Awareness Raising for SLM Using Conservation Agriculture [คาซัคสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kulyash Iskandarova
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Awareness and knowledge on Conservation Agriculture for rainfed crop production
approaches_5677 - คาซัคสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
วิทยากรหลัก
expert/consultant:
Karabayev Muratbek
+7 (7172) 34 37 13 / +7 (701) 216-77-21
m.karabayev@cgiar.org / muratbek.karabayev@gmail.com
International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), CIMMYT-Kazakhstan
Office #7, B.Maylin str., 10, Astana, 010000, Kazakhstan
คาซัคสถาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Integrated natural resources management in drought-prone and salt-affected agricultural production landscapes in Central Asia and Turkey ((CACILM-2))ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kazakh Research Institute for Livestock and Fodder Production (Kazakh Research Institute for Livestock and Fodder Production) - คาซัคสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
02/02/2020
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM

Conservation Agriculture for cereal production in rainfed areas … [คาซัคสถาน]
Conservation agriculture applied in Northern Kazakhstan is based on no-tillage direct sowing of cereals into the soil permanently covered by crop residues. It contributes to reverse soil degradation, enhance water use efficiency, increase crop productivity in the rainfed lands.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kulyash Iskandarova
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Raising awareness and strengthening the capability and skills of farmers, agriculture specialists and researchers in developing and adoption resource-saving, profitable and environmentally friendly cereal production through Conservation Agriculture practices.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
The main features of the approach:
•Empower farmers to become self-sufficient in managing their lands under Conservation Agriculture through education, awareness raising with a focus on transferring knowledge, skills and tools to improve crop production, increase food security, and incomes of rural communities.
•Promote the transition from traditional farming to modern systems based on minimal soil treatment, diversified crop production, stubble retention and direct seeding by building capacity.
•Facilitate positive change by leveraging the strengths and capabilities of different partners to transfer skills, knowledge and resources to farmers and communities interested in active CA adoption.
In Kazakhstan the most of crop management experiences and education in universities emphasized conventional tillage based production systems. Changing minds to accept crop management practices based on the principles of Conservation Agriculture is one of the biggest constraint of CA adoption. Farmers are ready to change their mind set if they are knowledgeable, well informed and see the benefits of CA-based crop management practices in their fields. The approach is based on awareness raising, training of farmers and farmer testing of CA technology in close collaboration with specialists from international and local institutions. An active dialogue with farmers, knowledge and technology dissemination are built on participation of qualified specialists/experts who are part of the management team of each farm and are able to efficiently test and adapt new technologies to the local conditions. CA is a complex approach and system, it implies changes in a number of technological components of the existing traditional systems of agriculture. It is necessary to change two basic paradigms: the paradigm of soil tillage and the paradigm of linear knowledge flow.
Many agricultural research and extension systems are based on a linear model of knowledge flow, with new knowledge being developed in research organizations, passed on to agricultural extension agents who in turn pass on the new knowledge and information to farmers. While this model may be applied to simple technology, it does not always effectively work with complex technologies, especially when research institutes do not have the capacity to develop functional packages of multiple technological components for all farmer situations. Innovative approaches on the basis of complex technologies are needed in adaptation, system development process and promotion. Innovative approach (platforms) are based on networks of multiple agents, including farmers-innovators and decision-makers, all utilizing their own knowledge, external information and policy support to help overcome problems and develop functional systems for local farming conditions and farmer circumstances.
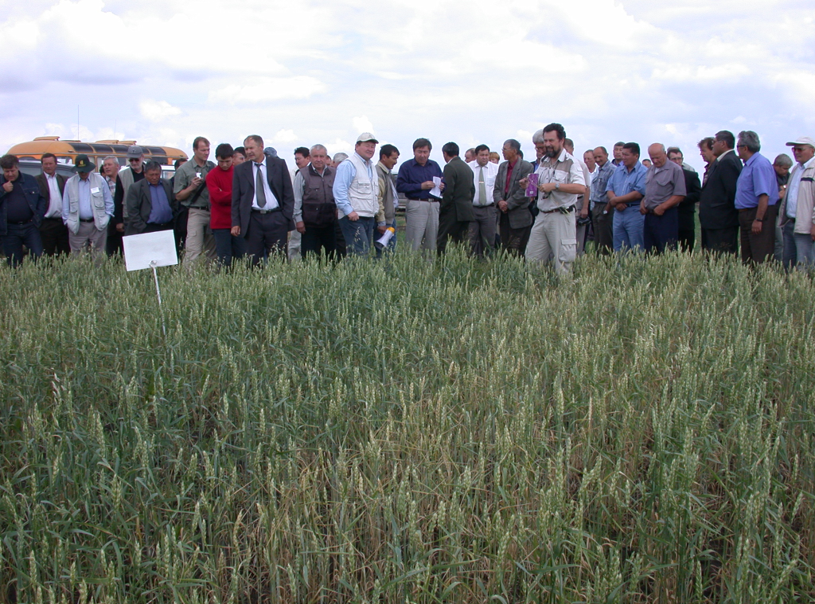
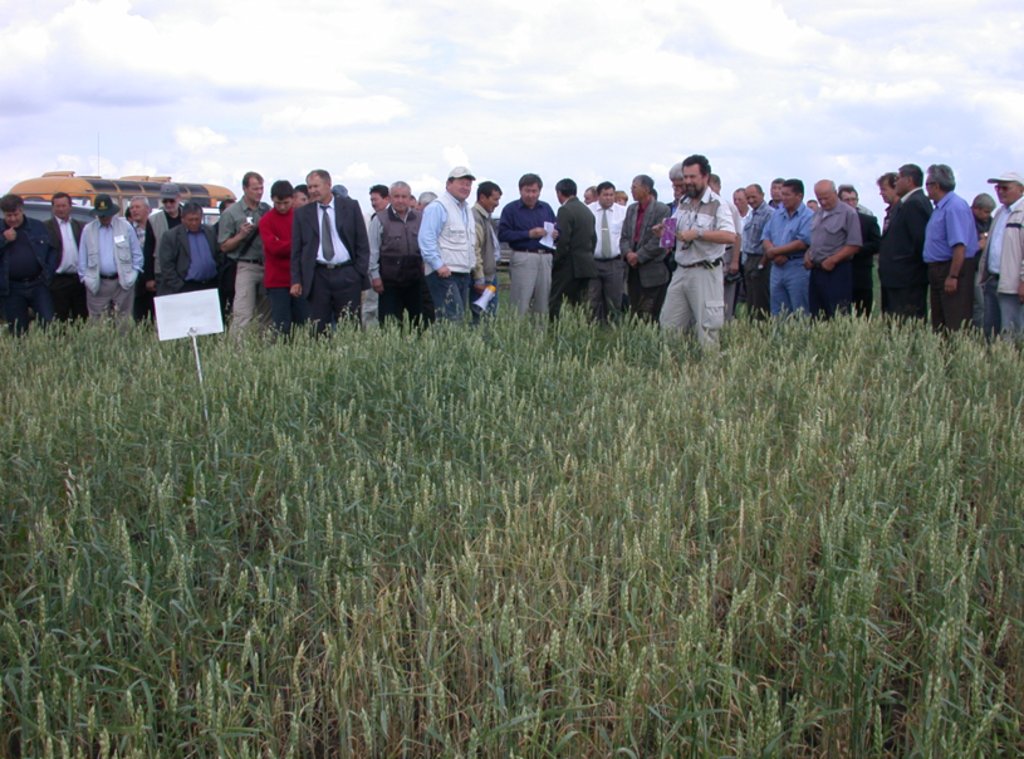
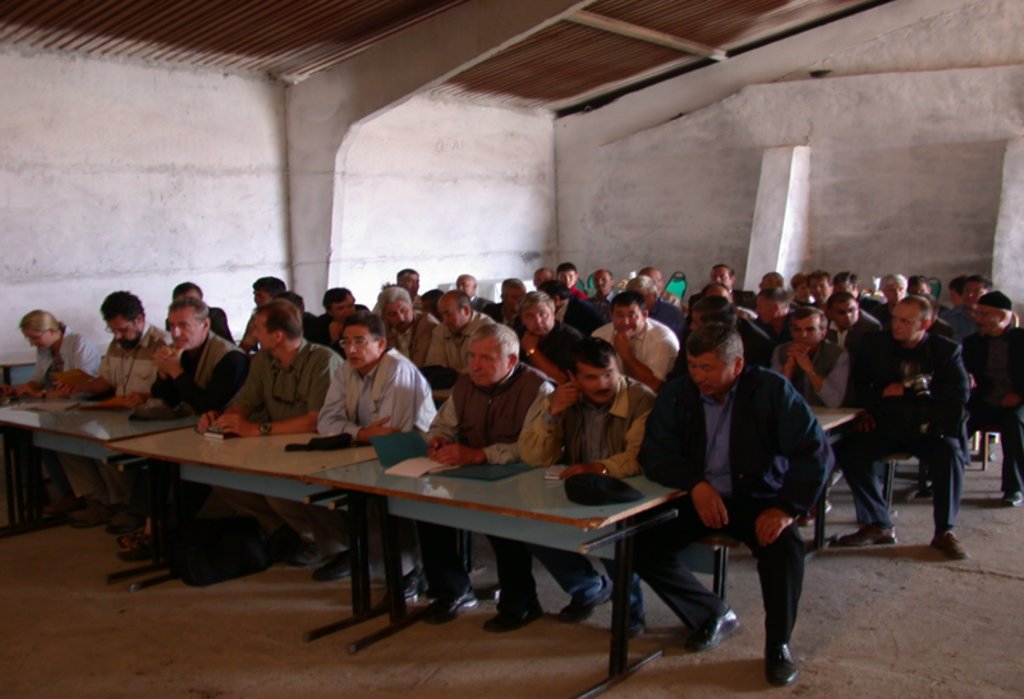
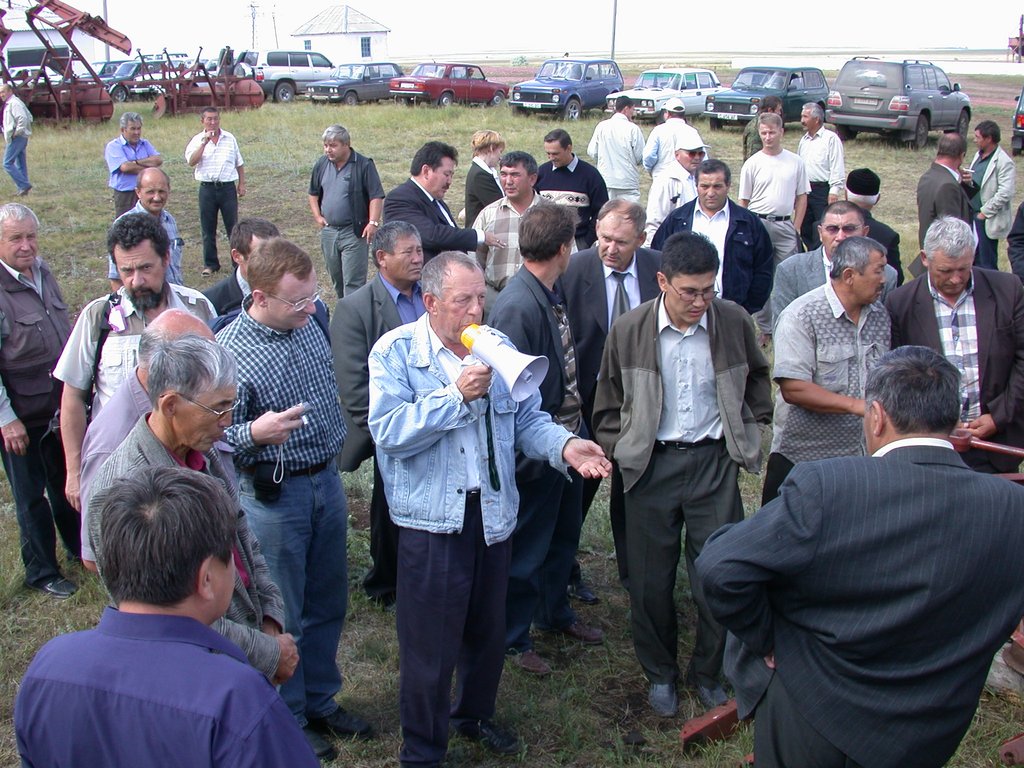
The target farmers as well as farmers of the neighbouring farming community were trained on-the-job on key topics of CA such as diversified cropping systems, chemical fallow, minimum/no-tillage, direct seeding, and snow and residue management. Altogether four training workshops were carried out. In each session international and national experts trained about 30 farmers. Conservation Agriculture study tour to USA (Washington State, Idaho State) and Canada (Saskatchewan Province) was organized. Public awareness and also training on CA-technology also were generated through six field days and seminars bringing together farmers, stakeholders, policy-makers and researchers to observe and discuss key field demonstrations.
Large-scale adoption of Conservation Agriculture (zero/minimum soil tillage, leaving crop residues in the fields, direct seeding with narrow chisel and disk openers, permanent bed-planting and furrow irrigation, etc.) were initiated by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and FAO in 2002. Thanks to the joint efforts of national scientists and farmers, international organizations (CIMMYT, FAO, ICARDA, World Bank, UNDP, USAID, etc.), support by the state and government bodies, the areas under no-till have been increasing from virtually none in 2002 to an estimated area of 3 000 000 ha in 2019.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.4 วีดีโอของแนวทาง
ความคิดเห็น อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Not available
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
คาซัคสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Northern Kazakhstan: Akmola and North Kazakhstan regions (provinces)
ความคิดเห็น:
CA approaches and principles are not site specific and can be applied to essentially all crop production systems.
1) Farm “Cherezdanov”, Smirnovo village, Akkayinskii district, Northern Kazakhstan region, located approximately 60 kilometers south of Petropavlovsk and 700 km from Astana (Nur-Sultan). The farm Head is Vyacheslav Cherezdanov.
2) Farm “Daryn”, Valikhanovo village, Zharkainsky district, Akmola region, located approximately 600 kilometers southwest of Astana (Nur-Sultan). The Head is Auezkhan Darynov.
3) Farm “Dostyk 06”, Astrahanovka village, Astrahanskyi district, Akmola region, located approximately 110 kilometers west of Astana (Nur-Sultan). The Head is Meyram Sagimbayev.
4) Farm “Surayev”, Vishnevka village, Arshalinsky district, Akmola region, located approximately 60 kilometers south of Astana (Nur-Sultan). The Head is Viktor Surayev.
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2002
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2004
ความคิดเห็น:
CA system approach continues adoption in the Kazakhstan and Eurasia region
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
Improve knowledge, raising awareness, enhance capability of farmers, agriculture specialists and different partners in using CA-farming practices for a more sustainable and profitable crop production in rainfed lands of Kazakhstan
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การร่วมมือหรือการทำงานประสานกันของผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติ
- เอื้ออำนวย
The CA approach is based on collaboration and network of multiple agents and actors (farmers-innovators, decision-makers, national and international institutions, researchers, experts, etc.) to enable and help overcome problems and develop functional systems for local farming conditions and farmer circumstances.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เอื้ออำนวย
•Knowledge of weed control: Options for weed control with different weed spectra and these different conditions must be available.
•Knowledge of crop rotations incorporating species profitable for farming, demanded by the market, tolerant to dry conditions and enriching soil, e.g. legumes.
•Knowledge and information about the CA equipment most appropriate for use in the country conditions are significant factor in the spread and successful management of CA, especially direct seeders, sprayers for uniform herbicide application and straw spreaders for the combine harvesters.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
1) A.Darynov, “Daryn” Farm, Valikhanovo village, Zharkainsky district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan
2) M.Sagimbayev, “Dostyk06” Farm, Astrahanovka village, Astrahanskyi district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan
3) V.Surayev, “Surayev” Farm, Vishnevka village, Arshalinskyi district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan
4) V.Cherezdanov, “Cherezdanov” Farm, Smirnovo village, Akkayinskii district, Northern Kazakhstan region, Kazakhstan
Coordination of field works, adoption at the farm
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
1) Dr.M.Matyushkov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, adviser in agriculture equipment
2) Dr.I.Vasko, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, adviser in agronomy and economics
1) Adoption of CA equipment at farms
2) Assessment of CA technology effectiveness
- นักวิจัย
1) Dr.A.Bektemirov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, consultant on soil science
2) Dr.A.Kenjebekov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, consultant on agronomy
1) Soil investigations and analysis
2) Agronomy research and analysis
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
Prof.K.Elemesov, Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Head of Science Department, National Project Coordinator
Coordination of the CA adoption project on behalf of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan
- องค์การระหว่างประเทศ
1) Dr.Th,Bachmann, FAO Specialist on Agronomy
2) Dr.Th.Friedrich, FAO Specialist on Engineering
3) Prof. M.Karabayev, CIMMYT Representative in Kazakhstan
1) Consultations on agronomy issues of the CA technology adoption
2) Consultations on engineering issues of the CA technology adoption
3) The Project Leader
- Foreign organization
Prof. L. Makus, Professor of Economics, Idaho State University, USA
Economic research and assessment of CA adoption at farms
ถ้ามีผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียหลายคนที่เกี่ยวข้องให้ระบุหน่วยงานตัวแทน:
The lead Agency - Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ไม่ลงมือ | Farmers involved in the project realization participated at the different seminars on CA technologies and innovations in land management organized by international institutions (FAO, CIMMYT) |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Definition of the most appropriate (location, size) lands, needs in labour, equipment, technique support for the project trials. |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Organization, manage and control field works. |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Active participation and assistance to the project consultants in monitoring and evaluation processes. |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
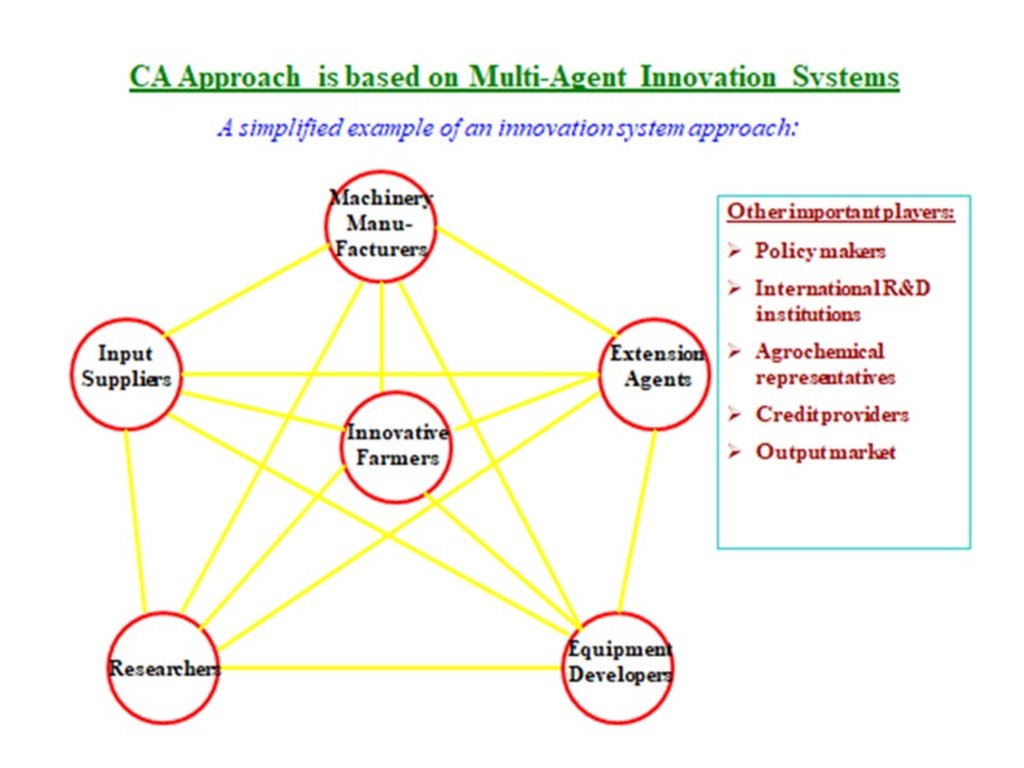
Conservation Agriculture Innovative approach (platform) is based on networks of multiple agents, including farmers-innovators and decision-makers, all utilizing their own knowledge, external information and policy support to help overcome problems and develop functional systems for local farming conditions and farmer сircumstances
ผู้เขียน:
M. Karabayev
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดในฐานะที่เป็นส่วนรวมของแนวทาง
การอธิบาย:
Innovative approach on the basis of complex technologies, like Conservation Agriculture, is needed in adaptation, system development process, comprehensive assessment and promotion. That is why and main reason of all relevant actors participate in decision making on the selection of the technology
ระบุว่าการตัดสินใจตั้งอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ:
- การประเมินความรู้ SLM ที่ได้ทำการบันทึกไว้เป็นอย่างดี (การใช้ข้อมูลในการตัดสินใจ)
- สิ่งที่ค้นพบจากงานวิจัย
- ประสบการณ์และความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว (ไม่ได้ลงบันทึกไว้)
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- เกษตรกรกับเกษตรกร
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
- จัดการประชุมสู่สาธารณชน
หัวข้อที่พูด:
“Conservation Agriculture for rainfed crop production”, “Conservation Agriculture for irrigated crop production”
ความคิดเห็น:
An important factor of wide-scale extension of CA is training and introduction of farmers and specialists with the new innovations and approaches, on-farm demonstration of technology components, expertise of foreign specialists, and wide public awareness activities. As a total, 12 different project events (workshops, training seminars, field days, study tours for farmers and specialists, consultations, lectures and methodological assistance provided by foreign specialists and scientists, etc.) were conducted. The implementation process of the project was regularly highlighted in newspapers, journals, radio and TV.
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
National Agriculture Research System (NARS) of Kazakhstan represented by the National Agrarian Research and Education Center (NAREC) of the Ministry of Agriculture has research institutes and extension centers in all main agriculture regions of the country where farmers and all needed persons have access to advisory service, including CA-based technologies.
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ภูมิภาค
อธิบายถึงสถาบัน บทบาทและความรับผิดชอบ สมาชิก เป็นต้น:
Agricultural Centers for extension and dissemination of knowledge are located in all main agriculture regions of Kazakhstan. Roles and responsibilities: advisory service, consultations.
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
Agricultural Centers for extension and dissemination of knowledge conduct and carry out on regularly basis trainings, seminars, workshops, meetings for and with farmers, visit farm fields and trials to provide on-place consultations and monitoring.
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
Monitoring and evaluation were carried out by the project team, consist of National Coordinator, Project Leader, national and international consultants and advisors, heads of the project farms. Also together with agriculture workers implementing field works at farms the project team members participated in main field activities: seeding, weed control, harvesting.
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ แสดงว่าการจัดเตรียมเอกสารนี้มุ่งหวังที่จะเอาไปใช้สำหรับการติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลใช่หรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
By collaborating with national and international partners the project evaluated progress and perception of the aproach by farmers. The documentation of the project, activities realized, reports of the project implementation are to be used for monitoring and evaluation. Defining real "win-wins" in the specific context of the project area as well as whole country aimed at increased understanding to improve and replicate the CA approach and technology on a broader scale.
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เศรษฐศาสตร์หรือการตลาด
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Technology and economics research were carried out by two main national research institutes: 1) Kazakh Research and Production Center for Grain Farming, Shortandy settl., Akmola region (province); 2) Kazakh Research Institute for Farming and Crop Production, Almalybak settl., Almaty region (province).
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Main sources/donors of funding of the SLM component of the approach: FAO (80%), International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center – CIMMYT (20%). The FAO TCP/KAZ/2801 (T) “Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Crop Production in Northern Kazakhstan” project duration: 2002-2004.
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
ความคิดเห็น:
not applicable
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยในการตัดสินใจโดยดูจากหลักฐาน ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Land-users and decision-makers are convinced to adopt and promote CA as key element of the agriculture system in the country
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The approach helped land users to clearly understand all components and stages of CA, to follow and abide main requirements for the technology introduction and maintenance.
ปรับปรุงความร่วมมือกันและการดำเนิน งานของ SLM ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
CA adoption and promotion implies participation of multiple agents the approach suggested ways to effective coordination and implementation of SLM
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The approach enabled farmers and national specialists to recognize as perspective, economically and ecologically profitable of Conservation Agriculture based on no-till and direct seeding systems.
นำไปสู่ความมั่นคงด้านอาหารหรือปรับปรุงโภชนาการให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Yield of spring wheat under CA, in average, 50 to 60% higher in comparison with the conventional technologies.
ปรับปรุงความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการปรับตัวให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงของสภาพภูมิอากาศหรือสภาพที่รุนแรงและภัยพิบัติหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The advantages of CA are especially evident in the years of drought, that is extremely important for Kazakhstani soil-climate conditions (called as “Area of Risk Farming”)
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
In relatively long-term perspective (at least, after 4-5 years of introduction) adoption of CA definitely leads to sustainable increase of crop productivity
- การเสื่อมของที่ดินลดลง
CA stops and reverses widespread soil degradation and enhance the sustainable management of the natural resources
- ความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติลดลง
Because of CA enhances water accumulation and its use efficiency for both rainfed and irrigated crop production systems the technology reduces risk and effect of droughts – main constraint factor for sustainable crop farming in Kazakhstan
- ภาระงานลดลง
CA considerably decreases number of field operations and hereupon reduces workload, resulting in crop productivity improvement by increasing the efficiency of time and input use
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่แน่ใจ
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
While CA provides many benefits for farmers and the environment, farmers can face constraints to adopt these practices. Wetlands or soils with poor drainage can make adoption challenging. When crop residues are limited, farmers tend to use them for fodder first, so there might not be enough residues for the soil cover. To initiate CA, appropriate seeders are necessary, and these may not be available or affordable to all farmers. Conservation agriculture is also knowledge intensive and not all farmers may have access to the knowledge and training required on how to practice conservation agriculture. Finally, conservation agriculture increases yields over time but farmers may not see yield benefits immediately. However, innovations, adapted research and new technologies are helping farmers to overcome these challenges and facilitate the adoption of conservation agriculture.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Because the approach is focused on awareness raising and the transfer of skills, knowledge and world experience it facilitates the mobilization of strengths and capabilities of farmers and different partners for effective adoption and promotion of CA. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The approach aims at sustainably intensifying farming systems and have a positive effect on the environment using natural processes. It helps farmers to adapt and increase profits in spite of climate risks. This approach by bringing awareness on advantages of CA to farmers, decision-makers, general public is a way of highest importance for Kazakhstan's “Area of Risk Farming”. Conservation agriculture can be considered climate-smart as it delivers on the objectives of climate-smart agriculture. |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| At farms level CA approach, especially on initial stages of its introduction and adoption, requires regular consultations and support by visiting foreign and international specialists on the issues and problems where national personnel is not enough experienced. Financial support of these visits and activities is necessary. | CA-based projects, especially those funded by international R&D agencies, can to some extent help with foreign experts visits and consultations. To accelerate introduction of CA it would be timely and effective if government allocates special funds for invited foreign and international experts through national programs on agriculture research and education. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Effective promotion of the CA-based approach in the country requires further measures to improve coordination between government, non-governmental and international organizations working in this area | As an innovative approach a CA platform must consist of and be based on interaction, cooperation, and a network of multiple agents: farmers, researchers, specialists in extension and marketing, manufacturers, policy-makers, state bodies, international R&D institutions. The establishment of a National or Regional “Network on Conservation Agriculture” coordinating all necessary activities and processes is considered important to effectively promote CA in the country and region. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
4 visits, field days
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
4 interviews with land users
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
2 experts
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
1.Karabaev M., Vasko I., Matyushkov M., Bektemirov A., Kenzhebekov A., Bakhman T., Friedrich T., Makus L., Morgunov A., Darinov A., Sagimbaev M., Suraev V., Perezdanov V., Rodionov A., Wall P. Zero-processing and direct sowing technologies for the cultivation of grain crops in Northern Kazakhstan. 2005. FAO-SIMMIT, 64 p. (in Russian)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
2.S. Shpigun, M. Karabayev. No-till and direct seeding technologies for cereals in North Kazakhstan. - Practical recommendations for farmers. Astana, Kazakhstan, 2007, 15 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
3.M. Karabayev, N. Yuschenko, A. Akramkhanov, and S. Shpigun. Forage crops production in dry areas with an allowance for ecological risks. - Methods of seeding and growing of perennial and annual grasses. Astana, Kazakhstan, 2007, 112 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
4.CIMMYT Wheat Improvement Program for Kazakhstan. Together in 21st Century. - 2008, CIMMYT, 56 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
5.Yushenko N., Iskakov Z., Karabayev M., Shpigun S., Yushenko D., Shaushekov T., Baitassov A. Perennial grasses cropping in abandoned lands of Central Kazakhstan based on Conservation Agriculture. – Drylands Management, World Bank-GEF-MOEP Kazakhstan, 2008, p.38-43
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
6.No-Till with Soil Cover and Crop Rotation: A Basis for Policy Support to Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Production Intensification. – Proceedings of the International Consultation Conference, 8-10 July, 2009, Astana-Shortandy, Kazakhstan. CIMMYT, FAO, Ministry of Agriculture, Kazakhstan, 2009, 350 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
7.Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International (CABI). 2011. Climate Change and Crop Production. Oxfordshire, UK: CABI, 292 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
8.FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). 2011. Save and Grow: A Policymaker’s Guide to the Sustainable Intensification of Smallholder Crop Production. Rome, Italy: FAO.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
9.Ospanbayev Zh., Koishibayev M., Karabayev M., Zhapayev R., Bedoshvili D., Zhunusov K. 2010. Winter wheat direct seeding technology on rainfed lands. Recommendations for farmers, Almaty, Kazakhstan, 13 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
10.Karabayev M., Ushenko N., Baitassov A., Ushenko D., Ishmukhanbetov S. 2011. Conservation agriculture for hayfields and pastures under agricultural landscapes of Central Kazakhstan // INAT-AGRO, GEF, UNDP, CIMMYT. Astana, Kazakhstan, 39 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
11.Ushenko N., Ushenko D., Baitassov A. 2011. Adaptation of no till and direct seeding of cereals in agricultural landscapes of Central Kazakhstan // CIMMYT, ACP, Astana, Kazakhstan, 22 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
12.Advancement and impact of conservation agriculture/no-till technology adoption in Kazakhstan. FAO Investment Centre, Information Note, December 6, 2012
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
13.Karabayev M., P.Wall., K.Sayre, R.Zhapayev, A.Morgounov, V.Dvurechenski, N.Yushenko, T.Friedrich, T.Fillecia, A.Jumabayeva, M.Guadagni. Adoption of Conservation Agriculture in Kazakhstan // Soil-Water Journal. 2013, Vol. 2, #r 2, p. 2003-2006.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
14.Zhapayev R., K.Iskandarova, M.Karabayev, K.Toderich. Ecological testing of the sorghum genotypes in South-East Kazakhstan // Agroecological bases of improvement the productivity and sustainability of Agriculture in the XXI century. 2013, Kazakhstan, p. 124-127.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
15.Karabayev M., V.Dvurechenski, P.Wall, K.Sayre, T.Friedrich, N.Yushenko, Zh.Ospanbayev, R.Zhapayev, A.Morgounov, A.Darinov, A.Nazarenko, E.Gossen, T.Fillecia, M.Guadagni. Conservation Agriculture in Kazakhstan // CIMMYT-Kazakhstan, 2013, 32 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
16.Karabayev M., A.Morgounov, P.Wall, K.Sayre, Y.Zelenskiy, R.Zhapayev, V.Dvurechenskii, A.Akhmetova, T.Friedrich, T.Fileccia, M.Guadagni. Conservation Agriculture and breeding for sustainable wheat production in Kazakhstan // Journal of Bahri Dagdas Crop Research, 2014, (1-2), 50-53 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
17.Nurbekov A., A.Akramkhanov, J.Lamers, A.Kassam, T.Friedrich, R.Gupta, H.Muminjanov, M.Karabayev, D.Sydyk, J.Turok, M.Bekenov. Conservation Agriculture in Central Asia (chapter) // Conservation Agriculture. Global prospects and challenges. CABI (CAB Int.), 2014, UK-USA, p.223-248
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
18.Karabayev M., A.Morgounov, H.-J.Braun, P.Wall, K.Sayre, Yu.Zelenskiy, R.Zhapayev, A.Akhmetova, V.Dvurechenskii, K.Iskandarova, T.Friedrich, T.Fileccia, M.Guadagni. Effective approaches to wheat improvement in Kazakhstan: Breeding and Conservation Agriculture // Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, USA, 2014, v.4, #10, p.761-765.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
19.Goddard T., Basch G., Derpsh R., Hongwen L., Jin H., Karabayev M., Moriya K., Peiretti R., Smith H. Institutional and policy support for CA uptake // Advances in Conservation Agriculture, Volume 1: Systems and Science, Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2020, (ISBN: 978 1 78676 264 1; 52 p.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
www.bdspublishing.com
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
1.No-Till: A Climate Smart Agriculture Solution for Kazakhstan
URL:
http://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2013/08/08/no-till-climate-smart-agriculture-solution-for-kazakhstan
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Conservation Agriculture for cereal production in rainfed areas … [คาซัคสถาน]
Conservation agriculture applied in Northern Kazakhstan is based on no-tillage direct sowing of cereals into the soil permanently covered by crop residues. It contributes to reverse soil degradation, enhance water use efficiency, increase crop productivity in the rainfed lands.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kulyash Iskandarova
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล