Barley fodder management for livestock production among smallholder farmers [Uganda]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Sarah Babirye
- Editor: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- Revisores: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel, Donia Mühlematter
Balle
technologies_3453 - Uganda
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Kabanda Fred
0794661269
Kyanja Agricultural Resource Centre
Kyanja Agricultural Research Organizations Gayanza Road ,Parish P.O BOX 7010,KAMPALA
Uganda
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - Uganda1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
29/1/2018
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Barley fodder technology is a livestock feed that grows under a hydroponic system. This green feed is highly palatable, rich in protein and energy yet cost-effective. It takes few days to maturity (5-6 days) and can be grown in a smaller area. One kilogram of barley seeds can yield up to 6 to 6.5 kg of green feed.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
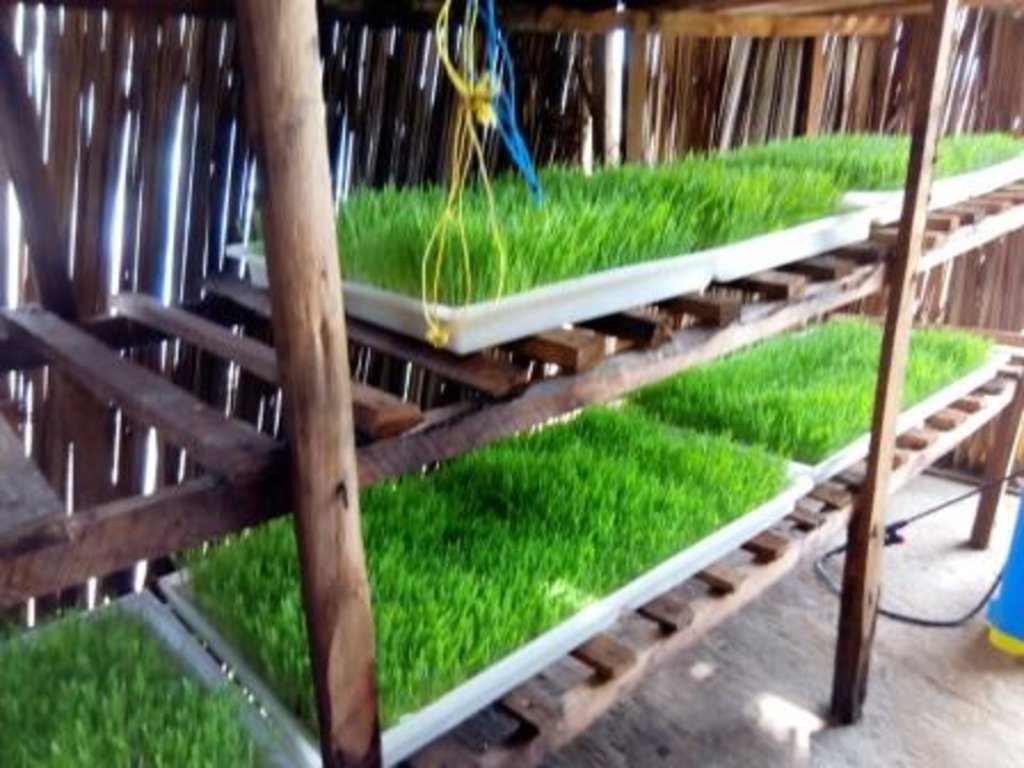
Barley is a cereal grain that grows with hydroponic system to supplement on the feeds for livestock. This system enables crops to grow without soil so easily yet they mature within the shortest time in a smaller area. It is commonly used in finishing rations for livestock. Barley sprouts the best, grows the fastest and is cost-effective. This green feed is less expensive yet highly palatable and nutritious for animals.
To work well for sprouted fodder, the barley seed needs a high germination rate. Sprouting barley consistently and economically needs a climate-controlled space, light (18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness) and a watering system. The ideal temperature being 75 degrees F and 70% humidity. Air movement is necessary to control mold.
The technology ensures a reduction of pesticides and herbicides because the plants are in a protected environment . The sprouts are high in protein and fiber, and are naturally balanced in protein, fat and energy. Barley fodder has 95% of the energy and higher digestibility hence reducing the occurrence of digestive diseases, such as bloat. It is one of the most nutritious sprouts and is full of essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals. These are absorbed more efficiently due to the lack of enzyme inhibitors in sprouted grain. Dry barley seeds yields between 6-6.5kg of green feed. Feeding barley fodder will improve the overall health and wellbeing of animals. With this technology, farmers can easily anticipate the expected amount of feeds. Despite the benefits, growing barley requires skills, knowledge and constant supervision especially maintaining the conditions required. Barley seeds are at times hard to get. In case of commercial/large livestock farming, the technology is not economically feasible. Bacterial and fungal growth is also another challenge like the common bread mould therefore seeds must be sterilized. The steps taken to grow barley seeds are as follows:
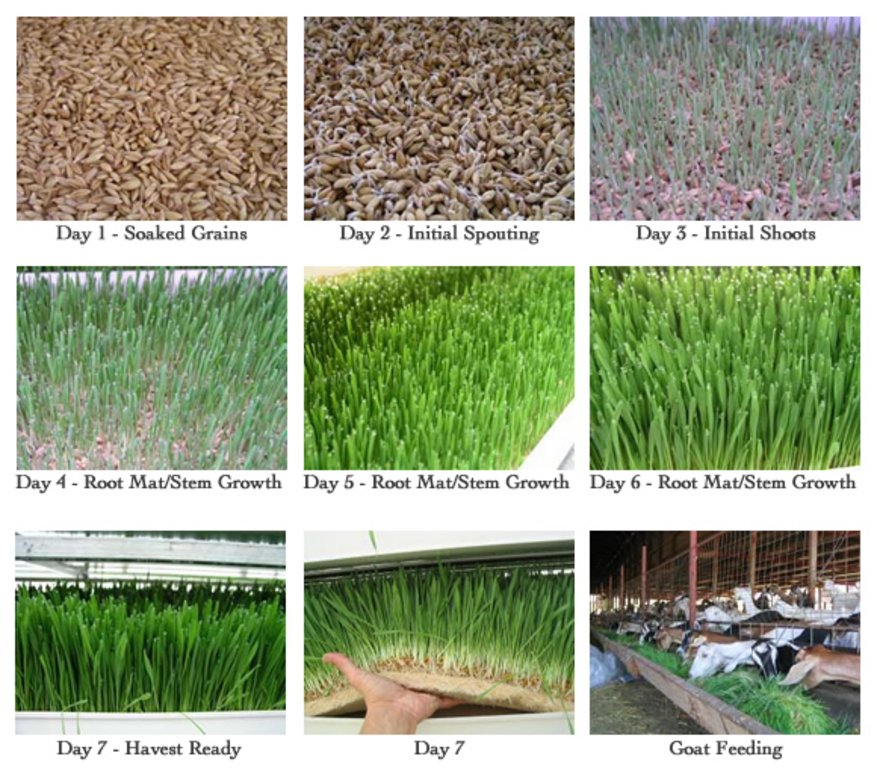
•On day 1, the barley seeds are laid on plastic trays after being soaked in water for 8-12 hours or an overnight. These seeds must be moist and kept clean. In case of any moulds, hydrogen peroxide may be used in the soaking water to kill mould.
•On day 2, the trays are placed on shelves where they are stacked. On this day, initial sprouting begins. Seeds must be kept moist, but not water-logged. Manually, water should be spread every after 4-5 hours. The seeds will usually sprout within 24 hours.
•On the third day, initial shooting begins. Watering still proceeds.
•From the 4-5th day, the root mat or the mat stem begin to grow.
•On the 6-7 the day, the farmers begins to harvest the barley grass and gives to the livestock. The grass has produced a 6-8 inch high grass mat with a 2 inch mat of interwoven roots.
The sprouted grain is harvested by removing the tray or sliding the mat off the tray in one long sheet. The mats can be cut to the appropriate size and fed to animals. Livestock will eat the whole thing like seeds, roots, and grass therefore, there is minimal waste. Barley is a major feeding option when pastureland and/or hay are in short supply, or adds a highly nutritious and relished supplement to traditional grazing.
Initial costs involved to a small scale farmer are minimal. This includes buying clean seeds, 5 kg costing 15,000/=, 10 plastic trays (50000), 2 watering cans (20000), 1 bucket for soaking seeds (10000), watering seeds 6 times (18000), soaking seeds (3000), labour for making shelves (30000), papyrus mat (20000) ,2 kg of nails (10000), timber for making shelves (50000), chopping ready folder (3000) totalling to 232,000/= for a start. However, this depends on the amount of fodder a farmer wants to produce.
A kg of barley seeds yields to 7-10 kg of green fodder. Each kg of fodder is sold at 1500 hence in a kg planted (i.e. 3000 invested), a farmer is likely to earn 15000/=
The technology is advantageous in that there is little or insignificant costs involved on maintenance of the technology. Maintenance only involves daily watering of seeds (18000 for 6 days), cleaning the treys after use (3000) and supervision on barley during growing for 6 days (18000) totaling to 39000/=.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Data:
29/01/2018
Localização:
Kyanja Agricultural Resource Centre
Nome do cinegrafista:
Babirye Sarah
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Uganda
Região/Estado/Província:
KAMPALA
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kyanja, Gayaza
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Outros
Especifique:
Laboratory
Observações:
The demonstration was done at Kyanja National Research Organization in a laboratory.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Water can be collected from national water (water supplied to people by the government of Uganda, National Water and Sewage Cooperation). Water from rainfall is be used in the process.
Especifique:
Not seseonal, can be grown any time
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
Basically after building a structure with shelves, barley seeds are planted into trays.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Barley seeds are cleaned before being planted to avoid the risks of fungal attack e.g moulds
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Outro
Comentários:
Not applicable
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Não aplicável
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
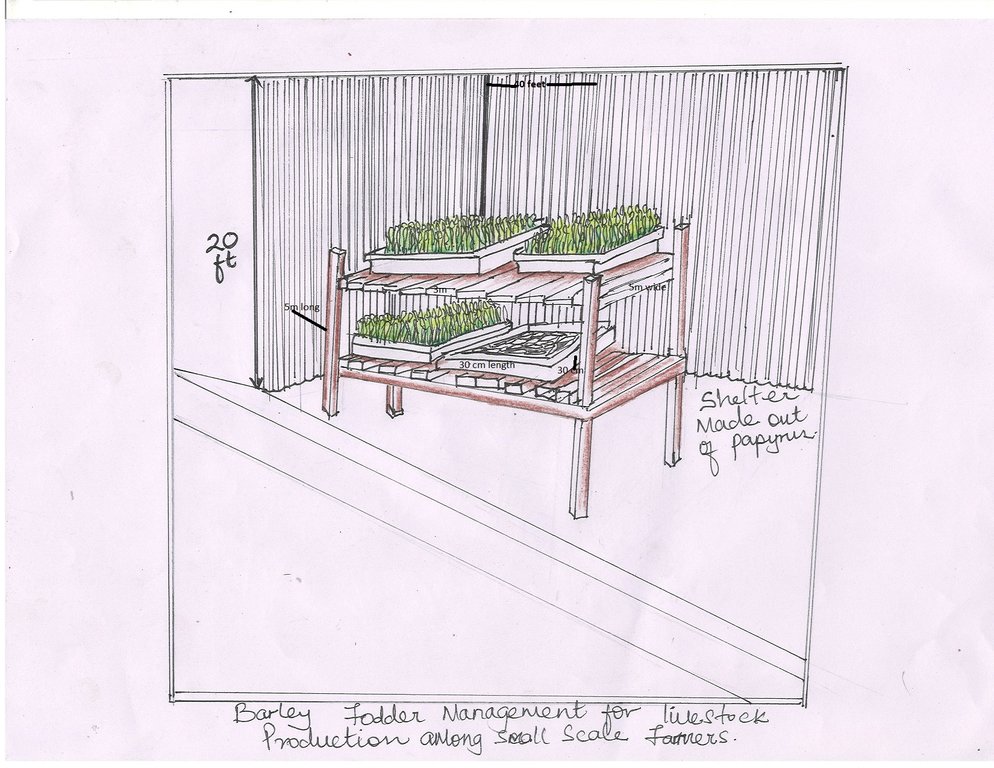
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The shelter is constructed at 20 feet long and 20 feet wide
Trays(10) of 30cm wide and 30 cm length
Barley seeds (5kg)
Shelves (20) of 3m wide and 3m long
Papyrus mats (2) of 20 feet wide and 40 feet long
Shelves stand of 5m long
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique volume, comprimento, etc (se relevante):
20feet long*20feet wide
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
UGX
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
3600,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3000/= per day
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying seeds | Outras medidas | Every planting time |
| 2. | Clean the seeds if dirty to avoid molds | Gestão | Before planting if they are dirty |
| 3. | Soak the seeds for 8-12 hours | Gestão | 8-12 hours |
| 4. | Place the trays on the shelves | Gestão | Once from 1-5 day |
| 5. | Water the seeds planted on the tray every 4-8 hours | Gestão | 4-8 hours for 5 days after planting |
| 6. | Harvest and chop the leaves,stems and roots,then give to the livestock | Agronômico | After harvesting |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Making shelves | Man day | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Clean the seeds if they are dirty | Man day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Soaking the seeds into water | Man day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Chop the fodder ready for feeding | Man day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Equipamento | Water the seeds planted on the trey in every 4-8 hours | Man day | 6,0 | 3000,0 | 18000,0 | |
| Equipamento | Buying trays | piece | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Buying seeds | Kg | 5,0 | 3000,0 | 15000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Buying a watering can | piece | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Buying a bucket | piece | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Timber making shelves | piece | 5,0 | 10000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Nails | Kg | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Papyrus mats | piece | 2,0 | 10000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 232000,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
All costs are covered by the Resource Centre
Comentários:
The costs are estimated.
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering the seeds | Agronômico | Every day after planting to harvest |
| 2. | Maintaining the room temperature | Agronômico | Every day after planting to harvest |
| 3. | Replacing poles | Estrutural | Once a year |
| 4. | Cleaning the equipments like treys | Outras medidas | After harvesting |
| 5. | Replacement of shelves | Estrutural | Once a year |
Comentários:
Maintenance activities are few. Equipments are only replaced when damaged which can take a year.
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Watering seeds | Man day | 6,0 | 3000,0 | 18000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning the equipments( trays) | Man day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Equipamento | Spervision of the growing barley | Man day | 6,0 | 3000,0 | 18000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 39000,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The Resource Centre caters for all the costs.
Comentários:
These are estimated but almost in the range. This makes the technology more cost efficient.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour costs represent the largest cost element.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Arrendado
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Improves on fodder for animals. That is 1 kg of barley yields 7-10 kg of green fodder
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
The animals that feed on barley supplements reduced suffering from bloating because of high digestibility
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Barley is a supplement to the conventional grass
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
It requires a small production area
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Land well managed
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Barley grass is highly nutritious with a lot of protein content. Coupled with being a very palatable fodder, the growth rate of animals increases.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
One kg of harvested green fodder is sold between 1500-2000/= hence increase in income to a farmer
Impactos socioculturais
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
The health situations of animals is improved. Barley fodder has 95% of the energy and higher digestibility hence reducing the occurrence of digestive diseases, such as bloat. It is one of the most nutritious sprouts and is full of essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
The technology requires enough supply of water for watering the growing barley
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem em absoluto |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Infestação de insetos/vermes | não bem em absoluto |
Outros extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
| Outros (especificar) | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? |
|---|---|
| Too high temperature | não bem em absoluto |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 10-50%
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mudança climática/extremo
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
It is operated in a moist, cool environment
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| It is less cost effective yet highly nutritious. A kg of barley is nutritionally equivalent to 3Kg of other grass like the lucerne. |
| Barley grows in a very short period of time |
| It requires a small piece of area to grow barley |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Barley improves the overall health and well-being of animals |
| It has higher digestibility hence reduces on some diseases like bloat |
| Barley growing does not involve the use of soil hence cost effective |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology requires skills and knowledge especially to manage the conditions for growth | Encouraging farmers to train from model farmers |
| Barley seeds are at times hard to get. | Promoting the barley seed multiplication in large quantities |
| The technology requires maximum supervision | Always endeavor to do maximum supervision |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Bacterial and fungal growth is also another challenge e.g the common bread mould. | Seeds must be sterilized |
| Barley is not economically feasible for large scale farmers on pasture production | To grow more pastures in addition to barley as feed supplements |
| It cannot be stored for a long period of time | Serve it in the first days after harvest. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
2
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
2
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Growing Sprouted Fodder For Livestock by Jason Wiskerchen Monday, March 19, 2012,
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.peakprosperity.com/growing-sprouted-fodder-for-livestock-2/
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
https://www.hydroponics-simplified.com/hydroponic-fodder-advantages.html
URL:
http://www.fodderconsultants.com/advantages.html
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos