Pits [จีน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Baoyuan Liu
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2555 - จีน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - จีน1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
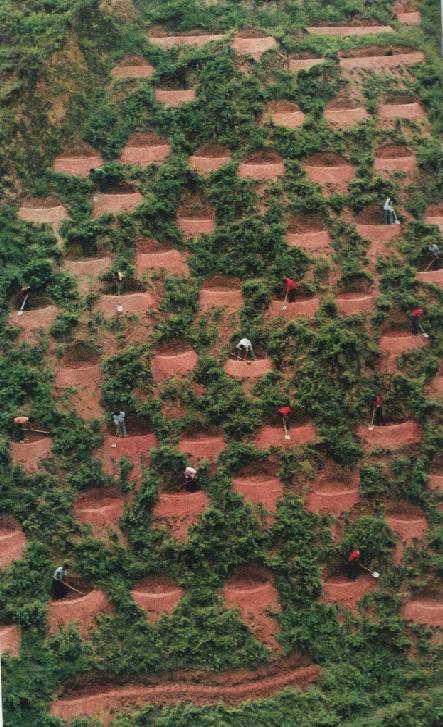
The pits are constructed by hand on steep slope by government investment.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
The purpose is to control soil loss and protect environment. Hence the pits are constructed on steep slope. To control watershed erosion, government have to invest. Soil and water conservation bureau is in charge of planning and implementation. Farmers provide labors to construct pits. Tools are shovel and hoes. Pits are constructed on steep slope, so mechanical machine can not be used.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
จีน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Gansu, Shanxi
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
1958
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2005
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The aim is to control soil and water loss and protect environment.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Pit is one of the structural measures to control steep slope soil and water loss. It is difficult to build using mechanical machine but easy to make by hand with simple tools.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Only when government invests, the technology can be implemented
Treatment through the SLM Approach: investment
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation Land resources belongs to state and land user can only lease the land for a period of time, land users worry about their land would be transferred to others.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
existing groups of land users; Specific ethnic groups:: Islam, Korea.; Working land users were mainly men (Men are the main work forces to build the pits.)
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | interviews/questionnaires; Land users participate. |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | No land users participate |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | responsibility for major steps; No land users participate |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ไม่ลงมือ | No land users participate |
| Research | ไม่ลงมือ | No land users participate |
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM เพียงผู้เดียว
การอธิบาย:
Decisions on the choice of SLM Technology were made directive (top-down).
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by politicians / leaders (directive ,top-down).
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- planners
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- เกษตรกรกับเกษตรกร
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
หัวข้อที่พูด:
Mainly setup demonstration areas for visit and illustrate.
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Name of method used for advisory service: Local government and SWC station (office).; Key elements: Planning, Build pits, Maintaining; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents 2) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; At each government level, there is a SWC office which is in charge of SWC activities including extension.
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ไม่
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Research was carried out on-farm
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - state): 100.0%
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เครื่องมือ | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
- โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- จ่ายเป็นเงินสด
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The wrapped water by pits can plant SWC trees and other fruit trees.
ปรับปรุงประเด็นของการถือครองที่ดินหรือสิทธิในการใช้ ซึ่งขัดขวางการนำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Local government can manage it. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Prolonging the contract period of the leased land.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่แน่ใจ
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
If there is not continuously financial support.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is better to make pits in the farming leisure time(winter). |
| It is easy to build a pit |
| low inupt and land users can bear (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: With favourable policies) |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| easy to make pits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Repairing and planting trees in pits timely) |
| harvest water on steep slope (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Reasonable size of pits based on local rainfall.) |
| Better ecological benefits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Partly financial support.) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Not any economic benefits | Planting economic trees or fruit trees. |
| Not any funds for maintain exsiting pits. | subsidy. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Little economical return | Planting economic trees or fruit trees. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Zhou yugui, Zhang cheng. Effectively comprehensive control in Xinangou watershed, 2000.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, 6, 36-38
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Wang ling. Pits in soil and stone hilly area, 1984.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Soil and Water Conservation in China. 11, 14-16.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Li yanchang. Storage capability and excavating volume of pits, 1984.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Soil and Water Conservation in China. 11, 17-19.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Yang yansheng. Technological measures suitable for red earth region in southern China, 1999.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Research of Soil and Water Conservation. 6(2):117-120.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Dou yuqin. Hydraulic property and design criterion of pits, 1986.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation.,4,53-58.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Shi shengxin, Jiang dingsheng. Impacts of several soil and water conservation measures on strengthening rainfall infiltration and reducing sediment yield, 1994.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Research of Soil and Water Conservation. 1(1): 82-88.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mu Xingmin, Chen jiwei. Effects of measures of soil and water conservation on soil water content in the Loess Plateau, 1996.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Journal of Soil Erosion and Soil and Water Conservation, 5(4):39-41.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mu xingmin, Wang wenlong, Xu xuexuan. The influence of the soil and water conservation on the surface runoff in the watersheds in the gully plateau region of Loess Plateau, 1999.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
Journal of Hydraulic, 2:71-75.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล