Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1317 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Penaranda Melijoy
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bernardino Renel
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Magno Beatriz
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
5th Floor, Department of Agriculture Building, Elliptical Road, Quezon City, 1100 Metro Manila, Philippines
ฟิลิปปินส์
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Ambrocio Acosta
09179258499
Master's Garden
Lamtang - Pico Road, Sitio Piinalayok, Pugis, La Trinidad, Benguet, Philippines
ฟิลิปปินส์
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - ฟิลิปปินส์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Master's Garden - ฟิลิปปินส์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
15/09/2013
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
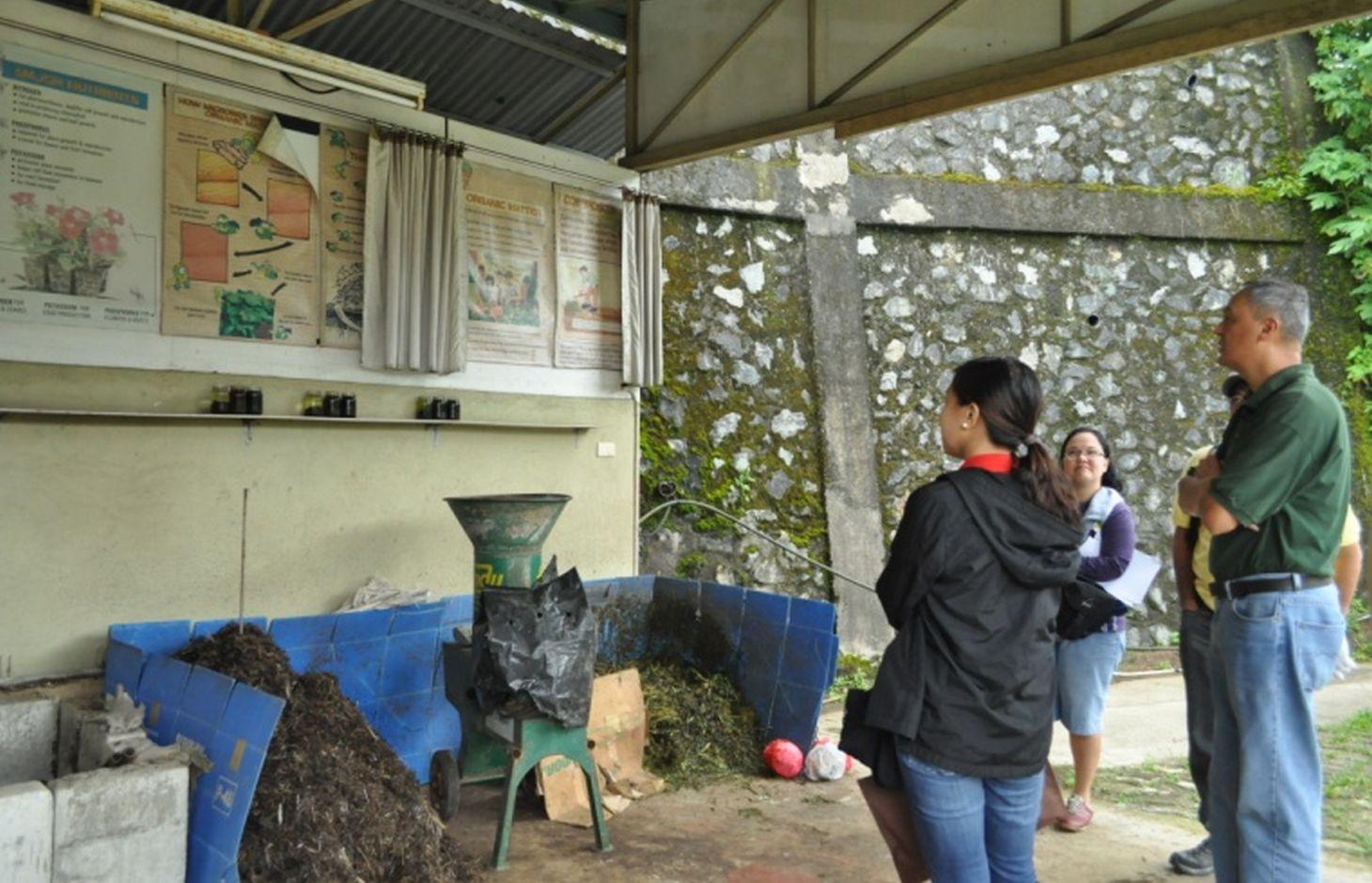
Composting is the decomposition of grass and weeds as fertilizer with the aid of indigenous microorganisms (IMO). This technology is practiced to produce compost used in the farm. Compost is a rich source of organic matter which improves soil tilth. Its decomposition slowly release available nutrients for plant uptake.Material used in the production are weeds and bio waste available in the farm which include Agetarum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia, Ipomea aquatica, Echinochloa crusgali, Helianthus annuus and Digitaria ciliaris. The compost is applied in the organic vegetable production of the farm. Vegetables planted include lettuce, herbs, kale and others that are used for garden salads.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of composting is to produce compost that is utilized as fertilizer for the soil. It is done to reduce the input cost of using chemical fertilizer and to avoid lasting harms to the soils and the environment (e.g. formation of impermeable layer "hardpan", affection of micro-organisms, and upsetting of pH).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The initial step in making compost is gathering of raw materials such as weeds and grasses available in the farm. Then, these are shredded and sprayed with IMO to hasten the decomposition. IMO is produced by mixing one tablespoon of forest soil and one tablespoon of sugar/molasses in one liter of water. A portion of the mixture (250ml) is extracted and diluted in a 16 liter knapsack sprayer. The diluted mixture is sprayed to the shredded grasses/weeds and left to decompose for 14 days. For a 1 ton of shredded grass and weeds, 16L of diluted mixture is needed.
Natural / human environment: Master’s Garden of Mr. Ambrocio Acosta is located at Barangay Puguis, La Trinidad, Benguet. The province is under Type I climate by the Coronas system of classification with distinct wet and dry seasons with an average annual rainfall of 3,879 mm. The dry season is from November to April while the wet season is from May to October. The farm has an elevation of 1,342 meters above sea level with less than 40% slope. The farm was manually terraced and arranged into beds with UV treated plastic shed. The production system is managed and cultivated by Mr. Acosta and his two farm laborers.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
La Trinidad, Benguet
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Composting was practice since they started developed the farm on year 2000.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop annual cropping: lettuce, tomatoes, cucumber, sugar beets, salad pe
Major cash crop perennial (non woody) cropping: Thyme, mint, tarragon and chives
Major food crop annual cropping: lettuce and tomato
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Since the farm has steep slope, soil erosion was prevalent resulting to low fertility of the soil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion caused by rainfall leaving them nothing but an exposed subsoil layer.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Average annual rainfall is 3,879 mm), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (extreme topography(steep slope >40%)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
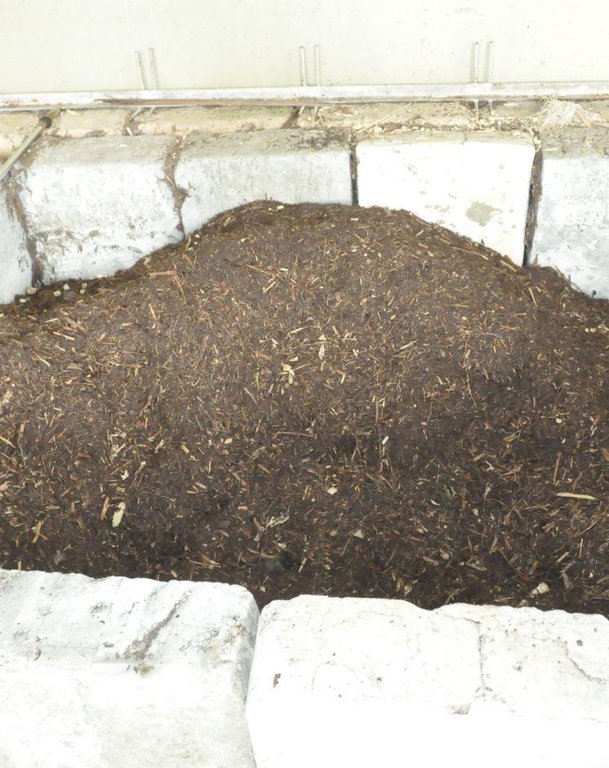
Compost piled in a cemented box.
Location: Brgy. Puguis. La Trinidad, Benguet
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Grass and weeds available in the farm( Ageratum houstonianum, Dentella repens, Setaria palmifolia,
Quantity/ density: 500kg
Remarks: the pile to be converted into compost should be under a shed protected from rain to prevent the avai
Agronomic measure: Indigenous microorganism (IMO) solution
Material/ species: forest soil, sugar/molasses, water
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
pesos
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
45.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.56
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays | จัดการพืช | |
| 2. | Establishment of composite chamber (shed) | จัดการพืช |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Sprayer | ha | 1.0 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Shredder | ha | 1.0 | 2222.22 | 2222.22 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Compost chamber | ha | 1.0 | 155.56 | 155.56 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Seedling trays | ha | 1.0 | 55.56 | 55.56 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Seedling pots | ha | 1.0 | 2.22 | 2.22 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2457.78 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Life span of sprayer and shredders more than 20 years
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm | จัดการพืช | Once a month |
| 2. | Shredding of grass and weeds | จัดการพืช | Once a month |
| 3. | Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO) | จัดการพืช | |
| 4. | Leave for 14 days to decompose | จัดการพืช | |
| 5. | Application of Compost | จัดการพืช |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 55.57 | 55.57 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 55.57 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: shredder
The calculation is based on the initial establishment cost (e.g. machine and tools) spend by Mr. Acosta on 2003.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The determinate factor affecting the cost is the cost of mechanical shredder. This machine is considered as important investment to those who is serious in engaging and practicing organic farming in a sizable farm like Mr. Ambrocio Acosta.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (1,342 meters above sea level)
Landfroms: Mountain slopes (the technology was applied at the farm with > 25 ° or >40 % slope and in concave situation)
Slopes on average: steep (31-60%) (the mean slope is 40%)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage is low
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Level of mechanization: manual labour (Vegetables and herbs were planted at beds which were cultivated manually)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) ( Harvested vegetables and herbs were for the subsistence of his family and were sold commercially at leading groceries and supermarket through a private marketing corporation known as KIAS Organic Gree)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase in yield was observed as response to compost especially as a source of N and P on the soil
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass and weeds are free and readily available in the environment thus reducing the expenses.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Composting is the decomposition of organic matter into compost which is the alternate for chemical/inorganic fertilizer as source of nutrients for crops. The use of compost prevents the farmers from exposure to harmful effects of chemical fertilizer and protects the consumer on the adverse effects of chemicals on the farm produce. Increased awareness and market demands including premium price for organic crops makes the Organic Farming an impressive source of livelihood and business.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil aggregation was enhanced because of the added organic matter from compost
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The pile of shredded grass and weeds that will be decomposed into compost were housed under a shed protected from rain and exposure from heat of the sun.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Voluntary adoption of the technology was observed since the land owner, Mr. Ambrosio Acosta , was a member and a previous officer of a small group of organic farmers, the La Trinidad Organic Producers (LATOP) and was also an accredited resource speaker/ trainer for Organic Agriculture-related events/forum.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It was observed that there is an increased awareness on the harmful effects of chemical inputs on the soil and its negative impact on human health. There is also an increase in demand for organically grown vegetables in the local market.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Compost increases the organic matter of the soil thus improving soil tilth. Also, it contributes to prevent incidence of plant pathogens,and insect diseases, infestation. |
| Compost as fertilizer provides nutrients to the crops |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Application of compost increases soil organic matter that promotes soil aggregation and improves soil condition. |
| Decomposition of the compost slowy releases nutrients like N, P and K that were readily available to plants. |
| It reduces farm production cost. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost in the purchase of equipment, tools and other supplies to start the technology. | Equipment and materials purchased are used for long term. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล