'Forage Christine' [บูร์กินาฟาโซ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Nouhoun Zampaligré
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Simone Verzandvoort, Donia Mühlematter
Forage Christine
technologies_2994 - บูร์กินาฟาโซ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
INERA Institut de l'environnement et de recherches agricoles (INERA Institut de l'environnement et de recherches agricoles) - บูร์กินาฟาโซ1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/06/2017
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
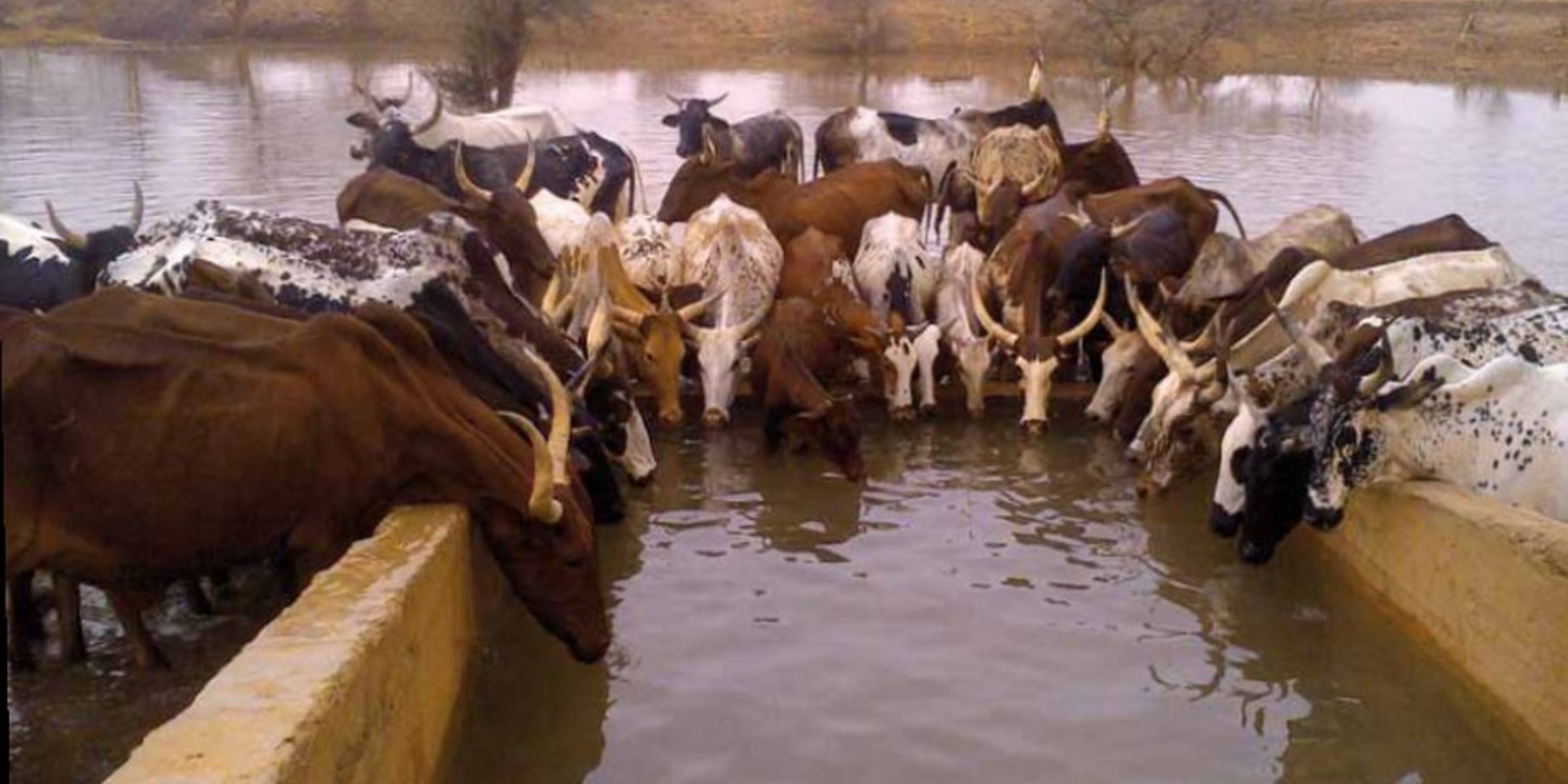
A modern hydraulic complex in the centre of the Sahelian region of Burkina Faso for watering livestock in the dry season.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
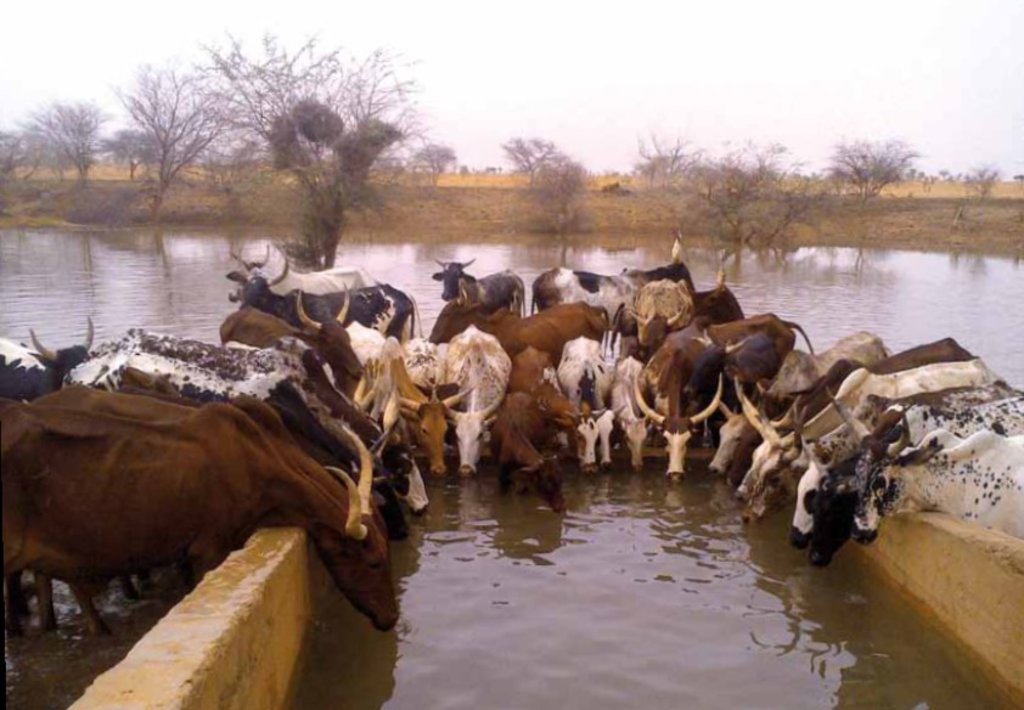
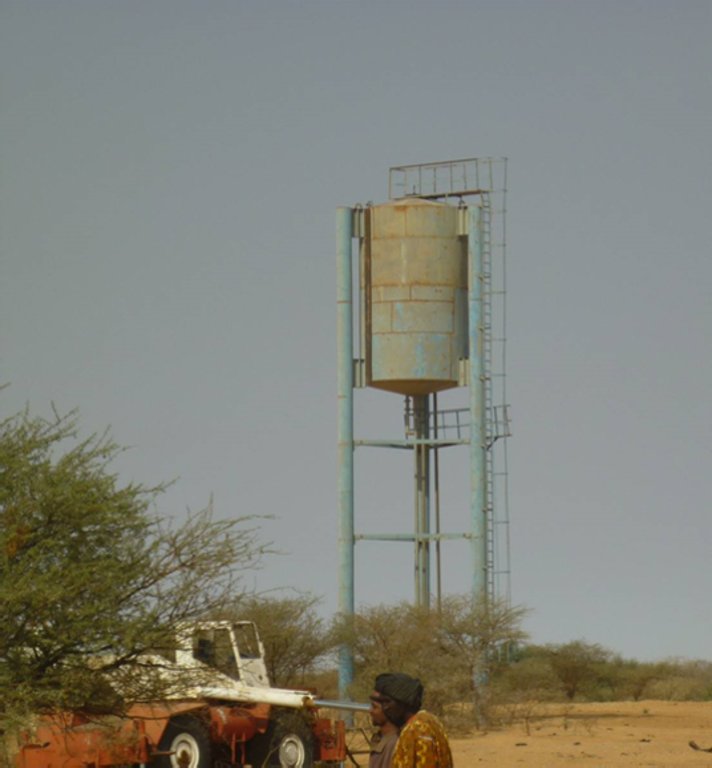
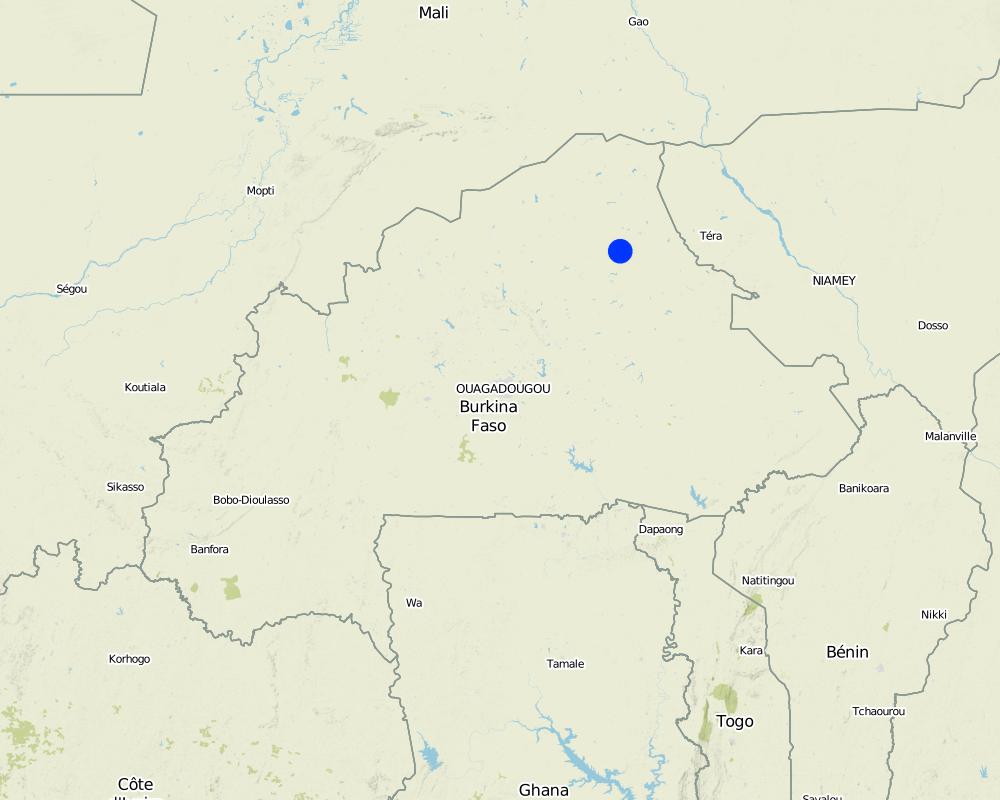
'Forage Christine' is a major water infrastructure, established in the northern part of the Sahel region in Burkina Faso between longitude 0°45’W and latitude 14°48’N, providing drinking water to herds within an area of 100 to 300 km from its central location between Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger. It was established in 1971 in the context of major droughts that had affected the Sahel, and it was opened for the first time in 1972. It is located in the middle of the Sahel region of Burkina Faso, at two km from the pond of Tin-Arkachen in the department of Déou, at approximately 45 km from the capital of the department, and 85 km from Gorom-Gorom. At the sub-regional level, the well is a around ten km from the border with Mali, and at 100 km from the border with Niger. The climate is of Sahelian type, and has a rainy season of 3 to 4 months (from June-July to September), which is subject to strong temporal and spatial variations in precipitation, and a dry season of 8 to 9 months. The climatic conditions are characterized by highly irregular winds, precipitation, evapotranspiration and moisture due to fluctuations in atmospheric circulation patterns. Annual precipitation is around 500 mm on average, with roughly 30 rainy days, and is marked by significant inter-annual variations. The stream network of the region consists of several streams, with one permanent river: Béli. To this river, ponds and many depressions are connected, which disappear after the month of January. The soils are very diverse in general, and mostly of sandy texture. They do not provide a good medium for plant growth due to the low permeability, which reduces water infiltration. Therefore water availability appears to be one of the major limitations for rainfed agriculture, in addition to the limited retention and availability of nutrients. According to the phytogeographic division of Burkina Faso (Fontes and Guinko, 1995), the area of 'Forage Christine' is situated in the northern or strict Sahelian phytogeographic sector. This sector is characterized by a set of typical Saharan and Sahelian vegetation species which mainly occur in shrub and woody steppes (48.85%) and grassy steppes (24.37%), which form the larger part of the rangelands (***). This vegetation provides the most important natural grazing land to livestock.
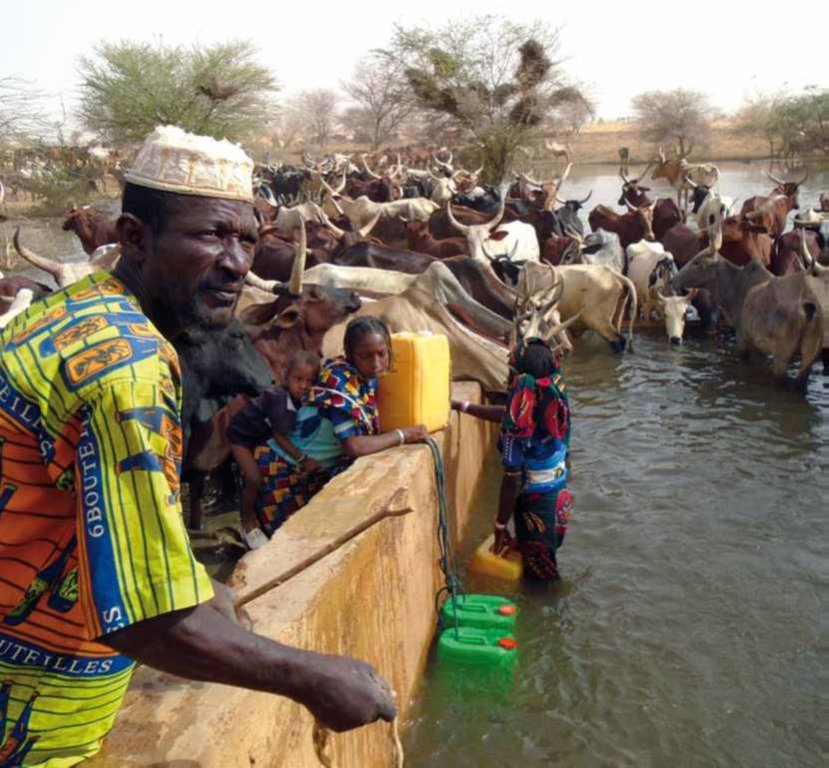
With regard to the human environment, the last General Population and Housing Census mentions a population of 25321 inhabitants for the municipality of Déou. Yet this number varies significantly due to the seasonal migration of people from other regions to use water and forage resources. The ethnic groups in the region are mainly Fulbé, Kurumba, Songhai, Tuareg, Mossi and Hausa people.
Economic activities in the region are livestock keeping, farming, craftmanship, fishing, trade, tourism and hunting. Several socio-economic groups are guiding these activities. Some 60 farmer groups, 53 groups of livestock keepers, six of which for female livestock keepers, and three organisations for environmental protection. With regard to infrastructure for education, sanitation and socio-economical conditions, the municipality of Déou has three markets, 18 schools, one middle school, 47 permanent functional literacy centers (CPAF), one recreation center, six cereal banks, three healthcare and welfare centers (CSPS), three medical stores, one tourist camp and one financial institution.
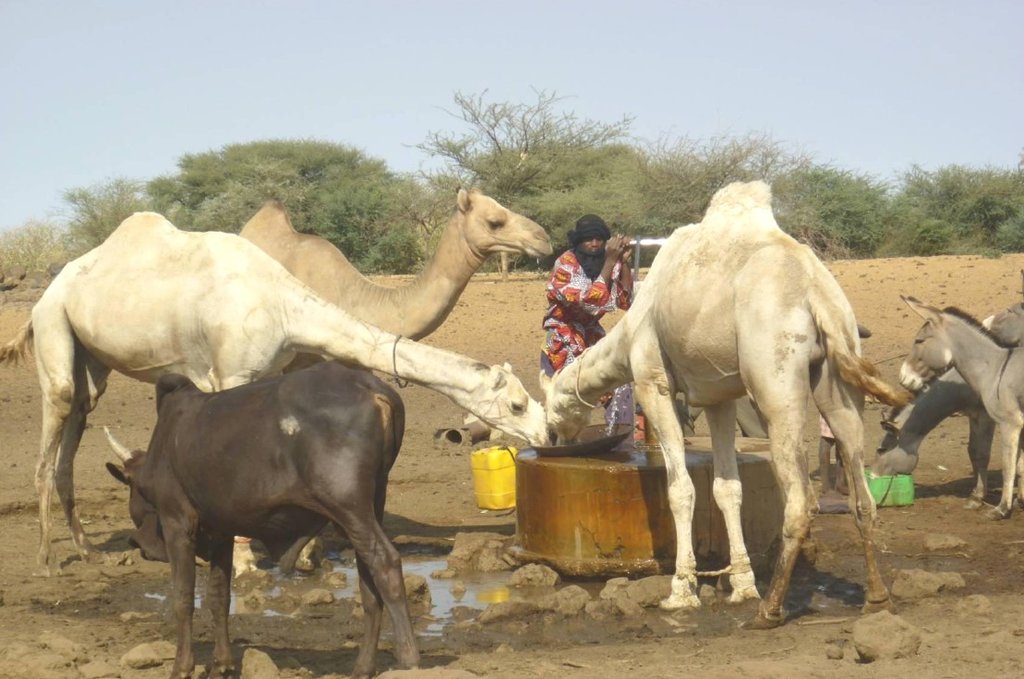
Farming and livestock keeping continue to be the most important socio-economic activities. The agricultural crops produced include millet, sorghum, maize, cowpea, rice and groundnut. In 2009, a total area of 345.5 ha was sown for these crops. The Sahel region in Burkina Faso has excellent conditions for livestock keeping. The animal species found in the region are mainly cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, camels, donkeys and horses and poultry. Several facilities and installations for water supply to pastoral areas are available in the region, as well as storage facilities for agricultural and agro-industrial by-products (SPAI) and infrastructure for trade and animal health care. The municipality of Déou disposes of one reservoir, five artificial ponds, 43 firm wells, ten vaccination centers, one store for agricultural and agro-industrial by-products (SPAI), one animal shelter, a facility for slaughtering and a livestock market.
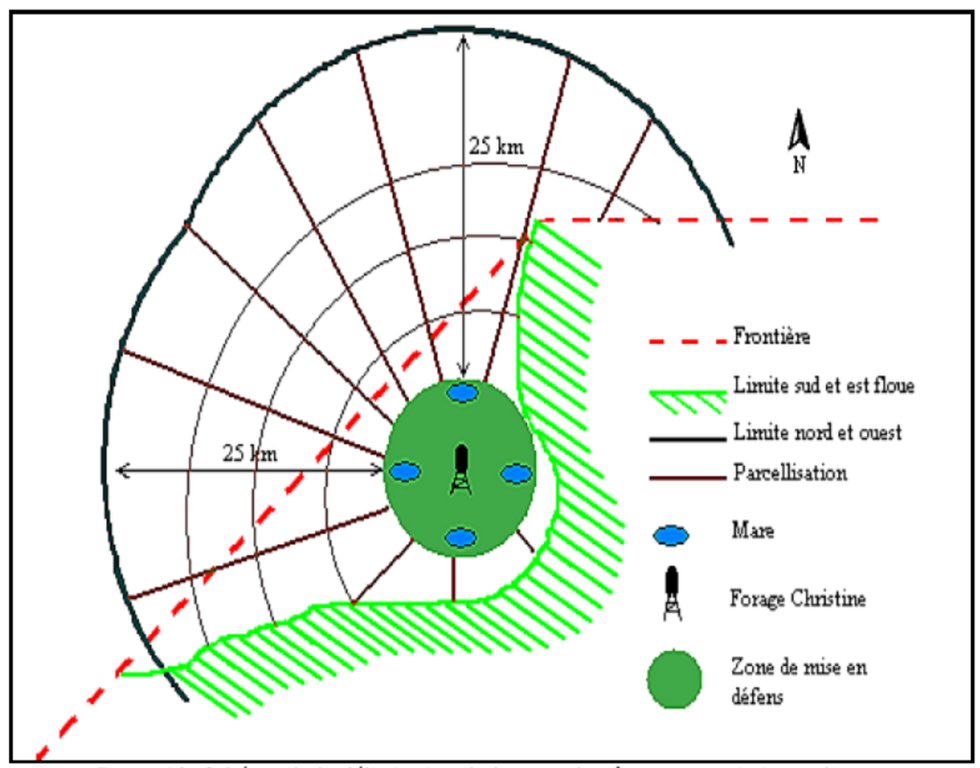
The well called 'Forage Christine' was constructed in 1971 by a French engineer, which named it after his wife, and opened it for the first time in 1972. Due to conflicts between Burkina and Mali it was ruined in 1976, and then again in 1985. In 1996 the National Office for Wells and Boreholes (ONFP), a government agency, rehabilitated the well and made two supplementary boreholes. The complex consists of a main well with an operating flow rate of 120 m3/h, having a submersible pump of brand KSB, type OPA 150s-65/8, and a pump capacity of 60 m3/h. Next to the main well there is a secondary well, which is equipped with a hand-operated pump with a capacity of 18 m3/h.
The energy for pumping water from the wells is provided by a generator with an engine of brand DEUTZ (type: F3 - 6L 912) and a switch of brand LEROY SOMER – Type LSA 42.1 L8L C1/4, a voltage of 400 V and continuous power of 50 kW. The generator has a switch and a battery. A diesel tank with a volume of approximately 9 m3 was installed for the power supply to the generator. The pumped water is stored in an elevated water tank, which is located at a distance of about 200 m from the well, and has a volume of 50 m3. The water from the elevated water tank is distributed to four artificial ponds with a dimension of 50 m x 50 m x 1.5 m at equal distances on all sides of the central reservoir. The water is conducted to the artificial ponds through PVC piping, which is buried underground over a distance of 8 km, or 2 km for each pond. The water flow is controlled by nine valves of type Nr. 4000, Reg. Nr. W 1.129, installed on the pipes. The hydraulic complex was installed in 1996 by the National Agency for Water and Sanitation (ONEA). The complex is managed by the livestock keepers through the User Association of 'Forage Christine' (AUFC). The statutes of this organisation were adopted on 2 May 2014. The well is managed according to a set of requirements which specify the terms for access to water: date of opening and closure of the well, the amount to be paid per animal and the management of the cash money provided.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
No video
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บูร์กินาฟาโซ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Sahel/Oudalan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Déou
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The infrastructure was created in 1971, but the facilities for use were installed in 1996.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
1971
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
A French aid worker introduced the technology with support from the government of Burkina Faso, through the National Agency for Water and Sanitation (ONEA).
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)
ชนิดพันธุ์สัตว์และผลิตภัณฑ์หลัก:
Animal species: cattle, sheep, camels, donkeys and goats.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In addition to livestock keeping, subsistence farming is practiced. The main crops are sorghum, millet, groundnut and cowpea. The size of the fields varies between 0.5 and 3 ha. The farm type is family-based.
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
No change in land use due to the implementation of the technology.
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Mid-June to September
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การจัดการน้ำบาดาล
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The well is located in the municipality of Déou, but is used for livestock from the entire Sahel region in Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน

อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology aims to remediate water scarcity for livestock during the dry season.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
1. Main well, flow rate 120 m3/h.
2. Secondary well, flow rate 18 m3/h.
3. Submersible pump, brand KSB, type OPA 150s-65/8, flow rate 60m3/h, year of constrcuction1996
4. Elevated water storage tank, volume 50 m3.
5. Four ponds of 50 m x 50 m x 1.5 m.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
FCFA
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
550.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
35 000 per month
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Main well | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 2. | Elevated water storage tank | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 3. | Artificial ponds | ด้วยโครงสร้าง |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not evaluated.
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not applicable.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Use of diesel | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 2. | Use of oil and filters | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 3. | Periodic maintenance of the generator | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 4. | Fuel delivery | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 5. | Transport costs of the maintenance operator | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 6. | Wage of the guard | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 7. | Compensation of the manager of the generator | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
| 8. | Charges for accounting | ด้วยการจัดการ | year |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Periodic maintenance of the generator | season | 1.0 | 150000.0 | 150000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Compensation of the GE manager | person-month | 12.0 | 37500.0 | 450000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Charges for accounting | person-month | 12.0 | 175.0 | 2100.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Wage of the guard | person-month | 12.0 | 50000.0 | 600000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Use of diesel | season | 1.0 | 2921000.0 | 2921000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Use of oil, filters | season | 1.0 | 68000.0 | 68000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Reparations to the hydraulic complex | season | ||||
| อื่น ๆ | Fuel delivery | season | 1.0 | 125000.0 | 125000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transport costs of maintenance operator | season | 1.0 | 60000.0 | 60000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4376100.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The municipality, the management committee and the NGOs operating in the area (SNV).
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
1. Availability of fuel for the generator.
2. Failures in the functioning of the generator to fill the storage tanks.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
500.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Mean annual rainfall is around 500 mm, with approximately 30 rainy days and characterized by a strong variation between years. The water system has many streams, of which only one is permanent (the Béli river). To this river, ponds and many depressions are connected, which disappear after the month of January.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Station of Gorom-Gorom
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
The climate is of Sahelian type, and has a rainy season of 3 to 4 months (from June-July to September), which is subject to strong temporal and spatial variations in precipitation, and a dry season of 8 to 9 months. The climatic conditions are characterized by highly irregular winds, precipitation, evapotranspiration and moisture due to fluctuations in atmospheric circulation patterns.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
The soils are very diverse in general, and mostly of sandy texture. They do not provide a good medium for plant growth due to the low permeability, which reduces water infiltration.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Limited water availability appears to be one of the major limitations for rainfed agriculture, in addition to the low retention and availability of nutrients.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The area around the 'Forage Christine' is characterized by a variety of typical Saharan and Sahelian vegetation units which mainly occur in shrub and woody steppes (48.85%) and grassy steppes (24.37%), and which form the larger part of the rangelands.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Several socio-economic groups are guiding the activities of land users. These include 60 farmer groups, 53 groups of livestock keepers, six of which for female livestock keepers, and three organisations for environmental protection.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Most of the agro pastoralist are smallholder farmers, livestock keeping is their main livelihood activity.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not applicable
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Existence of a temporary coordinating committee on the site of the well, acting as an interface between the authorities and the livestock keepers using the well. |
| The arrangement of the use of the artificial ponds according to the terms set by the authorities and the technical services. |
| Monitoring of animal health and informing the livestock keeping service in case of suspected infectious diseases. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Water availability and access to water for users when the well is operational; potential users are willing to contribute to the operation of the well. |
| Water availability for livestock. |
| Strong involvement of the authorities and the technical services in issues relating to 'Forage Christine'. |
| Implementation of several methods to solve management problems. |
| Good organisation of the management of the water source. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of transparency in the use and management of contributions intended to cover the functioning and the maintenance of the generator and the wage of the guard, who also operates the generator and supervises the related installations. | Good functioning of the management committee and committee meetings will enable to overcome this disadvantage. |
| A low level of representation of the different population groups in the management committee (only the Djelgobé of Gandéfabou are members; these people settled in the area in Boula and claim to be the indigenous people in the area). | Involving all groups using the well more closely in order to have an appropriate representative in the management committee. |
| Lack of consultation between the management committee and the livestock keepers having their residence in the area. | Stimulating the management committee to communicate more closely with the neighboring livestock keepers through a framework for consultation on the way in which they manage the infrastructure of the 'Forage Christine'. |
| Insufficient awareness of the roles and responsibilities of the management committee by the livestock keepers (only the role of the guard is known to the livestock keepers). | |
| The undemocratic establishment of the management committee (self-appointed members), which explains why livestock keepers consider the committee as an imposed structure. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The non-involvement of livestock keepers (potential users) in the management of the well in some management methods (concession to RMC); their weak involvement in the management of the well, and their continued low representation in the committees (2 to 3 persons). | Involving livestock keepers more closely in the management committees and in the decision-making bodies related to 'Forage Christine'. Increasing the number of representatives of livestock keepers in the management bodies of the well. |
| The failure to address the concerns of livestock keepers in the implementation of the management methods. | Ensuring that the livestock keepers are considered by the management committee, and that they can effectively participate in the committee. |
| The inappropriate use of contributions from users of the well for operating the facilities of the well in a sustainable way. | Ensuring that the funds generated by the well are managed properly by the management committee. |
| Competition for water between humans and animals. | Providing wells or pumps for human consumption of water. |
| Huge inflow of animals which overgraze the area, thereby threatening the environment. | Raising awareness among livestock keepers and herders on the need to manage the natural resources properly in the area influenced by 'Forage Christine', with the aim to mitigate the environmental degradation that could result from overgrazing. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
03
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
03
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Boundaoné et al., 2015. Textes fondamentaux et outils de gestion du forage Christine, PGP-FC/GRP, SVN, 60 p.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SNV, 2011. Etude pour la sécurisation des ressources foncières pastorales autour du Forage Christine dans la province de l’Oudalan. Final report, 142 p.
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
News paper article: Elevage dans le Sahel : "Christine" ou le symbole de l’hydraulique pastorale.
URL:
http://lefaso.net/spip.php?article31821
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล