed the hydraulic flange pump and has voluntarily taken the responsibility of maintenance activities; changing the oil and cleaning of the hydraulic flange pump's room and changing of the pipes in case of need. The owners of the orchards have to cover for all maintenance costs and the chairman of the Community Development Council (CDC) has the responsibility of managing the money for maintenance and other recurrent activities.
The flange pump technology contributed to the economic growth of the community members by increasing the orchards’ yields. Currently, the hydraulic flange pump irrigates 12 jireb/2.4 ha (30*800m2) orchards of apple, apricot, almond, pear and cherry trees. In addition to the orchards, alfalfa, potato, vegetables and other crops are as well cultivated on these lands. Furthermore, the pump supports the community members to settle year-round in their villages and prevents from their seasonal displacement. Moreover, the flange pump enables the provision of drinking water to the whole community and the school.
Natural / human environment: Samangan is one of the northern provinces of Afghanistan. Wheat, melons, pistachio,
almonds, potatoes, onions and caraway are important crops and Karakul sheep
and goats the main livestock for meat, dairy, and wool production. Rugs are the
main handicraft of this area. Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district in Samangan has two growing
seasons, the longest of which is 150 days from February to June and the second is 90
days from June to September. The average rainfall is below 500mm and the climate semi-arid.
The community members have limited access to off farm employment, market, energy,
financial services, roads and transportation and moderate access to health and education.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Samangan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Klor_e_Bala village
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
The technology area which is considered here is the distance from the water area where the machine exists to the reservoir and reservoir to the orchard and crop land.
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: February - June; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: June - September

Pastagem
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of safe drinking and irrigation water which makes agricultural activities difficult.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of cultivation due to the scarcity of water. High workloads and small incomes.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Linhas de drenagem, vias navegáveis
- Lagos, represas
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão natural e seminatural de floresta
- Agrofloresta
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
A detailed technical drawing of the hydraulic flange pump and the reservoir, Klor-e-Bala village, Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Samangan province.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Autor:
Eng. Saboor Popal, People In Need (PIN)
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
7.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundation | |
| 2. | Construction activities,Stone masonry foundation and wall: | |
| 3. | a:P.C.C concrete foundationb:R.C.C concretec:Iron shattering for walls, roof and floord:External and internal pointing | |
| 4. | a:Plasteringb:Steel barsc:Door and window | |
| 5. | Pipe scheme:a:Pipesb:Water tanksc:other equipmentd:Skilled and unskilled labor | |
| 6. | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Excavation of the foundation | square meters | 50,0 | 2,88 | 144,0 | 10,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Excavation of the foundation | cubic meters | 161,0 | 2,4037 | 387,0 | 10,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Skilled and unskilled labor | persons/day | 343,0 | 9,47521 | 3250,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Water tanks | pieces | 39,0 | 98,615384 | 3846,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Pipes | meter | 2900,0 | 2,9241379 | 8480,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Other equipment | all | 1,0 | 2424,0 | 2424,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump | pieces | 1,0 | 2200,0 | 2200,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Concrete foundation | cubic meters | 12,23 | 96,64758 | 1182,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Concrete | cubic meters | 8,4 | 114,0476 | 958,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Iron shattering for walls, roof and floor | cubic meters | 110,0 | 4,86363 | 535,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | External and internal pointing | square meters | 226,0 | 2,85398 | 645,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Plastering | square meters | 32,0 | 5,9375 | 190,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Steel bars | square meters | 364,4 | 1,21844 | 444,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Door and window | square meters | 3,98 | 28,8944 | 115,0 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Stones | square meters | 244,0 | 50,0 | 12200,0 | 10,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 37000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 37000,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Changing of the pipes | Once a year |
| 2. | Cleaning of the flange pump room | Six times a year |
| 3. | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Changing of the pipes | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning of the flange pump room | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil | persons/day | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Pipes | meter | 20,0 | 0,65 | 13,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Oil | times/year | 4,0 | 4,5 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 52,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 52,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labor, stone and equipment are the main fundamental factors which need high initial investments.
After a couple of years pipes may need to be changed.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Nômade
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Constructional activities which are done outside of the houses and compounds are mainly applied by men in Afghanistan.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
In case the owner of the first orchard do not obey the water use right
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The pump improved households’ economy through increasing agricultural yieIds and by decreasing the need for a generator pump. It has as well reduced the workload of the community members
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Salinidade
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
It has decreased the water flow only in the place where the hydraulic flange pump is installed.
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação súbita | não bem |
Outros extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
| Outros (especificar) | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? |
|---|---|
| length of growing period | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
98 households covering 50 percent of the stated area
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
98 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to high expenses of the implementation of the technology, it has not been applied without any external support.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is of a high cost and needs external support to be established.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Application of the technology has reduced the workload for the families. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Greater awareness on water management can be created by training/workshop for the water users. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
The technology has supported the community members economically by increasing agricultural yields. Moreover, it contributes to reduce the costs of water during the summer season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The land users should try to plant local and native trees and cultivate the crops which are adapted to the land.Community members should actively participate in maintenance activities. |
|
Provides safe drinking water to the 43 households and the school at low cost. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pipe scheme and cover of the reservoir, should be cleaned regularly. If any leakages occurs in the pipes or reservoir, they should be sealed. Water taps and water tanks should be properly maintained. |
|
This technology has been applied in a low slope/latitude where the water flows with a very low speed and the application of other technologies was difficult. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protect from sedimentation. |
|
The hydraulic flange pump is produced locally. Procurement and installment of the pump contributes therefore to local economic growth and private sector development. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Link the company to the other potential buyers. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Social conflicts can occur during the distribution of water | The water in keeper/maintainer can be introduced by CDCs for the distribution of water. |
| Electricity cannot be produced by applying this technology. The slope and latitude of the location where the flange pump is installed is too small. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
|
It is difficult to apply the technology without any external and financial support. |
Locally available materials should be used to reduce costs. |
| High level of technical knowledge is required for the establishment of the technology. | The technical knowledge should be transferred to the extension workers or local people to provide technical support in the future. |
|
This technology needs regular maintenance and the reservoir has to be properly cleaned after heavy rainfalls. |
The CDC should monitor maintenance activities by the caretaker as well as manage funds for maintenance costs. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos